Fusarium and verticillium wilt of cucumbers: what is it?
Before you begin treating cucumbers, you need to understand the characteristic features of verticillium and fusarium wilt.
Verticillium
Verticillium is a fungal disease that occurs not only in cucumbers, but also in other vegetable crops. The disease appears in any climatic conditions, but most often wilting develops in the southern regions.
Verticillium wilt develops differently, it all depends on the age of the bushes being grown. Young branches that become infected with verticillium begin to turn yellow and dry out. On adult bushes, small yellow or brown spots first appear, which over time lead to drying of the branches. The main difference between the disease and fusarium is that on diseased plants, signs of wilting can appear only on one of the branches.
Fusarium
Fusarium is a common infectious pathology that affects both wild and cultivated plants. Fusarium can affect both young seedlings and old bushes. However, wilting most often develops in weakened vegetables that have recently been transplanted to a new location.
In plants that are infected with the disease, the functioning of the root system deteriorates and rotting begins. This leads to drying out and death of the bushes.
Resistant varieties of cucumbers
Each variety of cucumber has its own characteristics. Gardeners should choose seed based on climatic conditions, soil properties, and resistance to infectious diseases, in particular fusarium. The best varieties in the latter category are considered to be:
- Rowanushka;
- Vocals;
- Zhukovsky;
- Hector;
- Raphael;
- Noble;
- Christina.
Despite the increased immunity of resistant varieties, we must not forget about prevention when growing them.
Fusarium wilt of cucumber is an insidious disease, the symptoms of which can appear suddenly. The better the gardener is prepared, the fewer plants will suffer. Their condition directly depends on compliance with agricultural technology and proper care.
Who is the causative agent of the disease?
Many people who have encountered fusarium are interested in who is the carrier and causative agent of the pathology. The disease is caused by fungi that belong to the genus Furasium. The distinctive features of Fusarium pathogens include the fact that they can easily tolerate low temperatures and cope with unfavorable climatic conditions.
Fungi are activated at high air humidity and temperatures of about 25-30 degrees above zero. The pathogen from the top layer of soil penetrates the root system and gradually infects the cucumber bush.
Fusarium soybean (root rot, tracheomycosis wilt)
Pathogens: saprobionts Fusarium oxysporum
Schlecht, Fusarium solani
(Mart.) Appel et Wr.,
Fusarium gibbosum
App.
et Wr., Fusarium avenaceum
(Fr.) Sacc.,
Fusarium culmorum
(Sm.) Sacc.,
Fusarium heterosporium
Nees.
The disease is ubiquitous in soybean crops. Sources of infection: contaminated soil, seeds and plant debris. There are several types of manifestations of fusarium: root rot, death of the growing point, wilting, leaf spotting, rotting of beans and seeds. On seedlings, the disease manifests itself in the form of browning of the root collar and root. The cotyledons have deep brown ulcers, which in wet weather are covered with white-pink sporulation of the fungus. When the growing point is damaged, the seedlings often die. Root rot on adult plants is characterized by thinning and browning of the root collar, which leads to breaking of stems and rotting of roots. Small, then increasing spots appear on the leaves, the unaffected part of the leaf turns yellow and dries out. Tracheomycosis wilt (caused by F. oxysporum
) is observed mainly during the flowering and pod formation phase. In this case, the leaves lose turgor, turn yellow, and then the entire plant dries out. Browning is noticeable on the transverse path of the stem. As a result of Fusarium infection, flowers and ovaries fall off. On beans, fusarium blight appears at the end of the growing season in the form of spots and ulcers. A mycelial film is formed on the wall of the valves, penetrating into the seeds. Infected seeds are wrinkled and puny. During the growing season, the fungus forms spores on the affected plants, consisting of numerous conidia of two types: small microconidia and large macroconidia. The shape of microconidia is varied: oval, ovoid, club-shaped; macroconia are most often crescent-shaped, fusiform, lanceolate with 3-5 septa. Fungi also produce chlamydospores. Root rot predominates with sufficient and excessive moisture. The greatest fermentation of the plant root system occurs at soil moisture of 70%. Tracheomycosis wilt develops in dry and hot weather. The causative agents of Fusarium are widely specialized, affecting many plant species from different families. The disease is very harmful. Development on seedlings leads to plant death. Diseased adult plants are stunted, produce puny pods, or do not set pods at all; produce puny, non-germinating seeds. When plants are severely damaged, grain weight can decrease by 57-77%. The development of the disease is restrained by compliance with crop rotation, fall plowing, optimal sowing dates, timely harvesting and drying of grain; seed treatment, chemical treatment of plants during the growing season, use of resistant varieties.
Causes of infection of cucumbers
To understand why bushes develop wilting, you will have to familiarize yourself with the main reasons for the appearance of fusarium:
- Infection with fungal spores. The main reason that leads to the appearance of fusarium is infection of the root system by fungal spores. When the fungus enters the plant, the bush becomes covered with yellow spots, its leaves curl and dry out.
- Overheating of grown bushes. Another reason for leaf lethargy and the development of an infectious disease is considered to be overheating of cucumber seedlings. Signs of overheating appear if vegetables are grown at air temperatures above 35 degrees. Fusarium symptoms also appear when the soil warms up to 25 degrees.
- Increased soil moisture. Fusarium wilt develops at high soil moisture in which the vegetable bush is grown. Most often, the humidity level rises due to frequent watering or prolonged rains.
- Infected seeds. Some gardeners plant undisinfected seeds. This leads to the fact that plants begin to suffer from fusarium immediately after planting.
See also
How to properly plant cucumber seedlings at home and what to feed them with
Read
Measures to protect against fusarium and wilt
Pathogenic microorganisms are very resistant and measures to protect against them are not always successful. The best preventive measures are sowing healthy seeds. If, after removing the dead plant, another one is planted, then disinfection of the soil in the hole should be provided, otherwise the newly planted plant will also die.
See also
What to do if yellow spots appear on cucumber leaves and how to treat themRead
Signs of the disease
Before starting treatment, you need to understand the main symptoms of Fusarium wilt of seedlings:
- Change in foliage color. The leaves on diseased bushes turn brown. Yellowish spots appear on their surface, the size of which gradually increases.
- Deformation of sheets. If you do not treat the disease, the edges of the yellowed leaves will begin to dry out and curl into a tube.
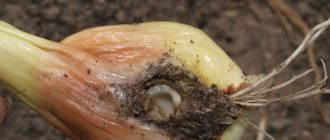
- Darkening of the stems. Darkish stripes appear on the surface of the stems of cucumber bushes. Gradually, cracks form in their place, around which you can see a pink coating. Fungal spores develop in the cracks and are carried by the wind to neighboring plants.
- Deformation of the root system. At the initial stage of development of fusarium, the root collar darkens and turns burgundy. Over time, it becomes more brittle and begins to rot.
- Curling of the peduncle. In the end, fusarium affects the cucumber peduncle, which, after infection, stops growing and curls.
How dangerous is the disease for cucumbers?
Infection with fungal pathogens most often occurs through the soil. Fusarium affects the vessels inside the shoots, which leads to slower growth. The younger the plant, the more damage it causes to them.
Did you know? The Slavs used lye as soap - wood ash steamed in boiling water.
With timely treatment, the problem can be eliminated, but, unfortunately, it becomes noticeable not at the seedling stage, but when the plants enter the flowering phase. The main danger is that infected specimens begin to wither and die en masse at the fruiting stage.
Infected specimens have reduced immunity, as a result of which they become more susceptible to other infections and bacteria. In this state, cucumbers are often affected by bacterial wilt.
This disease occurs in plants with reduced immunity and cannot be treated. In addition, weakened cucumbers are more often attacked by pests. As a result of such difficulties, losses can amount to up to 70%.
How to save plants: methods and means for treating cucumbers
You can fight fusarium blight on cucumbers using various means. It is necessary to figure out in advance what exactly is used to eliminate the symptoms of wilting.
Biological agents
Most often, gardeners use biological products, which are considered the most effective means against late blight. The most well-known drugs against wilting include:
- "Trichodermin." A biological product produced in the form of soluble granules. Before spraying the plants, Trichodermin is dissolved in heated water. For each infected bush, use a liter of the mixture.
- "Fitosporin". The drug is produced in the form of a powder mixture that must be dissolved in water. Among the advantages of Fitosporin is its long shelf life, which is 4-5 years. The bushes are treated with a biological product 3-4 times a month.
- "Vitaros". Quite a popular remedy used for watering sick seedlings. Vitaros contains components that destroy fusarium pathogens and prevent further development of the disease.
Chemicals
Before flowering and fruiting begin, cucumbers can be treated with chemicals. There are several means that are most often used in the fight against fusarium:
- "Fundazol". This is an effective fungicidal drug used to treat and prevent wilt. When creating a solution, 200 milliliters of Fundazol are mixed with ten liters of water. This is enough to process 10-15 adult cucumber bushes.
- "Maksim". Contact fungicidal solution, which is used to treat potatoes and cucumbers. Before processing vegetables, Maxim is mixed with water in a ratio of one to ten. Spraying is done 2-3 times a week.
- "Glyocladin." A chemical fungicide used to combat fungal diseases. To make your own spray solution, mix 150 milliliters of Glyokladin with 5-7 liters of water.
Folk wrestling recipes
Many vegetable growers refuse to use biological or chemical preparations and prefer to use folk remedies instead:
- Milk-soap solution. It is used if you need to get rid of fusarium and other fungal diseases. In the process of preparing the mixture, 50 grams of grated laundry soap are mixed with iodine and 200 milliliters of milk. The prepared liquid is used to treat the stems and leaves of diseased bushes.
- Wood ash. A medicinal mixture prepared from wood ash helps get rid of fusarium within 2-3 weeks. To prepare it, add 350 grams of ash and 50 milliliters of liquid soap to two liters of water. The bushes are sprayed with liquid once a week.
- Onion peel. 3-4 cups of dried onion peels are poured into a bucket of water, after which the liquid is boiled for 40-45 minutes. Then the mixture is filtered through cheesecloth and cooled.
See also
Description and characteristics of Libella F1 cucumbers, cultivation and care
Read
Preventive measures
In matters related to fusarium blight on cucumbers , gardeners pay the main attention to prevention. The disease is transmitted mainly through soil and contaminated seeds. Therefore, special attention should be paid to them when preventing Fusarium wilt of cucumbers.
Effective prevention measures:
- soil disinfection - treatment with boiling water, removal of the top layer of soil and replacement with a new one, disinfectants;
- careful selection of seeds - choose healthy ones, purchased from a trusted manufacturer or collected from high-quality, even fruits;
- treating seeds with antifungal drugs - soaking in fungicides;
- correct crop rotation - cucumbers can be returned to their original place only after 4 years;
- systematic examination of the plant for symptoms of the disease - it is important not to miss the very first signs;
- timely harvesting - every 2-3 days, so overripe fruits do not weigh down the vine and do not deplete the bush;
- timely fertilizing - plantings are covered with mullein, during flowering - with chicken droppings, and during fruiting - with ash; during the growth of the bush, fertilize it with nitrogen, during flowering and fruiting - with potassium and phosphorus, completely eliminating nitrogen from fertilizing;
- spraying and watering the plant with fungicides;
- sterilization of tools and clothing - fungal spores can remain and overwinter on clothing or garden tools;
- compliance with the temperature regime - at temperatures above 35°C, cucumbers wither and weaken (the ideal air temperature for the plant is 20-25°C);
- correct watering - cucumbers should be watered with warm rainwater 1-2 times a day, depending on the air temperature; at temperatures below 15°C, stop watering;
- pest control to avoid reducing plant immunity;
- removing diseased plants and burning them so that the fungus does not have time to move to neighboring healthy bushes;
- selection of cucumber varieties resistant to fusarium.
And a little about crop pests:
Why do spider mites appear?
How to fight melon aphids quickly and effectively
Nuances of treating cucumbers in greenhouse conditions
Sometimes vegetable growers encounter fusarium when growing cucumbers in a greenhouse. In greenhouse conditions, the following folk remedies are used:
- Milk serum. Plants that have become infected with Fusarium wilt can be cured with whey. It is heated to 25-30 degrees, after which it is mixed with water in a ratio of one to seven.
- Sulfate mixture. When the leaves begin to curl due to fusarium, copper sulfate is used. It is mixed with crushed solid soap and dissolved in warm water.
- Soda solution. This remedy helps restore rotten areas of cucumbers. To make the solution, 8-9 liters of water are mixed with 75 grams of soda.
Ways to fight
Treatment of fusarium is carried out using drugs of biological and chemical origin or traditional methods. Therapy is selected depending on the intensity of plant damage and their response to the agents.
Chemical protection is often combined with folk remedies in order to increase the effectiveness of the impact on harmful microorganisms and enrich plants with nutrients.
Biological drugs
This group of drugs is safe for the environment and humans, but is not always effective at stages of severe damage.
Important! Biological products can be used not only during the infection stage, but also to prevent the disease. It is advisable to spray throughout the entire growing season, starting from the stage of sowing and seed germination
.
The most effective among these means:
| Drug name | Directions for use and doses |
| "Baktofit" | 20 ml/10 l of water for spraying on the leaf (treat both sides), a total of 7-8 applications every 7 days, does not cause resistance |
| "Fitosporin" | 10 g/5 l of water for spraying on the leaf, frequency of treatments - 3, with an interval of 10 days |
| "Trichodermin" | 20 g/5 l of water for spraying throughout the entire growing season at intervals of 7 days, stop spraying 21 days before harvest |
The listed drugs are not compatible with chemical fungicides.
Video: Fusarium blight on cucumbers
Chemical
Of the chemical preparations used to treat fusarium, “Fundazol” is used. Add 10 g of product to 10 liters of water. The solution is enough to spray on leaves and soil over 100 m². A total of 2 treatments are carried out with an interval of 20 days. The last spraying should be carried out no later than 1 month before harvesting.
When using a fungicide, you must strictly follow the instructions and observe your own safety measures. It is advisable to use chemical protection only before the formation of the ovary. At a later date, the risk of getting poisoned when consuming products increases.
To remove foci of disease, cucumbers are watered with a 0.2% solution of the Topsin-M fungicide. Add 10 g of product to 10 liters of water. It is recommended to treat plants when the first signs of disease appear during the growing season. The protection period lasts about 12-15 days. It is recommended to moisten the soil with a 0.15% PrevikurEnergy solution. To prepare a working solution, dilute 3 ml of Previkur Energy per 2 liters of water, or 15 ml per 10 liters of water. Working fluid consumption – 2 liters per 1 sq. m of soil.
At the initial manifestations of the disease, it is recommended to treat plants with the following preparations:
- "Gymnast";
- "Maksim";
- "Acrobat MC";
- "Quadris".
To increase the resistance of cucumbers to wilting, seed material and seedlings should be treated with Humisol. The existing group of benzimidazoles drugs successfully copes with wilting.
Folk remedies
Read more
Treatment of cucumbers against diseases with folk remedies. From folk remedies, a solution of whey is used to combat the disease. Dilute it in a ratio of 4:10 with water. Spray the leaves and soil every 10 days.
Wood ash is an effective remedy. Ash is used to dust all plants and the soil around them. Such treatments can be carried out throughout the season.
They not only help eliminate harmful microflora, but also enrich plant tissues, as well as the soil, with potassium and phosphorus. This helps to increase immunity and improve the quality of fruits.
Prevention of disease occurrence
To ensure that the seedling never gets sick with fusarium, it is necessary to prevent the occurrence of the disease.
Proper care and timely processing
The main preventive measure that will protect cucumber seedlings from withering is proper care.
When caring for vegetables, the following procedures are performed:
- Watering. Water the cucumbers regularly, at least three times a week. During summer drought, the bushes are watered every day. The soil is moistened in the late evening, after sunset.
- Feeding. Plants that are regularly fed with nutritional components are much less likely to suffer from fusarium. Cucumbers are fed 3-4 times per season. In this case, they use superphosphate, mullein, bird droppings and potassium sulfate.
- Loosening. After each watering, the soil near the bushes is weeded and loosened. This helps the soil better absorb moisture and allow oxygen to pass through.
We choose varieties resistant to fusarium and verticillium
Experienced vegetable growers recommend planting cucumbers that are resistant to wilting. Resistant cucumber varieties include:
- Rowanushka. A tall vegetable that is resistant to fungal pathologies and frost. You can grow Rowanushka both outdoors and in a greenhouse.
- Dunyasha. A productive variety with juicy and sweetish fruits. Dunyasha's immune system reliably protects her from powdery mildew, fusarium and mosaic.
- Sir. A plant with compact bushes that do not need staking. Sudar does not suffer from fusarium and is not attacked by insects.
Varieties resistant to fusarium
The modern seed market allows you to select varieties that are resistant to this type of disease, which will make the gardener’s task easier.
Several varieties that have quality characteristics and are especially resistant to fungal diseases:
- Vocals are resistant to fungal diseases, high humidity, insufficient lighting, and temperature changes. Parthenocarpic, universal purpose, high-yielding.
- Raphael is a self-pollinating, vigorous hybrid, resistant to root rot with smooth cylindrical fruits, good taste.
- Obsky is a medium-sized hybrid resistant to peronospora, fusarium, bacteriosis and sudden temperature changes, the taste is wonderful.
- Dvoryansky is a mid-early pollinated hybrid with an early type of flowering, resistant to anthracnose, ascochyta blight, cladospora blight, fusarium blight, bacteriosis and viral infections.
Anthracnose
| Symptoms of the disease | The first signs of the disease may appear on seedlings. On adult cucumbers, anthracnose spots most often affect the leaves, on which they are yellow and brown, angular-rounded, and uneven in size (from 20 to 30 mm). Usually they are located throughout the leaf, and between their veins a pink coating of mycelium forms. The spots may merge together. This causes the sheet to tear in this place. Depressed copper-brown (rusty) spots are visible on the stems, petioles and fruits. The fungus penetrates tissue to a depth of 3-4 mm. In wet weather, the affected parts of the plant become covered with pink pads. |
| Photo | |
| When appears | During different periods of the growing season. |
| How it appears | The fungus that causes anthracnose, in the form of sclerotia or pseudopycnidia, remains to overwinter on plant debris, and in greenhouses - on supports, glass or film. The source of this infection can also be seeds collected from cucumbers with anthracnose. This disease of cucumbers spreads at elevated air temperatures and high humidity, with fallen dew and rain or insects. |
| Where appears | Everywhere, but more often in greenhouse conditions and in large areas sown with cucumbers. |
| Result | The quality of products decreases, the taste of greens decreases due to a decrease in sugars and acids in the fruits, the crop shortage can be 50% or more. |
| Control measures | Preventive measures: treatment of cucumbers with “Fitosporin-M”. Treatment of anthracnose in cucumbers is carried out with a solution of Bordeaux mixture. You can also spray cucumbers with Zineb (processing in a greenhouse is prohibited). |
Ordinary mosaic on cucumbers
| Signs of illness | Small light green spots form on young leaves, later turning yellow. They become wrinkled and bulges appear on them. Yellow spots are noticeable on the greens, they are sometimes deformed. |
| Photo | |
| Manifestation period | With the beginning of the cucumber growing season and throughout it. |
| How do plants become infected? | The pathogen is found in the soil, inside seeds, and on plant debris. The common cucumber mosaic virus is transmitted when tending crops with the sap of an infected plant. Spread by aphids and some other sucking insect pests. |
| Where is it found? | On greenhouse cucumbers and on open ground plants. |
| Result | Due to poor functioning of the leaf apparatus, the yield is reduced. |
| How to deal with the disease |
|
Fusarium wilt of cucumber - treatment, the most effective methods
Fusarium treatment of cucumber, the treatment of which is described in detail in the article, is a rather labor-intensive process, but necessary to obtain a good harvest, and there are several methods for treating this infection.
Agrotechnical method - in order to prevent bacterial wilting of cucumbers, it is important to pay great attention to the procedure for preparing the substrate and not to allow a shift in the schedule for their use. To ensure that cucumber vines grow healthy and strong, it is good to add natural fertilizer, such as humus, to the soil. Do not forget to loosen the soil between the cucumbers, this is necessary to saturate their root system with oxygen, and to prevent moisture from accumulating at the roots of the plant, carefully monitor the operation of the drainage systems or simply remove the moisture yourself
The root system will also be strong and healthy if you properly care for the above-ground part and pluck the vines in time, thereby reducing the load on the roots
Do not forget to loosen the soil between the cucumbers, this is necessary to saturate their root system with oxygen, and to prevent moisture from accumulating at the roots of the plant, carefully monitor the operation of the drainage systems or simply remove the moisture yourself. The root system will also be strong and healthy if you properly care for the above-ground part and pluck the vines in time, thereby reducing the load on the roots.
Method of using drugs - spores that play the role of the causative agent of fusarium have a high survival rate, so it is quite difficult to deal with them, but this can be done most effectively if you use professional drugs to combat fusarium:
- Bioactive agents - a bright and effective representative of drugs in this category - Trichodermin, and it will be most effective if it is added to the soil for cucumbers 2 days before the seedlings are transplanted into open ground. Another way is to use special suspensions, for example, Baktofit, Planriz and others. For preventive purposes, these agents can be used to treat not only the soil, but also the seedlings themselves;
- Chemicals - one of the most powerful drugs in this category is Fundazol; this product is optimally used for treating cucumber seeds before placing them in prepared soil. Once the seeds are in the open ground, it would be a good idea to irrigate them with Previkur solution, but a product called Quadris is best used in the early stages of infection;
- Remedies popular among the people are the most effective folk remedy for fusarium - a solution that contains a bucket of water (10 liters) and 4 liters of whey; the resulting solution must be sprayed on the plants, preferably in the early stages of cultivation.
According to experts in this field, in the progressive phase it is almost impossible to cope with fusarium wilt - diseased lashes must be promptly removed and burned. Such branches are not used to obtain organic fertilizer; plants that grew near the sick person must be immediately treated with the above means.
Fusarium wilt of cucumber, which can only be treated in the early stages of infection, may not appear in your garden if you choose the right cucumber varieties for planting. In the characteristics of the seeds on the packaging, look for the letter F1 - this marking indicates that the variety is hybrid, and therefore more resistant to fusarium.
Protection measures
a) Preventive protection
Preventive protection is the most effective measure in protecting against the occurrence and spread of the disease, and includes simple, but at the same time important measures:
- disinfection of greenhouses and soil treatment before planting;
- mandatory processing (dressing) of seed material;
- use of high-quality seed material;
- preventive treatments with fungicides, including the active use of biological protection agents, for example, biofungicides “Fitolavin”, “Gamair”, etc.;
- cleaning and disposal of plant residues;
- ensuring proper growing conditions (drip irrigation, humidity, ventilation, temperature, etc.), since the temperature inside should not exceed 25°C and humidity - 70% (optimal - 60%).
| READ MORE: “Methods of soil disinfection before sowing seeds and planting seedlings“ |
Bacteriosis (corner spot) of cucumber
Symptoms and external signs
The pathogen affects the leaves, flowers and fruits of cucumber. Small light brown spots appear along the edges of the cotyledons; later, most of the surface dries, turns yellow and becomes covered with necrosis. External signs are similar to peronosporosis (downy mildew) of cucumber.
Yellow-brown spots begin to form on lower leaves, which may be oily, and then dry out and become necrotic. The leaves wither and cloudy yellowish sticky droplets may appear on the underside. They contain the maximum accumulation of bacteria, which actively spread to healthy parts of the plant. Damaged leaf tissue near the veins necroses, which leads to complete death of the leaf.
Small, shallow, round ulcers appear on the fruits. Subsequently, the fruits become distorted. The infection can also penetrate into the seed chambers, causing putrefactive processes there.
Corner spot (bacteriosis) of cucumber is a common disease in protected soil.