History of the variety's creation
This variety was obtained by crossing pears such as Venus and Forest Beauty. The latter generally served as the ancestor of many crops, since it imparts resistance to cold, a good harvest and pleasant-tasting fruits.
The breeding work was carried out by Yu. A. Petrov and N. V. Efimova at the All-Russian Selection and Technological Institute of Horticulture. It entered the Veles State Register in 2001. It is recommended to grow the plant in the Moscow region and surrounding areas.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of diseases or attacks by harmful insects on Veles pear trees, certain preventive work should be carried out:
- In the autumn, when preparing trees for the coming winter, you need to put things in order in the tree trunks - collect all the remains of vegetation, fallen leaves, fragments of shoots and burn them outside the site, since pests can hide in this plant debris for the winter. You cannot put all collected vegetation residues into compost. But the resulting ash can be used as fertilizer.
- It is necessary to constantly monitor the condition of the trunk bark and skeletal branches and constantly inspect the trees. Any cracks or damage found should be treated. All damage is cleaned down to healthy wood or bark, disinfected with copper sulfate (1% solution), then covered with garden varnish.
- Before the onset of frost, the soil in the tree trunk circles is dug up using 1 shovel, turning over but not breaking the earthen clods. At the same time, harmful insects and their larvae, which could hide in the ground for the winter, will appear on the surface and freeze out over the winter.
- After the soil has been dug up, it and the crown of the pears should be sprayed with Bordeaux mixture or any copper-containing preparations (3%). In the spring, before sap flow begins, this treatment should be repeated. Instead of copper-containing preparations, you can use a 5% solution of ferrous sulfate.
- In the spring, before the buds on the trees swell, their crowns and trunks can be sprayed with a DNOC solution to reduce the risk of pathogenic infections and harmful insects. Treatments with this drug can be carried out once every 3 seasons. And in other years you need to use a Nitrafen solution.
- To prevent awakened pests from crawling onto trees in the spring, special trapping belts should be installed at the base of the trunks. They are usually made from any available materials: roofing felt, thick polyethylene, burlap. Such a belt should be tied at a height of 0.5 m from the soil surface.
- To reduce the risk of fungal diseases, after flowering, Veles pears are sprayed with a solution of a systemic fungicide. The interval between treatments should be 15-20 days. To do this, you can use Chorus, Skor, Quadris or Strobe. To prevent pathogenic fungi from developing resistance to these drugs, each fungicide can be used no more than 3 times per season.
To reduce the risk of fungal diseases, after flowering, pears are sprayed with a fungicide solution.
After all such preventive measures have been taken, the risk of the appearance of pathogenic microorganisms and harmful insects is significantly reduced.
Main characteristics
At first, the pear has a wide crown of moderate density, but gradually the shape changes to a wide pyramidal one. An adult reaches a height of 4 meters. The main branches are thick and curved. The ringlets are large and evenly spaced. Fruiting mainly occurs on them. The foliage is dark green in color and smooth to the touch. There are small needles along the edges.
The tree trunk is thick, the bark and old branches are brown-gray, younger shoots are brown. The flowers are small in size and white. The plant always produces a lot of flowers.
The variety does not like drought; this negatively affects the quantity and taste of the crop. In terms of winter hardiness, the crop tolerates frosts down to -35 degrees. But if it gets colder sharply in the spring, it will harm the kidneys.
Strengths and weaknesses of the variety
Among the many advantages of the Veles pear, the following stand out:
- high environmental sustainability;
- immunity to leaf and fruit scab;
- frost resistance in temperate climates;
- preservation of ovaries during frosts down to −2 ℃;
- consistently high yield without periodicity;
- marketability of fruits;
- excellent taste;
- transportability;
- versatility of application.
The main advantages are considered to be high productivity and the ability of the vegetative organs of the plant to quickly recover
There are practically no disadvantages. The main problem that gardeners may encounter when growing “Velesa” is the tendency for the fruits to become smaller when the harvest is abundant, as well as on old trees in the absence of regular pruning.
Description of fruits
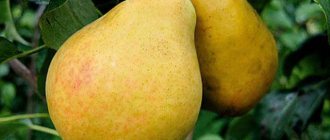
The fruits are medium in size, reaching a weight of 120 grams. They have a regular pear shape, slightly beveled, no ribbing. The fruit stem is long, slightly curved. Color green-yellow. There are small dots under the skin that are very difficult to notice.
The pulp is cream colored and not too dense. The structure is half buttery, very juicy and pleasant. Tasting score of the fruit – 4.6 points out of 5 possible.
The fruits are usually eaten fresh, although they are also suitable for canning.
The fruits reach maturity in the fall, somewhere in early September (sometimes at the end of August). It is advisable not to harvest the entire crop at once; the largest pears are removed first, and then those that remain. If you plan to store fruits, it is better to pick them unripe.
If you leave the harvested crop in the refrigerator, its shelf life is about two months. It is worth noting that the fruits tolerate transportation well.
Productivity
The Veles variety does not have a high early fruiting rate. Pear trees produce their first harvest 5-7 after planting. They bear fruit annually, yielding 60-90 kg of fruit per tree. Fruit ripeness can be easily determined by color. Fully ripe pears begin to turn yellow. The ripeness of pears is also determined by touch: if they are hard, it takes longer to ripen.
In August and early September it is time to harvest. Fruit ripening is simultaneous. It is recommended to remove them, starting with large specimens, in 2 stages: at the end of August and in mid-September. Experienced gardeners who have fully appreciated the advantages of the Veles variety advise picking the fruits from the tree when they are slightly greenish and unripe.
This increases their shelf life. Fruits left on the tree until fully ripe have a much shorter shelf life. Veles pears have a minor drawback: as a result of abundant harvests and lack of pruning on old trees, they are prone to shrinkage.
The ideal conditions for storing Veles pears are a refrigerator or a cool, dark basement without foreign odors or mold. The Veles variety does not like high humidity - the storage should have an optimal humidity level of 80-85%.
You can preserve the harvest until spring in a wooden box, wrapping each fruit in newspaper. Fruits stored in this way can be stored in a cool place for several months. When fresh, the autumn Veles pear is very tasty. It will serve as an excellent basis for delicious compotes, preserves, and jams.
Pollinator trees
Although Velesa is self-fertile, to increase the amount of harvest it is advisable to place other varieties of pears next to it. The optimal pollinators are:
- Severyanka;
- Rogneda;
- Chizhovskaya;
- Lada;
- Otradnenskaya;
- Voskresenskaya large;
- Simply Maria.
Severyanka
Chizhovskaya
Lada
Otradnenskaya
In addition, you can use other varieties of pears that bloom at approximately the same time.
Cross pollination occurs between plants whose flowering dates overlap for at least a week.
Reproduction methods
These trees can be propagated by layering or cuttings. Both of these methods are quite simple, and the survival rate of the resulting planting material is close to 100%.
By layering
In mid-May, an even, healthy branch is selected, 3 buds are counted from above, and on the next three buds the shoot is buried in the soil, which should be watered regularly, not allowing it to dry out.
After 25-30 days, the cuttings take root, they are cut off from the mother branch and transplanted to a permanent place.
Cuttings
Cuttings are cut from healthy shoots of the current season, placed in water so that they develop roots - usually this happens after a month. After this, the cuttings can be transplanted to a permanent place.
Diseases and pests
Although the variety has very good immunity compared to other representatives of the crop, it may still encounter some problems. Let's consider the main diseases and pests, as well as preventive measures.
Powdery mildew
To prevent this disease from affecting the pear, it is recommended to carry out treatment using copper sulfate in the fall. If the disease has already manifested itself, you can use the following drugs: “Hom”, “Topaz”, “Skor” in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
Fruit rot
To avoid this problem, gardeners advise pruning the tree in time, this will ensure good ventilation of the crown. Also, the entire plant will receive enough sunlight. For treatment, the drugs “Hom” or “Oxychom” are used.
Bacterial burn
For prevention, treatment with copper sulfate is carried out (in autumn). Treatment consists of getting rid of and disposing of all affected foliage and using the drug “Hom”.
Bark cracking
If the pear bark is cracked, then you need to treat it with lime mortar in the spring. There are no special medications to correct this problem.
hawthorn
To avoid this pest, the pear needs to be treated in the spring using special preparations. An example is “Entobacterin”. If the butterfly is already active, then use a soap solution.
Medyanitsa
Prophylactic treatment is carried out against the copperhead in the spring. The following drugs are suitable: Vermitek, Apollo. When it has already shown itself on the pear, it is recommended to treat the crop with garlic or dandelion infusion.
codling moth
Gardeners advise carrying out preventive treatment against codling moths in the spring using Vermitek. To get rid of it, insecticides are used: for example, Karbofos.
General preventive recommendations
Of course, it is much easier to avoid illness than to deal with its consequences later. Experts advise regularly carrying out the following activities:
- Constantly remove and burn fallen leaves.
- The crown needs to be thinned out frequently so that the tree is ventilated and receives light.
- As necessary, loosen the tree trunk circle, removing weeds.
- In early spring, before the leaves appear, and in the fall, after the leaves fall, use 1% Bordeaux mixture, 1% suspension of colloidal sulfur, 0.3% suspension of 90% copper oxychloride for treatment.
Features of cultivation and subtleties of care
It is enough to master the basic techniques of agricultural technology for fruit crops in order to grow a Veles pear without any problems.
Watering
The pear tree should be watered regularly, especially in dry years. If there is a lack of moisture or nutrition in the soil, the fruits become smaller and may even simply fall off. They begin to water the pear in the spring, before flowering begins. In the future, watering intervals should be within 3-4 weeks. Young trees with fragile root systems and shallow roots may need more frequent watering. The depth of moisture should be controlled - after watering it should be 25–30 centimeters. Before watering, protect the tree trunk with an earthen roller from direct contact with water. This will avoid possible damping off.
Before watering, protect the tree trunk with an earthen roller from direct contact with water.
After the soil has dried, the tree trunk circles should be loosened and covered with a layer of mulch 5–10 centimeters thick. In the future, you can water without removing the mulch layer - this way the soil will remain moist for a longer period of time and will not require additional loosening. From time to time you need to check the condition of the mulch - slugs, beetles and other pests can collect in it. In this case, they should be collected and destroyed, the soil should be dried, and then the mulch should be returned to its place. In late autumn, you should not forget about pre-winter moisture-recharging watering - it contributes to better winter hardiness of the plant.
Feeding
The planting hole is the main source of nutrition for the young tree for 3–4 years after planting. In the future, the pear will need additional feeding.
Table: types of fertilizers for pears, when and how to feed
| Types of fertilizers | Timing and interval of fertilizing | Methods of application and dosage |
| Organic | ||
| Compost, humus or bottom peat | Spring or autumn every 3–4 years | Incorporation into the soil during digging. Dosage - 5–10 kg/m2. |
| Liquid fertilizers | With the onset of fruiting in June - July annually. Carry out 3-4 feedings with an interval of 15-20 days. | Prepare an infusion in advance from two liters of mullein (you can also use one liter of bird droppings or 5–7 kg of freshly cut grass) and ten liters of water. Infuse for 5-7 days in a warm place, then filter. Dilute the concentrated infusion with water in a ratio of 1: 10 and water the plant at the rate of one bucket per square meter. |
| Mineral fertilizers | ||
| Nitrogen-containing (nitroammophoska, urea, ammonium nitrate) | Spring, annually | Incorporation into the soil during digging. Dosage - 20–30 g/m2. |
| Potassium containing (potassium sulfate, potassium monophosphate) | May - June, annually | Dilute in water when watering. Dosage - 10–20 g/m2 |
| Phosphorus-containing (superphosphate, double superphosphate, superagro) | Autumn, annually | Incorporation into the soil during digging. Dosage - 20–30 g/m2. |
| Complex fertilizers | Apply following the directions in the attached instructions | |
Trimmings
Without a series of prunings, it is difficult to get a decent harvest.
Crown formation
For the Veles pear variety, it is recommended to use a crown molding similar to an improved bowl. This shape is suitable for trees of low and medium height. It ensures good ventilation and illumination of the internal volume of the crown. In addition, caring for the tree and harvesting becomes much easier. This formation is not difficult to carry out. The procedure is as follows:
- It is assumed that the first step of pruning the seedling was completed during planting.
- In the second third year, in early spring before the onset of sap flow, the second stage of formation is carried out. In this case, it is necessary to select 3–4 strong branches, growing in different directions and located at a distance of 15–20 centimeters from each other. These are future skeletal branches. They should be shortened by one third, and all other branches should be cut into a ring.
- The central conductor is cut above the base of the upper branch.
- In the third or fourth year after planting, branches of the second order are formed. To do this, select two branches on the skeletal branches, located at a distance of 50–60 centimeters from each other. They are shortened by 50%. All other branches grown on the skeletal ones are cut into a ring.
- In the future, you need to ensure that all branches remain the same length. If one of them becomes dominant, then it will take on the role of the central conductor, and this should not happen.
When shaped like an improved bowl, good ventilation and illumination of the internal volume of the crown is ensured
Regulatory trimming
The point is that when it is carried out, the density of the crown is regulated. To do this, cut out part of the shoots that grow inside the crown, creating conditions for good ventilation and illumination. This pruning should only be done when necessary. If there are branches growing inside the crown, but they do not intersect or shade the neighboring ones, there is no need to cut them out. After all, they also contain ringlets on which fruits grow. This pruning is carried out in early spring.
Maintenance pruning
Needed to maintain stable yields. A simplified version is chasing young green shoots, carried out in the summer by shortening them by 5–10 centimeters. This provokes the growth of additional ringlets on them, on which flower buds are formed. More experienced gardeners use the method of replacing fruiting shoots, forming replacement shoots similar to the formation of grapes.
Experienced gardeners use the method of replacing fruiting shoots, forming replacement shoots according to the type of formation of grapes
Sanitary pruning
Sanitary pruning is carried out annually in late autumn by removing dry, diseased and damaged branches. If necessary, it is also carried out in early spring if frostbitten and broken branches have formed as a result of the winter.
Rules for pruning
Certain rules must be followed when pruning trees. Otherwise, you can cause harm to the plant instead of benefit. The rules are simple and clear:
Recent Entries
Lilac perennials that are beautiful, compact and do not crowd out other plants Why when buying seedlings you should not take the sellers’ word for it and how to determine the age of the plant using 3 signs Tomato seedlings have turned purple or whitish: why the color has changed and how to save the plants
- Do not start pruning if the cutting tool (secateurs, loppers, saw, knife) is not sharpened.
- Before starting work, it is necessary to treat the tool with a disinfectant solution. You can use: 1% solution of copper sulfate;
- 3% hydrogen peroxide solution;
- alcohol, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages
Before planting a pear on your plot, any gardener should study the pros and cons of a particular variety. Regarding Veles, we can talk about the following advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Ovaries are not afraid of frost.
- The plant does not require care.
- It has good immunity, so with proper prevention it will practically not get sick.
- Fruiting is stable.
- The yield is always good.
- The commercial characteristics of the fruit are high.
- The fruits are pleasant to the taste and suitable for fresh consumption.
- The harvest has good shelf life and can withstand transportation.
Flaws
- The pear is not early fruiting.
- Requires nearby pollinating plants.
- The winter hardiness of wood is not the best.
- If you do not normalize the ovaries, the fruits will be small.
- The branches require support during fruit set.
Description of the plant, characteristics of fruiting
The tree is medium-sized, fast-growing, at a young age with a spreading crown (which then becomes wide-pyramidal and drooping), of medium density, and therefore well lit. The bark on the trunk and main branches is gray and flaky. The main branches are curved, with fairly large ringlets. The shoots are medium long, thick, brownish-brown. The leaves are medium-sized, green, smooth, with wavy curved finely serrated edges. Petioles are long, thin with lanceolate stipules.
Flowering begins in the second decade of May. The Veles pear is distinguished by its high bud arousability and shoot-forming ability. Fruiting is concentrated on simple and complex ringlets.
Snow-white flowers begin to bloom en masse closer to mid-May
For stable formation of ovaries, “Velesa” needs additional pollinating partners that bloom at similar times, for example, “Bere Moskovskaya”, “Bere Dil”, “Beauty Chernenko”, “In Memory of Yakovlev”, “Autumn Dream” and “Dobryanka” ( "September")
The early fruitfulness of the variety is assessed as average. Trees on a seed rootstock begin to bear fruit 5-7 years after planting in a permanent place. Productivity increases rapidly: by the age of 7, the average is about 20 kg per tree; during the period of full fruiting in industrial plantings, more than 10-13 t/ha are obtained with standard agricultural technology.
Landing
In order for a pear to delight you with a stable and rich harvest, it must be planted correctly. It is very important to follow the technique of this event, since the culture does not tolerate transplantation very well.
Selection of seedlings
The age of the seedling should not exceed two years, and its height should not exceed one and a half meters. The crown should include 1 main shoot and a pair of side shoots. The plant itself must be in good condition, without any damage or signs of disease. The same applies to roots.
If the seedling is an autumn seedling, leaves are unacceptable, but a spring seedling may have several open buds. It is best to buy a young plant in special nurseries or farms.
When is the best time to plant?
You can plant it either in the fall: from mid-October to early November, preferably after the leaves have fallen. Spring planting is also allowed: from April 20 to April 30. It is best to hold events in the fall.
Preparing the seat
To place the pear, you need to choose the most illuminated place, in no case a lowland. The soil should be light and fertile. It is advisable to prepare the pit in advance, at least 3 weeks before the event. Depth and diameter - approximately 70 and 80 centimeters.
The fertile part of the land must be mixed with fertilizers: 20-30 liters of humus + 200 grams of superphosphate + 200 grams of wood ash. About 3 buckets of this mass are added to the bottom.
Planting step by step
- Form a mound at the bottom of the hole to distribute the roots. Make notches on the walls for oxygen.
- Place a one and a half meter long stake in the center of the pit.
- Place a young specimen to the north of the stake.
- Add soil to the hole. The root collar should be 6 centimeters above the ground level.
- Thoroughly compact the soil and water with 30 liters of water. As soon as the liquid is absorbed, add more soil.
Feeding and fertilizer
Fertile soil becomes depleted over time and loses nutrients. To restore it, mineral and organic fertilizers are used. Only with adequate nutrition will pear trees produce regular and abundant harvests.
Table: feeding pear trees at different times of the year
| Season | Period | Preparations, proportions, method of application |
| Spring | Bloom | Root: 1. Saltpeter is diluted in a ratio of 1:50. For 1 sq. m requires 30 g of substance. 2. Urea: 80-120 g per 5 liters of water for one tree. |
| After flowering | Root: 1 kg of nitroammophoska is diluted in 200 liters of water. Use three buckets for each tree. | |
| Summer | End of June – beginning of July | Root: 1. Dilute manure with water in a ratio of 1:20. Let it brew for 3-5 days. Water at the rate of 5 liters per 1 sq. m. 2. 7-10 days after the first. For 10 liters of water, 1 tablespoon of urea, superphosphate, potassium salt. One tree requires 1-2 buckets of solution. |
| Foliar: Ready-made mixtures containing potassium and phosphorus are purchased. Dilute in water according to instructions. Alternate with nitrogen and mineral fertilizers. | ||
| Autumn | End of September | Root: 1. Dilute 1 tablespoon of potassium chloride and 2 tablespoons of superphosphate in 10 liters of water. Bring it into the tree trunk circle. 2. Feeding with ash. For 1 sq. m requires 150 g of ash. It is laid to a depth of 10 cm during digging. |
Care
In the first few years after placement, it is advisable to constantly mulch the tree trunk circle using rotted manure or peat. Watering on a regular basis is important only for a young individual; in the future it is carried out according to the following scheme:
- in April, before flowering begins, if there was little snow in winter and no rain in spring;
- during fruit set;
- late autumn, during the preparation of the crop for wintering.
For irrigation, use a large amount of water so that it saturates the soil well. Autumn watering should be the most abundant. After these activities, the soil must be loosened.
It is forbidden to use cold water for irrigation.
How to improve your harvest: tips and tricks
To fruitfully grow a pear and obtain high yields, experienced gardeners adhere to three main secrets that affect its size:
- Correct choice of location and planting of seedlings in compliance with generally accepted technology.
- Timely care not only for a young seedling during the adaptation period, but also for an adult tree.
- Careful preparation for wintering.
Timely completion of all the above stages allows the pear to feel comfortable at any time of the year, receive the sun, moisture and nutrients in the required volume.
The result of careful care will not be long in coming: the pear will thank gardeners with abundant flowering in the spring and large harvests in the fall.
Trimming
Veles is advised to prune at the end of February. It is worth remembering that culture does not easily tolerate such manipulations, so you need to act carefully. What to avoid when pruning:
- Thin branches directed vertically or at an acute angle (tops).
- Injured or dried branches.
- Branches shading each other.
- Branches looking deep into the crown.
Rejuvenating pruning is also required, which involves cutting all branches to such a length that you can easily care for the plant.
The more the pear is pruned, the more tops are tied on it.
Reviews
Valery Sergeevich, Saratov: Once Velesa was very cold, but she quickly recovered. That year it yielded less, but now everything is fine. An amazing variety that we are very pleased with. I recommend it to everyone who lives in cold regions.
Larisa, Longitudinal : This variety has been growing at our dacha for a very long time. All this time, the plant pleases with a constant and stable harvest. Pears are very tasty and juicy, children especially like them.
Alena Moroznaya, Moscow region. : I recently planted Veles on the plot, and now the harvest has been harvested. The taste is the best pear I have ever tasted. If you live in Central Russia, be sure to take note of this variety!
Reviews from gardeners about Veles pear
Velesa is a good variety, tasty and quite reliable in my conditions, but I have a plot in the east of the region and the place is quite cold due to the microrelief. Velesa is tastier (in my opinion), but we also eat Cathedralnaya, especially since it ripens a little earlier.
Vaska
https://www.websad.ru/afsearch.php?code=808077&go=1&query=%C2%E5%EB%E5%F1%E0&author=1
We have a Veles pear growing here. Last summer we got our first harvest. We liked the pear - tasty, moderately sweet, juicy. Our Memory of Yakovlev is still growing, but I liked this one better.
Lara
https://www.tomat-pomidor.com/newforum/index.php?topic=2061.0
Velesa has been growing as a tree for me for 7-8 years now (it was planted when she was two years old). Now a solid tree, in some winters it froze slightly, but quickly recovered. The fruits are large and tasty. But Vidnaya grafted onto it seems tastier to me.
April
https://www.websad.ru/afsearch.php?code=638737&go=1&query=%C2%E5%EB%E5%F1%E0&author=1
I really liked Velesa and nothing about Chizhovskaya - ours is small, for me this is a big minus.
trophy
https://www.tomat-pomidor.com/newforum/index.php?topic=2061.0
I have Veles in the crown, it was very frozen after the winter of 2005-2006 (that winter all the pears near Moscow got it), but now everything is fine (it has recovered).
AndreyV
https://forum.prihoz.ru/viewtopic.php?f=30&t=6273&hilit=%D0%B3%D1%80%D1%83%D1%88%D0%B0+%D0%91%D0%B5%D1 %80%D0%B5%D0%B7%D0%BA%D0%B0&start=1095
My Veles tree froze in 2005-6. After 2010, it began to fall out in parts. In 1012 she was uprooted, and Thumbelina was with her. Preserved in the crown of Veles.
Alina
https://forum.prihoz.ru/viewtopic.php?f=30&t=6273&hilit=%D0%B3%D1%80%D1%83%D1%88%D0%B0+%D0%91%D0%B5%D1 %80%D0%B5%D0%B7%D0%BA%D0%B0&start=1095
Veles grows in the form of grafts on Chizhovskaya branches. The winter before last (i.e. the winter of 2009-2010), almost all of my branches froze on all varieties, including Veles (to about the same extent as Lada and Chizhovskaya). It didn’t bloom, but it moved away and gave growth. I overwintered well last winter and am looking forward to flowering. I can’t report on the yield yet - the grafts are not very old, they have only borne fruit twice so far. I liked what was ripe.
Vaska
https://www.websad.ru/afsearch.php?code=638737&go=1&query=%C2%E5%EB%E5%F1%E0&author=1
I liked Velesa, it was delicious. It’s good that I managed to take a cutting from it before cutting it down.
April
https://www.websad.ru/afsearch.php?code=808077&go=1&query=%C2%E5%EB%E5%F1%E0&author=1
I had Velesa and Lada, Velesa froze right away, Lada suffered longer.
Georgy Ivashevsky
https://forum.prihoz.ru/viewtopic.php?f=30&t=6273&hilit=%D0%B3%D1%80%D1%83%D1%88%D0%B0+%D0%91%D0%B5%D1 %80%D0%B5%D0%B7%D0%BA%D0%B0&start=1095
My Veles grew for eight years, there were no fruits at all. She began to waste away. They dug it up in the fall. It didn't even bloom. When they dug it up, we noticed that the trunk at the roots was somehow compressed.
Ruho
https://www.nn.ru/community/dom/dacha/?do=read&thread=2192472&topic_id=48314413&year=2012
This is the first time my Veles pear bears fruit (no one believes that these grow in the Moscow region), but it is most likely not long-lasting.
Water meter
https://forum.auto.ru/garden/19149/#post-19183
Veles pear grows here. It was purchased in Biryulyovo. There's nothing in it. A tough one with rough skin hangs on a tree; you take it off and after three days it’s cotton wool. At different times they tried to collect it, both on the tree and at home. I don’t recommend either juice or compote, or I didn’t find a common language with her.
crown
https://pesiq.ru/forum/showthread.php?s=a922f7cc4f410cf0a1f80b1fd065e19e&p=7427129#post7427129
There is Velesa and another unknown variety on the site. Only Velesa bears fruit, although she is the youngest. A three-year-old seedling, planted 2 years ago, produced a harvest the next year. Pears are very juicy and tasty.
Hazelnut
https://www.websad.ru/archdis.php?code=288296
I have Velesa, in the form of vaccinations in the crown. Tasty and quite large, I like it. But it doesn’t seem to be that late, I remember that just when I was buying cuttings, I was looking at varieties that weren’t late, since I don’t intend to store them, and I was afraid that the ones that were too late wouldn’t have time to ripen. In the descriptions of VNIISPK it is listed as autumn, and it is written that it is stored until mid-November. Unfortunately, last year I forgot to record when it was ripe. In the photo from August 19, it is still hanging on a branch and looks quite green.
Vaska
https://www.websad.ru/afsearch.php?code=731004&go=1&query=%C2%E5%EB%E5%F1%E0&author=1
I have Veles growing and Vidnaya grafted on her. Both have very good taste and health. Productive. Vidnaya - summer, Velesa - late summer, early autumn.
April
https://www.websad.ru/archdis.php?code=547924
The Veles pear gives its owners juicy and sweet fruits, and abundant harvests allow them to stock up on vitamins in the form of homemade preparations for the whole winter. Proper tree and fruit care will provide your family with immunity and good mood for the whole year.
- Author: Vita Gornaya
Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)
Share with your friends!