One day, going out into the garden and touching the tomato leaves, you can notice how small black insects fly off in all directions. This is a rather dangerous symptom, because black flea beetles on tomatoes are nothing more than a type of aphid.
These pests cause a lot of trouble, so you need to fight them immediately, especially if the tomato seedlings are just planted in the ground. Young plants do not withstand the pressure of pests well, so if they are not stopped, the plantings may die.
What does a cruciferous flea beetle look like (description and photo)
The cruciferous flea beetle is a shiny black bug that damages plants of the cruciferous family. Favorite plants for pests to eat are cabbage seedlings, radishes, radishes, turnips, arugula, etc. Heat-loving beetles prefer to feed on the apical and illuminated leaves, the damage increases in hot, dry sunny weather. Then their gluttony increases significantly.
By June, the aggressiveness of pests decreases. But here comes the second dangerous period - the time of reproduction. Females begin to lay eggs in the surface layer of soil. The eggs take approximately 12 days to develop. The hatched larvae feed on the roots of cruciferous crops and do not cause much harm. The development of larvae lasts 15-20 days. Pupation also occurs in the soil and after about 2 weeks a new generation of beetles is born.
Having emerged on the soil surface in the second half of July, the bugs begin to feed on the leaves of already strong plants. Of course, the harm from them during this period will be much less. They can damage flowers and seed fruits of vegetable crops. However, if no measures are taken to destroy the pests, with the onset of cold weather in the fall, the beetles return to the soil for the winter. And the breeding cycle repeats next spring. Look at the photo to see what the cruciferous flea flea looks like.
Prevention
Cruciferous flea beetles overwinter:
- on plant residues;
- on fallen leaves;
- in the top layer of soil;
- in the cracks of greenhouses and greenhouses.
To prevent the appearance of these pests, you should:
- After harvesting, dispose of plant residues in compost. If they have been damaged by diseases and/or pests, then such fruit-bearing crops are burned or disposed of in other ways.
- With the onset of autumn frosts, the soil is dug up. Then the pupated larvae of cruciferous flea beetles will appear on the surface, and at negative temperatures they will die.
If these pests were noticed in greenhouses or greenhouses last season, it is necessary to wash these structures with soda, laundry soap or a vinegar solution.- After planting seedlings of cabbage or other cruciferous crops, you need to cover them with non-woven material. Then pests will not be able to get here from other areas.
- Crop rotation must be observed. If a cruciferous crop grew in this area last season, then the flea beetle can overwinter in the soil and, emerging from there in the spring, begin to harm the seedlings.
- It is important to weed out weeds (especially the cruciferous family) in a timely manner so that flea beetles do not move from them to cultivated plants.
- Since flea beetles are especially active in hot, dry weather, you need to water the beds on time to keep the soil moist.
The famous summer resident Oktyabrina Ganichkina advises, after sowing turnips, rutabaga, and other cruciferous crops, to sprinkle dry mustard, ash or ground black pepper on the beds. Then the cruciferous flea beetles will leave this area. If you are planting cabbage seedlings, spray them with a solution of liquid soap and then sprinkle with sifted ash. This way it will better stick to the cabbage leaves and protect them from pests.
You can also use tobacco powder.
When you work with ash, pepper, or tobacco, do not forget to wear a protective mask, as these products can irritate the nasopharynx.
The famous gardener and garden designer Olga Voronova advises thinking about mixed plantings. An experienced summer resident says that cruciferous flea beetles do not like the smell of marigolds, calendula, and nasturtium, so you need to plant these flowers near the cabbage seedlings.
This pest also cannot tolerate the aroma of dill, cumin, onions, coriander, garlic, tomato tops and potatoes. Therefore, place some of these plants near the planting of cruciferous crops.
If dangerous bugs do settle in the plantings, then it is necessary to take control measures. If the degree of damage to plants is small, it is better to use traditional methods; if the scale of the harmful activity is global, then chemical methods may be required.
Cruciferous flea flea - how to fight it using folk methods
Since pest beetles prefer to feed on young leaves of cruciferous crops, the fight against them must begin literally with the appearance of the first shoots. The real danger awaits the seedlings when the first seven-lobed leaves appear on them. Do not wait for fleas to appear, they can instantly jump over a number of growing weeds, start fighting immediately.
Remove all weeds from the bed where radishes, cabbage or turnips grow, loosen the soil between the rows. And then cover the seedlings with a light sponbond, securing it on the sides with stones or boards so that the covering material does not blow away in the wind. The sponbond will protect the seedlings from insects, and water will pass through it well during watering and rain, so the plantings will not suffer from lack of moisture.
If there is no covering material, plantings are dusted using
- tobacco dust,
- wood ash,
- a mixture of wood ash and tobacco dust,
- ash and street dust,
- a mixture of cement powder and street dust.
It is best to pour the prepared powders into a sieve or one layer of gauze, and then sprinkle the plants from them. It is better to treat plantings early in the morning, when the plants remain damp from dew or evening watering. Dusting is not carried out on dry grass. When sprinkling dry foliage, the slightest wind will blow the powder off the leaves, and the treatment will not give any results.
The use of various repellent plants shows good results. Thus, the aroma of marigolds, calendula, garlic, coriander, dill, and wormwood planted next to cabbage, radishes or turnips will repel pests. Moreover, the effect will also be from the dry grass of these plants laid out next to cruciferous crops.
Preventive measures to protect strawberries from pests
Everyone knows that it is easier to prevent a problem from occurring than to look for ways to solve it later. In order not to waste time, effort and money on strawberry pest control, you must first of all follow the agricultural practices of the crop:
Predatory insects can help protect strawberries from pests indoors: the entomophage gall midge aphidimiza can cope with aphids on strawberries, and the entomophage phytoseiulus can cope with spider mites and strawberry mites.
You can purchase these bioagents at a pet store or garden pavilion. Gall midges are introduced into strawberry beds 2-3 times per season, and phytoseiulus - every 7-14 days until the pests are destroyed.
How to get rid of cruciferous flea beetle on cabbage and radishes
There are other folk ways to combat fleas. After all, chemicals cannot always be used. For example, radish is an early ripening crop; the use of chemicals is not advisable for it. Therefore, take into account the products that are used to spray the plants.
- Birch tar . For 1 liter of water add 1 tsp. tar, shake well in water. Since birch tar does not dissolve well and settles on the walls of the watering can, experienced gardeners advise first stirring the tar with liquid soap, and then slowly adding water and only then spraying the plants.
- Ash infusion . Pour boiling water over the wood ash in a ratio of 1:3, leave to steep for two days, then strain and add liquid or soaked laundry soap, then spray the plantings.
- Garlic solution . Pass 1 cup of garlic and the same number of tomatoes through a meat grinder. Dilute the mixture with 10 liters of water, strain, add 1 tbsp. l. liquid soap and start spraying.
- Solution with dandelions . Grind 500 g of dandelion leaves and roots in a meat grinder, dilute the mixture in 10 liters of water, strain. Add 1 tbsp. l. soap The solution is ready for use.
How to fight cruciferous flea beetle with vinegar
Pests do not like strong odors; the use of table vinegar is based on this property; it has a detrimental effect on bugs. If you take vinegar essence, then dilute it at the rate of 1 tbsp. l. essences per 10 liters of water. When using 9% table vinegar, it is enough to dilute 1 tsp. for 1 liter of water. Remember that you need to spray on dry foliage.
Ammonia to combat cruciferous flea beetle
To prepare the working solution, 1 tsp. ammonia is diluted in 1 liter of water, stirred and sprayed on the plants. The treatment is carried out on dry leaves. When treating with ammonia, in addition to repelling pests, you also fertilize. Ammonia is like a nitrogen plant.
A similar action - processing and fertilizing at the same time - is used when using a weak solution of chicken manure. The leaves, absorbing nitrogen fertilizing, will develop faster, gain strength, and become stronger. The coarsened leaves will no longer be suitable for the bugs and they will not eat them willingly.
Folk recipes
In addition to store-bought chemical compounds, the gardener’s arsenal also includes safer folk methods.
Powdering
Over time, people noticed that if they treat cabbage with flea ash, insects do not appear in the treated area. Wood ash is placed in the hole when planting plants. At the end of planting work, ash is also sprinkled between the rows.
To prevent the leaves from being exposed to insects, they are sprinkled with:
- Composition of ash from the kiln and lime (slaked).
- Dust from tobacco leaves.
Spraying
In addition to dry formulations, spraying with solutions according to folk recipes is used. They can be different:
Garlic and tomato tincture. It is prepared from 250 grams of tomato tops and 10 heads of garlic. They are passed through a meat grinder and placed in 10 liters of warm, clean water. Next, you need to infuse the resulting mixture for 24 hours. The strained liquid is mixed with a small (up to 50 milliliters) amount of liquid soap. This is necessary so that the composition lingers on the surface of the sheet. Dandelion tincture. Place 0.5 kilograms of dandelion leaves in 10 liters of warm water and infuse for three days. Then, also after filtering, add 50 ml of soap to the mixture. A solution of ash and soap. Add one gram of ash to 3 liters of boiling water. The solution is infused for about two days. After this time has expired, about a quarter of tar or laundry soap is added to the container. Tobacco tincture. Add 200 grams of tobacco leaves and a little soap to 10 liters of clean water. Chicken manure tincture. Water and litter are mixed in a ratio of 20:1. After fermentation, the composition can be applied. Composition with wormwood. Add a kilogram of crushed wormwood to 10 liters of boiling water.
You need to infuse the resulting composition for a day. Another remedy that must be used with caution is vinegar.
Folk remedies, unlike chemicals, do not have such a strict frequency and dosage (they can be used more frequently). It should be borne in mind that their action may not be effective enough. Therefore, if within a week there are no noticeable results, you should resort to the help of store-bought substances.
Chemicals to combat cruciferous flea beetle
The use of chemical insecticides is sometimes not justified, since some crops have a short growing season. Chemicals can be used no earlier than 20 days before harvesting vegetables. If you notice more than 5-7 insects on one plant, then you can’t do without chemicals. And if you decide to use them, choose the most harmless ones.
The most effective and frequently used means:
- Actellik is a drug from the Swiss company Syngenta. The product protects plants well from many pests, including the Colorado potato beetle. Easy to use, just dilute the concentrated emulsion with water and the product is ready for use. Economical: one ampoule of the product (2 ml) is diluted in 2 liters of water; if the pest population is larger, the contents of the ampoule are diluted in 1 liter of water. The death of insects occurs after 10 minutes for 5-6 hours.
- Aktara is a contact-intestinal insecticide that begins to act on pests half an hour after spraying the plants, maintaining effectiveness for 3-5 weeks. Before use, 3 g of the product is diluted in 10 liters of warm water. The product does not accumulate in plants and fruits and is not addictive to insects. However, it is quite effective on other insects, so it is not used during flowering so as not to cause the death of bees.
- Intavir is a universal, inexpensive, effective drug - a tablet used to destroy a large number of pests. It is quite simple to use; you need to dissolve 1 tablet in a small amount of warm water, and then increase the volume of liquid to 1 liter and spray the plants with the resulting solution. During processing, the plant itself is not damaged, but the death of insects occurs as a result of paralysis, due to which the insect stops moving, feeding and dies.
- Bankol is a biological, low-toxic drug that quickly decomposes in the soil, but with its help you can get rid of pests in one treatment. The main active ingredient of Bankol is bensultap, a neurotoxin of annelid sea worms. This product does not accumulate in treated plants, soil or water. Before use, the product is first diluted in a small amount of water, then the volume of the solution is adjusted to 5 liters and the plants are sprayed. The drug acts on bugs through contact and through the intestines, the pests stop moving and feeding, and as a result die within 1-3 days.
Chemical treatment is carried out in dry, windless weather on dry foliage. If it rains within 1-2 hours after treatment, the treatment must be repeated. Also, do not water the plants immediately after treatment.
When using chemicals, always carefully read the instructions for use of the drug, dilute the drugs and work using protective equipment.
Chemical treatment
Of course, the chemical method is not the best method, but it often turns out to be the most effective. Preparations that can be used to treat tomatoes are divided into 3 groups:
- contact (Fury, Arrivo, Inta-Vir);
- intestinal (Tantrek, Konfidor);
- systemic (Aktara).
All these compounds are extremely toxic, so when processing you need to take personal protection measures. In addition, substances are removed from tomatoes gradually, over 20-30 days, which means that spraying should be carried out before the ovary appears.
How to poison cruciferous flea beetle on strawberries
Some gardeners complain that the cruciferous flea beetle appears on strawberry bushes. Strawberries do not belong to the cruciferous family and the appearance of bugs on strawberry leaves only indicates that cruciferous plants grow nearby - radishes, turnips, cabbage. etc.
A fairly common reason for the appearance of pests on strawberries is the proximity to planted green manure - rapeseed and mustard. Since bugs are highly mobile and easily move from one plant to another, it is not surprising that pests are found here too.
But the voracious insect does not disdain strawberry leaves, eating both old and young leaves. In order to somehow preserve the harvest, if you find fleas on strawberry leaves, you need to urgently get rid of them. Since strawberries quickly begin to bloom and then bear fruit, chemicals obviously will not help. Therefore, it is better to use folk remedies: dusting with wood ash, tobacco dust, spraying with solutions of vinegar, ammonia, infusions of strong-smelling plants.
Description of the pest
Cruciferous flea beetles are frequent guests in areas where plants from the Cruciferous family are cultivated or grow independently. The length of these small bugs with a slightly convex elliptical body does not exceed 2-4 mm. Once formed, the beetles can be a variety of colors: metallic green, blue or black. Some have longitudinal yellow stripes on the elytra. Cruciferous flea beetles not only fly well, but also jump well, which is why they got their name. The worm-like larvae are pale yellow.
The pest wakes up from winter sleep when the air temperature reaches +15 C and, without any delay or convention, actively begins to eat young leaves, which quickly turn into a “sieve.”
Starved flea beetles can attack not only cruciferous plants, but also strawberries, wild strawberries, raspberries and some other crops!
Young leaves are primarily affected, on which many small holes appear in a short period of time. As a result of the resulting injuries, plants stop growing and may even die completely.
How to prevent the appearance of cruciferous flea beetle on plants
It is best to prevent the appearance of the pest in advance. Preventive measures are based on how the pest lives and reproduces.
- Fleas are most active in dry, hot, sunny weather. In cool, damp weather they are less active. Therefore, water plant seedlings and cabbage seedlings more often; pests do not like damp soil.
- To reduce damage from insects next year, dig up the area before winter as late as possible, literally before the frost itself. This will release overwintering bugs to the soil surface. If you dig up early, the bugs will go underground again and quietly overwinter there.
- In addition, it is necessary to observe crop rotation and plant cruciferous crops in a different place every year. When planning the beds, keep in mind that for cabbage, radishes, radishes, arugula, etc., allocate other places where cruciferous crops have not previously grown.
- In early spring, before planting seedlings and sowing early-ripening cruciferous vegetables, the beds must be kept clean, that is, weed them in advance. This will not create conditions for the bugs flying out of the ground to feed.
- Among cabbage, turnips, radishes, watercress, arugula, plant dill, garlic, coriander, caraway seeds, as well as marigolds and calendula. Their pungent smell will repel pests.
Identifying the pest
Cruciferous flea beetles are not like regular fleas. These insects were named so because they are able to jump a sufficient distance thanks to their hind legs. Insects are bugs with a body length of 1.8-3 mm.
Here are the types of cruciferous flea beetles that exist:
Each species of these insects is named so because of its color. They are called cruciferous because these bugs love to feast on plants from the cruciferous family.
These insects are also called flea beetles, as they prefer to overwinter, including in the soil. Pupation also occurs in the ground.
Earth fleas begin their harmful activities with the arrival of spring warmth. Then they crawl out of their hiding places and begin to feed on weeds from the cruciferous family. When gardeners plant seedlings, nimble insects move here. They gnaw numerous through holes in young leaves, and destroy the surface layer on older leaves.
Here are the crops that can be attacked by this pest:
Flea beetles not only spoil the appearance of flowers and vegetables, but can also significantly reduce crop yields. Therefore, it is necessary to fight them, but we should start by preventing the appearance of the pest.
Signs of appearance
To recognize the pest in time allows you to be savvy in determining the appearance of an insect by the first signs. The signs are:
- Detection of ulcerative gnawing marks on the leaf parts of plants.
- The appearance of damage on the leaves in the form of skeletonization.
- Detection of interveinal gnawing.
- Detection of the insect itself.
Damaged foliage begins to dry out, which leads to the death of the young plant. The cruciferous flea beetle damages the leaves and stems of young seedlings, which subsequently turn yellow and die.
What are black midges and why are they dangerous?
Black midges are a type of plant aphid, which is called black aphids (along with brown, white, green and others). These are small insects with a soft, round body (diameter from 1 to 5 mm). They feed on the juices of green tissues of tomatoes and other plants, piercing holes on the surface with the help of their proboscis. They multiply quickly and move to neighboring plants.
The danger of the pest is that it not only parasitizes the tomato, but also carries dangerous pathogens:
- late blight (leaves curl, black necrotic spots appear on tomatoes);
- stolbur (deformation of leaves and inflorescences);
- viral infections (curling, spots on leaves, wilting of the plant).
Black midges first settle on weeds, mainly on quinoa, after which they quickly fall on tomatoes. Therefore, it is advisable to detect them as early as possible, and then immediately begin destruction.
Attention!
The pest multiplies quickly and also contributes to the infection of tomatoes with dangerous diseases. Therefore, if you do nothing, you can lose a significant part of the harvest.
Already at the beginning of June, the first individuals appear (immediately with wings), and if not treated, the tomato bushes seem to freeze in development and almost do not grow. Clickable photo:
Do not create favorable conditions for the fungus gnat to reproduce
High humidity is most often the cause of mass reproduction of pests.
Know all the features of black midges:
- It has different names - fungus gnat, tomato gnat, soil fly . This is a small dark-colored midge with a body length of 3-4 mm. Found in most regions with temperate and warm climates.
- It reproduces in moist soil and in semi-decomposed plant debris . Very often, midges lay eggs on surfaces that have been watered with mullein or a solution of bird droppings, so you should not use these fertilizer options too often.
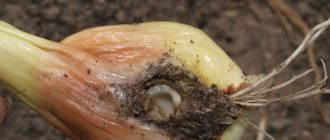
- The eggs are translucent, with a whitish tint . The larvae are worms from 3 to 8 mm long. They are white with a black head. They live in the upper layers of the soil, feed there and then pupate in the root part of tomatoes.
- After hatching, the larvae begin to feed on small roots . If the scale of infection is small, then the plant continues to develop normally, new roots grow to replace the damaged roots and no problems are visible outwardly. But if there are a lot of pests, then the damage becomes significant, the plants look bad, lag behind in development and do not form ovaries.
- In hot weather, adult midges damage the growing point of tomatoes . They also very often carry bacteria from diseased plants to healthy ones.
The fungus gnat larva develops normally only in a humid environment.
The author of the video talks about his method of combating the fungus gnat. A product is prepared from ash, laundry and tar soap. The finished solution is effective not only against black midges, but also against aphids.