Cultivated varieties of honeysuckle appeared quite recently, compared with other popular berries - already in the last quarter of the 20th century. Despite this, they have managed to fall in love with many gardeners, especially in cool regions where the choice of garden plants with tasty fruits is limited. And it is probably no coincidence that out of the hundreds of currently known honeysuckle varieties, 80 percent were created in Russian nurseries. One of them, who gained popularity, is our current hero.
Benefits of honeysuckle
The fruits are endowed with a pleasant, sweet taste; many varieties have a slight bitterness. Honeysuckle contains a lot of substances that are beneficial for the body. Not only are jams made from the berries, they are added to compotes, medicinal infusions and decoctions are made, and fresh ones are often added to tea for flavor. Honeysuckle is useful for diseases of the heart, blood vessels, and gastrointestinal tract. Fruits cleanse the body of toxins, “bad” cholesterol, toxins, and help improve immunity.
The fruits are not contraindicated for consumption by people with diabetes; they are recommended for hypertension. Honeysuckle is a real natural first aid kit. Scientists have proven that its constant consumption significantly rejuvenates the body and slows down the aging process. We invite you to get acquainted with Silginka honeysuckle. A description of the variety will be given below.
Which type of honeysuckle is better?
Guided by many years of gardening experience, we have compiled a review of the most popular varieties. The priority was indicators of productivity, unpretentiousness to growing conditions, and only after that we assessed the decorative qualities. Having compared all the pros and cons, Vyborexperta.ru identified several nominees:
- Siberian - high ratings from tasters, an ornamental bush with stable productivity for Siberia;
- Cinderella - the best taste without sourness, a pleasant strawberry aroma, high expert ratings and ease of care;
- Leningrad giant - cluster ovaries, long harvest period, excellent option for storage and transportation;
- Pushkinskaya is the sweetest berry, a new highly adaptive species, earlier ripening and a dessert sweet and sour taste;
- Bakchar giant - minimal shedding and high transportability, the best option for growing for industrial purposes;
- Fire opal – the highest indicator of productivity, early ripening, non-shattering, endurance in terms of transportation and storage;
- Nymph - large berries, firmly attached to the branches, better frost resistance, long fruiting period.
Honeysuckle has long been grown with the same frequency as gooseberries, raspberries, and currants. Several dozen new varieties were developed based on the edible species. Our top includes both “pioneers” and representatives of the new generation.
Honeysuckle Silginka: description of the berry
A distinctive feature of the variety is that the berries do not have the bitterness characteristic of many varieties of honeysuckle. The taste is very pleasant, sweet, refreshing. The berries are all the same size, their average weight is 1.4 grams. These large fruits are dark blue with a slight purple tint. The surface of the skin is covered with a white waxy coating. It is thin, but dense enough to protect the pulp from damage. The skin is tender, almost imperceptible when eaten. The pulp is juicy, refreshing, aromatic. The honeysuckle variety Silginka received a high tasting score, scoring 4.9 points out of five possible.
Rating of honeysuckle varieties
When compiling a rating of honeysuckle varieties and descriptions of each, we studied various projects (photos, video reviews) of breeders and gardeners for growing such a plant. The test results showed which varieties are most adaptable to the climate of our country and rich in yield, as well as in what characteristics they outperform others.
We assessed the candidates for inclusion in the top on several points:
- Taste qualities, tasting assessment;
- Maturing period;
- Yield level, stability;
- Degree of shedding;
- Ability to self-pollinate;
- Resistance to weather conditions, diseases;
- Transportability of fruits.
The result of the comparative analysis was a top list with a description of 12 positions. To make it easier to get to know them, we have divided the review into 3 categories - sweet, large-fruited, and frost-resistant species of shrubs. Review monitoring showed the pros and cons of each nominee.
The best varieties of roses
Characteristics of the variety
Gardeners love this honeysuckle because it is suitable for absolutely all regions. It tolerates heat and drought well and is not at all afraid of frost. The yield of the variety is high; according to statistics, from one bush you can collect from two and a half to three kilograms of fruit. Ripe berries can be stored for up to a month in a cool, dark place. Transportability is average, can be transported over short distances.
The peculiarity of Silginka honeysuckle is that fully ripened berries do not fall off the branches, they continue to wait until they are picked by the caring hand of the owner. Ripening occurs simultaneously, this is a huge advantage. It will appeal to gardeners whose plots are located far from their permanent place of residence. Silginka honeysuckle needs pollinators for good productivity. The best variety for her will be the Bachkarsky Giant variety. Planting shrubs together will allow you to obtain high and stable yields from both species, bearing fruit simultaneously.
No shortcomings have been identified in the variety; absolutely everyone who decides to plant it on their plot likes it. A photo of Silginka honeysuckle is presented in this publication.
How was the variety created?
Its history is simple and sparse. Created in Siberia, through the works of breeders of the Bakcharsky research nursery, famous in the Tomsk region. Year of birth: 1978, this is one of the first “cultivated” varieties of honeysuckle. It was obtained by crossing two varieties: Roxana and Turchaninova. When creating Silginka, the authors sought to obtain a plant that can withstand severe frosts and spring frosts well, and also produces tasty fruits of commercial quality. And the breeders succeeded in this!
Preparing the landing site
This variety, however, like all others, is undemanding to the condition of the soil; it can be loam or sandy soil. The main criterion is the presence of good lighting and protection from winds. The more sun the bush gets, the better the taste of the berries and the higher the yield.
When preparing holes for planting, consider the distance between them. The bushes should be located at a distance of one and a half meters from each other. The depth of each hole should be from fifty to sixty centimeters.
Agricultural technology
The main requirement for growing honeysuckle is the availability of free space. The bush can live up to 100 years and its diameter is at least 1.5 m. In addition, to get a harvest you need to plant at least 2 different varieties of bushes.
Did you know? If the shrub is older than 4 years, you may notice the bark peeling off, revealing wood underneath. This condition is not a disease, but a feature of the bush that does not require any action from the gardener.
There are also a few other points to consider:
- A seedling with a pair of strong stems and no external damage is suitable for planting.
- Despite the fact that the variety tolerates any lighting well, the more sunlight “hits” the bush, the more fruits you will get.
- Plants are planted in well-drained soil at a distance of 1 meter from each other.
- Honeysuckle will need high-quality watering.
- Be sure to spray against pests. Aphids and bugs “adore” this shrub.
Remember that semi-evergreens shed most of their leaves in late winter, just before new ones begin to grow in the spring, and so the bushes remain leafless for a short time
Selecting a location
Honeysuckle is undemanding to growing conditions, as it grows everywhere in the wild, including on rocks. But it is preferable to choose an area for planting with drained soil and good lighting . Avoid planting in wetlands and low-lying areas where damp air accumulates.
Important! During the first 2
—
3 years after planting honeysuckle, only watering and weed removal are required.
Regardless of which site is chosen, the plant will definitely need support for the stems . This could be a wire lattice, a fence, the wall of a building, or a trellis. Walls facing south are excellent for bushes to produce the maximum amount of fruit. The absence of sun will result in a lack of flowering. And soil that is too clayey and poorly permeable to moisture can cause disease.
Planting and care
You can buy and plant plants in both spring and autumn. It is important to do this when there is no threat of frost. According to gardeners, it is more correct to plant deciduous varieties in the fall, and evergreens in the spring or autumn.
Prepare a supporting structure: trellis or lattice. Place the wires about 45cm apart. There should be at least 10 cm of space between the supporting structure and the bush. This will create conditions for air flow around the plant, and will also allow the gardener to care for the bush - pruning and harvesting.
Video: Planting a honeysuckle seedling
Planting technology:
- The distance between plants is about 1-1.5 m, depending on the “adult” size of both bushes. When planting in rows, a minimum width of 2 m will be required between them.
- A hole about 50 cm deep and the same width is dug in the area. You need to focus on the size of the root ball, to which 20 cm is added in order to relieve soil pressure and improve conditions for root growth.
- If the soil is clayey, then the excavated soil is mixed with compost (1 bucket) or other organic fertilizer.
- Pour some of the soil mixture into the hole.
- Carefully remove the seedling from the container in which it arrived from the nursery. And without removing the soil from the roots, lower it into the recess.
- Add soil to half the volume of the planting hole.
- Water thoroughly.
- Add the remaining soil. Compact to remove air pockets.
- Now prune the existing shoots back by two-thirds to encourage new shoots to grow at the base. This will also promote the growth of the root system.
Check the soil moisture regularly, and water the plant at least once a week during the first growing season . Dry areas may require more frequent watering.
Feed honeysuckle once a year (in spring). On a clay plot you will need 2 buckets of compost, 50 g of superphosphate and 50 g of potassium salt. To apply them, create a small furrow around the perimeter of the bush, pour fertilizer into it and fill it with water - this way they will be better absorbed. Then the furrow is filled in.
If the root zone is covered with mulch, this will keep moisture from evaporating, the soil from compacting and will prevent the growth of weeds. During watering, the mulch partially decomposes and nourishes the soil with useful substances. But this only applies to organic types of mulch: wood chips, pine needles, straw or sawdust.
Features of pollination
In spring, honeysuckle blooms profusely. Its flowers are bisexual. But they are self-sterile and to obtain a harvest, it is necessary to have another variety nearby with which it will be pollinated.
The originator of Silginka indicates that the following varieties are suitable for pollination: Vostorg, Yugan, Bakcharsky giant, Sinilga, Daughter of the giant. Pollen is carried by bees and other insects. Gardeners note that the more different varieties grow in the garden, the greater the yield will be obtained from the plants.
Important! Be sure to take into account that each flower will bloom only for 1 day. If there are few bees in the garden, spray the bush with sweet water. Its aroma will attract pollinating insects.
Disease and pest control
Honeysuckle is a “reliable” plant that rarely gets sick. For Silginka, it is indicated that its resistance to disease is at the standard level.
However, in hot weather it is prone to contracting powdery mildew . The disease most severely affects honeysuckle growing in a shady place. The fungus appears as a white powdery coating on the leaves. They subsequently darken, dry out and crumble. To combat the fungus in the fall, they destroy fallen leaves, weeds and other organic remains on which spores can overwinter. If a disease is detected, the bushes are sprayed with a sulfur solution.
If you notice spots on the leaves, then this is the result of the activity of various fungi. To combat them, spray with 1% Bordeaux mixture before flowering, after flowering and in the fall.
In the spring, check young shoots, as they may be susceptible to aphid attack . Insects settle in colonies on leaves and cuttings. They are removed by spraying with soapy water at intervals of 7 days.
Scale insects can also attack young shoots . As a result, the shoot slows down in growth and dies. The insect is covered with a chitinous shell, under which chemicals do not penetrate. Therefore, scale insects are removed manually by cleaning them from the shoots.
Pruning and crown formation, preparation for wintering
It is necessary to prune the bush so that the honeysuckle bears fruit abundantly. The plant “gives” up to 12 new shoots in one year. Therefore, it must be thinned out.
Did you know? Honeysuckle is often used in making toys for cats. Animals are attracted to its scent. The plant is also used in making aromatic pillows for people.
Trimming algorithm:
- In the spring, before the buds open, remove those shoots that were broken in winter by the wind or animals. Next, cut all stems to a height of 60 cm to stimulate the development of new ones. To stimulate flowering, the lateral branches are shortened, leaving short shoots of 2–3 buds.
- In autumn the bush is rejuvenated. This is done once every 4-5 years. Remove all old shoots older than 4 years, then those that creep along the ground and weak ones. Branches with small growth are shortened.
Honeysuckle is frost-resistant. Therefore, the bush does not need winter protection
Landing
Before planting, it is necessary to prepare the holes. Each needs to be filled one-third with good rotted humus, two hundred grams of complex fertilizer added, and if the soil is acidified, then it needs to be neutralized by adding a glass of dolomite flour or wood ash. After this, fertile soil is added. If all these recommendations are followed, then for the next three years there will be no need to feed the plant; such pre-planting refueling will be sufficient for this time.
The Silginka honeysuckle seedling must be prepared for planting. It is necessary to place the roots in water for several hours so that they are sufficiently saturated. After this, it is recommended to treat them with a root former, this will allow the seedling to take root faster and grow.
Place the seedling in the hole so that the root neck remains on the surface. Spread the roots evenly and sprinkle with soil. After this, you need to press the soil around the trunk and compact it a little. Water thoroughly, adding ten liters of water under each bush.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Honeysuckle Pride of Bakchar
Among the main characteristics that distinguish the Silginka honeysuckle variety from other plant varieties are:
- High yield;
- Early fruit ripening;
- Pleasant taste and aroma;
- Juicy fruit pulp;
- Tolerance to frost and low temperatures;
- Frequent haircuts are not required;
- The bush is unpretentious in care;
- Versatility of use.
Honeysuckle is the very first one in the garden to produce a harvest.
There are no major shortcomings in this variety of honeysuckle. Not a single gardener who chose Silginka for his plot complained. A small disadvantage is the low transportability of the berries - when fresh they are very difficult to transport over long distances.
As you can see, Silginka honeysuckle is a universal shrub that copes well with harsh winters and does not require complex care. A little attention from the owner, as well as a sufficient amount of light, will help to obtain an excellent harvest every season.
Further care
Silginka honeysuckle will grow well in moist soil; it also likes humidified air. Water abundantly, and in the evening she will not refuse to “take a shower.” The foliage will straighten out, become moisturized, and the plant will thank you in return, bearing good fruit.
There should be no weeds near the bushes; weed so that the grass does not take nutrients and moisture from the cultivated plant. It is necessary that air penetrates well into the soil, so loosening is required. Carry out the procedure very carefully so as not to accidentally damage the root system with the tool.
To save yourself the hassle, mulch the soil around the bushes. Sawdust or peat laid in a two-centimeter layer is suitable. This will prevent the development of weeds and retain moisture in the ground.
Three years after planting the plant, provided that it was planted according to all recommendations, it will be necessary to fertilize annually. In the spring, when the buds swell, nitrogen fertilizers will be needed. In summer and autumn, potassium and phosphorus preparations are needed, and the addition of other microelements is also necessary.
Secrets of proper cultivation
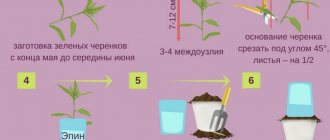
Honeysuckle Silginka reproduces by almost all methods known in botany. Most often, gardeners use cuttings, which help preserve all the varietal characteristics of the mother plant. To do this, pieces of 10-15 cm long are cut from a young large spring shoot and planted in planting containers, and in the southern regions - directly into prepared holes. The seed propagation method is extremely labor-intensive, therefore it is practiced only among breeders.
Tip: In mid-spring, honeysuckle takes root well in powerful side shoots. They are covered with soil and watered regularly. After a few weeks, roots form on the shoots, and then buds begin to grow quickly.
Watering and weeding
Honeysuckle variety Silginka tolerates drought well, but is moisture-loving. Gardeners often water shrubs, immediately applying a large volume of water to the roots. It is better to water the plant after sunset so that a dense, airtight crust does not form on the ground. Honeysuckle also likes regular spraying, after which the leaves are straightened and moistened, and buds are abundantly laid on the shoots.
The roots of the Silginka variety are located close to the soil surface, so when weeding and loosening, you should not bury garden tools too deeply. The plant forms its crown correctly - there is no need for frequent pruning. Gardeners only periodically trim dry shoots and remove darkened leaves.
Feeding
The first application of nitrogen fertilizers is carried out in early spring during the period of bud swelling. This will help the bush to form correctly and form a large number of buds. In mid-summer, after flowering has ended, honeysuckle is fed with organic fertilizers high in potassium and phosphorus. These microelements are also necessary for the plant at the beginning of autumn to prepare for a long, harsh winter.
Important: An additional fertilizer is to sprinkle the soil with high-moor peat, sawdust, and rotted leaves. Mulching allows you to retain moisture in the soil for a long time and prevents the growth of weeds.
Reproduction
There are several ways to propagate honeysuckle in your area. We invite you to familiarize yourself with each one.
- By cuttings. For this method, you need to select annual green shoots at the end of May. In order for the new plant to take root better, do not cut the branch, but break it off right at the heel. After this, plant the cuttings in moist, loose soil and create greenhouse conditions. To do this, you will need to place a cut plastic bottle on top of it.
- By layering. Propagation is carried out as follows: bend the lower annual branch in the ground, secure it with a bracket and sprinkle the contact area with earth. After a year, the shoot will take root, and you can separate it and plant it in another place.
- Seeds. The process is complex and long, but we will still describe it. Select ripe berries from the bush, crush and separate the seeds, rinse. Put it in the refrigerator for a month, then sow it in a plastic container and bury it under the snow. In spring, cover the box with film and care for the seedlings as if they were seedlings.
- The last method is to divide the bush. To do this, dig up a bush with its roots, carefully divide it into the required number of parts, and plant it.
Description of the variety
Silginka was created in 2004 by the Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Bakcharskoe" by hybridizing Turchaninov's honeysuckle and the Roxana variety. In 2011 it was included in the State Register. Now cultivars are being developed so intensively that Silginka is no longer considered the newest variety.
Specifications
The honeysuckle bush of the Selginka variety is medium-sized, no more than 1.5 m high, about 1.2 m wide. Rigid straight branches form an oval crown of medium density. Mature bark peels off, which is typical of all edible honeysuckles.
The fruits, weighing 1.0-1.4 g, are elongated-oval, with a pointed apex, reaching a length of 3.5 cm, at the widest point - up to 1.5 cm. For honeysuckle, this is considered a large size, although it does not fit into What is the comparison with the varieties Bakcharsky Giant or Daughter of the Giant. The yield of an adult bush is about 2.5 kg, up to 8.2 tons are harvested per hectare, and in a particularly favorable year - up to 11.5 t/ha.
Honeysuckle Silginka: reviews
As we have already written, there are no shortcomings in the variety, and this is confirmed by the comments of gardeners. They write that the yield is excellent, the fruits are large, their taste is excellent, and the pulp is juicy. They praise the aroma of the berries and their versatility.
Reviews about the plant in general are also good. They write that the bushes are unpretentious, it does not require much time and effort to care for the plant, it does not thicken, so there are no problems with frequent haircuts. It looks good on the site, the bushes are neat, beautiful, and look great along paths and near fences.
We hope our recommendations will help you grow a healthy bush that will produce a bountiful harvest!
The best sweet varieties of honeysuckle
The first category of the top rating is the sweetest varieties of honeysuckle according to experts and the editors of VyborExpert. Leaders in taste are actively used for making desserts, juices and compotes, and making jam for the winter. The harvest is also suitable for fresh consumption.
Siberian
A frost-resistant sweet variety of honeysuckle for Siberia, bred by specialists from the village of Bakchar, Tomsk region, by crossing in 1972. Since 2000, the plant has been officially included in the State Register. Growing is possible in any region of Russia.
The spreading shrub reaches a height of 160 cm. It is distinguished by a moderately dense oval crown of broadly lanceolate leaves with a small edge on both sides. It blooms in a two-flowered reduced inflorescence - these are medium-sized flowers of a pale yellow hue with semi-closed petals. The degree of crumbling is weak.
After planting, it produces a harvest in the second year, the ripening period is early (approximately the first half of summer). The dark purple berries are large, up to 1-1.4 g each, elongated, slightly curved, teardrop-shaped. There is a waxy coating on the thin skin.
Taste qualities are at a high level - 4.9 points according to expert tasters. The chemical composition includes 8.2% sugar, no more than 1.9% acids. It is a source of vitamin C – up to 32 mg. The plant is self-sterile; pollination requires another variety or hybrid with flowering during this period.
Advantages:
- Fast ripening;
- Sweet taste with sourness;
- Large berries;
- Resistance to frost and disease;
- Decorative properties;
- Collection stability.
Flaws:
- When overripe, the fruits become wrinkled;
- Bent branches make harvesting difficult.
The decoration is good, the Siberian will decorate the site. With proper care, it promises an annual harvest of berries in mid-June - this is 3.2-3.7 kg per bush. The winter hardiness indicator is high - up to -50°C, and it is also drought-resistant. Transportability is average.
Silginka
One of the most delicious varieties, according to tasters, is Silginka. It was developed by crossing Turchaninov and Roxana in 1978. Officially entered the register and was recognized in 2011. It has a high level of transportability.
The vigorous bush reaches a height of 180 cm. It is distinguished by its strong spreading, sparseness and a beautiful round crown. The bright green leaves are smooth with thin sparse hairs on both sides, medium in size, oval and slightly elongated. A characteristic difference is that the flowering structure is irregular according to the quinary plan.
The fruits are large in size - 1.4-2.2 g each. Oval in shape, elongated with a pointed tip. The color of the thin skin is dark blue with a coating; inside there is delicate flesh with a pleasant aroma. The fastening strength is weak, so crumbling is possible.
Taste qualities also have a predominant difference - sweetness without astringency. Expert rating – 4.9 points. Sugar content 9.8%, ascorbic acid 42.3 mg, titratable acids 1.32%. The ripening speed is medium-early. Harvesting from one bush per season is 1.5-3 kg.
Advantages:
- Sweetness without bitterness;
- Transportability;
- Juicy and tender pulp;
- Ease of picking berries;
- Large fruit;
- Resistant to frost and drought.
Flaws:
- Falls off;
- Self-sterility.
The shrub requires pollination by selected and simultaneously flowering forms of honeysuckle (Kamchatka, Turchinova). It is resistant to low temperatures, various diseases, and drought. Life expectancy reaches 30 years.
Cinderella
This plant is distinguished by its compactness, early ripening, decorative properties and ability to resist disease. The authors are considered to be specialists from the NIISS named after M.A. Lisavenko, date of creation 1974. Approved for landing since 1991.
The low-growing deciduous shrub can reach a height of 50-70 to 100 mm, depending on pruning. It is distinguished by an uneven, wide-rounded crown, large light green egg-shaped leaf plates with an elongated tip. Flowering begins early and is characterized by abundance - these are light, large flowers.
The subspecies Cinderella is an early one, producing berries by the second year of life. Large berries 1-1.4 g can be harvested in mid-June. The shape is spindle-shaped, cylindrical, the skin is compacted, almost black, and there is juicy pulp inside. Sugar content 7.28%, vitamin C up to 140.8 mg, acids 1.37%.
The characteristic difference is the strawberry aroma. The degree of crumbling is average. Experts' assessment regarding taste is 4.8-5 points. According to the method of pollination, Cinderella is self-sterile, pollinated by Gerda, Azure, Blue Bird, Bachkar's Pride, Fire Opal.
Advantages:
- Consistently high productivity;
- Strawberry aroma;
- Early maturation;
- Weather resistance;
- High expert assessment;
- Unpretentious to grow.
Flaws:
- Possible shedding;
- Difficulty in harvesting.
Cinderella can withstand temperatures as low as -40°C. It is a source of vitamin P and pectin. In one season you can collect 2-2.8 kg here. Periodic crown molding is required.
The best raspberry varieties