Is it possible to propagate cherries from cuttings in summer?
Experienced gardeners often use this method when expanding the area of gardens or replacing old or diseased fruit trees.
Cherry responds well to cuttings, and it is important to follow the technology of cutting, rooting and planting the source material. The cuttings take root well, but require care.
Attention! Due to the biological characteristics of cherries (lack of self-fertility in some varieties), it is recommended to grow at least one pair of trees nearby with the same flowering periods.
Advantages and disadvantages
It is not always possible to find a suitable seedling, but summer cherry cuttings are an effective solution that has many advantages:
- preservation of the properties of the mother tree variety: external and taste characteristics, yield, ripening time, resistance to frost and diseases;
- the possibility of independent rapid propagation of the crop;
- simplicity of the procedure that does not require specific skills;
- obtaining several dozen cuttings without damaging the plant;
- saving money;
- confidence in the quality of planting material as opposed to purchased material;
- the formation of a strong root system at the time of planting, which facilitates the establishment of the plant;
- rapid growth, entry into fruiting already in the 3rd year of life.
Among the disadvantages, it is noted that the survival rate of cuttings of many varieties does not exceed 50%. Plants need shelter for the winter, regular and abundant watering, and the addition of drugs to stimulate growth.
What cuttings are suitable
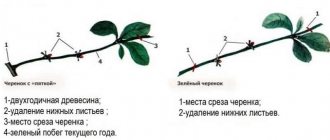
For propagation and rooting, cuttings from the tops of last year's or current year's shoots, with a diameter of 4-5 millimeters, are suitable. The process of lignification has just begun. In addition to cuttings taken from shoots, you can use root shoots. Do not confuse them with suckers, which are small cherry bushes.
Root shoots
They are sections of the root 12-15 centimeters long, with a growth bud. The advantage of such planting material is that it does not need to be rooted - the plants already have a root - you need to try to grow an even, strong central shoot. From such shoots, self-rooted seedlings of the required diameter are obtained - more than 7 millimeters. Preparing root cuttings is labor-intensive: in order to breed several varieties, you need to search and dig up the root system of a large number of trees.
Green shoots
These shoots have the highest growth vigor. The top part of them remains green and continues to grow, which is why they are called “green”. The surface of the growing branches at the base already has areas of burgundy bark. It is much easier to plant such cuttings than root cuttings.
Many gardeners ask the question: is it possible to take cuttings from the shoots around the mother tree, since the shoots on the plant itself bear the harvest? The answer is no, since there is no certainty that the mother plant did not grow from the graft.
Optimal timing for summer cuttings
Summer is the most active season of work at the dacha, among which plant propagation plays an important role. Suitable air temperatures and long daylight hours help accelerate the formation of roots in young plants and their survival.
Cherry cuttings are carried out throughout the summer, but the result will be more effective if the procedure occurs at the beginning of June. During this period, the plant develops most intensively, saturated with nutrients for growth: nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, carbohydrates.
Favorable days
Many gardeners cut cherry trees in accordance with the lunar calendar, which indicates the phases of the waxing and waning moon and favorable days for such procedures.
Initial material for planting is harvested only on the waxing Moon on the following dates:
- June: 1–4, 21–31;
- July: 24–27;
- August: 1, 2, 20–31.
Diseases and pests
The most common disease in cherries is clusterosporiasis. It manifests itself in the form of light brown spots, which lead to the appearance of holes in the leaves, and in advanced cases, the disease causes complete loss of foliage and death of the tree or shrub.
To combat the disease, gardeners use Bordeaux mixture and copper chloroxide, which are diluted with water and used as a spray. Before treatment, be sure to remove all damaged areas.
Cherries can get fruit rot, which affects the plant during the period of fruit ripening. Each affected berry becomes stained and begins to darken, after which it falls off or dries out. High humidity and temperature contribute to the development of the disease. To prevent the disease, the tree is sprayed with fungicidal preparations.
Cherry trees are very attractive to pests, which include caterpillars, plum moths, weevils, aphids and cherry sawflies. To prevent their appearance in early spring, the trunk should be treated with copper sulfate.
Suitable cherry varieties
As a result of cuttings, not all varieties show equally high survival rate.
The most suitable ones with an effectiveness of up to 80% are:
- Vladimirskaya. An ancient (more than 300 years old) and very popular variety in Russia with fruits of medium ripeness. It grows as a large bush (2.5–4 m) with several central conductors and a dense weeping crown. When grafted, it is a single-trunk tree. The fruits are small, turnip-shaped, weighing a maximum of 3.4 g (usually 2.5–3 g). The variety is characterized by frost resistance, productivity and good transportability. The outer shell of the berry is burgundy, almost black, dotted with gray dots. The pulp is dark red, dense, juicy, the taste is pleasant sweet and sour, with barely noticeable tart notes.
- Rastunya. Local variety of the Middle and Lower Volga region of folk selection. The tree is tall, with a wide pyramidal crown of medium density. Fruits in 4-5 years. The fruits are small (up to 2.5 g), round, slightly flattened, formed in inflorescences (from 1 to 3), ripen in mid-July. The pulp is dark red, medium density, juicy. The taste is sweet and sour, slightly astringent. A medium-ripening variety with above-average yield, winter-hardy and drought-resistant.
- Nadezhda Krupskaya. The variety is widespread in Vladimir and other regions of the Non-Black Earth Region. The tree is bush-shaped, reaches a height of 2 m. The crown is dense, rounded, somewhat weeping. The branches are thin and hang down to the sides. The elasticity of their wood allows them to withstand abundant harvests of large berries. Cherries begin to bear fruit 2-3 years after planting. The fruits ripen mainly in July. The yield is high and annual: an adult tree produces an average of 10–12 kg of berries. The fruits are medium in size (3.5–4 g), the skin is very thin, the flesh is light red. Winter hardiness is average.
Selection and preparation of cuttings
How to take cherry cuttings? 2 days before the procedure, the mother tree is watered abundantly so that the plant tissues are well saturated with moisture. The best time for this is early morning or evening.
A higher survival rate is observed for green cuttings taken from the top of the current year's shoots.
Advice! Gardeners have a way to check the suitability of planting material for cutting - wrap it around your finger. If it doesn't break, you can start the procedure.
First inspect the young branch, which should be healthy and without damage. Cut cuttings with a diameter of 4–5 mm and a length of 5–7 cm so that each has 2 buds. 1.5 cm of the cutting is left under the bottom, and a cut is made from the top directly above the bud.
A sharp knife or razor is used for this work, since a blunt instrument damages the vascular system of the workpiece. The cut cuttings are immediately immersed with their bases in water to prevent the leaves from drying out.
How to propagate cherries using woody cuttings? To do this, at the end of summer they are cut 10–12 cm long from annual shoots. The lower cut is made 3–5 mm below the bud, the upper cut 5–10 mm above.
The cuttings are tied into bunches, buried halfway in sand or wet sawdust in a cool room and stored until spring. At the same time, the substrate is moderately moistened; drying out or soaking is unacceptable.
Cherries are propagated by air layering much less frequently, but some gardeners resort to this method. Work order:
- In early June, the lower branch of a young tree (thin, unbranched, 3–5 years old) is bent to the ground and pinned.
- Make sure that the shoot lies horizontally.
- The folded area is sprinkled with soil and watered.
A full-fledged root system is formed within a year. Then the cuttings are separated from the mother tree and planted in a permanent place of growth.
The branch for air layering is taken above the grafting site, as a result a young self-rooted cherry of an identical variety is obtained.
Cherry cuttings
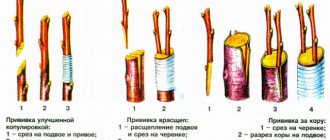
Rooting methods
Before rooting, the cuttings are kept for 12–24 hours in a solution of a root formation stimulator (“Epina”, “Kornevina” or “Heteroauxin”).
Rooting in the ground:
- Take any container: containers for seedlings, cut-off 2-liter plastic bottles, or specially put together boxes.
- Fill it with a nutritious substrate of turf soil and humus (1:1), add superphosphate, nitrogenous fertilizers and ash.
- Carefully moisten and deepen the cuttings by 3 cm, keeping a distance between them of at least 10 cm.
Immediately after planting, the container is covered with film to create a greenhouse effect and accelerate root formation. The mini-greenhouse is located in a shaded place outside or in a bright room with an air temperature of +22...+25°C.
It is important to create high humidity in the greenhouse, so once every 5 days the cuttings are sprayed with warm water from a spray bottle, periodically watered and ventilated. With proper care, roots will appear in 2 weeks. It will take the same amount of time for them to take root.
Some gardeners use a simpler rooting method. To do this, cuttings kept in a growth stimulator and moistened with a spray bottle are packaged in plastic bags and placed in partial shade.
At summer temperatures and high humidity, root buds will form. In September, plants are planted in light soil and mulched in late autumn.
Is it possible to propagate a tree by shoots, and will they bear fruit?
Is it possible to grow cherries from shoots? This method is considered the easiest, but only varietal or own-rooted plants are suitable for it . Their shoots will produce trees that will fully retain their varietal qualities.
Only strong, developed offspring 1-2 years old are selected. In early spring, cut the root coming from the mother plant. After this, the shoots are shortened by 1/3, watered and fertilized.
In October, the root is cut from the second side. After a year, the plant is dug up and transplanted to a permanent place.
Caring for seedlings after planting
If rooting went well, this does not mean that the plant should be left without attention. It is necessary to continue to care for him. The success of all actions depends on how correctly this is done.
Watering
Immediately after the cuttings are planted in the ground, they should be constantly watered, not allowing the soil to dry out. But don’t forget to take it in moderation. Excess moisture will not lead to anything good.
When future seedlings begin to take root, watering is reduced and the polyethylene is removed. But they do this in stages, first accustoming the plants to open air for several hours, gradually reaching the whole day. Then remove them completely and leave them open. As they grow, the frequency of watering is reduced to 1-2 times every 10 days.
Grown young trees are watered several times a season:
- during the period of kidney swelling;
- during flowering;
- after partial shedding of fruits;
- after fruiting is completed.
The tree does not need an abundance of moisture; it will not cause anything but diseases. After each watering or rain, it is recommended to loosen the soil; this will help retain moisture in the soil longer, prevent the appearance of weeds and provide oxygen access to the root system.
Fertilizer
Any plant responds positively to fertilizing. It's important not to overdo it here. Complex mineral fertilizers will help restore the lack of nutrients in the soil.
Organic fertilizing is recommended once a season. Wood ash, which, in addition to nutrition, performs 2 more functions, repels insect pests, and fights the causative agents of certain diseases, will not interfere with the growing tree.
Cherries need liming, but before adding lime, you need to know the pH of the soil in which the seedlings are growing. This procedure is carried out every 5-6 years. The application rate for each bush depends on the acidity level of the soil.
Treatment against diseases and pests
In order to get a harvest and not ruin the young plant, it is necessary to process the seedlings. Particular attention should be paid to young, fragile shoots. They need care. Preventive treatments against diseases characteristic of the crop are required.
The exception is those cases when the mother plant is immune to the disease. Then no processing is needed. Chemicals are used, but only before flowering. Subsequently, special mixtures are prepared according to folk recipes. Their effect is lower, but they are safer for human health.
Traps are installed against insects, special sweet mixtures are poured into them and lure pests.
Growing cherries from cuttings is not a quick process, but it is simple and effective. You don’t have to do anything special and you don’t need to have any special skills. And the result is your own tree, in which the gardener is completely confident.
Planting ready-made cuttings
After rooting, the finished cuttings are planted in light soil. To prepare the substrate, take garden soil, peat and sand (1:1:2). Add 20 g of superphosphate per 1 kg of soil to this mixture.
Important! Choose a place for planting that is slightly shaded and protected from the winds.
The cuttings are planted in the soil to a depth of 3–5 cm and placed strictly vertically. The earth around is compacted and watered. After water is absorbed, mulch with peat.
How to propagate cherries from cuttings?
Despite the fact that it is not difficult to find and grow cherries from seeds that inspire sympathy, this breeding system is used only for breeding work. When propagated from seed, the tree loses the flavor of its variety.
The most convenient and suitable method of breeding cherries is considered to be propagation from cuttings. As opposed to grafting, self-rooted trees are acquired in this way.
To harvest cuttings, it is best to find properly developed and tall branches, preferably no longer than 30 cm, because large growth will stop the formation of flower buds.
It is best to cut shoots when it is cool, early in the morning or late afternoon. Before you begin cuttings, cut off shoots should be placed in a jar of water.
The branches are cut so that there should be 3-5 leaves on the stem, and an average of 2-3 cm in the lower part. The cut is made with a stationery knife, preferably not a dull one, at an angle of 45 degrees. From above, the petiole is cut off slightly above the leaf (at a right angle).
Before planting cherry branches in the ground, it is advisable to treat them with a special solution of a growth stimulator. The right time to process is from 11 a.m. to 7 p.m. It is advisable to dip the cuttings into a growth stimulator by 1-3 cm.
Features of cuttings depending on the type of cherry
Not all cherry varieties are capable of rooting.
Well-rooted (80–90%) include:
- Shubinka;
- Zhagarskaya;
- Dawn of the Volga region;
- Vole.
The following varieties take root moderately (up to 50%):
- Fertile Michurina;
- Half fat;
- Apukhtinskaya;
- Dessert Volga.
Depending on the region
In the central zone and southern regions of Russia, where there is stable snow cover in winter and the ground does not freeze much, cuttings are planted in the soil in August.
In harsh climatic conditions, planting is carried out in early June. For the winter, young plants must be protected from frost.
Further care
Propagation by cuttings is a relatively simple procedure, but after planting the plants require care, which includes the following:
- Watering. Young plants need a lot of moisture. The soil in the temporary area is constantly moistened, but waterlogging is not allowed. When water stagnates, the root system will begin to rot.
- Feeding. The cuttings are fertilized every 2 weeks. For this, superphosphate, ammonium nitrate and potassium salt are used. To speed up the appearance of green shoots, nitrogen is added.
- Protection from drafts. In the first month after planting, the cuttings are covered with a jar or plastic wrap. This helps maintain a relatively stable microclimate. The cover is removed every day for a couple of hours.
- Insulation. For the winter, the cuttings are covered with a large layer of sawdust, peat, vegetable tops or spruce branches.
Advice from experienced gardeners
To get healthy and strong plants, it is important to listen to the recommendations of experienced gardeners:
- The cutting location on the shoot is chosen 2 weeks before cutting. It is wrapped in black material for 3 cm. This stimulates cell degeneration and increases the likelihood of rooting by 30%.
- Green cuttings are taken from young trees.
- When applying fertilizer, the cuttings are watered with clean water.
- The cut is made with a sharp knife to minimize damage to the plants.
Propagation by seeds
Not every gardener takes the risk of propagating cherries with pits at home. The fact is that the process is long, labor-intensive, and the result may not meet expectations. Varietal qualities are not preserved with this method of propagation, therefore it is used mainly by breeders to develop new varieties and varieties.
Planting cherry pits in open ground is most often done in spring or autumn. In the summer, you can sow them in separate pots, and with the onset of spring, move them to the garden. Seedlings germinate for more than a month and gain no more than 0.5 m in growth each season. The tree begins to bear fruit no earlier than after 4 years.
In order to plant cherry pits, you need to fill the pots with garden soil, placing a layer of drainage material on the bottom. Next, the seed is buried no more than 3 cm and watered with a spray bottle. The pots are placed under glass or cellophane and placed in a well-lit, warm place. As soon as the first shoots appear, the shelter is removed.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
Important! If there is insufficient lighting, the seedlings will stretch out.