The main reason why summer residents do not plant felt cherry is its tendency to disease. Indeed, why waste effort and money on a seedling that, most likely, will not only die itself, but also infect others. How to protect your garden?
The felt cherry tree does not have many diseases, but it suffers greatly from them, even to the point of death. In order to understand what happened to your still very young bush, you need to know what misfortunes it is susceptible to, and take preventive and protective measures in a timely manner.
Signs of moniliosis on cherries and plums
Moniliosis, or monilial burn, is a common and dangerous disease of cherries, plums, cherries, cherry plums, apricots and other stone fruits. On cherries and many other stone fruits, moniliosis is caused by the fungus Monilia cinerea. The causative agent of the disease overwinters on mummified fruits and infected branches.
Many people mistake the sudden death and drying out of branches with blossoming leaves as the result of winter freezing, burns from pesticides or fertilizers. But in cherries infected with moniliosis, the flowers suddenly wither, turn brown and dry out, then the leaves and young fruit branches wither and dry out, and annual non-lignified shoots become like burnt ones.
It is during flowering that fungal spores fall on the pistil and germinate, affecting the conducting vessels.
The first signs of moniliosis on cherries
Pest and disease control
Felt cherry is practically resistant to disease. The pests that attack it are the same as other trees.
Moniliosis
This disease is caused by a fungus that first gets on the flowers, then on the leaves, and then is transferred to the shoots. Penetrating into the wood and destroying it, it quickly spreads throughout the tree. Cherry blossoms are most vulnerable to moniliosis. Externally, branches affected by the fungus look like burnt ones.
Under the influence of fungal spores, the tree dies by the end of spring if the fight against the disease is not started. Rainy weather promotes its development. Because of this disease, the tree is greatly weakened, and all its fruits rot. If this phenomenon occurs for several years in a row, the plant will die.
To prevent the appearance of moniliosis or cure cherries at an early stage of the disease, you need to treat the leaves and branches of a young tree with fungicides - special preparations against fungal diseases. To prevent the fungus from spreading from affected shoots to healthy ones, they must be cut out.
Coccomycosis
Another disease caused by fungal spores is coccomycosis. Because of it, the leaves on the tree fall off ahead of schedule. This worsens his immunity and changes his developmental cycle.
To defeat the disease, it is necessary to spray the seedling with chemicals. If this is not done, the fungus will not only destroy the cherry, but will also be able to spread to other stone fruit trees located in the same area. It is very rare to observe bacterial canker on felt cherries.
Pests
For pests, this variety of cherry is no different from other trees, so you can see aphids, caterpillars, leaf borers and plum moths on the seedlings. To prevent their occurrence, you need to follow simple rules:
- fulfill basic agrotechnical requirements;
- collect and burn fallen leaves, preventing them from rotting and spreading infections;
- destroy caterpillar cocoons;
- use the necessary fertilizers and adhere to the norms and rules of fertilizing;
- spray seedlings with pesticides.
These rules are simple even for novice gardeners. By following them, you can protect your trees from pests and save your harvest.
How does moniliosis develop?
Monilial burn can develop in two forms.
1. After a warm winter, in the spring, with the onset of rainy and cool weather during flowering, the symptoms of the disease resemble the effects of frost or fire, which is why this form of the disease is called “monilial burn.” Flowers, leaves, shoots and branches are affected.
VIDEO:
2. The second form is fruit (gray) rot. First of all, fruits become infected through damage resulting from mechanical stress or caused by insects. Small dark spots appear on mature fruits, which quickly grow and cover most of the fruit, and sometimes the entire fruit.
Later, similar sporulation pads form on the affected fruits. They are located in a random order, which distinguishes moniliosis fruit rot from fruit rot, in which sporulation is arranged in concentric circles. Diseased fruits shrink and dry out, mummifying.
Moniliosis rot of cherry fruits
Let's talk about varieties
Bearing in mind that felt cherries will not bear fruit if you have only one variety planted, you need to know what varieties of this crop exist.
Early felt cherry
Natalie
The group of early ripening varieties includes the Natalie variety, which is currently one of the most widespread. It is distinguished by very juicy large berries that have a dark red color. The fruits ripen together, approximately in the second half of July. Productivity – up to 10 kg per bush. The best pollinators: varieties Ogonyok and Damanka.
Fairy tale
This variety is popular both in the Moscow region and in Siberia because of its magnificent flowers and delicious fruits. In addition, Skazka is one of the shortest varieties of felt cherry, its height reaches an average of one meter.
The berries are large, sweet, and have dense pulp. Skazka is distinguished by a high degree of resistance to fungal diseases.
Felt cherry average ripening time
Anniversary
This is a new variety that was bred by breeders in 1997. It is distinguished by a not too thick crown and an interesting slightly concave shape of the leaves.
The berries have an oblique shape, burgundy, the pulp is sweet, with a refreshing taste. From one bush you can collect up to 8-9 kg of fruit.
Eastern dark-skinned woman
The variety differs from others in that the flowers are located on long stalks, and the branches have a reddish tint. The berries are medium-sized, have a small “beak”, and are dark burgundy at the ripening stage. Productivity is average.
Late felt cherry
Firework
This variety of felt cherry is characterized by massive fruiting and good yield (up to 10 kg of fruit from one bush).
Feature of Salyut: the first fruits begin to appear only 4-5 years after the seedlings are planted in a permanent place, so you need to take this fact into account. The berries are large, oval, the pulp is slightly sour.
Autumn Virovskaya
A tall, productive variety with good winter hardiness. The fruits are large, highly palatable and delicious.
Ocean
It is a tall variety and can reach a height of up to two meters. The berries are not particularly large, very beautiful, the flesh is dense and juicy. Productivity is approximately 8 kg of fruits per bush. Feature of the variety: the fruits lack a pronounced cherry aroma.
When planting, varieties of the same flowering period should be planted nearby so that pollination takes place effectively and fruits set.
We think that our article will help you choose the best varieties of felt cherries for the garden and correctly plant this wonderful fruit crop.
Severova Natalya
Why do you need to cut off dry branches from a cherry tree?
The pathogen is well preserved in winter in affected twigs and shoots, as well as in dry mummified fruits. In spring, sporulation pads form on them. The spores are spread through the air by raindrops or insects, and infect plants through flowers or damage to the bark.
Why does cherry dry? The primary infection occurs through the stigmas of the pistils, then the mycelium penetrates the wood of the branch through the peduncle and partially destroys it. As a result, after about a month, the flow of water completely stops, and the part of the branch above the site of infection dries out. With repeated re-infection, severe weakening of plants and their death occur.
If there are dark rings on the cut of a cherry branch, this is a symptom of moniliosis.
Dark rings on a cut cherry are a sign of moniliosis
To stop the development of diseases, all drying cherry shoots must be cut out, capturing the healthy part 10-15 cm below the drying area, and burned! The same is then done with the fruits (ash-gray cushions are clearly visible on the affected ones) and with dried ovaries. Trimming branches along the border between the affected area and the healthy one will not bring results, since the transparent threads of the mycelium, invisible to the human eye, have most likely already spread along the branch, but have not yet given obvious signs of damage to the wood.
Branches affected by moniliosis, this can be seen on the cut
Cherry: how to trim correctly>>>
Landing rules
Like other cherry trees, this variety is recommended to be planted either in mid-spring or early autumn
But it is important to plant the tree before the buds begin to bloom. To get a high and high-quality harvest, you need to know how to plant felt cherries correctly
Selecting a location
When choosing a place for planting, you need to take into account its illumination. In order for a tree to grow quickly and well, it needs a lot of sunlight. If the bush is located in a predominantly shady place where little sunlight reaches, this will affect its fruits: usually cherries decrease in size and become drier, and their ripening occurs later.
It is important that water does not accumulate or stagnate at the site of the seedling. This can lead to root rot, since young roots are especially sensitive
Felt cherry trees need other varieties to fertilize, so you need to plant several of these trees at once.
The ideal varieties are: Delight, Triana, Leto, Skazka, etc. It is better not to plant coniferous trees next to Chinese cherries. If they are within a radius of five meters, then this place is not suitable for this variety.
Soil selection
Proper cultivation of felt cherries involves choosing fertile soil. Light loamy or sandy loam soil is ideal. Peat and other heavy soils are not needed for this variety.
It is recommended to choose neutral, well-drained soil. Make sure that the soil is not waterlogged, as this may cause the plant to die. If the acidity of the soil is high, then it must be fertilized periodically with lime.
Main stages
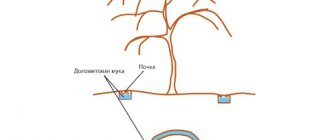
Felt cherries are planted in open ground in a pre-prepared hole, the depth of which is at least 50 cm. The width of the hole should be 60 cm. Before lowering the seedling into it, the hole must be filled with soil mixture, which must be mixed well. The soil mixture should include: 3 buckets of organic fertilizers, 500–800 g of lime, 30 g of potassium and 50 g of phosphorus.
Before planting, the root system of the cherry seedling must be trimmed to 20 cm. This will help the lateral roots develop better. It is recommended to treat all roots with a clay mash to prevent all possible problems, and then you can immerse the seedling in a hole to a depth of 5 cm. The depth should be the same as in the greenhouse or other place where the young tree previously grew.
After the seedling has been placed in the hole and covered with fertile soil, the soil must be compacted and watered well. It is recommended to mulch the soil with peat or organic fertilizers. This will help regulate its humidity and reduce the amount of watering.
Planting scheme
In order for the trees to develop well and receive all the necessary nutrients, you need to adhere to the planting scheme. It is not recommended to plant more than three felt cherries in one area. Trees should be 1.5–2 m apart from each other
It is important that the seedlings are at least 1 year old. Ideal age for planting: 2 years
When does moniliosis develop more strongly?
Moniliosis spreads in the spring (during flowering) by spores carried by wind and insects. In humid weather, ash-gray sporulation pads of the pathogen develop on dead areas. At first they are located separately, then they increase in size and merge. Cracks and gum droplets also appear on infected large skeletal branches.
The disease spreads especially strongly in years with prolonged flowering and high air humidity. For the development of moniliosis, damp weather is favorable at a temperature of +15...+20 ° C or with prolonged rains in spring and summer. The development of the disease is facilitated by the density of plants and location in the lowlands.
In the relatively arid steppe zone, cherries are affected by moniliosis much less frequently, although in certain years that are favorable for the development of the pathogen, the disease also becomes widespread here.
Description of the variety
This Chinese cherry was brought to the Far Eastern regions in the 19th century and gained the greatest popularity due to the breeder Michurin, who developed a new variety - Ando.
Gardeners love this variety for several reasons:
- unpretentiousness;
- frost resistance;
- bountiful harvest;
- heat resistance;
- resistance to coccomycosis;
- immunity to insects.
Among the disadvantages of this cherry is only its relatively short lifespan - up to 10 years, but gardeners have learned to correct even this, doubling the lifespan thanks to correct and timely pruning.
Due to its resistance to coccomycosis and pests that especially often attack trees, felt cherry is almost invulnerable.
There are some diseases to which the tree is still susceptible:
- moniliosis;
- pocket disease;
- a certain type of pest.
Each type of disease is dangerous in its own way for felt cherries, because there is a possibility of losing a plant, and even more than one, if treatment is not started in time. If you have a felt cherry tree on your site whose branches dry out after flowering, this is most likely due to a fungal disease.
The disease is dangerous not only for cherries, but also for all stone fruits. The pathogenic fungus is dangerous because it withstands winter cold and attacks trees very quickly. Most gardeners often confuse the manifestations of moniliosis with fertilizer poisoning or freezing. The disease is very similar to a regular pesticide burn, which is why it is more difficult to recognize. Felt cherry branches dry out, even young shoots seem burned, and the color becomes brown.
If the felt cherry dries out after flowering in a year after a warm winter or during heavy spring rains and damp weather, there is only one reason - moniliosis. It develops rapidly and resembles the effects of fire or frost. This disease is often called monilial burn, because. the appearance with such an effect is very similar.
The area affected by this disease is colossal - leaves, branches, even small shoots. This type of fungus also appears on fruits, which look very unattractive and subsequently rot. Moniliosis on berries is located in a chaotic manner and differs from ordinary fruit rot in that it has a clear form of appearance and location on the fruit.
The cherry fruit darkens first on one side, the affected area is small, and then this disease spreads to the entire fruit and further to the neighboring ones. Due to its fairly rapid spread, this may not be noticed immediately, but only after the cherry tree branches begin to dry out.
This disease is the answer to the question of why felt cherry dries: due to its instability to fungal diseases, the tree is susceptible to drying out of the ovary, branches and leaves. A particularly favorable time for the spread of moniliosis is spring. During the period of abundant flowering of cherry trees, disease spores are carried by wind and insect pests.
Due to too wet weather, gray marks begin to appear on the plant, which grow due to increased air humidity. Infested drying felt cherry branches can be identified by gum formations on them or by small cracks.
Which cherry varieties are unstable and which are resistant to moniliosis
The degree to which cherry trees are affected by moniliosis depends on the variety, the density of the area, and the weather during flowering. Trees that bloom during rainfall are most severely affected. One year these may be early-flowering varieties, another year they may be late-flowering varieties. The most susceptible to moniliosis are ancient varieties of folk selection: Vladimirskaya and Lyubskaya , as well as felt cherry .
Cherry varieties resistant to moniliosis : Anadolskaya, Shpanka Krasnokutskaya.
- Cherry varieties for the middle zone>>>
- Cherry: how to choose a variety and plant a seedling correctly>>>
Pruning, depending on the crown of the felt cherry
Felt cherry can grow in the form of a real bush or in the form of a tree from one and a half to two meters high, less often - higher, so gardeners divide felt cherry into bush-type and tree-type plants, in this regard, slightly adjusting the pruning rules.
Pruning bushy felt cherry
Such cherries very actively increase the vegetative mass literally from the first season after planting in the garden, which (planting), by the way, should be carried out exclusively in the spring. You can tell that a tree is already old and needs pruning by looking at the shoots that are starting to become bare. Such shoots can be safely cut off by one third, carrying out this operation at the end of February or at the beginning of March.
If there are too many growths of the felt cherry and the cherry looks like a hedgehog, it is necessary to prune the shoots not in one season, but at least two or three, otherwise you will greatly weaken the plant, and it may even die.
At the end of such thinning, every year in early spring, be sure to thin out the crown, removing all the shoots that thicken it, or use a formation specially designed for bush felt cherries, which is called “slender spindle.” Its essence lies in the fact that it is necessary to periodically remove shoots that are one or two years old, cutting out shoots that bear fruit.
Tree felt cherry pruning
It can stretch one and a half or two meters; here it is important to reduce its growth by shortening all shoots by 20-25 centimeters at the end of February or beginning of March. Such shortening will actively stimulate the formation of bouquet branches and create a compact and low crown
Naturally, it is necessary to remove all those shoots that have managed to grow during the season and are directed to the center of the crown, creating ballast unnecessary for the tree
Pay attention to dry shoots; they should also be removed.
All shoots that are a year old and longer than the length of a simple pencil can be safely cut off by five centimeters.
Formative pruning allows you to give the crown of the felt cherry a decorative spherical shape. David Winger
Formation of the felt cherry crown
Even an old felt cherry tree can either be returned to its former crown shape or created anew. But with young plants the situation is simpler. In the initial six seasons, about seven shoots should be left on the tree for the tree-like felt cherry and no more than one and a half dozen shoots for the bush-like cherry. All second-order skeletal branches should be shortened by half.
Naturally, you need to remove all those shoots that grow deep into the crown, which will further thicken this very crown. Next, all annual growth remains to be shortened to a length of half a meter, otherwise the growth buds can be damaged.
Then we thin out the crown of the old felt cherry: we cut out all broken or damaged shoots, all shoots thinner than a pencil and those that grow deep into the crown. Those shoots that will eventually become bare after bearing fruit also need to be removed.
Conclusion. Felt cherry, although a simple tree or bush, usually grows somewhere in the corner of the garden, protected from cold winter winds and where more snow accumulates, but also needs pruning. First, decide what exactly is growing on your site - is it a tree or a bush, and then proceed to the pruning techniques that we talked about.
Prevention of moniliosis
- Choose cherry varieties that are most resistant to moniliosis and other diseases and pests for planting .
- Plant plants sparsely (every 2–3 m) in elevated, well-lit and ventilated areas, where groundwater is no closer than 1.5 m from the soil surface. It is better to plant near fences or buildings, where the microclimate is warmer and more snow accumulates in winter.
- Thin out the crowns in a timely manner and rejuvenate old trees.
- Avoid mechanical damage to plants.
- Remove all plant debris and growth from the site, loosen the row spacing.
- Water and fertilize in a timely manner.
- In winter or early spring, trim and destroy dried branches affected by pests and diseases, clean off old dead bark on trunks and skeletal branches, remove and burn pest nests.
- Immediately cut out (taking healthy wood 10–15 cm below the drying area) and burn branches damaged by moniliosis.
Removing cherry branches affected by moniliosis
- Harvest carefully to avoid damaging the fruit. Store only fruits without mechanical damage. At the first signs of disease, damaged fruits should be immediately removed from storage.
- In the fall, collect and destroy all mummified fruits hanging on the tree, rake and burn old leaves, since some of the infectious agents can overwinter on fallen leaves, especially in the southern regions.
- Dig up the trunk circles around the trees after the leaves have completely fallen.
- plants and tree trunks can be treated with 1–3% Bordeaux mixture against overwintered pathogens
- Destroy moth larvae, weevils, cherry flies and other pests of fruit trees.
- Use biological drugs.
During the growing season, spray cherries with the following preparations:
- Fitosporin-M (20 ml/10 l of water) in the phases: coloring of buds, beginning of flowering, after flowering, formation of ovaries up to 1.5 cm in size, formation of fruits the size of a hazelnut (hazelnut);
- Phytolavin (20 ml/10 l of water) in the phases: bud formation, flowering, ovary formation, fruit formation with a diameter of up to 2 cm, fruit formation with a diameter of up to 4–5 cm.
Read in detail:
- Preventive measures against diseases of stone fruit crops.
- How to care for cherries.
- Why don't cherries bear fruit?
- How to prepare fruit trees for winter.
- How to protect stone fruits from diseases: cherries, plums, apricots, cherry plums.
Getting rid of fungal diseases
The first signs of the disease become obvious when the cherry tree dries out after flowering.
Clusterosporiosis or hole spot is caused by a fungus that overwinters in damaged areas, including buds and shoots
Symptoms:
- leaf and flower buds turn black and fall off
- light brown spots on the leaves followed by the formation of holes;
- when the root is damaged, the leaf falls off, exposing the branches
- spread over the entire tree crown
- the fruits themselves bleed juice and lose their roundness (pressed points)
- fruits stop developing and dry out at the site of fungal damage
Preventive measures:
- regular cleaning of dry and broken branches
- treating damaged areas with garden varnish
- before buds open, treat the entire tree with a 1% solution of copper sulfate (100 grams per 10 liters of water)
Treatment methods:
- immediate pruning of affected parts
- copper oxychloride treatment
- Spray with 3% Bordeaux mixture after the flowering process is completed and treat with a 1% solution before flowering begins.
Coccomycosis is a fungus that lives in fallen leaves and shoots, which actively spreads countless spores after flowering, and the cherry dries out
Symptoms:
- red dots on cherry leaves
- the reverse side of the leaf is covered with a pinkish coating
- as the disease progresses, they become yellow and then brown
- premature drying and falling of leaves
- deformation and cessation of the ripening process of berries
Preventive measures:
- regular cleaning and burning of fallen leaves
- cutting dry and broken branches
- timely removal of rotten berries
- autumn and spring digging up the soil around the tree
Treatment methods:
- at the time of flowering, treatment with a solution of copper sulfate (350 grams per 10 liters of water)
- 1 month after flowering and after harvesting the berries, treat with Horus at the rate of 1 gram per 5 liters of water.
- treat the root part of the soil with urea (40 grams per 1 liter of water)
Moniliosis, gray mold or moniliosis burn is caused by a fungus that lives in fallen leaves and fruits and is most active at the time of cherry blossoms.
Symptoms:
- brown shoots and leaves
- in the active phase of the disease, gray-green growths appear on the bark
- gray "warts" on fruits
- rotting berries
- affected branches cause complete death of the tree
Preventive measures:
- cutting dry branches
- burning fallen leaves
- timely treatment of harmful bugs
- active cleaning of rotten cherries throughout the entire fruiting period
- When harvesting, removing damaged berries, do not touch healthy cherries and collect separately
Treatment methods:
Before the flowering period begins, actively spray with fungicides
- drug "Nitrafen"
- inkstone
- copper sulfate
— 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture
- after flowering, spray with the fungicidal preparation “Fthalan”
- cutting damaged branches, capturing up to 10 cm of the part not affected by the fungus
Athracnose or bitter rot is caused by a fungus whose activity increases in wet, windy weather, causing the cherry to dry out.
Symptoms:
- black rot on fruits
- some of the affected fruits fall off or in dry weather the berries dry out and remain on the tree
- the leaves first become covered with rusty spots, turn yellow and quickly fall off
— preventive measures:
- autumn and spring whitewashing of trunks with lime milk (1 kg per 10 liters of water)
- feeding with potassium sulphide (1 tbsp per 3 liters of water)
- treating damage with garden varnish
- Regular pruning of dead branches
- collection of damaged berries
Treatment methods:
- treatment with Polyram (10 grams per 5 liters of water) three times: at the beginning and 2 times after flowering with a 15-day interval
- copper sulfate is used in a proportion of 50 grams per 10 liters of water
- destruction of leaf rollers and codling moths
- spring treatment with 1% Bordeaux mixture
False tinder fungus is a fungal disease that causes white rot on the inside of the tree.
Symptoms:
- black veins in wood
- fragility of branches even with minor gusts of wind
- soft and light wood at the cut point
- perennial flattened growth
- a large bluish-yellow mushroom with small veins
- located in the lower part of the tree in places of cracking
Preventive measures:
- regular treatment with lime milk
- spring organic feeding
- lubricating damaged areas with copper sulfate (3% solution) or garden pitch
Treatment methods:
- cutting mushrooms in July until the spores ripen
- A tree that is too damaged can no longer be saved, so it must be uprooted and definitely burned.