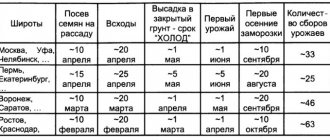
Timing for sowing seeds for seedlings
They need to be tied to different regions and methods of growing seedlings. In any case, it is necessary to take into account that it will grow at home for at least 45-60 days. Based on this, you can calculate the approximate date of sowing seeds and planting seedlings in open ground or in a greenhouse.
For southern regions
Open ground
The climatic conditions of this region make it possible to plant seeds directly in open ground. But to get an earlier harvest, it is still better to use the seedling method and sow the seeds at home in cups. The time for sowing seeds for seedlings for OG is early March.
Greenhouse or greenhouse
For closed soil, sowing is done earlier. For heated greenhouses with the ability to illuminate plants - during the 1st-10th decade of January, and for greenhouses without heating - the beginning of February.
For the middle band
Open ground
It should be taken into account that in the central zone and the Moscow region, recurrent frosts occur until the end of May - beginning of June. Therefore, for open ground, seeds begin to germinate to obtain seedlings no earlier than the first ten days of March.
Greenhouse or greenhouse
In greenhouses with heating and additional lighting, seedlings are planted a little later than in the south and only because energy costs will be high. If such a problem does not concern summer residents, then everything is done as in warmer climes. For greenhouses, the deadline is shifted by 2 weeks and the seeds begin to be prepared for planting in early March.
For the Urals and Siberia
Open ground
Given the harsh climate of these regions, only early varieties of tomatoes are grown in open ground here. Planting of seedlings in the OG begins no earlier than the end of the 1st decade of June, which means that the seeds are sown for seedlings in cups around the beginning of April.
Greenhouse or greenhouse
The start time for preparing seedlings for greenhouses in Siberia and the Urals is approximately the same as in the Moscow region. And the most suitable time for greenhouses is the first ten days of March.
Favorable and unfavorable days for sowing tomatoes for seedlings according to the Lunar calendar
Conditions for growing strong tomato seedlings
Tomato seedlings need bright lighting, warmth, and fertile soil for 50-70 days at home.
The gardener needs to give the seedlings a place on the eastern or southern windowsill, away from drafts. If the windows face north or west, tomatoes are grown entirely under artificial light. Seedlings are grown in common boxes, at least 8 cm high, or in separate pots with a volume of up to a liter. The size of the container depends on the plant variety; low-growing tomatoes need containers with a volume of up to 500 ml. Holes are made in the seedling container to drain excess moisture from watering.
The substrate for seedlings is purchased ready-made, choosing “universal” or “tomato” soil. Do-it-yourself soil for tomatoes is made up of humus (vermicompost), sand (perlite), peat and turf soil. Before sowing, the substrate is sterilized: heated in the oven at 160 degrees, steamed in a water bath or poured with boiling water. This is necessary to destroy pathogens.
Seedling diseases
To get healthy seedlings, you need to carefully monitor their condition. If suddenly the leaves begin to turn yellow or wither, become covered with spots, etc., then this indicates that the seedlings are sick and measures need to be taken to save them. What diseases affect tomatoes at the seedling stage? They can be divided into two groups – infectious and non-infectious.
Infectious
Tomato plants and fruits with bacterial diseases become covered in places with a sticky coating and begin to rot. This is how they differ from non-infectious ones.
Blackleg
Symptoms of the disease - the lower part of the seedlings becomes thinner and becomes dark, almost black. The disease can affect a significant part of the seedlings in the planting box, so the seeds should not be sown very densely.
For prevention, phytosporin is used, which is periodically sprayed on seedlings throughout the growing season. If the first signs of the disease appear, then it is necessary to urgently remove the diseased specimens, thin out the seedlings, if they are planted densely and very carefully so as not to get on the stem, sprinkle the soil with sifted ash.
Septoria
More often it appears on adult seedlings ready for planting in the ground. Small grayish-white spots with a black border appear on the leaf blade.
The disease can occur due to poorly steamed soil, from where pathogens spread to plants. If signs of disease appear, spray with Previkur-Energy.
Late blight
This disease most often affects adult tomatoes in open ground, but it can also affect seedlings in a room if the humidity is very high - about 85-90%. It appears on the leaves in the form of brown or light brown spots, which subsequently dry out and the leaf dies completely. A very dangerous disease that can completely destroy all seedlings if it is not dealt with. As mentioned above, for prevention, plants are sprayed with a solution of phytosporin. But only for prevention. If the disease has fully manifested itself, it needs to be dealt with by more radical means. The same Previkur-Energy, or similar drugs will help get rid of late blight.
Non-infectious
Non-infectious diseases are often caused by violations of the rules for caring for seedlings or disruption of plant development for physiological reasons. This mainly happens due to a violation of the regularity of watering, when the dry soil in the cups is then watered abundantly. Too sudden temperature changes, as well as too high or low temperatures can also cause seedlings to become sick.
Sunburn
They arise from direct sunlight on the leaves of seedlings. In addition, splashes on the leaves due to careless watering can focus sunlight and cause burns in the form of small white spots.
Oedema
It appears as swellings on leaves, shoots or trunks. Occurs due to excessive watering and non-compliance with its regularity. The plant is not able to absorb a large amount of water at once and the vessels experience increased pressure, which swells the leaf from the inside.
Curling leaves
It may appear due to a deficiency of nutrients. In this case, you need to start feeding the seedlings with small doses of fertilizer.
How to care for tomato seedlings after germination at home
The sown tomatoes have sprouted, what to do next? The boxes with seedlings are transferred to a bright place and the glass (film) is removed. Next, the seedlings are provided with a comfortable temperature, regular watering and fertilizing.
Lighting for seedlings
For the full development of tomato seedlings, it needs to be provided with a lighting intensity of 10,000-16,000 lux. The duration of daylight hours should be 12-14 hours. Lack of lighting forces plants to stretch out and weaken.
In most regions of the country in February - March, there is not enough natural light for plants to grow normally. Seedlings need to be illuminated. For this purpose, phyto lamps are used, which emit light of the spectrum that is fully absorbed by plants. It is permissible to illuminate the seedlings with ordinary fluorescent lamps with warm light.
Attention. To illuminate seedlings, do not use conventional incandescent lamps. They produce a lot of heat and little light, which will make the tomatoes hot under it.
Lamps come in round, square and stick-shaped. They buy those that are more convenient for lighting seedlings. For example, pots arranged in a row on a windowsill are illuminated with a lamp - a stick.
The lamps are suspended above the seedlings at a distance of 25-30 cm. As the seedlings grow, the lamps are raised higher. If the tomatoes are located on a south or east window, the lamps are turned on only in the morning and evening.
Important! You cannot keep seedlings under the lamps on 24/7! Plants need rest in the dark.
Temperature and humidity
Tomatoes grow at daytime temperatures of +20 +22 degrees and night temperatures of +17 +18. Higher rates make the seedlings pampered. You can ensure the temperature drops at night by opening a window or balcony door. The seedlings are protected from the flow of cold air with a polyethylene screen.
To protect the tomatoes standing on the windowsill from the hot air emitted by the battery, cover them with a piece of polyethylene foam or foil.
The crop loves dry air, so a standard living room humidity of 50-60% is suitable for seedlings.
How to water tomatoes after germination
The crop is sensitive to excess soil moisture, so the watering schedule is drawn up very carefully. The substrate for young seedlings is moistened once every 2-3 days, in small portions. As the seedlings grow, they are watered more abundantly and no more than once a week.
Important! Excess liquid accumulated in the pan after watering must be drained.
Water tomatoes strictly at the root, without getting water on the leaves and stems. Before picking, it is convenient to water the seedlings using a syringe or syringe without a needle.
Irrigation water should be at room temperature. The liquid from the water supply is left to stand for 2 days in an open container. It is advisable to use melt or rain water for seedlings, as it is softer.
Picking seedlings
When the tomatoes form 3-4 true leaves, the seedlings dive. Transplantation with pinching of the central root has a beneficial effect on the development of the root system; lateral roots begin to grow more actively. Subsequently, such tomatoes consume nutrients from the upper, more fertile layer of soil.
The picking looks like this step by step.
- On the eve of the procedure, the seedlings are watered abundantly so that the plant roots are saturated with moisture and become elastic.
- Using a fork or wooden stick, the bush is removed from the ground. Wash the root from the soil in a bowl of water (pink solution of potassium permanganate).
- Cut (pinch) the central root to a quarter of its length.
- Plant the tomato in a new container, deepening it to the lower leaves.
- The transplanted seedlings are left in a shaded room for 4-5 days. It is useful to spray tomatoes on the leaves with a solution of Epin or Zircon.
Low-growing tomatoes are transplanted into common boxes, at a distance of 7-9 cm from each other. Indeterminate varieties are transplanted into pots with a volume of 700-1000 ml.
When and what to feed tomato seedlings
If at the stage of preparing the soil mixture, granular complex fertilizer was added to it, then fertilizing of tomatoes at the seedling stage is not necessary. Plants planted in plain soil must be fed three times before planting in the ground.
Feeding schedule for tomato seedlings:
- 10 days after emergence, tomatoes are given nitrogen fertilizing;
- 12-15 days after picking, apply phosphorus-potassium fertilizers;
- a week before planting in the ground, tomatoes are again fed with phosphorus and potassium.
Urea, ammonium nitrate, and chicken manure are used as nitrogen fertilizers (concentration 1 to 15). Phosphorus and potassium are found in superphosphate, potassium sulfate.
There are ready-made complex fertilizers containing all the elements necessary for plants. Simply dissolve them in water and pour over the tomatoes. Gardeners use the following preparations: Bona Forte, Krepysh, Ideal, Gumat+7, Zdraven, Fertika.
You can use folk remedies and affordable inexpensive products for feeding.
- Ash.
Wood or grass ash (from burning hay, straw, plant tops) is rich in potassium, phosphorus and other elements. An infusion is prepared from it by dissolving a glass of ash in 5 liters of warm water. The liquid is infused for 2 days, then filtered and watered at the root of the seedlings.
- Hydrogen peroxide.
Spraying seedlings with this preparation helps plants better resist stress and disease. This feeding is especially useful after picking and at the beginning of acclimating plants to the street. 1 tbsp. l. 3% peroxide from the pharmacy is dissolved in 1 liter of water.
- Iodine.
A useful microelement that strengthens the immunity of seedlings. 2-3 drops of iodine per 1 liter of water, spray the tops of tomatoes with the liquid after picking and when planting in the ground.
- Ammonia.
Ammonia saturates plants with nitrogen. 2 ml of alcohol is dissolved in 1 liter of water and the tomatoes are irrigated over the foliage, 10-14 days after germination.
- Banana peel.
The product is rich in potassium. It is useful to water the tomatoes with the infusion of the peel after picking. The crushed skin of 1 banana is poured into 2 glasses of warm water and left for 24 hours. The solution is filtered before watering.
- Onion peel.
Rich in microelements and phytoncides. Soak 2-3 handfuls of husks in 1 liter of hot water for 24 hours. Water the tomatoes with cool liquid or irrigate their tops.
Important! The concentration of the nutrient solution must not be exceeded. Fertilizer is applied only after watering the seedlings with clean water to avoid burning the roots.
After picking, tomatoes are not fed by watering at the root for 2 weeks. This time is enough to restore damaged roots. It is allowed to irrigate plants with nutrient liquid over the tops.
The first and very important feeding of tomato seedlings! - video
Hardening procedure before planting in the ground
Hardening off seedlings means acclimating them to open ground conditions (bright sun, wind, cool night temperatures). Tomatoes begin to be hardened 14-17 days before planting in the garden.
The seedlings are taken outside (to the balcony), first placing the plants in the shade of trees. Time spent on the street is 30-60 minutes. Every day the seedlings are left in the air longer and longer, after a few days they are exposed to the open sun. By the time they are planted in the garden, the tomatoes should spend all daylight outside.
If the gardener has a greenhouse or hotbed at his disposal, the seedlings are transferred there, leaving the tomatoes overnight. In the first days, seedlings are protected from the sun with white non-woven material.
Advice. Spraying tomatoes with Zircon or Epin will help smooth out the stress from taking plants outside.
Hardening of seedlings
Tomato seedlings are planted in open ground at the age of 45-60 days. But before you take the cups out of the room into fresh air, you need to harden off the seedlings that have been pampered in indoor conditions. Moreover, it is hardened not only by low temperatures, which is also important. It is also necessary to accustom the plants to open sunlight.
Very often, beginning gardeners make one, without exaggeration, fatal mistake. When the time comes to plant seedlings, they are immediately taken from the windowsill outside and planted in the ground. After some time, the leaves begin to fade and the next day they become almost white. This happens even if the landing was carried out on cloudy days. Such plants are almost impossible to save. They got sunburn. The plant can recover after 2 weeks, but will be weakened, the yield will be reduced several times.
To prevent this, it is imperative to harden the seedlings with ultraviolet light. A week before planting, the cups are taken outside on the first day in the open sun for 15 minutes and no more. On the second day of hardening, the duration increases by 10 minutes. And thus increase the time spent under open sunlight to one hour. After this, you can safely plant the seedlings in a permanent place.
Seed preparation
It would seem: what could be easier than sowing tomatoes! I threw the seeds into a box with soil, watered them with water - and wait for the shoots. And already at this stage, experienced summer residents will point out to you a serious mistake - the lack of pre-treatment of the seed.
Sorting
Working with seeds begins with their careful analysis. It is important to review purchased and home planting material and select the largest specimens with a symmetrical shape. Visual inspections take a long time, so there are ways to speed up the process.
- Method number 1 . Immerse the seeds in a 5% solution of table salt for 5 minutes. Those that have floated to the surface are empty, and it is better to get rid of them immediately.
- Method number 2 . Scatter the seeds onto the paper. Take a glass or ebonite rod and rub it with a cloth so that it becomes electrified. Move the stick about 1 cm above the seeds. Empty “seeds” will be attracted and should be removed. Then mix the remaining seeds and repeat the procedure again.
Warming up
Heat treatment is recommended for self-collected seeds, especially if the plants were sick in the previous season. There are several options for heating planting material.
- Method number 1 . Place the seeds in gauze and hang them near heating appliances for about 2 months. It is important that the room is no cooler than 20°C.
- Method number 2 . Place the seeds on a saucer and expose to open sunlight for 1 week. Stir occasionally so that sunlight can warm up all the planting material.
- Method number 3 . If you remember to warm up just before sowing, use the express method. Cover a baking sheet with parchment, pour the seeds there and place in the oven preheated to 60°C for 3 hours.
Etching
The seeds (especially if you bought them from grandmothers at the market or collected them from self-grown tomatoes) may contain pathogenic fungi and bacteria. Infected seeds often become the cause of a real epidemic when growing seedlings on a windowsill.
You can pickle the planting material by immersing it in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate for 15 minutes. Then rinse and dry the seeds. Purchased drugs are also suitable for disinfection, for example, Fitosporin M, Sporobacterin, etc.
Soak
A useful procedure is soaking. Place gauze at the bottom of a shallow container, place the seeds on it and fill it with melt water so that it does not cover them completely. Next, wait for swelling.
To enhance the effect, you can use special preparations for soaking, for example, Energen AQUA (10-15 drops per 50 ml of water, soaking time for tomato seeds - 4 hours). The solution contains potassium salts of humic acids and significantly increases germination energy, as well as increases the percentage of germination.
When seeds are soaked in a solution of biologically active substances, they are enveloped in a protective and nutritional film-shell. This gives more “friendly” seedlings and provides additional nutrition to the seedlings, increasing their immunity. Industrial panning is carried out according to a similar principle.
This can also be done using folk remedies, for example, in a solution of aloe juice, honey or wood ash.
Treatment at home is carried out immediately before sowing, because seeds treated in this way are not subject to further storage.
Hardening
An important growth condition for young plants is the ability to quickly adapt to cold and temperature changes. And for this it won’t hurt to harden the seeds:
- Wrap the seed in damp gauze, place it on a plate and leave it indoors for a couple of days.
- Place in the refrigerator for 8 hours.
- Repeat the contrasting content for 2 weeks until the seeds hatch.
- Sow hardened seeds without drying.
Bubbling
Sparging is a procedure for enriching seeds with oxygen. This is especially true for old planting material. Place the seeds in a gauze bag and lower them into a jar of water, where you start blowing air with a special aquarium compressor. Continue processing for about a day.
Bubbling reduces the inhibitory properties of essential oils, which are part of tomato seeds and can delay germination.
Many summer residents buy hybrid seeds. They do not require serious preparation before planting, because... they already go through it at the enterprise. Attempts to improve the germination of planting material may give negative results in this case.
What humidity and temperature do seedlings need?
In the room where tomato seedlings will live, it is necessary to maintain humidity at a level of at least 70%. If there is dry air or containers are placed in close proximity to central heating radiators, it is recommended to place bowls of water next to the plants and cover the radiator with a damp cloth. Such methods significantly increase humidity.
After the shoots appear, the temperature during the day should not be less than +18 degrees, and at night less than +12.
To regulate the indicators, you can use ventilation by opening a window or balcony door. With such measures, it is important to prevent the formation of a draft, which can lead to overcooling of the tomatoes.
Sowing methods
You can grow tomato seedlings in different containers: in cassettes, cups, in a plastic or wooden box, in a snail, in peat tablets.
To cassettes
Cassettes are very convenient for tomato seedlings, because when planting there is no need to maintain a distance between the seeds, the cells are already at the required distance from each other. The cassettes are very light, so they can be easily transferred from the windowsill to the garden.
In cups
Cups for planting tomato seedlings are very convenient, but do not have drainage holes. You need to do them yourself. They are necessary for draining excess water during irrigation.
Fill the containers halfway with soil, slightly moisten it, and plant 2 seeds. When they grow, leave the strongest sprout. As the soil grows, it is necessary to add more soil until the soil reaches the edges of the cup. This container can be used for several years in a row. Seeds should be planted to a depth of 1-1.5 cm. Tall tomatoes should be a little deeper.
To the general box
Seedlings in a box is an old way of growing tomatoes: pour soil into a box, then make grooves at a distance of 10 cm, place the seeds at a distance of 3 cm from each other, water with water and cover with soil. In order for the tomatoes to hatch faster, the box must be covered with film and placed in a warm place.
A box with sown tomatoes can be easily moved into the air to harden the seedlings and transported to the dacha. But such a landing has its drawbacks. When replanting, the roots of the plants are injured and the seedlings get sick for a long time.
In peat pots
The good thing about peat pots is that tomato seedlings can be planted in the holes along with the pot. It is made from pressed peat, which softens in the ground from watering and initially feeds the plant with all the necessary elements.
In peat tablets
Peat tablets are also made from pressed peat in a mesh shell. Before planting the seeds, they must be moistened. Tomato seedlings in open ground are carried out together with a tablet.
Having dissolved in the soil, it will feed the seedling with the necessary elements. But for tablets you need an additional tray.
In a diaper in a snail
The method of sowing seeds in a snail was proposed back in the USSR, in the 60s. Yulia Minyaeva improved this method by proposing to make a snail from polyethylene or a laminate base. This reusable material is very durable, accessible and cheap.
Tomatoes can be planted in a “snail” without soil or with soil. How to make a “snail”:
- Let's prepare a strip of backing for the laminate 10 cm wide and 80-100 cm long.
- Having straightened the strip on a flat surface, pour earth onto it, level it, and compact it slightly. The soil layer will be 1-1.5 cm thick.
- Moisten the soil with a spray bottle.
- Place the tomato seeds on the tape, 1 cm away from the top edge. Make the distance between the seeds 1.5-2 cm.
- Roll up the “snail” loosely so that the earth does not fall out.
- When the “roll” with seeds is ready, it must be secured with tape or rubber bands.
- Place the “snails” in a transparent container to monitor the water level when watering.
- Place a bag on top to create comfortable conditions for growing tomato seedlings.
- Move the structure to a warm place with t=25-28⁰
On toilet paper
Seeds germinate well without soaking on toilet paper, which is laid out on plastic film or on a backing under the laminate.
How to plant tomatoes in a “snail” on toilet paper:
- Prepare a strip of film the width of which is equal to the width of a strip of toilet paper.
- Place 2 layers of toilet paper on it.
- Moisten with a spray bottle containing one of the growth stimulants: Epin, Zircon or Energen.
- Stepping back 1 cm from the top edge, spread out the tomato seeds using a match, keeping an interval of 2 cm between them.
- Place another layer of paper on top, then lightly moisten.
- Roll the roll, secure it with tape or an elastic band, place it in a tray into which the growth stimulator solution is poured, 1-1.5 cm high.
- Write on the roll the dates for sowing tomatoes.
Without soil, seedlings can be grown until cotyledon leaves form. This technique is good for determining the germination of planting material.
Having received a large supply of it from the roll, choose the strongest sprouts and transplant them into cups. These seedlings will never get sick with blackleg.
If diving of seedlings in the “diaper” is excluded, then the distance between the seeds should be left 7-10 cm.
After 2-3 true leaves appear, the bundle is unrolled and fertile soil is added to the roots. Then the package is rolled up.
When should you water for the first time after picking?
Immediately after the tomatoes have been picked, they are watered generously. After this, the most favorable conditions are created with a certain air temperature in the room and a sufficient amount of light. However, watering should be postponed for a certain period.
The first water supply is carried out when the seedlings need it, it lets you know about it. As a rule, the ground has dried out enough by that time, and the leaves gradually begin to change, losing their elasticity. At this moment, the first watering of the picked tomato seedlings begins.
Subsequent watering must be done every three days. This frequency allows you to maintain the optimal amount of moisture in the vessel where the plant is located, not to dry it out, but at the same time not to saturate it with excessive moisture.
Possible problems with tomato seedlings and their solutions
It can be difficult for beginning gardeners to care for tomatoes after the seeds have sprouted. Due to inexperience, they make mistakes, which is why the seedlings grow poorly and even die. Below are ways to solve frequently encountered problems when growing tomato seedlings.
Does not grow well after picking
Seedlings stopping to grow for several days is a normal situation after transplantation. Plants need time to restore damaged root systems. Treatment with growth stimulants (Epin, Energen) will help facilitate the restoration of seedlings.
But if the tomatoes wither, dry out, or turn yellow, this indicates an incorrect transplant procedure. There are several reasons for the wilting of transplanted tomatoes:
- too much of the spine is pinched;
- the stem is damaged during transplantation;
- When filling the tomato, the soil was pressed firmly against the stem.
In a seedling with a damaged root system, it will sooner or later recover. You need to feed the plant with complex fertilizer, sprinkling it on the leaves. You need to water these tomatoes very carefully, not allowing the soil to dry out, but also not flooding them.
Compacted soil should be loosened with a toothpick.
Seedlings stretch out
A common problem when growing seedlings without additional lighting. Experiencing a lack of lighting, seedlings are drawn to a light source. Such seedlings have pale green foliage, a thin stem, and seedlings often fall to the ground.
You can correct the situation by installing fluorescent or phyto lamps and moving the seedlings to a south or east window. Installing reflectors: mirrors, pieces of foil or polished metal will help enhance the impact of natural light. Reflectors are placed behind the seedlings so that the light falling from the window hits them.
Diseases
The most common disease of tomato seedlings is blackleg. The disease is caused by pathogenic microorganisms (fungi) living in the surface layer of soil. When excessive moisture is combined with low soil temperature, fungi actively multiply and infect the tomato stem. A brown ring forms on the stem near the surface of the soil; soon the stem dries out in this place and the seedling falls to the ground.
It makes no sense to treat the “black leg” when it is already visible on tomatoes. It is necessary to prevent the development of the disease. Prevention of blackleg includes:
- sterilization of soil and seeds;
- compliance with the irrigation regime;
- watering plants only with warm water;
- regular loosening of the soil;
- sprinkling the soil surface with calcined sand mixed with ash;
- watering the seedlings every 2 weeks with a pink solution of potassium permanganate or Fitosporin.
Other, less common fungal diseases on seedlings: fusarium wilt, late blight. When a tomato wilts, the leaves wither and dry out; late blight appears as yellow-brown spots on the leaves. At the first signs of damage, seedlings are treated with Trichodermin, Fitosporin, Fitolavin, Previkur.
Root rot can develop on tomatoes due to overwatering. If pots of seedlings are placed on a windowsill, near a cold window, the soil and roots become supercooled. This can also lead to the development of the disease. It manifests itself as yellowing of the tips of the leaves, their wilting, and stunting of tomato growth. It makes no sense to treat root rot of seedlings.