Author: Elena N. https://floristics.info/ru/index.php?option=com_contact&view=contact&id=19 Category: Garden plants Published: September 09, 2016Last edits: January 06, 2021
- How to treat tomatoes against late blight
- How to fight late blight on tomatoes with folk remedies
- Protecting tomatoes from late blight
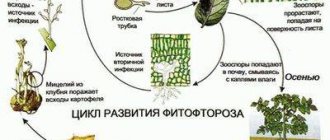
Late blight (lat. Phytophthora) is a genus of fungus-like protists that causes late blight disease, most often affecting nightshade crops, including tomatoes. Phytophthora has more than one hundred species. The name of the disease “late blight” consists of two ancient Greek words and translated roughly means “destroying or destroying a plant.” Indeed, this disease can destroy a plant in just a few days.
Late blight (late blight) of tomatoes - description
Phytophthora is tenacious and ubiquitous: it lives on seeds, plant debris, soil, greenhouse walls, and garden tools. The disease progresses in cold and wet weather. Most of all, late blight loves calcareous soils, thickened plantings into which fresh air is difficult to enter, temperature changes, dew, and plants weakened by poor or insufficient care.
Signs of late blight on tomatoes
This common and most dangerous disease can be diagnosed based on several signs:
- the underside of the leaf blade becomes covered with spots, gradually the leaves turn brown, dry out and fall off;
- the shoots of the plant darken and then turn black;
- Black areas form on the fruits.
We will try to give you as much information as possible about this disease and answer your questions:
- How to disinfect, germinate and sow pepper seeds
- late blight on tomatoes - what to do?
- How to protect tomatoes from late blight?
- how to fight late blight (late blight) on tomatoes?
- How to treat tomatoes against late blight in open ground?
- how to get rid of late blight on tomatoes?
Where and when is it formed?
Late blight is quite widespread; it can appear on potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants, and cucumbers.
The affected areas are:
- weak;
- average;
- strong.
Often the disease begins to progress in the second half of summer , it is at this time that temperature changes begin, and humidity rises in the morning or evening, and it often rains. The cause of this disease may be:
- excessive application of nitrogen fertilizers;
- strong thickening of plantings;
- incorrect proximity, for example, it is better not to plant tomatoes next to eggplants and potatoes;
- rare ventilation.
Therefore, it is advisable to use preventive measures rather than wait until the disease affects the crop.
Treatment of tomatoes against late blight
How to treat tomatoes against late blight
There are many chemical means of destroying late blight, but they have the same principle of action. In a long fight against late blight, it is best to alternate means of protection, since late blight is very tenacious and easily adapts to the drug if you use it from year to year.
Remedies for late blight on tomatoes
How to treat tomatoes against late blight? Tomatoes are treated for late blight with fungicides. In amateur gardens and vegetable gardens, the most commonly used drugs for late blight are Previkur, Fundazol, Fitosporin, Quadris, Ridomil, Switch, Skor, Topaz, Horus, Fundazim, Thiovit Jet, HOM, Bordeaux mixture, copper sulfate, copper oxychloride, Trichopolum and other. But sometimes the fight against late blight on tomatoes is carried out using old, centuries-tested folk remedies.
In the photo: Phytophthora on a tomato stem
How to treat tomatoes against late blight
How to spray tomatoes against late blight? Dissolve 2 tablespoons of copper sulfate in 10 liters of water and treat the tomatoes with this mixture before flowering. You can also use calcium nitrate as a fungicide - dilute 1 tablespoon of the substance in 10 liters of water.
The antibiotic Trichopolum is also used to protect against late blight, dissolving 10 tablets in 10 liters of water and treating tomatoes with this composition twice a month. And fungicides from the store (Fitosporin, Fundazol, etc.) are diluted in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. The first treatment of tomatoes is carried out at the stage of ovary formation, after which spraying is repeated every ten days.
If tomatoes are severely affected by late blight, it is necessary to remove and burn all the affected leaves, and treat the fruits, and especially the stalk, with a one percent solution of calcium chloride.
Watering tomatoes against late blight
You can maintain the level of protection of tomatoes from fungal infection by adding a fungicide to the water for irrigation every now and then. The dosage of the fungicide is determined based on the recommendations of the drug manufacturer.
In the photo: Tomatoes affected by late blight
Spraying tomatoes against late blight
Treating tomatoes against late blight with chemicals gives a quick and reliable result, but it is undesirable to use them on already ripening fruits, as this may negatively affect the quality of the crop. How to be?
How to deal with late blight so that it does not affect the quality of tomatoes? You can protect tomatoes from disease using preventive measures or non-toxic folk remedies. But if you decide to use fungicides, treat the tomatoes with them before flowering, before the first ovary appears, then again after two weeks to consolidate the result. In the future, the use of the fungicide should be stopped and only folk remedies to combat late blight should be used.
Folk remedies for late blight on tomatoes
How to fight late blight on tomatoes with folk remedies
Late blight on tomatoes at the very beginning of the disease can be destroyed using less radical methods such as treating the garden with fungicidal preparations. Folk remedies for treating tomatoes against late blight may not be so effective, but they are harmless to the human body. How to save tomatoes from late blight using folk remedies?
Late blight on other crops - treatment and prevention
Garlic-manganese infusion against late blight on tomatoes
You can treat them with an infusion of garlic with potassium permanganate - 100 g of garlic minced in a meat grinder (you can use not only the cloves, but also the leaves and arrows of the plant for this purpose), pour a glass of water, leave for a day, strain and, diluting this infusion in 10 liters of water, add 1 g of potassium permanganate to it.
In the photo: Tomato bush with late blight
Infusion of straw against late blight on tomatoes
Pour a kilogram of rotten hay or straw into 10 liters of water, add a handful of urea and let it brew for 3-4 days. Strain the infusion and treat the tomatoes with it.
Late blight yeast on tomatoes
Dissolve 80 g of yeast in a bucket of water and pour this solution over the tomatoes at the first symptoms of late blight.
Copper wire against late blight on tomatoes
Spraying tomatoes against late blight can be replaced by “copper piercing.” How to protect tomatoes from late blight using copper wire? The wire needs to be calcined over a fire or sanded, cut into pieces 3-4 cm long, insert such a piece into the stem of an adult tomato bush at a height of 10 cm from the soil and bend the ends of the wire down. Never wrap the wire around the stem!
- Protection from pests and bad weather when sowing cabbage in the ground
How to Grow Healthy Tomatoes - The Complete Guide
Some gardeners prefer to wrap pieces of copper wire around the roots of the seedlings before planting them in the garden. The fact is that microdoses of copper, enhancing oxidative processes, stabilizing the production of chlorophyll and stimulating oxygen metabolism, strengthen the plant’s immunity and make it resistant not only to late blight, but also to other infections.
Iodine for late blight on tomatoes
Everyone knows about the antimicrobial effect of iodine, so the method of spraying tomatoes with a milk-iodine composition is widely popular among gardeners. For 10 liters of water, one liter of low-fat milk and 20 drops of iodine are enough.
In the photo: What stem blight looks like
Ash solution against late blight on tomatoes
This treatment is carried out in three stages: as soon as the seedlings take root and begin to grow, before the tomatoes bloom and immediately before the first ovaries appear. Add half a bucket of wood ash to 10 liters of water and leave for three days, stirring from time to time. When the composition has settled, the liquid must be drained, its volume brought to 30 liters and 30-35 g of liquid soap added to the composition.
Serum against late blight on tomatoes
Treating tomatoes against late blight with curdled milk serum also gives good results. Dilute the serum in a one to one ratio with water and from the first days of July spray the tomatoes at least every day.
Signs of damage (symptoms of the disease)
Since the primary infection is hidden and difficult to diagnose, late blight is diagnosed at a late stage, when external manifestations are detected.
Tomato late blight occurs most often from late May to August. Late-ripening tomato varieties are most often affected. Fungal spores do not like high temperatures, so in the first half of summer it is not very comfortable for them to reproduce.
Tomato late blight affects leaves, stems, and fruits:
a) LEAVES . Brown dark spots appear along the edge of the leaf blade, quickly increasing in size. Over time, it takes over the entire leaf. The leaf turns black and dries out. With prolonged humidity, leaf rot may occur. A whitish coating forms at the border of the decaying part of the leaf with the healthy green part of the leaf.
b) STALK . Locally you can see the same dark brown spots. With rain, watering and moisture condensation, the infection quickly spreads along the stem. The stems turn brown and soften.
c) FRUITS . Brown solid rot can be detected with the naked eye on tomato fruits. The spots range in color from lilac-brown, brown to almost black. The spots appear from the inside. Intensely growing fruits are most affected; those that are beginning to ripen and those that are ripe are more resistant. Rot does not only form during the growing season; it continues to actively develop in infected fruits both during transportation and storage.
Prevention of late blight on tomatoes
Protecting tomatoes from late blight
It is no secret to any gardener that it is better to prevent a disease than to fight it, even successfully. In order to protect tomatoes from late blight infection, there are effective preventive measures. How to spray tomatoes against late blight? What preventive measures can protect them from infection?
In the photo: Late blight disease of tomatoes
Prevention of late blight on tomatoes in open ground
Dissolve a glass of table salt in 10 liters of water and treat saturated but still green tomatoes with this brine - the composition forms a film on the fruits that protects them from infection.
You can dilute 1 liter of kefir, fermented for two days, in 10 liters of water, mix thoroughly and treat the tomatoes with this composition. The first spraying should be carried out two weeks after planting the seedlings in the ground, and then repeat the treatment of tomatoes with kefir weekly.
Agrotechnical methods of prevention from late blight
If you follow crop farming techniques, you can reliably protect your tomatoes from late blight. Here is a list of activities that serve this purpose:
- in areas with excess lime content, the natural balance of the soil should be restored by adding peat under digging. When planting seedlings, it is better to fill the holes with sand;
- observe crop rotation: do not plant tomatoes in an area where carrots, turnips, cauliflower, beets, cucumbers or onions grew before them;
- do not thicken the plantings - follow the planting scheme developed by agricultural technicians;
- water tomatoes early in the morning or after sunset, trying to pour water so that drops of water do not fall on the plants;
- During periods of high air humidity, tomatoes may not be watered at all, but it is very important to loosen the soil between the rows during this period of time;
- feed the tomatoes with phosphorus, potassium and other useful elements that help strengthen the plant’s immunity - strong, healthy tomatoes are not affected by fungal infections.
In the photo: Phytophthora on a tomato
Prevention of late blight on tomatoes in a greenhouse
Late blight on tomatoes in a greenhouse is almost a more frequent visitor than in garden beds. Prevention of late blight in a greenhouse should begin with disinfection of the room. Before planting seedlings, sanitize the greenhouse: wash away dirt, cobwebs, and remove plant debris.
To disinfect a greenhouse, you can use fumigation: place a piece of clean wool in a bucket of burning coals, place the bucket in the greenhouse and tightly close all windows and doors for a day.
Growing healthy tomatoes from seeds in a telly
As a preventative treatment for the entire greenhouse and tomatoes, dusting with a mixture of wood ash and tobacco dust is used at the rate of 2 cups of dust per bucket of ash. Don't forget to wear a mask and goggles before doing this.
Instead of tobacco-ash powder, you can use a solution of the drugs Baikal EM, Siyanie or Fitosporin to treat the room in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
In greenhouse conditions, it is better to use drip irrigation to moisten the soil by connecting a special hose to a container with warm water to gradually saturate the soil with moisture throughout the day.
In the photo: Rotting tomatoes due to late blight
Do not forget to regularly ventilate the greenhouse and do not allow large amounts of condensation to accumulate in the film greenhouse.
- Seedlings: care, temperature, lighting, watering
As for the preventive treatment of tomatoes themselves, in the greenhouse it is carried out at the same stages as in the garden: a week after planting in the ground, before flowering and before the first ovaries appear. If you do everything correctly, these measures will be enough to ensure that you never see symptoms of late blight on your tomatoes.
If late blight does end up in your tomato bed, prepare yourself for a long and stubborn struggle - late blight doesn’t just give up.