Currants seem to be an unpretentious plant, but if you don’t take care of them, they will produce small, tasteless berries. In order to manage everything and not forget anything, you need to create a currant care calendar. To do this, in a notebook, write down the stages of care by month, which includes protection from pests, fertilizing, watering, mulching, pruning.
Each month has its own tasks for caring for red and black currants. We suggest making a calendar by month, according to the advice of agronomists and experienced gardeners.
End of March, beginning of April
It is necessary to draw up a calendar from the very first days of spring, as soon as the snow begins to melt. After the snow has melted, when the cover has been removed from the bushes (in cold areas, many gardeners cover currants with covering material), it’s time to start caring for the currants.
Sanitary pruning
Next, caring for currants after winter, in spring, begins with sanitary pruning. Broken, twisted, thickening bushes and diseased branches are cut out, and at the same time an inspection is carried out to detect pests.
Formative pruning can be done. Find 2-4 year old shoots. They are not too hard, not old yet. Leave 5-7 buds on their branches, the rest should be cut off. Annual shoots are shortened by 10-15 cm.
Red and white currants need to be pruned differently, as their branches can produce a large harvest for up to 8 years. And the most popular variety of red currant, called “Red Cross”, produces a harvest of up to 15-20 years.
In red currants, you can only cut off the unripe tops of the shoots, tops, and very old branches. After trimming, there should be 20-25 healthy branches left on the bush, which are 1-8 years old.
Pay attention to the buds; if they are “swollen,” then the plant has already been attacked by a bud mite. Without sparing, pinch off the swollen buds before the pests wake up and begin to harm the currants.
Do not forget to inspect the core of the cut layer. If it is not green, but dark, its center has been turned into dust, it means that the bush is infected with the larvae of the narrow-bodied borer. If a seedling has many affected branches, then it must be dug up and burned.
Treatment of currants against diseases
Caring for currants of all varieties is almost no different. As soon as the snow melts, the mulch must be removed around the bushes, and before the buds swell, that is, before the sap flows, you must treat them with 3% copper sulfate in order to prevent plant pests from waking up.
For processing currants: copper sulfate, Bordeaux mixture 3% solution
Didn’t have time to treat with a highly concentrated composition? Then, after the buds open, you can treat them with 1% copper sulfate. Thanks to the low concentration of the drug, the kidneys will not be burned, and the pests will disappear.
After bud break - treatment with 1% drug.
If the currants are healthy, then preventive spraying can be carried out before the buds open. To protect each bush, treat the currants with one of these preparations:
- Fitosporin-M,
- Gamair,
- Sporobacterin or
- Topaz.
Biological products Fitoverm and Bitoxibacillin will also help protect currants. For severely affected plantings, Aktar and Biotlin are used. Fufanon-Nova and others.
For mild infestation, folk remedies will help: garlic infusion, soap solution, onion peel infusion.
Some gardeners' spring care for currants includes scalding the currants with boiling water. But such a procedure will not have a strong effect on pests. While the boiling water is pouring, it will cool down, and warm water will have no effect on the larvae.
If you practice scalding, then add 10 aspirin tablets or 100 grams of vitriol to a bucket of boiling water. Raise the watering can 10-15 cm from the branches and pour over the entire bush. One bucket should be enough for 2 bushes. The hot water temperature should be 80 degrees.
Preparation of cuttings for planting
When pruning currants in the spring, which is carried out before the buds open, set aside healthy branches and place them in a jar of water.
You can cut cuttings 25-30 centimeters long with 5-7 buds, plant them immediately in loose soil, where a bucket of humus was added for digging and 1 sq. meter 1 gram of nitroammophoska.
For rooting, branches of annual growth are useful, but old ones also take root well.
For cuttings, branches that are 2-3 years old and about the thickness of a pencil are more suitable. The time for cutting cuttings is the end of March, the beginning or middle of April, it all depends on the region. Once sap flow begins, it is too late to prune.
The top of the cutting (2 buds) must be cut off. The lower part is about 2 buds deep and immersed in the ground.
In the southern regions they can be planted in the ground, but in the Moscow region and in cold areas, the cuttings are placed in a jar, leaving about 2 centimeters under water or up to the second bud from the bottom. If you lower it lower, the cutting may rot. The water must be settled. Make sure that the water does not drop lower and does not become cloudy; it must be changed more often and added when it evaporates.
How to cut? It is recommended to cut obliquely. If it doesn’t work out, the cutting will still take root. The best place for cans of water is a windowsill, so that the temperature is no higher than +23...+25 C.
When will the roots appear? You will have to wait 2 or 3 weeks for the roots to appear. After 30-40 days, the roots grow to 3-5 cm. When the weather becomes warm, these roots can be planted in the ground.
To protect against the return of frost, the seedlings can be covered with a cut-off water bottle. Before planting, the lower ones, which have begun to bloom or have not yet blossomed, must be removed.
Pests of red currants and their control
The reason for the appearance of any infection on red currant plantings is not only spores of various fungi and bacteria. Flying and crawling insects can cause enormous harm to red currants. Moving between bushes, they actively transmit various infections, which will subsequently turn into a large-scale threat to plants and crops. When choosing a drug to control insect pests, pay attention to the presence of a nervous system in the parasite.
Over time, an addiction to certain compositions of the chosen product develops. The action of such after addiction is not effective. Habituation occurs within two years. Therefore, there is a need to periodically change means of control. Then there will be no adaptation in insects, and the treatment will bring its results. It is advisable to poison insects only as a last resort. It is better to use folk remedies, both for prevention and for the destruction of small pest formations. Experienced gardeners use such products to repel pests from areas planted with berry bushes. The effects of folk remedies are environmentally friendly, safe for humans and animals in any case.
2.1. Sawfly.
This insect causes enormous damage to berry bushes. The revealed external resemblance to an ordinary fly, of the same small stature. The sawfly midge appears from the cocoons at a time when young leaves begin their life activity. The process of laying eggs begins; the selected location is the slits of the leaf plate. The larvae develop by feeding on leaves. If measures are not taken in time, the larvae will destroy all green cover. The plant does not receive the necessary nutrition and dies. The sawfly itself is quite noticeable and is not difficult to detect: the larvae develop into false caterpillars with a light green body, the head is bright brown. Treatment to destroy the pest is simple:
- the use of standard chemicals, for example the well-known Spark;
- make a solution of garden wormwood and regular tobacco, spray the plants. Has a repellent effect;
- manual collection, shaking off all visible larvae onto a film located under the bush or any other smooth flooring. The harvested larvae must be destroyed;
- ignoring the presence of insects on currants will lead to the destruction of the plantings and the crop itself. Sawfly reproduction is progressive, capable of producing two generations in a season.
Red currant pest Sawfly: photo
2.2. Leaf roller.
The representative of this red currant parasite is a butterfly, its color is dark brown, there is a remarkable pattern on its wings in the form of a triangle, eggs are laid on currant stems, in some cases on buds. The appearance of caterpillars brings the death of the flower closer, since nutrition occurs from the insides of the inflorescences. Young, green branches suffer, which are also destroyed by the eater. The second generation can destroy the entire crop.
The name comes from the caterpillar’s ability to wrap itself in leaves, form cocoons, and wrap itself in cobwebs. To combat this you can use the following:
- insecticides Phosfamide, Ripcord, apply early spring by spraying;
- immediately destroy any discovered cocoons to prevent the emergence of an adult butterfly;
- an infusion of tobacco dust in combination with soap will bring a significant effect;
- elderberry is a plant that can repel insects. Plant an elderberry bush nearby and part of the prevention is completed;
- You can make a fire when there is no wind and fumigate with smoke.
Red currant pest Sawfly: photo
2.3. Fire.
Caterpillar, green, with a black head. Settles on leaves and berry clusters, enveloping them in cobwebs. The discovery of such a picture indicates that a pest has appeared on the site. It feeds on buds, moves to inflorescences, if the plant did not have time to die after the attack of the Firefly, it will feast on the fruits. The caterpillars are fast and quickly devour the entire plant.
The most effective drugs are: Rovikurt (before the formation of buds), after flowering, use Fufanon. During the period of fruit ripening, use exclusively biological products - Fitoverm, Iskra-Bio. If the plantings are small, use manual collection of damaged berries. From popular advice - a decoction of tobacco, pine needles, wormwood.
Pest of red currant Ognevka: photo
2.4.Aphids.
It forms colonies, is a small insect, pale green in color. Reproduction is rapid and numerous, enough to cover the entire plant. The tops of the currants are the first to suffer; the leaves later turn yellow and curl. The development of the bush freezes. Treat berry plantings with Fitoverm, Taran, Karbofos. There are folk methods - decoctions of wormwood, chamomile, wormwood. If the listed plants are planted along the bushes or under them, the effect will be slow but constant.
Red currant pest Aphid: photo
2.5.Moth.
Another representative of butterfly pests of red currants. The color certainly attracts with its beauty - white wings with black and blue spots, yellow body. The spectacle in this case is very deceptive. The butterfly is a malicious pest. The caterpillar almost completely destroys the greenery, gnawing right through the foliage. It forms a cocoon on the bottom of the leaf, which is quite heavy. The leaf cannot stand it and falls off. The fight is carried out with Karbofos and sprayed. Traditional methods are to use the decoctions listed above.
Red currant pest Moth: photo
2.6. Tick.
Diseases of red currant were discussed above and the name was mentioned. But there is also a pest, the spider mite. In some cases it can be confused with a simple spider. It sticks to the bush, feeding on the juice of the cells of young leaves and shoots. The vital activity of currants is disrupted. Immunity decreases, the plant is not able to fight an insect attack. A change in the color of the leaves, turning pale, followed by yellowing, indicates that a settlement has occurred. In a short period of time, the leaves dry out. To destroy, spray the bushes with biological agents - infusions and decoctions of tomato tops, chamomile, wormwood, dandelion. Karbofos, Fufanon - apply in case of widespread tick spread. Insecticides-Fitoverm. Liquid soap solutions as a preventive measure. The greatest danger of ticks is that they carry various viruses and fungal diseases.
Red currant pest Mite: photo
2.7.Glass box.
The currants have not yet bloomed, but the plant is withering - the diagnosis is known, it is the Glasswort that has taken up residence. The larvae are very small. They are invisible because they parasitize inside the trunk. They completely eat away the internal composition. They remain to live there until the next season. Early in the spring they come out of hiding and build cocoons-pupas. Improvised methods are not effective. Strong artillery is required.
Experienced gardeners use long-term exposure therapy: - leave the cuttings in sand soaked in a biological solution that contains nematodes. Direction of the drug directly to the glass; -spray tobacco dust, ash, ground pepper onto the soil and loosen thoroughly; - before bud break - treatment with Anthonem-F; -you can use the folk methods listed above; the smells of some plants are repulsive, but the bird cherry next door, on the contrary, attracts the attention of the glass.
Red currant pest Glasscap: photo
2.8.Gall midge.
Representative eating the stem inside. The branches begin to darken, break off, and the bark forms cracks. The leaves turn yellow and fall off. The pest becomes active during flowering. It forms clutches of eggs in the cracks, opening up a large space for the emerging larvae to eat. Lumpy, red spots form on the leaves.
To combat this pest of red currants:
- fluff lime is mixed with tobacco dust in a 1:1 ratio, treat the root area;
- wood ash or naphthalene;
- chemicals-Karate, Kemifos;
- you can use vitriol for spraying;
- The Antacoris bug is an enemy of the gall midge, you can artificially attract it to currant plantings, just plant dill nearby.
Red currant pest Gallica: photo
April
In April, fertilizing and treatment against pests, as well as loosening, are carried out. You need to loosen it like this: step back 50 cm from the bush, loosen it to a depth of 7-9 cm to remove the crust after the snow melts. At the base of the bush you can loosen it to a depth of 3-5 cm. If it is hot in April and the ground has become dry, then the seedlings need to be watered.
Mid-April: Fertilizing with nitrogen fertilizers
By mid-April, currant plantings should be fed with nitrogen fertilizers so that the currants begin to grow green mass. Many people add ammonium nitrate in solution: dilute 20 grams in a bucket of water, pour 4-5 liters under each bush.
For the first feeding of currants - ammonium nitrate. The concentration of the solution is 20 g per 10 liters of water.
During the period of bud pecking, ammonium sulfate (40-50 g) or dry ammonium nitrate (25-30 g) is added per 1 sq. m. meter. Slurry diluted 1:4 is also suitable for spring feeding. You need to pour 1 liter under the root.
Late April early May: Treatment of currants against pests
The most common diseases of currants: anthracnose, rust, septoria, gray rot. If these diseases have been noticed, then before the buds open, the bushes are irrigated with the following preparations:
- Copper sulfate (3%), iron sulfate (5%), or Bordeaux mixture (3%).
- Heavily infected currant bushes can be treated with Gamair, Fitosporin-M, Topaz, and Fundazol. Use strictly according to instructions.
- Irrigate with infusion of ash: pour 100 g into 4 liters of water, leave for 3 days, then strain and spray..
To prevent the appearance of currant glass, bud mites, borers, sawflies, moths, gall midges, as well as aphids, you should use “Bitoxibacillin”, “Fitoverm”.
Against kidney mites - preparations based on colloidal sulfur. Or Tiovit Jay.
Against kidney mites - preparations based on colloidal sulfur. Or Tiovit Jay.
If you do not want to use purchased products, you can spray 4-5 with infusion of tobacco, onion scales, garlic or laundry soap. But folk remedies will be effective only at the beginning of the disease. For serious lesions, you will need “Aktara”, “Karbofos”, “Fufanon”, “Aktellik”, “Biotlin”.
The drug PFCleros against kidney mites
In order for currants to be less affected by mites, it is necessary to choose varieties that are less susceptible to the attacks of this pest, for example, the Black Stork variety.
All varieties of black currants, apple trees, cucumbers, and tomatoes can be treated with the effective preparation “PFKleros” (PSK 25% aqueous solution). The product was developed jointly with the Belarusian Institute of Plant Protection.
This drug helps fight the pathogens of powdery mildew, currant bud and spider mites. It should be sprayed with a solution of the drug “PFKleros” (PSK) during the growing season according to the instructions. The consumption rate is 2-4 liters per 1 ha. When spraying, it is necessary to ensure complete wetting of the leaves and branches of the plants.
Advantages of the drug "PFKleros" (PSK):
- Has a dual effect (fungicide and acaricide);
- Endowed with high efficiency;
- Quickly decomposes on the surface of the crops on which the treatment is carried out: no polysulfides are detected on the leaves after 80 minutes;
- An aqueous solution is less toxic than dry products;
- Source of a number of macro- and microelements;
- Low cost. The drug "PFKleros" (PSK) cannot be used to treat gooseberries (do not allow the spray to get on the gooseberry branches), since all the leaves may fall off.
What drugs do NOT use before flowering?
Before flowering, you should not use too concentrated preparations, for example, 3% copper sulfate, iron sulfate (5%) and Bordeaux mixture (3%). Strong drugs can burn the buds that are preparing to bloom.
Systemic drugs should also not be used before flowering.
List of chemicals
Treatments for pest control on currants are carried out mainly in spring and summer. This is due to the specific effect of drugs that act on insects through contact or ingestion. However, some pests can overwinter on currants, for example
- gall midge;
- glass worm;
- Sawfly.
Currant control should be carried out in the fall, after removing fallen leaves, debris and mummified berries. Products that are suitable for use in private gardens are listed in the table below.
| Pest Control Products | The product's name | Mode of application |
| Gallica | BTB | 50 g/10 l water, autumn treatment as prescribed |
| Glassblower | Movento Energy | 120 g/l, spraying after completion of gardening work |
| Sawfly | Lepidocide | 100 g/10 l. Spraying immediately after picking berries |
The insecticides listed in the table also act on pest eggs. In addition to autumn, treatment should be carried out at other times in accordance with the rules or instructions for use.
In addition to insects, red and black currants are attacked by bacteria, fungi and viruses. Strong chemicals can also be used against them, but treatment in the fall is more of a preventative measure.
| Disease | What to treat? | How to treat |
| White spot disease | Alirin-B | One tablet per 10 liters of water. Post-harvest processing |
| Rust | ||
| Mold | Pentafag-S | 100 ml/10 l, spraying starting from bud break with an interval of 20 days, the last one in the fall. |
| American powdery mildew | Fondazol (Benamine) | 10 g/10 l of water, spray after picking berries |
| Gray rot | Trichodermin | 5 ml/10 l, autumn treatment, can be repeated after a week. |
For some diseases, no treatment will help. For example, if a currant is affected by a striped mosaic, the entire bush is uprooted and burned, and the ground is treated with Bordeaux mixture.
When working with chemicals, you must take precautions and use personal protective equipment.
May
At the flowering stage, a solution of superphosphate and potassium sulfate should be poured under the roots. The concentration of the solution should be 1-2%. You can use a solution of manganese sulfate and boric acid (0.1-0.5%).
“Protsvetok” recommends treating currants with BFC-Lera in early May. The drug is non-toxic. You don’t need to treat with other drugs; this remedy will be enough.
At the end of May, it is useful to treat currants with Fitoverm and Trichoderm. It is enough to pour Trichoderma once under the root and the pests that settle in the soil will be destroyed.
Red and white currants do not suffer much from drought, unlike black ones. The first watering of red and white currants is postponed to the end of May, or better yet to the beginning of June, when the ovary appears on the currants. Under each bush you should pour 2 to 5 buckets of water so that the soil is moistened to a depth of 35-40 cm.
Black currants should be watered immediately as soon as the soil begins to dry out. She does not tolerate drought well. But she doesn’t like strong swampiness either.
Second feeding of currants with potassium-phosphorus fertilizers
In order for the currant harvest to be generous, the plantings require fertilizing with potassium and phosphorus at the flowering stage, then at the planting of the crop and when the berries ripen.
For summer feeding, superphosphate and wood ash are used. Fertilizer must be incorporated into the soil. Make a hole at a distance of 30-35 cm from the bush, pour 200 g of superphosphate, 300 g of ash and 5 kg of humus into it. The bushes are watered. When the fertilizers are absorbed, the soil is leveled.
Ash solution for feeding currants
Dry ash is added to the holes when planting young currants so that the seedlings take root faster. The application rate is 200 g per hole. For adult currants, fertilizing in the spring is done in this way: 300-500 g of ash are scattered around the bush (depending on the size of the currant), then embedded in the soil by loosening and watered abundantly.
At the beginning of April or in the first ten days of May, ash solution is used for spraying, as well as for prevention and protection against diseases and pests.
The solution is prepared as follows: 200 g of ash, 1 glass of 9% vinegar per 10 liters of water.
For spraying, use a garden sprayer. Do not be afraid that the liquid will get on the leaves, flowers and berries. After treatment there is no need to water for 2 days.
Repeated treatment against diseases and pests
In summer, it is better not to treat currant bushes. First you need to harvest the crop, and then treat it with folk remedies, but they do not last long.
Currants can be treated with biological fungicides all year round. If there is no urgent need, then it is better after fruiting. After harvesting, you can treat it with a solution of Bordeaux mixture: 100 g per 10 liters of water.
Biological preparations for currant processing
Blackcurrant care includes protection and pest control. Many gardeners trust only biological products because they are non-toxic and safe for birds, animals and bees.
Lepidoid - effective against caterpillars and lepidopteran pests. Currant pests stop producing offspring. To get rid of all insects, it is necessary to process several times at temperatures above 15 degrees. The product does not work at low temperatures. It is better to carry out the treatment in the evening so that the sun's rays do not burn the foliage.
Bitoxibacillin is destructive to a large number of pests. During the season, treatment must be carried out 3 times. After exposure to the drug, the parasites stop gnawing on the leaves and die. Currants should not be processed during flowering and fruiting. Use in the evening at temperatures above 17 degrees.
Phyton - actively fights pathogens, preventing currant diseases. In addition, the drug improves soil microflora and can be combined with fertilizing and other preparations. Non-toxic to people and animals.
Denobabacillin has a detrimental effect on parasites that chew currant leaves. Insects die 2-3 days after they gnaw on the sprayed plants. Codling moths and cutworms do not die. The drug has no effect on them.
Trichodermin - adapted for processing currants and other horticultural crops. It improves growth, increases plant immunity, fights pathogenic microflora and diseases.
Its main advantage is that it is absolutely safe. The berries can be eaten on the same day by waiting several hours after spraying the currants and rinsing them with plenty of water. But it is recommended to use gloves when working with this product. Work must be carried out in the evening, at temperatures above 14 degrees.
Preparation based on Trichoderma
New generation biological fungicides based on Trichoderma are in demand for caring for currants and gooseberries in the fall and at any time of the year. It contains the soil fungus Trichoderma, so it is widely used in agricultural technology.
The elements of the product release carbon, which breaks down organic matter into components that are converted into phosphorus-nitrogen compounds, thereby helping to enrich the soil.
Preparations based on Trichoderma can rid the soil of many fungal diseases. Obvious advantages:
- Effective prevention of fungal diseases;
- Treatment of fungal diseases;
- Improvement and saturation of soil;
- Restoration of soil after chemical treatment;
- Disinfection of soil and holes before planting.
Action of Trichoderma: as soon as Trichoderma is in the soil, its fungi immediately begin work on creating their own colony of fungi. Gradually, the colony destroys other fungal colonies, clearing the soil of infection.
In addition, the fungus secretes antibiotics that prevent diseases from developing. All processes produced by Trichoderma fungi accelerate plant growth and increase resistance to diseases.
All varieties of this drug have an equivalent effect, so you can choose any one. Each of the preparations can be used for spraying plants, root watering, and treating seeds and soil.
You can spray several times during the season, since the biological product does not accumulate in plants and fruits.
Red currant diseases: description and control methods
1.1. Red currant diseases: reversion.
A disease of red currant that affects mainly black currant varieties, but cases of infection of red currant are increasingly being identified. The instigator of the appearance of this sore is the kidney mite. The tick will not be able to fly in from a neighboring area on its own, or be carried by any insect. It enters your garden with the already infected seedlings brought for planting. Having penetrated your garden, the disease will not leave it for a long time; for 5-6 years it can wander from bush to bush.
There is a very remarkable sign of the appearance of a sore: the shape of the flowers becomes slightly needle-like (curly), with a terry frame, the color changes to purple. The first area to suffer from the disease is the leaves. Gradually they become small, the shape is reduced to irregular, the aromatic, specific, beloved aroma of currants simply evaporates. A frame in the form of large denticles appears along the edge of the leaf. The bush begins to gain density at an accelerated rate, fruiting practically disappears completely. After a while, the diseased bush simply loses its varietal characteristics.
Why does this red currant disease have such dire consequences? The onset of infection is very difficult to detect and goes unnoticed by the naked eye. It is recommended to conduct a regular, thorough inspection of each bush. Not only after planting a seedling for permanent residence, but also within 3-4 years. Neighboring bushes are also inspected to determine the presence of reversion.
Let us highlight a few points on the prevention and treatment of red currant disease:
- to prevent the spread of the disease on your plantings, spray the bushes with colloidal sulfur, acaricides, special preparations, which can also be used in the same direction (example of drugs - Nitrafen, Vertimek). If you take biological products, then gardeners recommend Actofit, Fitoverm;
- the beginning of bud bursting, the period of bud formation - at this time it is necessary to carry out the processing procedure;
- any damaged, or simply damaged, branches are immediately cut out and must be burned in a designated place;
- when you notice extensive damage to a bush, or several bushes, you need to resort to more serious measures - the bush must be completely dug up. With this action you can save the remaining, neighboring, still healthy bushes.
In general, red currant disease can be eliminated by 80-90%. It is necessary to place all seedlings purchased somewhere, even in a special nursery, in a Fitoverm solution and keep it for at least 2-3 days, which will help in the future to avoid an “epidemic” of berry infection. There is also a folk method of disinfection. Use regular tea leaves in proportion with water: a bucket of water + 250 grams of tea leaves. The garlic smell repels ticks; we recommend planting garlic beds next to the currants, or at least a couple of bulbs for each bush.
Red currant disease Reversion: photo
1.2.Diseases of red currant: septoria (white spot).
This red currant disease is a fungal disease; it spreads by spores, which means it spreads very quickly to almost all currant plantings. Windy weather or an invasion of pollinating insects, or simply insects, is enough - these facts contribute to lightning-fast damage to plants over vast areas. Already in the first half of June, you can detect the first symptoms of the appearance of fungus on currants. The appearance of round spots of a gray tint on the leaves, along the edges of the leaves there is a brown edging. A little time passes and you can see light inclusions, black, on the leaf plate. These points are the spores of the parasitic fungus, only already ripe, ready to cause irreparable damage to the plant itself and, accordingly, to your long-awaited harvest. Urgent action is needed to prevent further growth and spread to neighbors. If this is not done, the foliage dries out completely and falls off. The synthesis of chloroform necessary for green spaces is simply disrupted. Without this biological process, the bush simply cannot exist, the plant dies.
If preventive methods do not help, treatment must be carried out without delay. Let's highlight some methods: -Cuprozan is a drug containing copper. Apply contact treatment to each branch on each bush. Solution concentration 0.4%. You can replace colloidal sulfur, 1%, spray the plant;
-fungicides are also used for spraying. For example, Acrobat, Ridomil, Fitosporin; -immediately remove the entire branch or even a shoot from the root if you find at least one infected leaf. Removing this leaf will not save the entire bush. The infection has already occurred and what you saw is just a part. The effectiveness of the measures taken is visible if the disease manifests itself at an early stage, not an advanced version. Examine all currant bushes not only throughout the season, but also from the beginning of the plant’s vegetative activity, that is, from the first days of summer.
Red currant disease White spot: photo
1.3.Anthracnose.
The appearance of this type of disease appears already in mid-May. The first signs are tiny spots appearing on the foliage, not very many, brown, slightly with a red tint. The number is rapidly increasing, all the small dots are merging. Already the entire leaf plate is under the control of infection. The leaves are painted a rich, brown-red color. The lethargy of the affected foliage does not allow the entire plant to continue its full development. Partial infestation allows the bushes to bear fruit, but the harvest is small and in small quantities. Taste qualities lose their specific brightness, sweetness disappears, and a spicy-sour taste predominates. Recommendations for the prevention and treatment of already manifested diseases exist. Let's highlight a few:
- use Bordeaux mixture, or Nitrofen solution, in a concentration of no more than 3%. Application is necessary before the currants begin to bud;
- before flowering or after the last harvest, spray the plants with 3% copper oxychloride, which can be replaced with 1% Bordeaux mixture;
- Damaged leaves found must be immediately collected and completely destroyed; preferably, burn them in a designated area.
Important information! Anthracnose is a disease of red currants that prefers increased moisture. Prolonged, damp weather contributes to the active activity of the disease. An intensive, preferably daily, thorough inspection of each bush is required. Carry out such preventive inspections even after every heavy rain. This will help you identify that elusive moment when the infection begins to manifest itself, expressed in the first reddening of individual leaves.
Red currant disease Anthracnose: photo
1.4.Diseases of red currant: goblet rust.
The essence of the fungal disease of red currant is revealed in the name itself. The formation of the disease is pronounced, growths appear, similar in appearance to the shape of a glass. Not only the underside of the leaf plate suffers from such a growth, flowers and berries are damaged. The color of the sores is red, and the pronounced, reddish tint can be compared with rust, so they came up with an appropriate name.
Rust is spread by spores that are stored in small containers that resemble flat, orange-colored pillows. When the leaf changes its usual green color, it is too late to treat. There is an inevitable fall of leaves. In this case, the fruits suffer no less. The development process slows down, nutritional and taste qualities are completely lost. Their value is reduced to zero. This is the harmful activity of rust. The damage to the foliage can be partial, the worst thing is that the future crop is infected, that is, the disease can greatly affect fruiting. Due to such extensive activity, it is necessary to begin preventive actions very early, during the swelling of the buds, but before the appearance of the first leaves:
- spray with 1% Bordeaux mixture in three stages: before the formation of leaves begins, the flowering time has ended - spray a second time, after seven days, carry out a third irrigation with the drug. This must be done carefully, each branch separately, not depriving even the trunk and root zone of attention;
- the development of the fungus will help to stop the solution of fungicides - Topaz, Previkur;
- products containing copper and colloidal sulfur can also effectively help fight the disease;
- extensive thickets of sedge are favorable neighbors for the active activity of the fungus. All preventive actions taken are meaningless; effectiveness will not follow unless the neighbor that contributes to the emergence of negative consequences for currants is destroyed;
There is a similar disease of red currant, which is expressed in the appearance of orange dots on the branches. It's called nectria drying out. No treatment will help save the bush from certain death. There is only one way out - urgent cutting out the entire affected part that needs to be burned. Treat the cut areas with a solution of Bordeaux mixture.
Red currant disease Goblet rust: photo
1.5.Diseases of red currant: spheroteca (powdery mildew).
The second name for the red currant disease appeared for a reason. External signs resemble flour dust, a white coating forms. All parts of the bush can suffer from the disease. Spheroteka does not particularly choose where to lead an active lifestyle.
You can notice the first appearance in late spring and early summer. The affected foliage begins to curl, the stems become deformed, and a little later they simply dry out. The development of fruits slows down, in severe cases the berries simply stop their development, all varietal, taste, and externally attractive qualities disappear. Pest spores live in formed container houses, which are attached to currant bushes using small suction cups. Entire colonies are rapidly formed. The parasite is active. If you do not take any measures and completely neglect your site, then the destruction of the berry garden is not far off. Just a couple of years is enough. Even subsequent new plantings may suffer, since the fungus will not go away, and digging up and destroying all diseased bushes does not mean killing the parasitic fungus.
The fight against dew must begin at the first appearance. At the initial stage, even simple folk remedies can help:
- Powdered sulfur has very effective properties. Use this powder to pollinate moistened bushes. The peculiarity of this treatment is to carry out it in the hottest part of the day;
- in a simple infusion of mullein, bacteria are formed that can completely destroy not only the effects of fungal activity, but also the mycelium itself. How to prepare the necessary infusion? Pour part of the manure with water in a ratio of 1:3 with the starting material, be sure to leave for at least 4 days, dilute the already fermented solution again in the same proportion. Proceed with direct treatment of the infected plant or several. Manure can easily be replaced with rotted leaves or hay;
- a soap solution can bring equally effective results. All the proportions given below are calculated for 1 liter of water: 25 grams of laundry soap + 2.5 g of copper sulfate, 4 g of soda ash + 4 g of soap, 10 g of any soap product mixed with three grams of baking soda, 1 g of salicylic acid and 5 grams of denatured alcohol;
- The well-known specific smell of garlic can work wonders. You can simply plant garlic next to or under a currant bush. But you will achieve greater effectiveness using garlic infusion. Grind the cloves, add 1 liter of water, leave for at least a day. We choose the time for spraying in the evening, it is advisable to repeat the procedure several times (the smell dissipates over time), maybe once a week;
- Among the wide-spectrum drugs, we can recommend proven ones - Nitrafen, Oksikhom. As for fungicides, you can use the well-known ones - Vectra and Topaz.
Planting marigolds and horsetail will serve as another (not strong) remedy in the fight against powdery mildew. Place their plantings near the berry garden. The effect can be noticeable; the action of this method is safe for all living creatures nearby and for humans. And it's just beautiful.
Red currant disease Powdery mildew: photo
June
In June, currant bushes need to be supported if they did not have time to do this in the spring. Bushes under the weight of berries can bend to the ground and become dirty with earth.
Watering and weeding
While continuing to care for currants, do not forget to weed and water
In June, the berries begin to actively fill, so watering will be very useful for the ripening of the berries. You can scatter 1 cup of ash under each bush and loosen it.
Powdery mildew or other diseases may appear this month. Foliage can be sprayed with Topaz or soda ash.
In June, the berries begin to ripen, turning black. To ensure that the berries ripen well, currant bushes can be fed. In a bucket of water, dilute 1.5 g of copper sulfate, 2 g of boric acid, 2.5 g of zinc sulfate and 2.5 g of ammonium molybdic acid. The solution should be sprayed onto the plantings, thoroughly moistening the leaves of the plants.
Collection of currant berries
When the first ripe berries appear, you can begin picking them, leaving unripe berries on the bushes. At the same time, you should inspect the bushes for the presence of pests. If pests or diseases are noticed, it is better to carry out treatment with folk remedies.
Watering the bushes
Watering currants in June must be carried out, especially during the dry month. Currants need them to fill the berries. Water 1 bucket per seedling as soon as the soil begins to dry out. The formation of crusts and cracks in the soil should not be allowed.
Mulching
After watering, mulching should be done to delay the evaporation of moisture. You can scatter a bucket of compost under each seedling. Many gardeners tear up grass and lay it under bushes.
Fighting aphids
Aphids can be removed with a solution of green soap. Some gardeners tie yellow ribbons to currant bushes. “Prosvetok” recommends that you can try it.
Fungus on red currants
The most common cause of disease in this crop is fungus.
Let's list its types:
- Reversion, or terry. The infection is in the sap of the bush. The disease affects the entire bush. Plant modifications do not take long to occur. The shape and color of leaves and flowers changes.
- Anthracnose. As a result of this disease, fruiting and shoot growth are significantly reduced. Dark brown spots of irregular shape form on the leaves. After which they turn brown, curl and fall off.
- Spheroteka (powdery mildew). The first signs of the disease appear on young shoots. It affects ovaries, leaves and fruits. Infected areas become covered with a powdery white coating. Outwardly, it resembles dark brown felt. The final stage of the disease is the drying out of all parts of the bush.
- White spot or septoria. It appears on the leaves of the plant in the form of gray spots, along the edges of which there is a dark brown rim. Afterwards, black dots of the fungus with spores form in these places. As a result of the disease, the leaves curl and then fall off.
- Glass rust. This disease also attacks leaves. Orange spots form on them, inside of which there are yellow spore pads. As a result, these formations turn into pimples that resemble the shape of a glass.
July
In July, you should continue to water the currants, as the berries fill with juice and ripen. Without watering they will be small and tasteless.
The harvest continues. The berries weigh down the branches more and more. If there are no supports, use a special hoop.
Harvesting, watering
In July, it is necessary to water, pouring 1 bucket of water under each bush. Gardeners recommend making an infusion of herbs. This will include watering and fertilizing. After fermenting the herbal infusion, pour 1 liter of infusion into a bucket of water and pour it under the root.
After watering, loosen carefully, retreating 50 cm from the bush so as not to touch the roots. In summer, crusting should not be allowed to form.
Other care
In July, it is important to monitor the condition of the young animals that were planted in the spring. It can be attacked by various pests. If you put fertilizer in the hole when planting, you don’t need to fertilize it yet. But we must not forget about watering.
Red currant: prevention from diseases and pests
For prevention:
- in the fall, dig up the entire soil surface under the bush;
- Leaves must be collected and burned;
- regularly inspect your bushes; if any damaged leaves or shoots are found, remove them immediately;
- treatment with fungicides before leafing;
- feeding should be regular;
- select only healthy material for planting;
- It is advisable to choose currant varieties that are resistant to diseases,
Red currant diseases and pests: useful video
August
During August, it is necessary to carry out 5 waterings, one bucket for each seedling. In August, you can start fertilizing the plants, since the soil has already been depleted, since all the useful elements have been used to ripen the crop.
In August, it is necessary to hill up those bushes that emerged from horizontally laid cuttings. The mother bush gave up all the nutrients, and the bushes managed to take root.
Pruning, sanitary and shaping
In August, sanitary pruning can be carried out, since some branches may have been damaged during harvesting. In addition, branches that are twisted or thicken the bush should be removed.
Fertilizing with potassium-phosphorus fertilizers
At the beginning of August, it is necessary to apply phosphorus and potassium fertilizers: 10 grams of superphosphate and 12 grams of potassium sulfate per bush. When watering, the granules will dissolve, feeding the plants not immediately, but gradually.
Treatment with systemic drugs for diseases
Aktrara and Fufafon are called systemic drugs. They are often used to treat currants against various parasites.
Aktara is the most effective systemic drug against aphids. After spraying, the elements of the product quickly penetrate the foliage, and then the juice spreads them to all above-ground parts of the plant (except fruits). After just 30 minutes, the aphids stop gnawing on the foliage and die.
Currants and gooseberries can be cared for using the drug Funanon. Fufanon will get rid of these berry crops from aphids, moths, moths, gall midges, leaf rollers, sawflies, and scale insects. Preparation of a solution for spraying: dissolve 12 ml of the substance in a bucket of water and spray. You will need 1.5 liters of diluted product per bush. Its validity period is 20 days.
Glass processing
Intavir is a contact-intestinal insecticide used to combat aphids, thrips, glass beetles, and leaf rollers. The duration of exposure is 10-15 days. The death of pests occurs after 2-3 days.
This drug is not selective; it can kill pollinating and beneficial insects.
Aktara is a contact insecticide that destroys currant pests, but use should be stopped 3-4 weeks before harvest.
To prepare a bucket of water you will need 2 g of Aktara substance. First, the substance is diluted in a small amount of water and then poured into a bucket. Harmful insects die even after one treatment.
When is the best time to spray currants?
Currants are sprayed against many diseases and pests immediately after harvest, usually in July and August, in cold regions - in September. However, you should not focus on this date: currants can be sprayed throughout the fall, if conditions permit.
- There should be no wind, even weak. Otherwise, the drug will land anywhere but on currants, and then it will be easier to get poisoned.
- Fighting immediately after rain is ineffective. At this moment, there is moisture on parts of the plant, this will reduce the concentration of solutions.
- The solution should remain on the branches for at least 3 days.
Another condition is that the sun should not shine strongly, otherwise it may burn the currants. A cloudy day is ideal for the procedure.
The end of Indian summer can be a good time to carry out work: the weather is dry, the sun is sometimes hidden behind the clouds, and the wind rarely blows during this period. However, it is better to check the weather forecast rather than rely on common sense to ensure you don't miss the best time.
Newcomers can count on advice from more experienced colleagues living nearby.
September
Caring for currants in the fall - replanting, fertilizing, watering. At the end of September, all cuttings should be separated from the bush and transplanted to a permanent place. If fertilizing with potassium and phosphorus fertilizers was not carried out in August, then in September is the time to fertilize.
Phosphorus and potassium supplements in the form of superphosphate and potassium sulfate are considered “long-lasting”. Plants gradually take up the components they need, especially after watering.
But it’s better not to add ash in the fall, and you shouldn’t add concentrated humus either, because it contains too much nitrogen.
In autumn, bushes are especially sensitive to moisture deficiency. After abundant fruiting, currants need watering. If the autumn is dry, then the currants should be watered as much as possible. Winter will not be so dangerous for watered bushes.
How to water? 4 buckets of water should be poured under each currant seedling so that the water penetrates into the dry soil to a depth of 50 cm.
Sanitary pruning
Autumn care for black currants includes both sanitary and formative pruning.
Pruning is important to increase yield. The fact is that bushes without excess greenery will bring 3-4 times more berries than neglected plants.
Trimming results:
- Will help get rid of 85% of fungi, parasites, bacteria;
- After pinching the shoots, fruiting branches begin to develop on the branches;
- Full illumination of shoots improves photosynthesis;
- Proper preparation for winter will help you withstand even very severe frosts;
- The harvest will be higher and the berries will be tastier than in the previous year.
When to prune? After the leaves turn yellow and fall off. The shoots must be cut completely to the ground level, without leaving stumps.
Plantings of white and red currants do not need to be greatly shortened, since most of the harvest ripens on the upper part of the branches.
A blackcurrant bush should consist of 6-8 main branches of different ages. And red and white - from 10-12. Renew the crown in stages: leave 5 young shoots every year, and cut out the old ones in the same quantity.
After all the manipulations, you should loosen the soil shallowly, moving away from the bush at a distance of 35-50 cm. Loosening protects the soil from freezing.
Preparation of cuttings for autumn planting
When pruning currants, it is necessary to leave healthy currant bushes and cut cuttings 30-40 cm in size.
Planting bushes
Planting currants by region:
- In central Russia, autumn planting is carried out from September 15-20 to October 15-20
- In the northern regions - from September 5-10 to October 5-10
- In the south of the country - from mid-October to the second ten days of November.
Currants planted in the fall will take root well if planted according to the experience of many gardeners. The sequence is shown in the picture.
Planting stages:
- First you need to dig a hole, 35-45 cm deep and 65-70 cm wide. A mixture of peat, ash and superphosphate must be added to the planting hole. The root system should be kept in the Kornevin solution for several hours.
- Next, bury the seedling, crush the soil, then slowly pour in a bucket of water so that it is absorbed into the soil.
- After watering, spread a bucket of humus around the bush.
Preventive measures
Autumn prevention
It is carried out after harvesting to prepare the plants for wintering and to prevent re-infection of currants in the future. The following measures are typical:
- Fallen leaves need to be raked and burned, and the soil under the bush should be treated with one of the fungicidal compounds.
- Carry out sanitary and anti-aging pruning. To do this, use pruning shears to cut off dry and old branches of the bush, leaving young shoots that form the crown. This is necessary so that after rain and watering the bush dries out more quickly, and the spores that fall on it do not ripen. Treat all cuts with garden varnish.
- Loosen the soil under the bush.
- Fertilize with the required amount of potassium and phosphorus.
- After harvesting, treat the bushes with a solution of potassium salt.
- Do not plant plants close to each other.
- If currants grow in a damp lowland or shade, it is better to transplant them into open space.
We recommend reading our article on how to care for currant bushes in the autumn.
Spring prevention
Spring prevention measures are no less important than autumn ones, especially if diseases or pests were observed last season. All actions will be aimed at obtaining a healthy harvest.
In the spring you should do:
- Before the buds open, treat the bushes and the soil underneath them with a solution of copper sulfate.
- Feed the currants with a solution of manganese sulfate by spraying it on the leaves.
- Pick off affected leaves and burn them.
- Get rid of weeds.
- Clear the area where the currants grow to give them access to sunlight.
- Treat the bushes with gall aphid pesticides after the leaves appear, but before the flowers form.
- The right choice of plant varieties. Each variety has its own strengths and weaknesses in terms of resistance and sensitivity to certain diseases. Read about currant varieties here.
- Plant plants near the currants whose smell repels aphids. It could be onions, garlic, calendula, chamomile.
- To attract insects that feed on aphids, such as ladybugs, bees, and goldilocks, to the site, sow meadow grasses next to the currant bushes.
- Make sure there are no anthills near the bushes, as ants are carriers of aphids.
- Periodically thin out the currant thickets.
By following recommendations for the prevention of diseases and pests, you will minimize the risk of red spots appearing on currants. These measures will save you from the need to treat your plants and increase your chances of getting a generous and healthy harvest.
0
0
Copy link
October
Before frost, you can add compost, mullein, and chicken manure, pouring them into the tree trunk circle. All components will decompose within 3-4 months, and then move into the ground.
Formative, sanitary pruning
When sanitary pruning, it is important not to leave old brown branches covered with lichen. Branches lying on the ground also need to be trimmed. Or you can sprinkle them with soil to root them. Next year they should be separated from the bush, then planted separately.
The middle of the bush must be thinned out especially carefully so that the sun's rays heat all the currant branches.
Short root shoots, which do not bear fruit but only thicken the bushes, are also removed. Annual growth is shortened by 5-7 cm.
Mulch update
We remove old mulch from the currant bushes
If the old mulch has been removed a long time ago, then after watering you can spread out new mulch. The best mulch is compost. It will gradually turn into fertile soil that will nourish currant seedlings.
What do red spots on leaves signal?
Most likely, red spots on currants indicate an infection with Anthracnose. The disease is caused by fungal spores and can have very negative consequences, including decreased growth and yield, deterioration in the taste characteristics of berries, and rapid infection of neighboring bushes.
As a rule, the disease manifests itself in rainy and warm weather, which is most favorable for the spread of fungal infections. Small red spots become larger over time, and their color changes to a more distinct brown. If this has already happened, then anthracnose on your bushes is simply rampant! Severely affected bushes can be seen in the photo.
November
In November, humus and compost can be placed in the tree trunk circle. When spring comes, the currant will receive all the substances it needs.
After dropping the leaves, inspect the buds. If they are large, it means the tick is ready for winter. Remove buds without regret.
Measures against kidney mites
It is useful to use a 2% solution of colloidal sulfur against kidney mites. To do this, dilute 75 g of colloidal sulfur in a bucket of water, stir well and spray the currant seedling. You can use the drug Tiovit Jet, but below 20 degrees it is not effective.
The following biological products are effective and safe for humans: Fitoverm, Bitoxibacillin and Akarin.
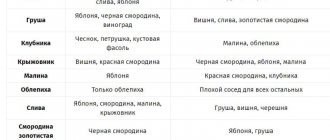
Resistant varieties of red, black, white and golden currants
There are a number of varieties that are highly resistant to infection. They are recommended to be used for planting in the garden.
| Type of currant | Varieties |
| Red |
|
| Black |
|
| White |
|
| Golden |
|
Winter months
In winter, currants are covered in places where there are severe frosts in winter. In regions with a temperate climate in winter, you can add snow and the bushes will not freeze.
Shelter depending on region
In order for currant bushes to survive until spring in cold regions of the country, they must be covered. There are several ways to cover bushes for the winter.
- Divide the bush into several parts, tie the branches and bend them lower to the ground. If the winter is snowy, then under the snow they will survive any winter. But you can cover them with spruce branches to trap the snow.
- Tie the bush with twine and put humus around it. You can hill up with dry, loose soil, making a high earthen mound.
- Sprinkle fallen leaves around the bush in a layer of 10-15 centimeters.
- The tied bush must be spudded and wrapped with burlap on top.
- You can purchase a ready-made kit specifically for shelter. You can even cover spreading currant bushes.
It is necessary to cover the currants when the temperature reaches minus 15 degrees. If it gets warmer, the root system will begin to rot.
Three effective solutions
Various solutions are used to combat various fungal diseases and some bacterial problems in gardening. In autumn, currants can be treated with Bordeaux or Burgundy liquid, as well as vitriol solutions.
Burgundy liquid
A good antifungal solution that forms a microscopic, water-soluble coating on branches to kill pathogens. To process currants you will need the following ingredients:
- baking soda - 25 grams;
- copper sulfate - 20 grams;
- laundry soap - 25 gr.
Water with a volume of 5 liters is heated to a temperature of about 40°C, then soda and grated laundry soap are dissolved in it. In another container, dilute copper sulfate in 5 liters of warm water.
Then pour the second solution into the first in a thin stream, stirring evenly. Wait until flakes appear, indicating that the burgundy liquid is ready to process the currants.
If you continue to infuse copper sulfate solution, coagulation will occur and the therapeutic effect will disappear.
Bordeaux liquid
More powerful than burgundy is Bordeaux liquid. However, it must be prepared correctly, and the reaction must be monitored using an indicator. Only then will the desired effect be achieved.
Recipe:
- Add 100 g of quicklime to 5 liters of water. This will produce lime milk.
- Dilute 100 g of copper sulfate in a small amount of water in another non-metallic container and add 5 liters of water to the solution.
- Pour the copper sulfate solution into the milk of lime in a thin stream. Do not mix liquids in the reverse direction.
If Bordeaux mixture is prepared correctly, it will have a turquoise color and a pronounced fungicidal effect. Please note that concentrated lime cannot be mixed with copper sulfate, so each composition is prepared in a volume of 5 liters, even if less solution is required to process currants in the fall. However, there will be no excess left - you can safely spray the soil under bushes and other trees prone to fungal diseases.
Checking the quality of Bordeaux mixture using an indicator or litmus paper should show a slightly alkaline or neutral reaction of the solution.
Iron sulfate solution
Fungal diseases can be prevented by using a solution of ferrous sulfate, which is much easier to prepare than the above drugs. Simply add 100 to 300 g of ferrous sulfate to 10 liters of rain or melt water and stir the liquid gently until the powder dissolves.
To prepare the solution, use plastic or wooden containers, and you can use a wooden spatula for mixing. Do not use iron utensils.
To consolidate the result, a repeat procedure can be performed after two weeks. To prevent re-infection of currants with fungi, you should also treat a section of soil along the projection of the crown.