Potatoes are one of the products that most people are accustomed to seeing on their table several times a week, or even daily. Many grow it on their plots, others buy it as needed. Quite often, root vegetables quickly darken, losing their attractiveness and taste.
Tuber spoiled by rot
Many people ask why potatoes inside are empty and brown, or even black, and what to do to prevent them from turning dark. Let's look at the reasons. It is important to know why potatoes turn black inside at the stage of growing, storing, and cooking, as this can be dangerous for humans.
Reasons for potato darkening after peeling
Potato tubers often begin to turn black immediately after cutting off the skin. This is a natural process and is associated with the presence of polyphenols in root vegetables. Under normal conditions, these substances do not come into contact with oxygen, but with mechanical damage, which includes removing the peel, everything changes. The intercellular membranes through which polyphenols were separated are disrupted. A chemical oxidation reaction begins, after which the raw potato pulp turns black, red, or blue.
Darkened peeled tuber
If we delve deeper into the biochemical processes, we can note that potatoes contain the enzyme tyrosinase , which is needed to capture oxygen and accelerate the oxidation process. It itself is colorless, but it is because of tyrosinase that the roots turn dark after oxidation. The amount of this enzyme increases in root crops overfed with nitrogen. This is why potatoes turn dark a few minutes after peeling.
Important! Tyrosinase is easily removed with plain water. Therefore, to prevent browning, peeled potatoes are placed in water. But when left in water for a long time, starch and other beneficial substances are washed out, after which the potatoes lose their pleasant taste.
Methods for storing peeled potatoes
Sometimes housewives are faced with the problem of preserving tubers after cleaning.
Preparing potatoes for freezing
To prevent the potatoes from turning black inside, use the following options:
- Freezing . Potato slices are placed in a bag and placed in the freezer. There they can be stored for a couple of months or until the first defrosting. First, the pieces are placed individually on a tray or board and placed in the freezer. When the slices are frozen, carefully remove them from the board and transfer them to a bag or plastic container and put them back in the freezer. This prevents the pieces from sticking together. They are prepared without first defrosting, otherwise everything will turn into jelly.
- Cold water . Place the peeled potatoes in a container with water and put them in the refrigerator. It will not turn black, will not turn blue, and will be suitable for cooking within 24 hours.
How to Keep Peeled Potatoes White
It is quite possible to keep potato slices, whole or grated tubers light and not blackened.
Water is a reliable way to keep potatoes light
There are several ways:
- Water . To prevent potatoes from darkening after peeling, they are immediately placed in cool, salted or acidified water. Soaking peeled root vegetables in cold water for an hour will keep them fresh and free of black spots. Boiled potatoes are preserved in the same way. After cooking and cooling, it is recommended to place it in cool, acidified water. The tubers will remain appetizing and attractive.
- Acidification . When cooking or stewing, add a little apple cider vinegar, bay leaf, a couple of grams of citric acid or a spoonful of lemon juice. These components stop oxidative reactions in potato pulp.
- Blanching . To preserve potato slices, immerse them in boiling water for 4 minutes (blanch). This will destroy the tyrosinase and the potatoes will remain light in color. Then they put it in a bag and freeze it or simply put it on the refrigerator shelf (but must be used within 48 hours).
What to do to prevent potatoes from turning black
Very often situations arise when potatoes lay in the basement all winter, and by spring they began to turn black. This could be due to poor ventilation.
As the weather gets warmer, the potatoes move into storage and sprout. The pulp darkens and becomes limp. There is a sharp jump in temperature, moisture is released, and the debate continues. Thus, you can lose the entire harvest.
To prevent potatoes from starting to turn black inside during storage, you must follow a number of rules:
- After harvesting, potatoes should be placed in the fresh air for 20 days;
- place it in wooden boxes equipped with ventilation holes;
- maintain the required temperature in the storage;
- boxes and pallets should be moved 20 cm away from the walls;
- potatoes are sorted at least once - sprouted and diseased tubers are removed, as well as healthy ones located next to them;
- if storage is carried out at home on the balcony, then it is recommended to cover the boxes with a warm blanket;
- Potatoes can only be stored together with beets, which will take away excess moisture from them; proximity to other vegetables is strictly prohibited.
If you follow these recommendations, the potatoes will last almost until spring, and the efforts to grow them will not be in vain.
Reasons for potato darkening after cooking
Housewives sometimes notice that beautiful, healthy tubers, after being cooked, lose their attractive appearance, acquiring a grayish or bluish tint.
Boiled potatoes should have a pleasant natural color
This depends on a number of factors:
- Violation of agrotechnical conditions . If the tubers were grown on poor soils with a lack of potassium fertilizers or, conversely, the soil was oversaturated with phosphorus, then an excess or deficiency of microelements upsets the balance of amino acids in the root crops. This leads to their darkening when boiled.
- Varietal features . Tubers belonging to varieties with a large amount of polysaccharides (dry starchy substances) quickly turn black when cooked. For example, Lady Claire, Red Scarlett, Nadezhda, Rosara.
- Presence of polyphenols . These substances react when exposed to high temperatures and oxygen, and the potato flesh turns black.
The potato inside the tuber is black: what is it?
Blackening is a defect caused by mechanical stress, infections, diseases, improper collection or growing process, or improper storage.
It is important not only to grow a large harvest, but also to be able to preserve it until next year. The most common problem is blackening of the tubers inside. No matter how good a potato looks, it may darken during storage or be darker when dug up.
We need to determine what exactly this is connected with. Otherwise, the entire harvest could be spoiled. A similar problem can be caused by both the physiological disease melanosis (gray spotting) and a variety of infectious diseases, mainly fungal.
Why do potatoes turn black inside during storage?
The blackening of potatoes inside is a consequence of several reasons. These include errors during crop cultivation, violation of crop storage rules, and damage by pests or diseases.
Tuber blackened inside
Black spots on the outside and inside of the potato may appear already at the stage of its cultivation. This happens in case of improper watering, application of undiluted organic fertilizers to the soil and other factors.
Infectious diseases and tuber damage
During harvesting and transportation, root crops are often damaged. They are injured with shovels and potato harvesters. During transportation, potatoes hit each other and dents appear on them. Damaged areas become entry points for the penetration of microorganisms (fungi, bacteria). And over time, the potato becomes black inside.
Tubers quickly become infected from each other
The appearance of dark spots is provoked by various potato diseases:
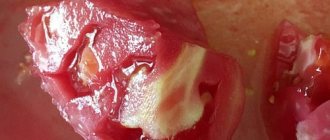
- Black leg . An infectious lesion transmitted from one tuber to another, even in bags after harvesting. When infected, you can see inside the potato an empty and brown notch in the flesh. It looks like insect damage, but it is the result of bacteria. Gradually, the blackness spreads along the vascular branches and appears on the peel. At the same time, an unpleasant smell of rot is felt. Potatoes infected with blackleg should not be eaten.
- Melanosis . This disease develops as a result of mechanical or other damage to tubers. The potatoes look healthy on the outside, but the blackness is spreading under the skin. If you have melanosis, you can eat darkened potatoes. But to preserve its attractiveness in dishes, it is necessary to acidify the water in which it will be boiled or stewed with lemon juice. Starchy varieties most often suffer from melanosis. In addition, the development of the disease is provoked by improper actions during harvesting, leading to its damage.
- Late blight . This fungal disease affects potato tubers and tops. They are unevenly colored black. If late blight is not eliminated in time, it will spread to all crops growing nearby and destroy the crop. The disease can be distinguished by brown dots and spots on the leaves, their rotting, drying out and falling off. Late blight appears if the weeds were not removed in time, the seedlings were already infected with a fungus, or errors were made in the potato growing technology. The spread of late blight is facilitated by rainy weather and excessive watering. In waterlogged soil, pathogenic microflora actively develops and moves throughout the area.
Late cleaning and improper storage
Every experienced farmer knows that it is necessary to harvest the potato crop on time. If the deadlines are not met, the potatoes become susceptible to infection and the appearance of blackness. Early harvesting of tubers results in the fact that they do not have time to form a thick skin that protects them from bacteria, pests, and diseases. Also, useful substances that help protect young potatoes do not have time to accumulate. Tubers become defenseless against diseases, and such potatoes quickly turn black.
Proper storage of potatoes
Delaying the harvest leads to loss of consumer qualities. If potatoes are dug up after frost, they have time to freeze. And in the heat, the decomposition of polysaccharides begins in root vegetables. As a result, the inside becomes soft, similar to jelly, it oxidizes and turns black. This happens if in the cellar or pit where the crop is stored, the temperature fluctuates: it drops below +2 and rises more than +5 degrees, and the humidity exceeds 80%.
You should not keep the tubers in the soil for a long time after mowing the tops. In warm and sunny weather, they will overheat without access to moisture.
Important! Timely harvesting of potatoes helps prevent the appearance of blackness inside the tubers during storage by 25% .
Often, potatoes turn black inside during storage just a month after they are placed in storage. This happens if the root vegetables are in a warm, poorly ventilated place.
The potato harvest should be stored at a temperature of +2 to +4°C. Increasing degrees provokes the appearance of dark spots. If the temperature drops below the required norm, the potatoes freeze. The first appearance of blackness can be noticed a month after the crop has been left in a room without ventilation. In this case, potatoes can become a real biological weapon. It releases gas, a small amount of which can kill a person.
Incorrect application of fertilizers
Inexperienced gardeners are of the opinion that if you apply as much fertilizer as possible, the harvest will be excellent. Therefore, they generously feed the soil with herbal infusions and organic matter, and plant green manure plants. But as a result of such active care, a large amount of nitrogen . On the one hand, this substance helps accelerate the growth of potatoes and increase the mass of tubers. On the other hand, an excess of nitrogenous substances in the soil causes potatoes to darken during storage.
Manure and compost must be rotted before being added to the soil.
Advice! You should be careful with fertilizing. Organic fertilizers should not be used fresh. The manure must sit for a year, otherwise it will simply burn the plants. The compost must also rot and rot.
In addition to nitrogen, it is important for potatoes to obtain potassium from the soil. It is thanks to this element that the tubers not only ripen in a timely manner, but are also perfectly preserved until spring. Therefore, for prevention, it is necessary to regularly apply potassium fertilizers to the soil.
Adverse weather conditions
Potatoes, despite their apparent unpretentiousness, prefer to grow and ripen at average temperatures and humidity. Deviations in these parameters provoke blackening of the tubers. A lack of moisture leads to their drying out, and an excess leads to a lack of oxygen and rotting.
Potatoes grown in good conditions
Due to high temperatures, the tubers overheat, fermentation processes begin in their pulp, and rot appears. This is especially true for varieties with a high starch content.
Turned black when growing
Why potatoes may turn black inside during the growing stage:
- Too much nitrogen in the soil, or potassium deficiency. Also, undiluted organic matter added to the soil can cause darkening of the pulp; potatoes do not like the introduction of concentrated products;
- During cultivation, mistakes were made in watering; this could be either overwatering or underwatering;
- The harvest was harvested either too early or, conversely, late. In the first case, the tubers simply do not have time to ripen; in the second, they spend too long in the warm soil and rot.
Can I eat browned potatoes?
Just because a potato has turned black does not mean it is forbidden to eat it. If blackness occurs under the influence of natural oxidative reactions, due to minor damage during transportation, the tubers can be eaten.
It is better not to eat tubers infected with the disease.
But if the potato is empty inside, has darkened due to the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, or there are other signs of the presence of a disease, it is better to throw it away. Fungi and bacteria release toxic substances and are not destroyed even during prolonged heat treatment.
Storage rules
How long the potatoes will last depends on proper preparation for storage and the conditions in the cellar itself. The choice of variety when planting also influences. The main factors that must be taken into account for the safety of the crop:
- When planting, you need to think about which varieties you will need, because they are stored differently. Late potatoes are intended for long-term storage in the cellar. Even under ideal conditions, early varieties will not last long. They are intended to be eaten directly during the season.
- Before being sent for storage, the tubers are sorted and sorted - diseased, damaged, and suspicious ones are removed. Potatoes that come into contact with diseased vegetables should also be removed; they may be infected, but symptoms have not yet appeared. Even a few diseased tubers can destroy the entire crop in storage. Potatoes must be dried, otherwise raw tubers may turn black inside and rot.
- Constant monitoring of the temperature in the place where the crop is stored is necessary. Special control is needed during the changing seasons in autumn and winter, when there is a risk of temperature fluctuations.
Important! Some potato varieties contain a lot of starch and a slight browning is normal for them.
To maintain the desired air temperature in the storage room, use ventilation and bottles of cold or hot water placed around the perimeter of the cellar. This reduces the risk that the vegetable will begin to turn black inside. With timely control of humidity and temperature, potatoes can be preserved.
Useful tips for housewives
It is quite possible to avoid the appearance of blackness in potatoes. You just need to use folk wisdom. Tricks have long been invented to help keep tubers healthy.
When growing potato bushes, they constantly pay attention to their health. Brown spots on the leaves and black rot at the roots indicate damage by the disease; such root crops should not be stored.
Excellent harvest of healthy potatoes without blackness
During the growing season, potatoes are fertilized with potassium fertilizers. In dry weather, the plantings are mulched and watered, and in damp weather they are hilled and loosened. Dig carefully, trying not to damage the tubers. Be sure to air dry them in the shade, preferably outside or on the veranda.
When storing, you need to use agrotechnical tricks:
- Place only healthy, tested, thoroughly dried tubers in storage.
- You need to lay out the potatoes in small boxes, a maximum of 2-3 layers. Otherwise, a lot of pressure is created on the lower layers, which provokes the formation of blackness inside the root crops.
- It is better to store the harvest in basements or cellars. In any season, it is necessary to maintain the same temperature (on average +2-+4), humidity 70-80%. Regular ventilation and absence of sunlight are required. Under such storage conditions, potatoes will not germinate and will be preserved well. If the temperature periodically stays from 0 to -10, the tubers will become sweetish, and dark spots will appear inside. High temperatures provoke the appearance of sprouts and the development of gray rot.
- Control the temperature in the vegetable storage room by opening the vents and ventilation holes. This should be done especially often in the fall and spring, when there are strong temperature fluctuations.
- Regularly sort through the tubers to detect damage, rot, mold, and other diseases.
When preparing potato dishes, you should remember about tyrosinase, which causes peeled root vegetables to darken. It is removed with water, so you need to use the following method: peel the potatoes, rinse and keep in water until cooked.
Fighting methods
What to do if, despite all preventive measures and sufficient care, the potato tops still turn black? In this case, you need to put all your efforts into overcoming the disease as quickly as possible, before the problem becomes more global. If you find slight blackening of the leaves on a potato bush, take the following measures:
- Spray potato leaves with Bordeaux mixture or copper oxide with chlorine; a seven-day treatment is usually enough to solve the problem of blackening of potatoes once and for all. In this case, each sheet is processed, and this must be done on both sides.
- If you discover the disease at an advanced stage, that is, the potato bush has turned pretty black, there is not a single green leaf left on it, there is no point in saving it.
- After all of the above steps have been carried out, it is necessary to mow and then destroy all the tops that have been affected by the disease, and this is done strictly 7 days before harvesting.
- After the crop is harvested, it is important to ensure normal storage conditions for the crop, that is, to comply with the requirements regarding ventilation, temperature and lighting. It is important to re-check the crop after 2-3 weeks of storage to eliminate black tubers.
Now you know why potatoes turn black inside during storage. In conclusion, let us say that blackening of potatoes occurs quite often; it is enough to follow all the requirements for growing and storing the crop, choose potato varieties with a normal starch content, thereby reducing the risk of the problem to a minimum.
Reasons for germination
A potato tuber is a nutrient-packed version of a bud. Its goal is to germinate in the spring and form a new plant. This process starts when it gets warm enough. Sprouted tubers become less nutritious as starch is used up for germination.
If the potatoes sprouted during storage, this means that the storage is too warm. Elevated temperatures can also develop in the depths of the stockpile if ventilation is insufficient. The sprouts are dangerous to eat, so they will have to be cut off. The potatoes must be sorted and placed so that the optimal amount of air enters.
So, to prevent germination, the room with the potatoes should be well ventilated and cool (but not too cold, otherwise the flesh will begin to darken).
Fungal diseases
To protect potatoes from fungal diseases, it is very important to follow all the rules of crop rotation and not plant other nightshade plants next to the crop.
Fungal diseases can affect single potato bushes, but they can quickly spread to neighboring rows.
Even if the plot is very small, there should be at least one bed of corn or any legumes between the nightshades.
For prevention, before planting, it is recommended to treat the tubers with suitable fungicides, a solution of Bordeaux mixture or copper sulfate. Plants should also be treated with fungicides during the growing season.
If symptoms of fungal infections are detected, a couple of weeks before harvesting, you should mow down all the tops and burn them . Even slightly rotten potatoes must also be destroyed.
Let's look at fungal diseases that cause dark spots in more detail.
Late blight
Late blight on leaves.
Late blight on tubers.
One of the most serious diseases in which an impressive part of the crop can suffer.
At first, brownish spots appear on the leaf blades, on the reverse side of which there are white colonies of growing mycelium. The disease develops especially quickly in wet and cool weather.
If you do not take action, the fungus will spread to the tubers, which will quickly begin to rot . In this case, only complete destruction of the diseased bush can save the harvest.
Alternaria blight
Manifestation of Alternaria on leaves.
Signs of Alternaria blight on tubers.
The leaves become covered with small, dried-out dots, which gradually turn into blurry spots with a dark core.
In an advanced stage, the disease descends to the tubers, on which small black spots appear. If such potatoes are left for storage, they will not only rot themselves, but will also infect neighboring tubers .
Fomoz
The fungus attacks the crop during flowering.
- At first, deep rotting streaks appear on the stems, causing the stems to become deformed.
The initial stage of Phomasis.
- It is difficult to detect the disease during harvest because it develops more slowly in tubers.
- Dark spots on potatoes have clearly defined boundaries, and dents with a hard surface also appear on the tubers.
Phoma on tubers appears during long-term storage.
Scab
There are several types of scab: ordinary, powdery, lumpy, silvery. The fungus infects potato tubers, which become covered with dark and light raised spots.
If scab affects planting material, it very quickly spreads to the entire future harvest. Infected tubers germinate extremely poorly.
The onset of the disease is diagnosed by small ulcers, which then grow and become covered with a cork-like coating.
The fungus feels very comfortable in alkaline soil . To neutralize it, it is recommended to use ammonium sulfate, 50 g of which should be diluted in 10 liters of water and moistened the soil. But you should also avoid fertilizing potato beds with manure. For these purposes, it is better to choose green manure (clover, mustard greens, soybeans, lupine).
Clover will perfectly saturate the soil after potatoes. Excellent green manure.
How to protect potatoes from rotting?
Based on all of the above, it is clear that the poor preservation of tubers during the cold period begins with a violation of the technology for growing and harvesting this crop. The following significant reasons are the unpreparedness of the storage facility (cellar, basement, vegetable pit, balcony, loggia, etc.) for storing products, incorrect selection of potato varieties, and violations of storage technology.
It is these reasons that cause damage to tubers by various fungal, mold and bacterial diseases; contribute to their rapid spread and loss of yield not only during cultivation, but also during storage.
To protect potatoes from rotting during storage, it is necessary to properly prepare the area for this crop. Apply fertilizers, fertilize, treat diseases and pests only in accordance with technology and recommendations.
For planting (for the purpose of long-term storage of tubers during the cold period), it is necessary to use only zoned, medium and late varieties (in terms of ripening), resistant to fungal and other diseases. Before planting, the seed material must be processed.
During the growing season, plant treatment must be carried out at the very beginning of the disease, and not wait for mass damage. It is more practical to carry out preventive treatments according to a previously worked out scheme.
Only absolutely healthy, undamaged tubers should be stored in prepared storage facilities.
Fulfilling the basic requirements for preparing tubers, planting them, caring for them and harvesting them will minimize damage to the crop during winter storage.
When planting several varieties on a site, each is harvested separately
Rules for protecting potato tubers from rotting during storage
- When planting several varieties on a site, each is harvested separately.
- Only mid-season, mid-late and late potato varieties are stored for storage. Early varieties after December are no longer suitable for use as food and remain as planting material or are used for animal feed.
- In order for the tubers to ripen well, the potato tops are mowed 10-15 days before harvesting.
- Potatoes are dug up in dry, sunny weather. If the weather is rainy, then the potatoes are slightly dried and manually cleaned of adhering dirt (to avoid mechanical damage through which a fungal or bacterial infection can penetrate inside the tuber).
- Mechanically damaged and diseased tubers are immediately put into a separate pile.
- Healthy, undamaged potatoes are transferred under a canopy (covered from the sun) or in a dark room with good ventilation for 5-7 days to ripen (coarse) the upper skin. Protection from light is necessary to prevent the potatoes from turning green. Solanine is formed in light, and such tubers cannot be used as food.
- Before storing, the storage facility is disinfected and dried.
- To protect against rotting during storage, dried and cleaned tubers can be treated with the biological preparations “Fitosporin” and “Anti-rot”, which will reduce the infectious background. They are harmless to humans and animals.
- If potatoes are stored in bulk, then it is advisable to place 1-2 rows of beets on top. It will absorb excess moisture, which will protect the potato tubers from rotting. The beets will not be harmed.
- It is more advisable to store potatoes in boxes (each variety separately).
- Once a month, the tubers are sorted, removing the diseased ones.
- Good ventilation will protect stored products from infection and rotting.
- The air temperature in the storage must be maintained at +2...+4°C, and humidity 80-91%. If the humidity in the room is high, you can place, in addition to ventilation, a container of quicklime and change the filler if necessary. With the arrival of spring, the temperature in the storage room may rise. Frozen water in plastic bottles with a capacity of 3-5 liters will help reduce it. Ice containers are placed in different places. Ice in closed containers will gradually melt and cool the room.
Tips on how to store it correctly
Prepare storage containers that allow the crop to be well ventilated.- Find a dark room in which you can ensure the optimal temperature (we wrote about where to store potatoes here, and what temperature is necessary for this is described here.
- Carefully sort through the potatoes and discard tubers with damage and rot.
- Some gardeners recommend treating the storage with copper sulfate or other substances to combat bacteria and fungi.
- You can bathe the tubers in a weak solution of potassium permanganate or brilliant green for disinfection.
- Remove soil from potatoes and dry.
If the potatoes were grown correctly, then careful preparation and compliance with all storage conditions will allow them to last all winter.
Cooking rules
The tubers are properly cleaned before cooking. First, the vegetables are washed well, removing all dirt and chemical residues. Peel the skin until the pulp becomes light. There should be no skin or greens left on the surface.
Immediately after peeling, place the potatoes in water, washing each tuber. The lack of oxygen prevents chemical processes from occurring that cause darkening.
Before cooking, wash the vegetables again. During storage and cooking, the tubers are completely covered with water. If you don’t cook it right away, change the water before putting it on the fire.
You can prevent the formation of dark spots by adding a bay leaf to the pan before cooking. And after cooking, add a few crystals of citric acid or a few drops of vinegar.
How to prevent darkening of tubers?
Not every person has a summer house or a garden where they can grow their favorite vegetables. Most of us buy all our products in supermarkets and markets. And there you can’t always be sure of the quality of the product. Therefore, to prevent the potatoes from turning black after cooking, it is better to prevent this unpleasant phenomenon.
How to prevent vegetables from browning:
- When planting yourself, you should remember about the correct fertilizer. There should be no chlorine impurities, but potassium sulfate will be beneficial.
- Prevent tubers from being exposed to low temperatures. And when buying, you need to choose a quality product, there should be no cracks or blackening.
- Make sure that moisture does not get on the root crop before storing. Ventilate the room and dry the tubers sufficiently.
- If there are rotten or moldy potatoes, they should be thrown away. Then other tubers will not be infected.
- During the cooking process, you need to completely cover the potatoes with water.
- After cleaning, raw tubers must be stored in cold water before boiling.
- Good cleansing is also important. If the tubers are very dirty, it is better to wash them. There may be fertilizer in the dirt.
- To reduce the level of starch in root vegetables, you can leave them in cold water for an hour. After which it is recommended to pour out the liquid and pour in fresh liquid for cooking.
- One effective way is to use bay leaves. Add a couple of leaves to the water and the tubers will not change color.
- The acid helps prevent blackening. Vinegar or ascorbic acid are suitable for these purposes.
If you want to prevent your potatoes from turning black after boiling, you can use these simple tips. You should try to choose good quality vegetables. After all, both the taste of food and the benefits to the body directly depend on this.
Potatoes can rightfully be called the second bread. It contains many useful components and vitamins. Dishes made from root vegetables are satisfying and tasty. To make them look appetizing and aesthetically pleasing, try to avoid the appearance of dark spots.
How to freeze raw potatoes
Peeled, smooth potatoes without eyes and with the least amount of starch are suitable for freezing. Pink-skinned varieties store especially well. The temperature in the freezer should be above 18 degrees.
If potatoes become sulfitated, they are stored in the freezer for 2 days at a temperature of 2-6 degrees. There are several ways to freeze raw potatoes:
- Entirely. Small tubers are washed and blanched for 5 minutes. After this, the potatoes are cooled in cold water and placed in vacuum bags. Large potatoes are cut into medium pieces and frozen using the same method.
- In pieces. The peeled tubers are cut into bars, washed and dipped in boiling water for 2-3 minutes. They are then cooled in cool water and placed on a dry towel to dry. The potato pieces are placed in bags and tied so that there is no air left in them.
To avoid potatoes sticking together, the product is frozen in several stages. It is laid out in one layer on a tray and kept in the chamber until frozen, and then packaged in bags.
Before cooking, potatoes are not defrosted, but used immediately for cooking. The result largely depends on the power of the freezer, the variety of tubers and the skill of the housewife. If you do everything according to the instructions, the vegetable will hardly change its taste, structure and color. It is recommended to freeze a small batch of potatoes to check how they behave after such storage.
Do you use expired food for cooking at home? Yes, the main thing is to process it if it is meat or expired kefir for pancakes. 27.71%
No, it is very dangerous and not useful. 37.66%
If the products have fungus or mold, then we throw them away; if they are a couple of days past their expiration date, we use them for food, even without heat or other treatment. 34.63% Voted: 693
Errors during the growing period
Darkening of the tuber pulp may be evidence of improper cultivation of the crop. When growing potatoes, gardeners often make the following mistakes:
- The soil is not fertilized correctly. Excessive application of nitrogen fertilizers and lack of potassium fertilizers leads to potato diseases, including dark spots on its pulp. Often a lot of fresh manure, grass clippings, green manure and buckwheat husks are added to the potato plot, and then they are immediately dug up for planting. This cannot be done - the harvest will be of poor quality, and the bushes will be infected by fungi. Within a month after placing the potatoes in storage, you may notice gray spots on their flesh. You should not plant an area with root crops immediately after applying organic fertilizers. Skip one season. It is best to first let organic fertilizers rot for 1-2 years, and only then distribute them throughout the garden.
- The second reason leading to crop damage is improper watering. During the formation of tubers, it should be moderate. An excess of moisture leads to a lack of oxygen in the soil, and with a lack of it, the tubers overheat. With any of these options, the shelf life of the crop will be reduced.
Special attention should be paid to potato varieties that contain a lot of starch; they suffer from gray spots more often than others.
Is it possible to eat darkened potatoes?
Potatoes that have changed color during heat treatment are considered quite suitable for consumption, since blackness is not a sign of a high concentration of nitrates or other dangerous substances in the vegetable pulp. The product loses only its aesthetic and taste qualities, and these factors cannot cause harm to health.
Before deciding to eat blackened potatoes, you should understand the reasons. If we are talking about cooking greened tubers, then it is better to refuse such a dish. Peeling the peel does not rid the vegetable of the solanine accumulated in it. The highest concentration of the toxic substance is located around the circumference of the potato in a centimeter layer.