Causes of white plaque on leaves, stems and cucumbers
Cucumber is one of the most popular vegetable crops among gardeners. But often when growing, you have to deal with troubles in the form of a white coating on the stems, leaves and fruits. The reasons for this phenomenon lie in:
- sudden changes in average daily temperature;
- prolonged rains;
- watering with cool water;
- dense planting;
- high humidity in the greenhouse;
- violation of the rules of agricultural technology (weeding, loosening);
- lack of sunlight;
- excess nitrogen in the soil;
- lack of phosphorus and potassium.
Such disturbances in crop cultivation lead to the development of fungal diseases and the spread of insect pests.
Cucumber leaves turn white: improper care
If the leaves of cucumber seedlings turn white after planting in open ground, this indicates improper care. An important factor is the time of planting. The period from mid-April will be suitable. Early frosts can destroy the crop. In a greenhouse, the leaves of cucumbers turn white much less often, since the plant is protected from temperature changes.
Leaves on seedlings may turn white due to increased acidity of the soil. You can check it with soda. Pour some earth into a container. Add distilled water, then add a handful of baking soda. If a reaction occurs, it means the soil is acidic. You can reduce acidity with ash. 500 ml is enough for a bucket of water. Pour the solution into the holes when planting.
Lack of light and nutrition
White spots on the leaves may appear in the garden bed and in the greenhouse due to lack of sunlight. This may be the reason for the wrong choice of planting site, as well as excessive thickening of the crop. The bush must be correctly formed. It is important to pinch the vine in a timely manner and remove excess and weak foliage.
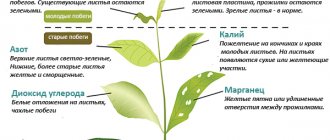
Due to a deficiency of important microelements, the lower leaves of cucumbers turn white and dry. Such signs indicate the need for additional feeding with magnesium and potassium. With a deficiency of the latter, the leaves turn white at the edges. A similar problem on cucumbers on the upper leaves indicates a copper deficiency. The appearance of dark stripes indicates a lack of iron or manganese.
Improper watering
Excess or lack of moisture also affects the appearance of the crop. Watering too much causes spots and then rotting of the vine and roots. Due to lack of liquid, the tips of the leaves dry out and turn white. It should be remembered that the roots of the plant are located near the surface, from where moisture evaporates quickly.
Water temperature is important. The culture is not suitable for watering with cold liquid. You should choose a large container, fill it with water in advance, let it sit, and water the plant with it. The optimal temperature is 20-25 degrees Celsius. During cold weather, the crop does not need abundant watering.
Diseases and pests that cause white plaque
Diseases that cause the appearance of a whitish or yellow coating on the leaves of cucumbers are mainly of a fungal nature (powdery mildew, downy mildew, white rot, ascochyta blight). White mosaic refers to viral diseases.
Spider mites that feed on plant tissue also cause white spots to appear on leaves - the result of impaired photosynthesis in damaged areas.
Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew (ashtray, white) is a fungal disease that occurs when a plant is infected with ectoparasites. At the end of May - beginning of June, whitish mycelium begins to develop on young shoots and leaves. Small drops of sticky, cloudy dew appear on the plants.
The pathogen overwinters in the upper layers of the soil, on plant debris, and with the onset of spring it spreads from the lower leaves up the stems.
Signs:
- whitish coating on leaves and stems;
- brown balls inside plaque;
- drops of dew on the foliage;
- dry, curled leaves;
- rot on the fruit.
Without treatment, the plaque thickens, turns brown and spreads throughout the plant. The cucumbers look like they are covered in mold. These symptoms indicate the last stage of the disease. Treatment in this case is pointless.
The photo shows powdery mildew.
The table presents effective folk methods of combating powdery mildew.
| Recipe | Application |
| 10 liters of water, 1 liter of yogurt, kefir, whey. | Daily treatment of plantings is allowed until the disease is completely eliminated. |
| 1 liter of water, 0.3 tsp. soda ash, 25 ml of liquid soap. | Treat the plantings once every 7 days. |
| Leave 1 liter of wood ash in 5 liters of boiling water for 24 hours. | Treat bushes once every 7 days. |
| Mullein infusion 1:10, leave for 3 days | Water at the roots in the evening every 7 days. |
| Infuse 100 g of dried horsetail in 10 liters of water for 24 hours, then boil over low heat for 2 hours, strain and cool. Dilute with water 1:5. | Treat bushes once every 7 days. |
| Pour 0.5 buckets of marigold inflorescences with warm water, leave for two days, add 50 g of soap shavings. | Treat plants twice a week. |
Effective chemicals:
| Name | Application | Toxicity |
| "Topaz" | Dissolve 2 ml in 10 liters of water and add another 10 liters. Carry out the first treatment after the appearance of 8-10 true leaves, the second - at the beginning of flowering, 10 days after the first. | Not phytotoxic, not dangerous for birds, fish, beneficial insects and humans. |
| "Fundazol" | Dissolve 10 g in 10 liters of water. Carry out the treatment at least three times, every 10 days. | Moderately toxic to insects and humans. |
| "HOM" | Dissolve 40 g of powder in 10 liters of water, add 100 ml of skim milk. Spray once a week in the evening. | Not phytotoxic, not dangerous for birds, fish, beneficial insects and humans. |
| "Skor" | Dissolve 2 ml in 10 liters of water, treat three times with an interval of 10-12 days. | Not phytotoxic, not dangerous for birds, fish, beneficial insects and humans. |
| "Tiovit Jet" | Dissolve 30 g in 10 liters of water. Treat bushes 2-3 times per season. | Not phytotoxic, not dangerous for birds, fish, beneficial insects and humans. |
Downy mildew (downy mildew)
Downy mildew , or downy mildew, appears as white-yellow oily spots on the leaves of cucumbers. As the disease progresses, the back side of the leaves becomes covered with a purple coating. The spots gradually increase in size and merge. The leaves wrinkle, dry out and die. Without treatment, peronosporosis can completely destroy cucumber plantings.
Reference. Downy mildew appears only under favorable conditions for it - prolonged rains, watering with cold water, excess moisture in the soil.
Folk remedies against peronosporosis:
| Recipe | Application |
| 5 liters of water, 40 g of soda, 50 g of soap shavings. | Spray the soil and plants 4 times per season with an interval of 7 days. |
| 1 liter of skim milk, 40 drops of iodine, 25 g of liquid soap. | Spray cucumbers regularly throughout the growing season at intervals of 10 days. |
| Bring 0.5 kg of onion peel and 10 liters of water to a boil and leave for 5-7 days. | Treat 3-5 times a month until symptoms disappear. |
The table describes chemical agents against downy mildew.
| Name | Application | Toxicity |
| "Acrobat MC" | Dissolve 50 g in 10 liters of water. Carry out the treatment at the first signs of illness, repeat after 2 weeks. | Non-toxic to birds, fish and humans. |
| "Alirin B" | 2 tables dissolve in 10 liters of water - for watering under the bush. 1 table per 1 liter of water - for spraying plants. The frequency of treatments is 2-3 times per season. | |
| "Oxyhom" | 30 g per 10 liters of water. Spray the plants in the evening. The frequency of treatments is 3 times per season with an interval of 15 days. | |
| "Ordan" | 25 g per 10 liters of water. Apply treatment at the first signs of illness, repeat after 2 weeks. |
White rot (sclerotinia)
The causative agent of white rot is the marsupial fungus sclerotinia. The spores penetrate plant tissue and provoke the development of mycelium. As a result, a cotton-like white coating appears on cucumbers, stems and leaves. The affected areas become watery, the tips of the shoots and leaves wither and die.
The table contains effective folk remedies.
| Recipe | Application |
| 1 liter of milk, 1 tbsp. l. shavings of laundry soap, 30 drops of iodine, 10 liters of water. | Treat bushes generously 3-4 times a week. |
| 10 liters of water, 8 tbsp. l., 4 tsp. potassium permanganate, 1 tbsp. l. soap shavings. | Treat plantings once every 7 days. |
| Mix wood ash and crushed chalk 1:1, add water to obtain a thick porridge. | Cut off the affected leaves and stems and coat the cut area with the resulting mixture. |
Chemicals to combat white rot:
| Name | Application | Toxicity |
| "Abiga Peak" | 50 ml per 10 liters of water. Treat plants 3 times within 20 days. | Non-toxic to humans and the environment. |
| "Acrobat MC" | 20 g per 5 liters of water. Carry out the treatment 2 times with an interval of 10 days. | |
| "Ridomil Gold" | 25 g per 10 liters of water. Treat plants 3 times every 7 days. |
Gray rot
Gray mold is a disease caused by the fungus Botrytis cinerea. As the disease progresses, a whitish coating with a gray tint appears on the fruits, leaves and stems. Affected areas rot and die. Cucumbers become watery inside and become covered with a gray fluffy coating.
Folk remedies are effective only at the first signs of the disease. They are also used for preventive treatments.
| Recipe | Application |
| 50 g of soda ash, 80 g of copper sulfate, 50 g of soap shavings per 10 liters of water. | Treat bushes 3 times a week. |
| 2 tsp. brilliant greens, 1.5 tsp. potassium permanganate, 25 ml of liquid soap per 10 liters of water. | Treat plants 2-3 times a week. |
| 10 g of boric acid, 1.5 g of potassium permanganate, 30 ml of iodine, 50 g of soap shavings per 10 liters of water. | Treat plantings 3-4 times a week. |
The table shows popular chemicals against gray rot:
| Name | Application | Toxicity |
| "HOM" | Dissolve 40 g of powder in 10 liters of water, add 100 ml of skim milk. Spray once a week in the evening. | Non-toxic to humans and insects. |
| "Rovral" | The powder is mixed with lime or chalk in a ratio of 1:1 or 2:1 and coated with infected stems 3 times a month. | |
| "Euparen Multi" | A 0.2% solution is used to treat bushes once every 14 days. |
White mosaic
White mosaic is a viral disease. Signs develop according to the following scheme:
- highlighting areas along the veins;
- spots in the form of stars and yellow rings;
- proliferation of white spots with a yellowish tint on foliage and fruits.
There are no effective treatments for the viral disease. Sick plants are completely removed from the site and burned.
Ascochyta blight
Ascochyta blight is a dangerous fungal disease that causes the gradual death of the bush. The spread of the fungus begins from the stem, without affecting the leaves, so the plant remains viable for some time. Leaves are affected at the beginning of the fruiting period.
Signs:
- blurry spots on the edges of the leaf blade are brown and then whitish with a yellow tint;
- raised areas on spots with spores inside;
- drying and dying of leaves.
What to do if the cucumbers are covered with a white coating? The fungus that causes ascochyta blight is unable to reproduce in soil. The pathogen is found on cucumber seeds. Therefore, the main measure to prevent the disease is pre-sowing disinfection of seed material with fungicides.
The table shows preparations for treating cucumber seeds before sowing.
| Name | Application |
| "Baksis" | Soak the seeds for 2 hours in 0.2% suspension. |
| "Planriz" | Soak the seeds for 6 hours in a 1% solution. |
| "Fitosporin-M" | Soak the seeds for 2 hours in the working solution. |
There are no folk remedies to combat ascochyta blight.
Spider mite
Spider mites feed on plant tissue. It affects cucumber plantings in open and closed ground.
The main sign of its presence is small white dots on the back of the leaves. Later, a thin cobweb envelops the foliage.
With severe damage, the leaves turn white from numerous damages. Hordes of spider mites are noticeable on the stems.
Chemicals are used in extreme cases when traditional methods have failed. Insecticides quickly kill pests, but they are toxic to humans and the environment. Another disadvantage of such treatments is the rapid development of resistance in insects. Therefore, it is recommended to change the preparations every 2-3 sprayings.
Spraying is carried out in the evening to prevent sunburn on the leaves.
The table shows effective insecticides. Treatment with chemicals is stopped 20 days before the start of harvest.
| Name | Application | Protection period | Treatment frequency |
| "Plant-pin" | The drug is produced in the form of sticks, which are immersed in the ground next to the bushes. | 1.5 months | 1 |
| "Karbofos" | 70 g per 10 liters of water, consumption - 0.5 liters per bush. | 7 days | 2 |
| "Flumite" | 5 ml per 10 liters of water, consumption - 1 liter per plant. | 30 days | 1 |
| "Aktellik" | Suspension with a high toxicity class. It is considered the best drug for spider mites. 2 ml are diluted in 2 liters of water and used immediately. Consumption - 2 liters per 10 sq. m. | 10-12 days | 2 |
The table contains folk remedies for pest control.
| Recipe | Application |
| Pour 0.5 buckets of potato tops with water, leave for 5-7 hours, add 50 g of soap shavings. | Spray the plantings once a week. |
| Infuse 30 g of dandelion roots in 1 liter of water for 5 hours. | Process cucumbers 2 times a week. |
| Infuse 1 kg of hogweed in 10 liters of water for 24 hours. | Treat plantings once a week. |
| Infuse 2 heads of garlic in 1 liter of water for a week, dilute with water 1:2 before use. | Spray the bushes 1-2 times a week. |
| Infuse 100 g of datura in 1 liter of water for 10-12 hours. | Spray cucumbers once a week. |
| Infuse 100 g of dry creeping mustard in 1 liter of water for 12 hours, dilute with water 1:2 before use. | Treat bushes once every 7-10 days. |
Conditions for normal seedling growth
Cucumber seedlings can be grown at home and in greenhouse conditions, or the seeds can be planted directly into the ground. In each of these cases, it is necessary to provide the plants with their needs for growth and development.
Note! Seeds that are 3-4 years old are best suited for planting. They have better germination.
At home
High-quality seedlings should be compact, have strong stems with short internodes, dense dark green leaves and a developed root system. To achieve this result, seedlings need proper care. It is advisable to maintain the daytime temperature on the windowsill in the range of 20-22°, and the night temperature not lower than 15°C. Seedlings must be additionally illuminated for 8 hours daily.
Important! The seedling method helps to get the harvest much earlier and extend the fruiting period.
Water the seedlings daily with settled warm water in moderate quantities; if there is a lack of moisture, the plants may dry out. Excess water from the pan must be drained. The seedlings are kept at home for about a month, during which time they are fed twice. The first feeding is carried out 2 weeks after emergence, diluting 1 tsp in 3 liters of water. urea.
In the house
With a lack of nitrogen, the leaves may turn white and become faded. After another 14 days, the seedlings are fed with a solution of nitrophoska (1 tsp per 3 liters of water) with the addition of wood ash (1 tbsp).
In the greenhouse
Planting cucumber seeds in a greenhouse should occur at a soil temperature of +12°C and air temperature of +15°C. Hybrids, parthenocarpics and bee-pollinated varieties are suitable for planting. If plant health and a bountiful harvest come to the fore, it is better to give preference to hybrids.
Note! Hybrid cucumbers are easier to grow in a greenhouse because they do not require pollination. These varieties are also more resistant to diseases and pests and, as a rule, do not have a bitter taste, which often affects varietal cucumbers.
Seeds can be planted in the ground dry or slightly hatched.
At the first stage of growing cucumbers, it is important to weed frequently so that the weeds do not take away nutrition. Be sure to loosen the soil, acting carefully so as not to touch the delicate roots. Water the seedlings once a week with warm water.
Important! Watering cucumbers at the seedling stage with cold water can cause the roots to die.
The first feeding is done at the stage of the appearance of the first 2 leaves. Pinching is carried out at the seedling stage - this procedure will contribute to the formation of more powerful roots. Watering is carried out 2-3 times a week, making sure that the soil always remains slightly moist. For fertilizing, mullein, chicken manure, humus, and compost are used, alternating them with mineral fertilizers. Cucumbers are fed no more than 5 times during the season.
Important! Excess nutrients for cucumbers are just as harmful as their lack. When overfeeding, plants actively increase green mass to the detriment of fruiting.
In the ground
If the gardener does not have time to grow seedlings, cucumber seeds can be sown directly into the ground. Sowing is done when the soil temperature is +14°C and the threat of return frosts has passed, to a depth of 2-3 cm. Cucumbers love warmth, moisture and nutritious soil. If there are concerns that low temperatures may return, the first weeks you can grow cucumbers under temporary shelter, which will also help maintain high humidity.
At first, the beds are regularly loosened, weeded and watered. The soil should not be allowed to dry out. To avoid excess moisture in the ground, it is better to make raised beds. Before flowering, cucumbers in open ground can be watered once a week, then watering is done every 3-4 days, and even more often in hot weather.
In the courtyard
Today, many early, abundantly fruiting, disease-resistant hybrids have been bred for open ground.
Note! Since F1 hybrids do not retain their properties in the second generation, there is no point in collecting their seeds.
The first fertilizing is carried out 3 weeks after planting, then the bushes are fertilized once every 2 weeks. It is best to alternate mineral mixtures and organic solutions. It is better to grow cucumbers tied to a trellis. To prevent weeds from growing, it is recommended to mulch the soil on the ridge. When the roots are exposed, the plants are earthed up.
Prevention
Measures to prevent white plaque on cucumbers:
- Timely removal of weeds and plant residues.
- Maintaining crop rotation. Cucumbers are best planted after cabbage, legumes, corn, onions, and garlic.
- Pre-planting treatment of the site with biological products “Alirin-B” and “Gamair”.
- Disinfection of holes with a hot solution of potassium permanganate.
- Control of nitrogen content in the soil.
- Planting varieties and hybrids of cucumbers resistant to fungal diseases.
- Sparse planting of seedlings.
- Preventive treatment of plantings with “Fitosporin”, “Kuprolux”, “Ordan”.
- Select a site in a sunny, draft-free location.
- Fertilization with potassium and phosphorus.
- Sprinkling instead of watering from above to prevent water retention on the foliage.
- Frequent loosening of the beds.
- Disinfection of greenhouses with sulfur bombs.
- Control of humidity in the greenhouse (above 80-85%).
- Air temperature control (optimally - +25...+27°C).
- Replacement of the top layer of soil.
White leaves on cucumbers: what to do
Resolving the problem depends on its origin. It is important to maintain optimal temperature and humidity conditions. If the lesion is caused by parasites or diseases, treatment with special drugs will be required. Mechanical removal of diseased greenery is necessary.
Important!
Diseased foliage should be cut off with a clean tool. After removal, equipment must be washed and treated to prevent the spread of disease. Treat sections for disinfection purposes. Infected foliage must be burned.
Spider mites on cucumbers
It will not be possible to detect this pest immediately, because it is incredibly small in size. In fact, a spider mite is just a black dot for humans. The insect hides on the back side of the foliage and weaves webs.
- You can notice a harmful insect after light, almost white spots begin to appear on the outside of the leaves.
- At the same time, cobweb lines are visible among the petioles and stems. Subsequently, the leaves begin to dry out and crumble.
Spider mites, as a rule, begin to attack cucumbers in hot, dry times, when air humidity is not high enough.
Parts of the plant affected by spider mites will need to be destroyed by burning. In addition, it is recommended to thoroughly treat the crop by spraying it with insecticides.
Folk remedies
Some vegetable growers, when cucumbers begin to turn white and wither, use folk remedies rather than drugs.
Onion peel
To protect cucumbers from parasites and pests, products made from onion peels are often used. To prepare a medicinal mixture, you need to mix 300 grams of husk with 5-7 liters of water. Then the container is placed on a gas stove and brought to a boil. The prepared mixture is infused for 10 hours, after which it can be used to treat plants. The product can be used not only for spraying leaves, but also for watering the soil.
Milk serum
Kefir with whey is recommended to be used when the tops of cucumbers have turned white. To prepare the working mixture, add 7 liters of water and 2-3 liters of whey or kefir to a 10 liter container. Some people add a little sugar to the mixture to improve the yield of cucumbers.
Baguette
To prepare the loaf mixture, soak several loaves of bread in a large container of water. It must be soaked for at least 12 hours. After this, a spoonful of iodine and 10 liters of water are added to the liquid. It is recommended to use the prepared mixture twice a month so that the leaves always remain green.
Ways to fight diseases
As soon as the first visible signs appear on the leaves, treatment should be started immediately. Powdery mildew can be destroyed using mullein infusion. 1 kg of cow manure or 800 grams of bird manure is poured with three liters of warm water and left to ferment in a warm place. Then add the same amount of water, mix well and spray the leaves.
If a white mosaic has settled on the beds, all vegetation from it is removed and destroyed. The soil and all garden tools must be treated with a solution of potassium permanganate, making it crimson in color. By the next planting season, the soil also needs to be treated with potassium permanganate, Fitosporin, or spilled with boiling water. Infected areas of the plant with white rot are removed, and the remaining stems are covered with earth. They are able to take root and form a new ovary. Bordeaux mixture can cope with ascochyta. All leaves are sprayed with it. Bushes that are very sick are removed from the garden and burned.