To get a good potato harvest, you need a sufficient amount of nutrients. This is difficult to achieve in a small area. Potatoes quickly deplete the soil; not everyone has the opportunity to plant them every year in an uncultivated area. To enrich the soil with the necessary substances, green manure plants can be planted.
What benefits do green manure produce?
There are about 400 species of such plants in the world. The roots of green manure are capable of extracting from the lower layers of the soil the necessary substances for growing vegetables. Their leaves and stems contain a large number of useful elements, which, after rotting, pass into the soil.
Green manure is a natural fertilizer for many crops. Thanks to them, the soil, during the time free from sowing crops, is not overgrown with weeds. They reduce soil acidity, activate the work of soil microorganisms, enrich the soil with organic matter, and promote the accumulation of vital nutrients in it: nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc.
The roots of some green manures loosen the soil. Increases its air and water permeability. The benefits obtained from such plants are comparable to the benefits from adding manure and peat to the soil.
What is better to cultivate in open ground next year?
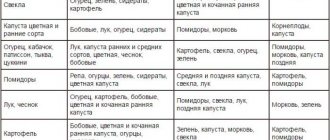
Let's figure out whether it is possible to plant, for example, garlic or onions, carrots, cucumbers, tomatoes, pumpkins, peas or strawberries after harvesting potatoes next year, what is undesirable and what will be useful for the soil and the future harvest. Having small plots, many gardeners cannot often use the land for green manure and use crop rotation, correctly planting vegetable crops.
According to the rotation of crops and further use, crops are divided into four groups:
- legumes;
- fruit;
- roots;
- leaves.
| Culture | Peculiarities. Recommendations for planting | Benefit |
| 1. Legumes | ||
| Beans | Sowed in spring. You can sow in the fall after harvesting the potatoes. In spring, mow 6-8 weeks after germination. If the soil is depleted and infected with fungi, legumes are grown until the end of the growing season. | Ensure crop rotation, saturating the soil with nitrogen. Legume compost replaces manure. |
| Vika | ||
| Peas | ||
| Soybeans | ||
| Beans | ||
| 2. Fruits | ||
| Eggplant | Do not plant after potatoes. They are affected by the same diseases. Late blight, macrosporiosis, and various types of rot accumulate in the soil. Consume the same nutrients. | The predecessors of nightshades can be any other crops. |
| Peppers | ||
| Tomatoes | ||
| Physalis | ||
| Zucchini | Hardy crops that are planted after potatoes | They do not require much care. Do not allow weeds to develop. |
| Patissons | ||
| cucumbers | Demanding on mineral and organic substances in the soil. It is not advisable to plant after potatoes. It is better if this is done in the second year after adding manure or humus to the soil. | Undesirable proximity to potatoes. The number of weeds is insignificant. |
| Pumpkin | Planting after potatoes is possible where potatoes were grown in sunny areas. | |
| 3. Root vegetables | ||
| Carrot | Sowing is carried out after potatoes in soil enriched with green manure or fed with mineral and organic additives. They consume large amounts of potassium from the soil. | The tops, decomposing in the soil, enrich it with nutritious humus. |
| Beet | ||
| Radish | ||
| Radish | ||
| Onion | They disinfect the soil well. | |
| Garlic | ||
| 4. Leaves | ||
| Cabbage | Undesirable but possible sowing after potatoes. Any variety of cabbage is demanding on nutrients. When planting, feed the soil well. | They are good “neighbors” for potatoes. |
| Salad | Planting is recommended after soil improvement. After potatoes, the number of weeds is significantly reduced, which is convenient for green crops. | |
| Spinach | ||
| Parsley | ||
| Celery | ||
| Dill | ||
| Parsnip | ||
| borage | ||
This means that, observing rotation, it is possible and necessary to plant vegetables after potatoes.
What can and will grow well in this place?
After potatoes the following will grow well:
- legumes (beans, vetch, peas, soybeans, beans);
- root vegetables (carrots, beets, radishes, radishes, onions, garlic);
- fruits (zucchini, squash, cucumbers, pumpkin);
- leaves (cabbage, lettuce, spinach, parsley, celery, dill, parsnip, borage).
What plantings should not be done?
These plants cannot be planted after potatoes:
- eggplants, peppers, tomatoes, physalis;
- strawberries, garden strawberries.
To prevent weeds from growing and to improve the soil
To prevent weeds from growing, plant:
- zucchini;
- squash;
- cucumbers;
- cabbage;
- mustard;
- rye.
To disinfect the soil, plant:
- onion;
- garlic;
- marigold;
- calendula;
- tansy;
- mustard;
- oats;
- rye.
To fertilize the soil, you can plant:
- carrot;
- beets;
- radish;
- radish;
- legumes;
- mustard;
- white clover;
- oats;
- phacelia.
Neutral
Neutral landings:
- corn;
- chard (chard);
- rhubarb;
- horseradish.
General growing rules
Green manures are selected according to soil type. It is best to plant legumes in clayey and swampy areas. Lupine will not grow in such a place. It is recommended to plant sainfoin in heavy, rocky soil. Cereals grow well in poor soils. You cannot choose green manure from the same family as the crop that will be planted after it.
It is recommended to plant cereals after harvest, as their ability to attract wireworms has been noted.
The best option for planting green manure for potatoes is to choose several types of plants from different families, each of which will be responsible for:
- repelling pests;
- preventing the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms;
- enriching the soil with organic matter and minerals.
The soil for planting should be loose. Seeds should be sown in furrows. Some gardeners throw them around the site and bury them with a rake. You need to water carefully so that they are not carried to the surface of the earth along with the water.
About 2 kg of seeds need to be planted per 1 acre. For each crop, it is necessary to know the sowing density. You cannot thicken green manure thickets, as they begin to rot, but sparse plantings do not give good results.
All plants must be cut before flowering begins.
How can you cultivate the soil after potatoes?
After the usual mechanical treatment, the potato soil can be populated with green manure. However, if there are no traces of late blight on the crop, the collected green potato remains can be left to humus to fertilize the ground. Anything is suitable for compost, the main thing is not to forget about moisture.
When the ground is cultivated and moistened, green manure can be planted:
- legumes;
- rape;
- lupine;
- rye;
- mustard.
In mid-autumn they are completely covered, the soil is fertilized as needed and left until the next crop is planted.
What kind of green manure to sow under potatoes?
The best green manures for potatoes are considered to be plants from the legume family and mustard. Legumes enrich the soil with nitrogen and phosphorus. They are planted immediately after harvesting the tubers.
Suitable green fertilizer for potatoes:
- oats;
- sardella;
- chickpeas;
- mustard;
- lupine;
- lentils;
- alfalfa;
- peas;
- soy;
- rye;
- sweet clover;
- beans;
- Vika;
- rape;
- alfalfa.
There is an opinion that corn can be planted as a natural fertilizer. It is recommended to plant it not in the ground under potatoes, but next to the beds. This way it will protect the vegetables from the sun and wind.
What are green manures?
Green manure is a special type of group plant that is placed directly into the soil to later become a natural fertilizer. First they grow, and then, very young, are distributed uncut over the entire area of the soil.
Another name for green manure is green fertilizer. And this is true - planted plants make the soil more fertile and saturated. Fertilizer decomposes into useful minerals and elements, which has a positive effect on the subsequent harvest.
Sowing time
Green manure can be sown both in the fall after harvesting and in the spring before planting potatoes. It is best to do this at the end of the season. During the autumn - spring period, they will have time to rot and give the soil all the necessary nutrients.
During the growing season, green manure is sown between rows of potatoes. The planting of green manure is alternated annually. It is not recommended to sow the same plants in one place every year.
Autumn to winter
Autumn sowing of natural fertilizer must be carried out no later than 1.5 months before frost. The best option is to start growing them immediately after harvesting. In order for them to gain a sufficient amount of green mass, they need to be watered regularly.
After the plants have gained sufficient greenery, they must be mowed and tucked into the ground when digging. They will have time to rot before spring.
In autumn, the following are most often planted as green manure after potatoes:
- white mustard;
- oats;
- alfalfa;
- peas;
- phacelia;
- radish;
- rape.
For sowing in late autumn, it is best to choose winter rye. Last year's seeds are sown by scattering over the site. Then cover them with a small layer of compost. The first shoots appear in early spring. Mow the rye a month before planting vegetables. It tolerates low temperatures well. It can be planted in any soil.
Rye is the best predecessor of potatoes. There is an opinion that planting this cereal attracts pests.
Rapeseed is second only to legumes in its quality. Its vegetative parts quickly decompose, saturating the soil with the necessary substances for potatoes. The essential oils in its composition repel plant pests. Spring rape is an excellent predecessor of nightshades.
How to plant potatoes in winter directly in green manure? More details in the video:
in spring
In spring, green manure is sown no earlier than the end of April, beginning of May. By the time of planting, the snow should completely melt and the ground should warm up.
Excessive overgrowth of green manure should not be allowed. They are grown for about 2 weeks. They should not have time to form seeds.
The best green manures before potatoes:
- oats;
- mustard;
- phacelia;
- lupine;
- rape;
- rye.
Plants are cut a few weeks before planting the tubers. Then they plow the earth along with the greenery.
Lupine is one of the best crops to plant in an area where potatoes will grow in the future. It takes about 5 weeks to grow. Long lupine roots improve soil properties.
When to plant green manure in the fall
At the end of the season, green manure can be sown in the beds and in the greenhouse in 2 periods:
In August, fast-growing plants are usually sown, for example, peas or barley, which have time to grow green mass before the onset of cold weather. And in mid-autumn it is recommended to sow winter rye, oats, vetch, lupine, clover, phacelia or other frost-resistant plants (separately or in a mixture). As a rule, when sowing in winter, plants have time to form a root system, and in the spring they increase the main green mass.
Phacelia forms a branched root system, due to which it develops well even on soils with erosion processes and is a good predecessor for zucchini, pumpkin, cucumbers, as well as plants of the Solanaceae family
When incorporating green manure into the soil in the spring, it is important to consider the needs of your site. If the soil is acidified, too much fresh organic matter will not benefit the soil or the future harvest. The greens simply won’t have time to decompose quickly and will begin to sour. Therefore, if the soil on your site is extremely poor and acidified, it is better to put part of the mowed green manure into a compost heap.
Green manure is an excellent organic fertilizer that improves the soil naturally. But if you don’t have time to mow them before the seeds form, these plants are quite capable of taking over your area, turning into annoying weeds. However, even after this they can benefit your green pets. Read about how to use weeds after weeding on our website.
Source
What kind of green manure can be planted between rows of potatoes?
Natural fertilizers can also be planted during the growing season of vegetables. In the summer, next to the rows of potatoes in the spaces between the rows, you can plant:
- calendula;
- legumes;
- buckwheat;
- nasturtium.
Calendula and nasturtium will not only nourish potatoes, but also repel insects.
Are there universal green manures for potatoes?
There is no universal crop for planting potatoes. Each plant has its own beneficial properties. It is recommended to plant several green manures together. There are crops that can provide many benefits to vegetables. Such plants include phacelia.
It not only nourishes the soil, but also protects the beds from overgrowing weeds and pest invasions. It can be planted either after potatoes or before them. It is also a crop that is planted between rows of vegetables and berries.
Companions in the garden
In mixed plantings, plants with different structures of the root system are usually well combined - its deep location and superficial, with a rod and fibrous shape. Such “neighbors” growing nearby consume nutrients from different soil layers and do not compete with each other.
Spices from the Apiaceae family release a lot of essential oils, which the potato does not like and depresses it
As a rule, other vegetables are not placed on a potato plantation due to the peculiarities of agricultural technology: the need for hilling and pest control treatments. Representatives of “foreign” families are planted near it: cabbage, sunflowers, corn, onions and garlic, peas and beans. Medicinal and ornamental flowering herbs can be good companions: sage, chamomile, yarrow, thyme, tansy, marigold, nasturtium, calendula, which will protect potatoes in the open ground, repelling harmful insects, and without interfering with their care.
For pest and weed control
Mustard can protect potato tubers from invasions of wireworms and beetle larvae. Crescent, phacelia, and sweet clover also have the same properties.
Mustard can be planted several times per season. It quickly gains green mass, which eliminates the possibility of the area becoming overgrown with weeds. Its ability to protect vegetables from late blight infection has been noted.
It enriches the soil with potassium and phosphorus. Helps retain moisture in the soil. It can be used for sowing between rows.
Due to its roots, sweet clover extracts nutrients from the deep layers of the earth and loosens the soil.
Another crop that can protect a site from weeds is oats. It can be planted both in spring and autumn. At the beginning of the season, oats are sown immediately after the snow melts and the soil warms up. Autumn sowing should be no later than mid-September. For the same purposes, you can plant such plants as:
- clover;
- buckwheat;
- alfalfa;
- radish;
- nasturtium.
To protect bushes from the Colorado potato beetle, it is recommended to plant flax. The ability to repel pests has been noted in calendula and nasturtium.
What's not good for potatoes?
It is not recommended to plant sunflowers before planting potatoes. It requires a lot of nutrients to grow, and its tops are difficult to decompose.
Areas with wheat crops may be favored by plant pests. Therefore, it should also not be chosen as a predecessor for potatoes.
What plants can be planted to “treat” the soil?
If the area where you plan to plant potatoes had crops that were affected by diseases, the soil should be “cured” before planting. For this, the following green manures are used:
- rapeseed;
- oilseed radish;
- rape;
- white mustard.
Green manure preserves soil fertility, fights plant pests and infections. To improve the health of the land, it is recommended to sow plants of different families in one place and alternate them annually. The best option for fertilizing potatoes is to plant legumes and mustard on the plot in the fall. These fertilizers are completely safe, and also inexpensive.
How to get rid of wireworms using green manure
To permanently get rid of wireworms in the garden, it is necessary to constantly deoxidize the soil. Therefore, to combat this annoying pest, natural fertilizers that are quite resistant to difficulties are suitable. The following elements are suitable for planting green fertilizers: chalk, lime, superphosphates.
What plants will help in the fight against wireworms:
- mustard;
- lupine;
- phacelia;
- alfalfa.
Read our article: Wireworm in the garden: how to deal with it