Pumpkin (or watermelon) has long been grown in Russian gardens; this crop is widespread. Most gardeners are accustomed to the fact that the pumpkin pulp should be sweet, and the seeds should be covered with a durable, hard, yellow-white shell. But there are other types of this melon crop, which have their own interesting characteristics.
At the beginning of the twentieth century in America, breeders developed a gymnospermous pumpkin, the seedless part of which was not used for processing, but the seeds were especially valued for oil production. The pulp of this pumpkin was used as compost to fertilize the soil. To this day, the main value of the gymnosperm pumpkin remains the bare seeds without skin, but the pulp in new varieties has acquired taste characteristics that allow it to be used for food purposes.
Appearance of gymnosperm pumpkin
The plant has a bushy or climbing form, the stems of which can reach 12 m. The faceted stem is covered with thorns and contains large, hard, toothed, five-lobed leaves. The flowers are large, yellow, dioecious, with a pleasant scent.
The fruits are greenish-yellow or orange-yellow. The pulp is coarse and fibrous, sweet or bland, and boils quickly. The thickness of the soft layer is about 2.5 cm and contains a small amount of light orange pigment. The bark on the fruit is thin. Seeds without an outer shell are green, light green or dark green. They can be eaten immediately.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of gymnospermous varieties:
- lack of a hard shell of seeds;
- a large amount of oil in them;
- relative precocity;
- can be grown in almost any region of Russia;
- resistance to infections and temperature changes.
Flaws:
- can only be grown by seedlings;
- low yield (compared to other pumpkins);
- the taste of the pulp is somewhat worse than that of other varieties;
- Doesn't last long.
Despite such disadvantages, gymnospermous pumpkin is still sown by vegetable growers in order to obtain its seeds without husks.
Selecting a location
The hard-barked gymnosperm pumpkin, reviews of which are spreading among summer residents, is grown in the same way as all other pumpkin crops. The main thing is to plant it away from squash, zucchini and other types of pumpkins, so that it does not cross-pollinate and lose its individual properties, for which it was planted. To grow pumpkins, choose a place on the sunny side with fertile, well-fertilized soil. Only in this case will the fruits grow large and sweet, which means they will be stored for a long time.
Pests and diseases
Gymnosperm pumpkin varieties are selective, created by selecting high-quality planting material, so the crop has stable immunity. The most common diseases are powdery mildew and anthracnose.
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that appears as gray spots on the leaves. The cause is excess nitrogen, lack of moisture, cold damp weather. Fighting methods:
- removal of problem areas;
- treatment of gymnosperm pumpkin with sodium phosphate or colloidal sulfur;
- using the drug “Topaz” or “Universal dew”.
The first signs of anthracnose are the appearance of dark yellow spots; over time they increase in size and become dark pink. The fungus completely infects the gymnospermous pumpkin, making the fruit unsuitable for consumption. If the plant is infected, it cannot be saved; the bush is completely removed from the site. Preventive action:
- compliance with crop rotation;
- disinfection of planting material with antifungal agents;
- treating the beds with a fungicide before planting;
- removing pumpkin residues and weeds after harvesting from the site.
Aphids parasitize pumpkins; get rid of the pest with Iskra and Fitoverm. The Whitefly moth is less common; caterpillars are destroyed with the Commander.
Preparing for landing
The planting site is prepared in the fall. They dig up the bed, add manure or humus, and you can add potassium and phosphorus fertilizers. Pumpkin grows very well on compost heaps. To do this, with the onset of autumn, healthy plant tops, food waste, foliage, sawdust, ash, small branches, and humus are piled up. In the spring, plants are planted in the prepared area.
The best predecessors for planting gymnosperm pumpkin are potatoes, onions, various root vegetables and cabbage. This crop should not be grown where vegetables from the pumpkin family grew, as they have the same diseases and pests.
Gymnosperm pumpkin: photo, growing rules
Gymnosperm pumpkin: photo, growing rules
This culture is quite demanding in terms of light. For planting, it is better to choose well-lit areas of land. Such a bed must be protected from winds and drafts. An elevated area with southern exposure is well suited. Gymnosperm pumpkins do not tolerate drought well; for normal development, the plants need regular watering. The rhizomes are located in the surface layer of the earth. For this reason, over-wetting the soil is also dangerous. Thus, the root system can become infected with fungal diseases.
As for the composition of the soil, it will be better if it has a neutral or slightly alkaline pH reaction. Acidic soil is not suitable for growing these varieties of pumpkin. The structure of the soil should be quite light, air and moisture should pass well into the ground. The composition of the soil must have a sufficient amount of nutrients. This parameter can be adjusted by applying fertilizers, as well as by observing crop rotation. You should not grow pumpkin in the same bed for more than three years. Melon plants are bad predecessors for pumpkin.
You should not plant an ordinary pumpkin next to a gymnosperm pumpkin. The fact is that the bushes will be pollinated, and next season you will not get the expected result. The area for planting is prepared in advance. It needs to be dug up and organic fertilizers added. Before sowing pumpkins, you need to thoroughly water the soil. When to sow pumpkin seeds depends greatly on the growing climatic conditions. In this case, the soil must warm up to +17 degrees. Frosts should not return. Planting material usually germinates within a week. If it so happens that cold temperatures return at this time, then the seedlings most likely will not recover.
In order to properly plant gymnosperm pumpkins, it is necessary to follow a certain algorithm:
- The seeds must be heated for eight hours. The temperature should be no more than forty degrees.
- After this, place the seeds in a growth stimulator for about five hours. Many experienced gardeners use Vympel for these purposes.
- The holes for planting are made approximately thirty by thirty centimeters. Then pour in the ash solution in the amount of one hundred grams. Add one hundred grams of potassium sulfate there. This amount of fertilizer is enough for two liters of water.
- Mix five kilograms of humus and one hundred grams of superphosphate. Hold this mixture at the bottom of the planting hole. This layer is usually about fifteen centimeters.
- Four seeds are placed at a depth of about five centimeters, the distance between them should be approximately four centimeters.
- Pour soil on top and lay a layer of mulch. For this you can use sawdust or straw.
After the first shoots appear, you need to leave two strong sprouts in one hole. Those that remain must be removed.
It is recommended to sow seeds in open soil in areas with a southern climate. For regions with a temperate climate, the seedling method of growing gymnosperm pumpkins is more suitable. This culture has a rather bad attitude towards the transplantation procedure. For this reason, it is best to use peat cups.
Gymnosperm pumpkin: planting and care, reviews
When growing pumpkin through seedlings, according to gardeners, it grows faster and produces a rich harvest. Plants are planted in the ground at the end of the first ten days of June, after the threat of frost. Even at slightly sub-zero temperatures, gymnosperm pumpkin seedlings will die. Often the seeds are sown directly into the ground. They are planted in warm soil when its temperature reaches about 12 degrees. Seeds are planted in the bed to a depth of 5 cm, 3 pieces per hole. There should be at least one meter between plants. The seedlings will hatch 12 days after planting. In inclement and cool weather, sometimes the seeds rot before they have time to sprout, so it is safer to use the seedling method for planting.
Gymnosperm pumpkin, reviews of which can be heard when purchasing seeds, is not picky when growing. Caring for it comes down to weeding, loosening the soil, fertilizing and watering. Loosening of the soil should be done 4 times during the summer period. The impressively sized leaves evaporate a large amount of moisture, so the plant should be watered once a week if there is no rain. During the flowering period, water less frequently than usual. This pumpkin variety does not require watering. The first time is fed 10 days after planting the seedlings, the next time - during flowering. Pumpkin responds well to watering with infusion of mullein and ash.
How to plant?
Pumpkin seedlings are planted in the southern regions in mid-May. Plants are usually placed in an open garden plot. The bed must be prepared in advance. Pumpkins need fertile soil, so in the fall, rotted compost is added to it. In the fall, Nitrophoska is introduced.
It will prevent insects from emerging after hibernation. In spring, potassium, nitrogen and phosphate fertilizers are distributed on the site. In this case, the soil should remain neutral acidity:
| № | Helpful information |
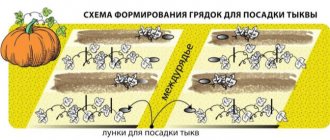
| 1 | Round holes with a well-designed ring are prepared for seedlings. Apricot pumpkin planting scheme 60*60 cm |
| 2 | make a 15 cm depression in the garden bed |
| 3 | sand and ash are placed at the bottom |
| 4 | lower the bush or container with the plant. Deepen to the bottom leaf |
| 5 | sprinkle with earth on all sides, water with warm water. Up to 1 liter is poured under each bush |
| 6 | if necessary, seedlings are covered with film |
More on the topic: How to grow Goose pumpkin in apples?
When planting pumpkin seedlings in a greenhouse, the same rules are used. The optimal temperature for the development of seedlings is 18-20 C. If in May it is still cold in the region, then heating is installed in the greenhouse.
Danae pumpkin (gymnosperm): reviews
The peel of the fruit of this variety is green-yellow in color with yellowish stripes. Pumpkins are small in size - 3-5 kg, the pulp is juicy, sweet, the seeds do not have a hard shell. The variety belongs to the mid-season species. A large amount of vitamins and microelements are contained in the seeds and pulp, so the fruit is often used for dietary and baby food. It is consumed boiled, baked, stewed, and also used for making juices and drinks. The vegetable is well transported and stored well.
Danae pumpkin is grown in two ways: in open ground and using seedlings. In March-April, seeds are sown in boxes. When 3 true leaves appear, the plant is transplanted into open ground (certainly after the threat of frost). The soil temperature at this time should be about 14 degrees. Seeds are planted at the end of May or early June, following a 1 x 1 m pattern.
Danae pumpkin, like all pumpkin crops, requires additional feeding. 10 days after planting the seedlings, the first fertilization of the soil is carried out, the second - during flowering. The plant should be watered and weeded in a timely manner. As the fruits ripen, they are cut and eaten, both seeds and pulp. Gardeners note that the seeds are very tasty and do not require peeling, although they are in film. The pulp is light orange in color and produces wonderful juice.
Harvesting and storage
Pumpkin Baby
Harvesting is carried out when the fruits are fully ripe: they acquire the varietal color of the rind, and their stalks, leaves and shoots dry out. Harvest dates come earlier if there is a threat of frost.
Large pumpkin size
Pumpkins are cut off along with the stem (this increases shelf life), wiped with a dry cloth to remove any remaining soil and stored in a cool, dark place. The seeds can be separated from the pulp by simply cutting the pumpkin in half and scooping them out with a regular spoon. The seeds are sent for drying, after which they become suitable for consumption.
Apricot pumpkin
This type of pumpkin belongs to the unique mid-early pumpkin varieties. It ripens approximately 3 months after planting. The fruit has a rounded-cylindrical shape with vaguely defined ribbing. At the stage of full ripeness, the color of the apricot pumpkin bark is yellowish with fairly wide stripes of green, looks bright and attractive. The rind of the fruit is not thick, but hard. The pulp is slightly fibrous, soft with a yellow tint. Pumpkin seeds without a dense shell, covered with a thin film. Apricot gymnosperm pumpkin, which has only positive reviews, belongs to the dessert varieties.
The variety is grown to produce pumpkin seeds, make purees, and produce juice that tastes similar to apricot. Pumpkin pulp is also consumed raw.
Gymnosperm pumpkin: benefits and harms of seeds and fruits
Gymnosperm pumpkin: description of the pros and cons of use
The chemical composition of this culture is quite rich in substances beneficial to the human body. For this reason, these fruits are often used for medicinal purposes, as well as in pharmacology. The pulp of gymnosperm pumpkins contains the same number of useful elements as regular pumpkins. The seeds, in turn, help fight helminths.
The distance between the seed and the surface coating is occupied by a kind of film, which contains a useful substance called cucurbitin. It should be noted that gymnosperm pumpkin has more of this substance than a regular pumpkin.
Regular consumption of pumpkin in food helps the metabolism to function well and gives the body strength. The chemical composition of pumpkin has a good effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as on the state of hemoglobin. Pumpkin contains a fairly large amount of choline; this substance has a beneficial effect on liver function and helps restore affected areas.
Thanks to zinc and phosphorus, which are also contained in pumpkin fruits, blood vessels become more elastic. Zinc helps produce estrogen as well as testosterone. Another benefit of gymnosperm pumpkin is that it contains calcium, which has a good effect on human bone tissue. The composition of pumpkin improves brain activity and also has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the bladder and kidneys. And pumpkin contains such an important element for humans as iron. It takes part in blood circulation. Regularly including pumpkin in your diet will help get rid of skin problems. In addition, the fruits help fight a variety of parasites that can form in a person’s body.
However, almost any fruit, even a very healthy one, has a number of restrictions on its use. For example, people suffering from dysbiosis should eat pumpkin with caution. Quite rare, but still sometimes pumpkin can cause allergies. People with diabetes should not consume pumpkin seeds in large quantities. The same applies to those who have an impaired acid-base balance. If you have an exacerbation of a stomach ulcer, then it is best to avoid eating pumpkin.