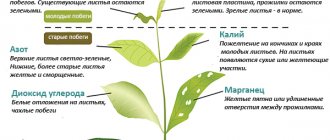
Symptoms of white rot on cucumbers
Before you start treating plants, you need to determine all the symptoms that this fungus exhibits. Here's what you need to pay attention to:
- Wet areas may appear on the leaf blade, which subsequently spread to other parts of the plant.
- In the place where a focal fungal infection is detected, a white coating forms.
- The leaves begin to wither, and the young shoots subsequently die.
- When the leaf is cut, black sclerotia are found.
What white rot actually looks like can be seen in detail in the photo.
Signs of infection
At different stages of development, the fungus exhibits different activities.
First, weeping spots appear that spread from the roots up the stem of growing cucumbers. Then a growth resembling cotton wool appears in this place. He moves to the top. This is how the abnormal mycelium increases in size. Mucus drips from the growth onto nearby bushes, infecting them too. Gradually, the mycelium becomes dense, compacted black sclerotia are formed, which look like peas. The entire stem is covered with rot, after which all parts of the plant wither and die - leaves, ovary, roots. Sometimes even fruits that look good are not suitable for consumption. Due to the rot of the cucumber, the fruiting vines dry out. Productivity is significantly reduced. His losses can be more than 50%. Control measures are varied.
Reasons for the appearance of white rot on cucumbers in a greenhouse
When white rot has formed on cucumber bushes in a greenhouse, it is necessary to urgently apply suitable treatment. But before that, you should understand what are the main reasons for this problem. Cases in which white rot appears:
- Most often it forms in greenhouse conditions, where constant air temperature and high moisture levels are maintained.
- If you add cold water to the soil, you can stimulate the development of the disease.
- The denser the planting, the greater the likelihood of white rot forming.
- When various salads, dill or other types of greens grow directly near cucumber bushes in the spring, it is from them that the spread of a fungal infection can begin.
- If tall cucumbers are pruned at the wrong time.
Disease prevention
A gardener growing cucumbers must organize the following preventive measures against sclerotinia:
- Regularly ventilate the greenhouse and ensure that the air humidity does not exceed 80–85%.
- Promptly remove disease-damaged bush tissues and disinfect the resulting wounds with the above-described soap and ash paste.
- Do not allow the soil under the bushes to become waterlogged.
- Monitor the temperature of the irrigation water: it should be warm.
- Treat the greenhouse structure before planting cucumbers.
- Disinfect the soil in which greens will grow, as well as disinfect the seed.
Make sure that the predecessors of cucumbers are not celery or parsley, which are often affected by sclerotinia.
Why is white rot dangerous?
It is important to understand that this fungal disease is very dangerous. Therefore, if white rot is detected on cucumber bushes, you should know exactly what needs to be done. If the problem is ignored, the landing is in danger of:
- decrease in yield;
- risk of disease spreading to other plants;
- damage to all parts of the crop, including the cucumber fruit itself.
General rules for processing plants
A pump sprayer is used to spray cucumber bushes. With its help, you can regulate the amount of liquid used and evenly cover the leaves and stems of cucumbers with the solution. The work is carried out using personal protective equipment: rubber gloves and a protective suit. The face is covered with a mask or plastic goggles and a respirator are put on.
Important! Spraying of bushes is carried out in the morning or evening, when there is no bright sunlight. Otherwise, the likelihood of sunburn on the leaves increases. The work is carried out in dry, calm weather and no dew on the leaves.
To be effective, the solution must remain on the surface of the plant for at least two hours. If it rains immediately after treatment, the effectiveness will decrease. Therefore, after the bushes dry out, spraying is repeated
The work is carried out in dry, windless weather and no dew on the leaves. To be effective, the solution must remain on the surface of the plant for at least two hours. If it rains immediately after treatment, the effectiveness will decrease. Therefore, after the bushes dry out, spraying is repeated.
The bushes are processed first from below, then gradually move towards the top. The device is kept at a distance of 10 to 15 cm from the surface of the plant. Spray the lower part of the leaves especially carefully. The soil around the bushes is also cultivated.
How to deal with white rot during fruiting of cucumbers
In order for white rot to disappear on cucumbers in a greenhouse during their fruiting, how to deal with it is decided taking into account the safety of a particular drug. When a crop is grown in open ground, it is a little more difficult - it is necessary to take into account not only the toxicity of the product, but also weather conditions. Each gardener chooses the most suitable option for himself, which corresponds to his growing principles, as well as certain conditions in the beds (depending on neighboring crops, lighting of the planting site, etc.).
Fungicides
In order to get rid of white rot in the shortest possible time and with a high degree of efficiency, you must use one of the following drugs:
- Planriza;
- Previkur;
- Profit Gold;
- Speed;
- Fundazol;
- Ordana;
- Abiga Peak.
Each of these preparations can be used in different ways, given that when mold spreads across a leaf plate, treatment is carried out along the surface of the leaf. If the root system is affected by white rot, these products are diluted as indicated in the instructions, and the resulting mixture is watered.
Agrotechnical measures
When white rot appears on cucumbers in a greenhouse or open ground, you need to know what to do in terms of agrotechnical measures. So, it is necessary to prune the bushes, especially when using tall varieties. It is also necessary to reduce the level of thickening by cutting off unnecessary shoots. This will reduce the risk of disease in all plants. At the same time, the necessary flow of fresh air appears to the surface of the bush, which increases the overall level of ventilation of the planting.
Folk remedies
Traditional recipes will also help solve the problem. But they have one distinctive feature - what distinguishes them from products that are produced industrially is that their level of effectiveness is high enough only when they are used at the initial stage of the development of the disease. With a more advanced spread of the disease, their effect may not be sufficient and will have to be supplemented with chemicals. Among the folk remedies for the treatment of white rot on cucumbers in a greenhouse, a solution of milk with iodine and soda with potassium permanganate is used.
Causes of rotting of greenhouse cucumbers
Growing in a greenhouse is good because it can create favorable conditions for plants. However, these conditions are also favorable for the development of harmful microorganisms. In addition to rotting, there are a number of diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria, pests or agricultural errors.
One of the common causes of diseases is insufficient feeding of cucumbers with mineral and organic substances or ignoring this process. Over time, this leads to weakening of the plant.
Downy mildew
The disease begins with the appearance of pale yellow oily spots on the leaves, which increase over 7-9 days. It looks like the leaves have been burned. Then their color turns brown, and then the plant dries out.
Causes of occurrence: sprinkling with cold water and the formation of condensation in the greenhouse. Because of this, the plantings are constantly in a humid environment. And with a sharp drop in temperature in the greenhouse, diseases begin to actively develop.
Treatment involves treating the plantings with a solution of Fitosporin or copper sulfate.
Powdery mildew
It begins with the appearance of a white coating on the leaves, which spreads very quickly. In appearance, it resembles as if the plant was sprinkled with fine flour. Powdery mildew causes cucumbers to dry out and die.
This disease is often transmitted from weeds on the site, as well as regular sowing of cucumbers in one place.
For treatment, a solution of Fitosporin or copper sulfate is used.
Tobacco mosaic virus
The first symptoms are marbling of the leaves (pale yellow stains on a bright green background). The remaining green parts of the leaf blades that have not changed their color become covered with bubbles.
As a result, the leaf dries out and dies. The fruits do not set well, and most of them fall off. The surviving fruits grow small.
It is better to immediately remove a sick plant from the greenhouse or greenhouse.
Bacteriosis (angular spot)
Caused by the bacteria Pseudomonas lachrymans. This disease is characterized by the appearance of brown cankers and polygonal spots on the leaves (because of their shape, this disease is often called angular spot). Then the affected tissues dry out and fall off, covering the leaves with numerous holes.
Bacteriosis even affects fruits. Brown round sores appear on them, and the tips begin to darken.
The fight against angular spotting is carried out with fungicidal preparations. But this should only be done if the fruits are not affected. Otherwise, the affected plant must be removed from the greenhouse.
Pests
In addition to beneficial insects that pollinate plants, there are many pests that can destroy crops in a few days. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly inspect the plantings in order to promptly destroy parasites.
Greenhouse whitefly
White midges that love warm places without drafts. Females lay eggs on the bottom of the leaves. A sticky coating forms, covering the stomata of plants, which are needed for respiration. After this, the cucumber leaves turn yellow and then fall off.
Fighting methods:
- device of glue traps;
- treatment with biological preparations against pests;
- treatment with water (especially the lower part of the leaves).
melon aphid
Damages flowers, ovaries, shoots and the underside of the leaf by twisting it. Appears in the second half of summer and develops very quickly. You can recognize melon aphids by their yellowish or dark green color.
Fighting methods:
- removal of affected plantings;
- spraying with infusion of wood ash;
- spraying with chemical or biological products.
Spider mite
A small arachnid pest, 0.5 mm in size, settles on the underside of the leaves and sucks out the cell sap. Infection can be identified by the appearance of cobwebs and white spots on the leaves, which soon become discolored.
Spider mites can only be destroyed by spraying with special preparations.
Unfavorable environmental conditions
- Temperature. Cucumbers are a very heat-loving crop. The optimal air temperature for them is 25-30 °C, and the soil temperature is not lower than 20 °C. In cool weather (below 12 °C), the flowering and ripening process may be delayed. Cucumber is also a moisture-loving plant. Comfortable air humidity for them is within 80-95%.
Cucumbers do not tolerate sharp fluctuations in daily temperatures, as well as high temperatures with a lack of moisture in the soil.
- Lighting. Cucumbers love light. They cannot develop properly in shady areas. Therefore, a good growing area is an unshaded, well-lit area.
- Soil requirements. This crop places increased demands on soil moisture. It must be maintained at 70-80%. With a lack of soil moisture, the water balance of the plant is disrupted, growth stops, and fruiting decreases. The best soil for growing cucumbers is loose and light, then it develops a powerful root system. The best organic fertilizers are rotted manure, peat, and compost.
Agrotechnical errors
- Incorrect formation . Often, gardeners who strive for high yields harm plants through their actions. It is necessary to understand and avoid such agrotechnical mistakes. In order for the bush to form correctly, it is necessary to remove excess shoots. Especially in the lower part of the bush. If this is neglected, the density of the plant increases greatly, the aeration of the plantings deteriorates, as a result of which the likelihood of developing fungal diseases increases.
- Landing in one place. When a crop is grown for a long time in the same places, pathogenic microorganisms accumulate in the soil, causing various diseases. It is necessary to monitor crop rotation and change planting sites at least once every few years.
This phenomenon is popularly called “soil fatigue.” It is believed that this may lead to reduced yields.
- Untimely transplantation of seedlings. The normal age of cucumber seedlings is 35 days. If they are not replanted for a long time, the root system is severely inhibited. Plants take root less well after transplantation, begin to bear fruit later, and also become unstable to various types of diseases.
- Lack of fertilizers. Many gardeners believe that it is better to abandon purchased types of fertilizers and chemical treatments, preferring folk remedies. But a large number of infections, pests and diseases are destroyed only by industrial means. In addition, this type of treatment will be effective and fast, whereas traditional methods require a longer time, which will lead to the spread of the disease from diseased plants to healthy ones.
- Plants planted too often. The optimal planting density is 2-3 bushes per square meter. Exceeding these indicators leads to excessive thickening of plants. This causes difficulties in regular inspection for the presence of diseases and pests, and will also cause inconvenience for processing the bushes and applying fertilizers.
- Wrong fertilizer. It is important to follow the proportions and instructions when feeding cucumbers. Overfertilization can cause various types of rot. And insufficient application of nutrients depletes the plants.
- Failure to comply with watering standards. Cucumbers love moisture, but too much water promotes the spread of rot and powdery mildew. It is best to water the plants once every 2-3 days at the root. An effective remedy for excess moisture is mulching the soil (covering the top layer of soil with mown grass, straw, sawdust or chopped bark). A sufficient amount of moisture remains under the mulch. Therefore, the regularity of watering is reduced to 1-2 times a week, even at high temperatures.
Preventive measures
The following preventive measures will help prevent the appearance of white rot:
- High level of ventilation in the greenhouse.
- Do not over-moisten the soil; the soil should not be constantly wet.
- The water used for irrigation must be warm. The use of cold liquid is unacceptable.
- Before young cucumbers are planted in a greenhouse, it is necessary to treat the room to get rid of possible spores of a fungal infection.
It is easier to prevent the problem of white rot than to treat plants for a long time and risk the future harvest.
How to treat a greenhouse?
Putrefactive spores settle in earnest and for a long time; getting rid of them on cucumbers is not so easy. Deep disinfection of the walls and greenhouse coverings will be required to prevent infection of subsequent generations of cucumbers. The whole process is divided into several stages:
- We get rid of damaged fragments of plants, leaves, fruits, cucumber ovaries, so that the garden bed becomes empty and clean.
- The soil is treated with a freshly prepared solution of copper sulfate - the fungus really does not like this element.
- All surfaces are washed with the same solution - floors, walls, windows, shelving, trellises.
- Upon completion of sanitation, the interior space is fumigated with the acrid smoke of a sulfur bomb, then ventilated.
- The earth is carefully dug up. In winter, white mustard will be sown in the beds; it will clean out the remaining rot.
- In the spring, repeated digging is carried out, and the soil is extensively treated with Baikal EM-1. This must be done 10-14 days before planting cucumber seedlings in the greenhouse.