Late blight is the most common disease affecting plants of the Solanaceae family.
Rarely does a summer resident avoid it when growing tomatoes. To avoid the appearance of a dangerous disease, gardeners resort to a variety of measures to protect against late blight. One of the reliable folk remedies for late blight is copper wire.
How does the product work?
Preparations containing copper have a detrimental effect on all fungal diseases, including late blight. A copper wire inserted into the stem of the plant will provide the tomatoes with some nutrition and protection. The plant juices flowing from the roots to the leaves will pass through the inserted wire and are constantly saturated with copper ions.
Copper ions have a double effect: on the one hand, they kill pathogenic fungi at the cellular level, on the other, they increase the plant’s resistance to unfavorable environmental conditions and many diseases (by participating in the process of photosynthesis, copper has a stabilizing effect on the intensity of respiration and metabolic processes).
Method 7. Interior items made of copper wire
From wire you can make original interior items that will look good not only in the country, but also in a city apartment. A little inspiration, patience, a coil of copper wire - and your home will be decorated with a stylish lampshade, basket, panel and other interesting things.
Decorative items for the kitchen are made from tinned wire because it does not oxidize. For other crafts, regular enameled copper wire is suitable.
Wire can be combined with other materials - it looks organically “in duet” with fabric, wood, paper, glass.
There are plenty of ways to use wire in the household, so don’t let it sit idle – put this multifunctional material to use!
How to use against late blight of tomatoes - step by step guide
- Copper wire with a diameter of 0.5-1.0 mm is cleaned from the coating to a shine (from PVC insulation - with a knife, from the enamel coating - with sandpaper).
- The wire is cut into pieces 3-5 cm long.
- If the wire is thick (1 mm), it is immediately pierced into the tomato stem. To insert a thin copper wire, you must first make a puncture with a needle.
- “Grafting” with copper wire is done when the stem acquires sufficient strength (2 weeks before planting seedlings in open ground or after).
- The ends of the wire are bent downwards on both sides.
The distance at which acupuncture needs to be done varies:
- for seedlings not planted in the ground - a place below 1 true leaf;
- for tomatoes in the garden - at a height of 4-5 cm from the ground.
Method 6. DIY copper wire jewelry
Wire is the favorite material of many needlewomen. Of course, this material can take any shape and still “hold” it. Jewelry made from metal tubes (the prototype of modern wire) were popular back in the days of Ancient Egypt. It is better to purchase copper wire for handicrafts in a specialized store, since wire of different thicknesses is suitable for different types of products.
| Recommended copper wire diameter for different products | |
| Product | Wire diameter, mm |
| Base for a bracelet or necklace | 1-1.4 mm |
| Ring base | from 1.3 |
| Earrings (bases for earrings) | 0,8-1 |
| Pins, pins (fastening elements) | 0,6-0,8 |
| Braid | 0,4 |
| Clasp | 1,3-1,5 |
For knitting or beading, wire 0.3 mm thick is suitable.
Soft copper wire is best suited for needlework. It should be borne in mind that such wire is easier to break, so for the manufacture of larger products you need to take a stiffer wire.
Common mistakes
- Wrapping around the stem. Sometimes in reference periodicals and on gardening forums there is advice to wrap the wire around the stem. As the stem grows, the wire will cut into it, permanently injuring the plant.
- Use on immature seedlings. Young seedlings have thin and weak stems. If you pierce such a stem, the plants will weaken and die (due to severe stress, the damaged area may also rot).
- Late piercing. When signs of disease have been detected on a plant, it is pointless to use preventive measures.
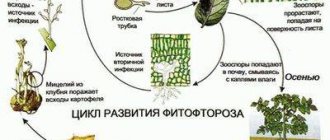
What is the nature of the disease
First of all, let's figure out what late blight is. The causative agent of the disease is the fungal organism late blight from the genus of the same name . There are many varieties of these fungi, but the most dangerous and also the most common is Phytophthora infestans.
Late blight is capable of destroying the harvest of all nightshade crops on the site in one season - potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants, peppers. Sometimes it moves to strawberries, and if you are especially unlucky, even to garden trees, in particular apple trees.
Late blight affects absolutely all plant organs - from flowers to roots . Cracks and spots of black rot form on them. Through cracks, secondary infection occurs with other types of fungi and pathogenic bacteria.
Fruits affected by late blight lose their marketable appearance, quickly rot, have an unpleasant taste and are not stored. Advanced forms of late blight end in the complete death of standing plants.
Effect of copper
It is known that copper and most fungi are not compatible with each other . Copper compounds quickly and effectively destroy mycelium cells, destroying the entire colony. This is the basis for the action of such proven antifungal drugs as a solution of copper sulfate (copper sulfate) and Bordeaux mixture (sulfate with the addition of a lime suspension).
And as a result, many gardeners came up with the idea: if copper kills fungi, maybe it’s worth using “heavy artillery,” that is, pure copper? And experiments began with pieces of copper wire.
Gardeners' opinions
- Victor: “I tried it last year. The procedure is simple and takes only half an hour. There was no rot on the tomatoes. There was no harm either, so I will continue.”
- Zakhar: “I’ve been trying copper wire to protect against late blight for many years in a row.
Mine is thick, 1 mm in diameter. I clean it with sandpaper and cut into 5 cm pieces. I pierce the tomato stem at a height of 10-15 cm. I consider it inappropriate to pierce the plant stem below, since they already become woody in July, and at a height of 10 cm they remain alive and green for a long time. The harvest is excellent and without any chemicals. I pierce the cucumber vines in the same way. Helps against powdery mildew.” - Tatyana: “Copper has been helping us for 6 years now. The husband cuts pieces of copper wire and, using pliers, inserts this wire directly into the stems of young tomatoes (while they are still tender) at a height of 2-3 cm from the ground. Our wire is from the strings of a broken piano, but I think any other wire will do.”
- Olga: “The method doesn’t work! I read about it in the magazine “Homestead Farming”. I grow tomatoes in a greenhouse. After planting, I pierced the stems of the seedlings with copper wire 0.5 mm thick. As a result, late blight still covered all the plants.
- Alexandra: “Wire can help if you understand a few things:
- This is not a panacea, but one of the possible methods of protection. A visible effect is achieved by combining several methods of protection at once.
- How it works. As a result of the injury, all the plant’s defenses are mobilized and it switches to active fruiting. Copper, supplied even in small quantities, provides nutrition to the plant and kills pathogens at the stage of penetration into the plant.”
- Nadezhda: “This is noodles for gardeners’ ears! The transfer of copper ions into the juice of a tomato bush is so unlikely that if this happens, it will be in such an amount that it will not affect the fungus in any way. You won’t save the harvest, but you’ll lose time.”
The method of using copper wire against late blight is a folk one. There have been no scientific experiments or evidence of the positive effect of copper wire on tomatoes either in Russia or abroad. To believe or not to believe in its effectiveness is a personal matter for each summer resident.
To protect plantings from late blight, it is important not to create conditions for its occurrence (dampness, thickened plantings, mechanical damage). If a gardener grows varieties that are resistant to late blight and organizes proper care, it is possible to do without this product or use it as additional protection, “just in case.”
Additional tips for treating the disease
In order to protect the tomato crop from late blight, in addition to copper wire, you can use the following special and folk remedies:
- preventively treat and feed the bushes with immunomodulatory solutions ;
- use fungicides and special chemicals to treat late blight;
- cover the bushes with film or non-woven material , which will protect them from heavy morning dew;
- use kefir solution , diluting 1 liter of fermented milk product with 10 liters of water. This method involves weekly treatment of the bushes from the moment the ovary appears;
- yeast can also help get rid of late blight at the initial stage. To do this, you need to dilute 100 g of fresh baker's yeast in 10 liters of water;
- garlic tincture can effectively counteract the development of fungal disease. To do this, you need to take 1.5 cups of finely chopped garlic and leave it in 10 liters of water for 24 hours, after which 2 g of potassium permanganate is added to the solution. The product can be used every two weeks;
- a salt film on the foliage prevents the spread of late blight . To do this, spray the bush with a solution, adding 250 g of table salt to 10 liters of water;
- ash can also be an excellent tool in the fight and prevention of late blight in tomatoes.
To prepare the solution, use 5 liters of ash per 10 liters of water, mix well and let it brew, stirring occasionally. Then water is added to the solution until a total volume of 30 liters is obtained, and soap or soap is added thereto, which will allow the resulting mixture to adhere well to the stems and leaves of the bush; Did you know? The “happiness” hormone is serotonin, which is contained in significant amounts in tomatoes and can lift your mood and get rid of the blues. To do this, it is better to opt for the fruits of pink varieties. - iodine solution is often used as an antifungal and antimicrobial agent . One of the cooking recipes is to add 1 liter of low-fat milk to 9 liters of water, and then add 20 drops of iodine;
- boric solution is also used , which is prepared according to the following recipe: 10 g of boric acid is dissolved in 10 liters of hot water, and then 30 drops of iodine are added.
Gardeners' opinions
As with any controversial method, the opinions of practitioners are diametrically opposed. Here are just a few reviews about the use of copper wire as a preventative against late blight :
Important . The full range of reviews of this practice is intentionally presented here. Whether to use the method or not is up to everyone to decide for themselves.
What is late blight?
The disease is caused by microorganisms that make up numerous races and biotypes. Their aggressiveness varies, changing within the fungus itself. This makes it very difficult to develop blight-resistant tomato varieties. The variability of the pathogen occurs faster than scientists create new hybrids.
From potatoes to tomatoes, from tomatoes back to potatoes, taking peppers and strawberries with you. It's still rubbish.