Edible honeysuckle is an upright deciduous shrub and is common in the temperate climates of the Northern Hemisphere. In wild species, the fruits are small, sour, often with a pronounced bitterness. They are prone to shedding and ripen unevenly. Despite the unique healing properties, the development of new varieties began seriously only in the 50s of the last century.
Characteristic
Blue honeysuckle is a low, perennial shrub. His height is 60 cm and above. In Russia it grows in the Central part, Eastern Siberia and the Far East, and is also found in other areas. There are wild and cultivated plant species.
In nature, it can be found in places such as:
- floodplain forests
- tundra
- marshy areas
- river valleys
Many plant varieties tolerate frost easily and are unpretentious. For successful growth, regular watering and loosening of the soil under the bush is necessary. It should be noted that the root system is close to the surface of the earth. The procedure must be carried out carefully so as not to damage it.
- When individual branches dry out, they must be removed with pruning shears.
- Experienced gardeners advise planting different varieties.
- This will ensure a fruit harvest.
- This happens due to mutual pollination.
The berries are oblong, deep blue in color. They have a sweet and sour taste. Some species have a bitter taste. When choosing a variety, you need to know that there are edible and poisonous fruits.
Farms specializing in breeding honeysuckle varieties
The Bakcharskoye horticultural enterprise is located in the Tomsk region. For 84 years, varieties of fruit and berry crops have been bred there. Unique, frost-resistant species are grown here. At the moment, honeysuckle is the main crop of this farm.
Her plantation covers an area of 50 hectares. Many of its varieties were created here: Bakcharsky Velikan, Tomichka, Bakcharskaya, Bakcharskaya Yubileynaya, Daughter of the Giant, Yugan and many others. Below we will consider each type in detail.
In 1926, the Pavlovsk Experimental Station of the All-Russian Research Institute of Plant Growing named after Nikolai Ivanovich Vavilov was opened near St. Petersburg. There are 4 plant research laboratories here. Employees study, grow plants, cross them and develop new species.
M. N. Plekhanova specializes in honeysuckle varieties. She and her students own the following varieties:
- Moraine
- Nymph
- Amphora
- Violet
- Yoke
- Vlad and many others.
In addition to Russian breeders and biologists, this crop is propagated in other countries, for example, Canada and China.
Origin of the variety
It was created in the village of Bakchar, Tomsk region, on the plantations of the famous nursery - the Bakchar stronghold of northern gardening. Now it is the Federal State Unitary Enterprise “Bakcharskoe”, with a history of more than 60 years. Among other things, the nursery has the largest experimental plot in Russia, given over to honeysuckles. It would not be a mistake to say that the lion’s share of varieties of this crop were born in Bakchar.
Read also: How to propagate walnuts
Bakcharskaya Jubilee is one of them, continuing the so-called “Kamchatka line”. It was included in the State Register of the Russian Federation in 2013, although it was created several years earlier. To date, it has been tested in many regions of the country, and has become one of the most popular varieties of garden honeysuckle.
Description of varieties
Pride of Bakchar
Pride of Bakchar
Bakcharsky Giant
Bakcharsky Giant
Bakcharskaya Yubileinaya
Bakcharskaya Yubileinaya
Moraine
Moraine
Leningrad Giant
Leningrad Giant
Silginka
Silginka
Nymph
Nymph
Delight
Delight
Yugana
Yugana
Cinderella
Cinderella
Sweet tooth
Sweet tooth
Borealis
Borealis
Amphora
Amphora
Siberian
Siberian
Bullfinch
Bullfinch
Blue spindle
Blue spindle
Blue bird
Blue bird
Bazhovskaya
Bazhovskaya
The Giant's Daughter
The Giant's Daughter
Long-fruited honeysuckle
Long-fruited honeysuckle
What varieties of honeysuckle should be planted together?
All varieties of blue honeysuckle are self-sterile. For pollination of flowers and the appearance of berries, representatives of another variety must be present within reach. The more there are, the richer the harvest. When selecting varieties for the garden, it is necessary to take into account the flowering time of plants. If they do not match, pollination will be impossible and fruits will not set.
According to most breeders, the taste of the berries and the size of the harvest depend on the choice of pollinator.
Table: the best pollinators for popular varieties
| Main variety | The best pollinating varieties |
| Siberian |
|
| Nymph |
|
| Silginka | Bakchar giant |
| Cinderella |
|
| Bakchar giant |
|
| Leningrad giant |
|
| Blue spindle |
|
| Swan |
|
| Blue bird |
|
| Amphora |
|
| Moraine |
|
| Malvina |
|
| The Giant's Daughter |
|
| Sweet tooth | Violet |
An important condition for obtaining a good harvest of honeysuckle is the correct choice of variety. In this case, it is necessary to take into account not only your own preferences, but also the climatic conditions of the region in which cultivation is planned. If this rule is followed, honeysuckle will delight the gardener for a long time with tasty and healthy berries.
- Author: Galina Panova
Since childhood, I have been interested in growing various plants and have achieved considerable success in this matter. I will be very happy to share my experience. Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(71 votes, average: 3.6 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
Benefits and harms
The benefits of edible berries are obvious. They contain a large amount of vitamins. Honeysuckle is considered a medicinal plant; it does not lose its properties when heated.
BENEFIT:
- Used to treat and prevent scurvy
- Boosts immunity
- Reduces high blood pressure
- Helps with migraines
- Strengthens the cardiovascular system
- Removes salts from the body
- Honeysuckle is recommended for gastritis, ulcers
- Treats sore throat
HARM:
- Excessive consumption can cause allergic reactions and intestinal upset. As in any other case.
- When consuming the product, you need to know when to stop and not overeat.
Interesting Facts
English, Honeysuckle
There are about 250 varieties of honeysuckle on planet Earth. Wild species are more often found in Siberia, the Himalayas and East Asia, on the coast of the Sea of Okhotsk, Kamchatka, and Sakhalin. There are 14 wild varieties growing on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Honeysuckle was nicknamed “shameless.” This nickname was given due to the fact that the bark of some varieties peels off and flies off, exposing the branches.
You definitely need to know that honeysuckle can be poisonous. One of these varieties is Wolf Berry. Dark colored berries are suitable for consumption: black, blue, purple. Red and orange fruits grow on poisonous bushes.
Honeysuckle ripens earlier than other berries. It will give you the vitamin boost you need after the long cold months.
8.4 Overall Score
The right variety will give a good harvest. The bush will decorate any garden plot or alley. We tried to collect the most popular varieties for you and give them a comprehensive description. If you do not agree with these ratings, leave your rating in the comments with the reasoning for your choice. Thank you for your participation. Your opinion will be useful to other users.
Relevance of information
Availability of application
7.5
Reliability of information
9.5
Add your review
A real record holder! This is exactly how some gardeners speak about the honeysuckle variety “Bakcharsky Giant”. And such a high assessment is not in vain. Honeysuckle was bred by breeders from the Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Bakcharskoe" in the Tomsk region. The bush is intended for cultivation throughout Russia. Let's take a closer look at this honeysuckle. Let's talk about:
- what the “Bakcharsky Giant” variety is;
- rules for planting and caring for plants;
- what diseases and pests threaten this honeysuckle;
- bush propagation.
This will show that the Bakchar giant honeysuckle is one of the best representatives of its species, which is why gardeners love it.
Large-fruited honeysuckle variety Bakcharsky giant
Features of agricultural technology and use cases
Gardeners fell in love with our heroine, in particular, for her frost resistance and unpretentiousness. It is noted that it is capable of bearing fruit well even in the southern, drier and high-temperature regions. What sets it apart from many other honeysuckles is the location of the berries on the branches: they grow in compact groups, which makes picking much easier.
Due to the extended ripening period, harvesting in 2-3 stages is recommended. Thanks to the strong skin, the berries can be transported over medium distances and stored in the cold for about a week.
Breeders call Silginka, as well as Bakcharsky giant and Delight, the best pollinators for the variety.
Bakcharskaya Jubilee berries can be confidently called universal. Most of them are consumed fresh, but they are also dried, frozen, and made into preserves, jams and preserves. They are also used as a good raw material for homemade wine. The fruits are rich in various vitamins and microelements.
This honeysuckle also has a certain decorative value; its bushes can decorate a garden plot or a corner in a country house.
Description of the variety
Let's begin the description of the honeysuckle variety Bakcharsky giant with the fact that it is a vigorous bush that reaches 2 m in height and the spreading of its crown is up to 1.5 m. The leaves are oblong, light green, matte with bluish hair. The fruits are elongated, cylindrical, large. One berry can weigh up to two grams. Its length is 4-5 cm, diameter is from 1 to 1.5 cm. The skin on them is slightly bumpy, of medium thickness, which allows you to store honeysuckle berries for a long time. Its color is dark blue with a touch.
Honeysuckle fruits Bakchar giant
The fruits of the Bakchar giant honeysuckle are edible. Their taste is delicate, sweet and sour, dessert, without bitterness. The berries ripen in June. The bushes begin to bear fruit in the third year, and produce a harvest of 2 to 5 kg.
This is interesting! The variety tolerates low temperatures well, down to -50°. And even during the flowering of the bush, it will withstand frost up to 10 degrees. In addition, the variety is resistant to many diseases.
Flowering honeysuckle Bakchar giant
Edible types of honeysuckle
Today, more than 100 species of honeysuckle are known. The fruits of almost all of them are inedible, and some are poisonous. Thus, eating honeysuckle berries (Lonicera xylosteum), widespread in the forests of our country, can be fatal.
The fruits of honeysuckle are very poisonous
In Russia and the CIS countries, only one species of this plant with edible berries is cultivated - blue honeysuckle (Lonícera caeruléa). It is a deciduous shrub 1 to 2 m high with blue-black oblong berries, the taste of which is reminiscent of blueberries. In the wild, honeysuckle of this species is most often found in East Asia.
Video: honeysuckle - a guest from the Far East
Blue honeysuckle has many subspecies. Among them:
- Altai honeysuckle. A shrub no more than 1 m high. Black-blue fruits with a pronounced bitterness ripen throughout the summer. This honeysuckle grows in the forests of Altai, Siberia and the Urals, but can also be found on open mountain slopes;
- Kamchatka honeysuckle. A highly branched shrub 1.5–2 m high. It begins to bear fruit in the second ten days of June. Dark blue berries have a sweet-sour, slightly tart taste;
- Pallas's honeysuckle. A shrub up to 1 m high. Its blue-black fruits ripen from late June to early September. Most often they have a bitter taste, but there are also specimens with quite sweet berries. Pallas' honeysuckle typically grows in moist coniferous forests of Northeastern Europe and Siberia;
- Honeysuckle Turchaninova. A shrub about 1 m high with a spherical dense crown. The berries come in both oblong and round shapes. Their taste ranges from sweet to bitter-sour. In the wild, Turchaninov's honeysuckle is found only on Sakhalin;
- honeysuckle is edible. A low-growing shrub, the maximum height of which does not exceed 1 m. The dark blue berries with a bluish bloom ripen in late June - early July. They are valued for their sweet-sour taste and pronounced aroma. Edible honeysuckle is often found in coniferous and deciduous forests of Eastern Siberia and the Far East.
Most subspecies of blue honeysuckle have similar characteristics. Often only professional biologists can distinguish them.
Planting and care
What does it take for a plant to be healthy and produce good yields? Here are a few points that are important to consider when planting and caring for Bakcharsky giant honeysuckle:
- choosing a suitable location;
- healthy seedlings;
- watering;
- applying fertilizer;
- loosening the soil.
Landing location
It should be sunny and protected from winds and drafts.
The place for planting honeysuckle should be well lit
After you have chosen a place for the bush, you need to prepare a planting hole. It should be at least 0.5 m deep and 0.5-0.6 m wide. Drainage is laid on the bottom, the top is covered with a mixture of humus and peat, then there is a layer of soil mixed with mineral fertilizers (200 g).
You can even make a small mound so that the roots of the plant are evenly distributed over its surface. Then you need to pour water into the hole, and do not bury it until all the water is absorbed. And only then sprinkle the plant, but do not cover the root collar.
Recommendations: If you plan to plant several bushes of honeysuckle Bakcharsky giant, then the distance between them should not be less than 1.5 m.
The best time to plant this variety is early autumn. Then the honeysuckle has time to take root before the cold weather, and the acclimatization period is less painful.
Selection of seedlings
If you have to buy seedlings, you need to carefully inspect them. The bush should not have less than 4-5 leaves. None of them should be damaged.
The health of the plant depends on the quality of the seedlings.
Honeysuckle care
Watering . Honeysuckle loves water, but you cannot overdo it, otherwise the roots of the plant will begin to rot. During planting, 10 to 15 liters should be poured under the bush in several doses. Subsequently, the bush should be watered abundantly, especially during the growing season. In autumn, it is recommended to reduce watering to a minimum.
Feeding. What fertilizers does the honeysuckle variety Bakcharsky giant need? In spring - nitrogen fertilizers. They need to be applied before the leaves appear, preferably as soon as the buds begin to swell. In summer - phosphorus-potassium preparations. In autumn - organic.
Loosening. Honeysuckle loves when there is free access to the roots of air. Therefore, it is imperative to loosen the tree trunk space after each watering. It is advisable to mulch the soil after this so that the moisture does not evaporate.
Wintering. The honeysuckle variety Bakcharsky giant tolerates frost well, and therefore no special preparation for the winter period is necessary.
Honeysuckle bush Bakcharsky giant in winter
Honeysuckle care
The culture is undemanding in terms of care, but the high-quality appearance of the shrub guarantees great fruiting.
We recommend reading the article on how to care for honeysuckle in the autumn.
Watering
The bush is watered 1-2 times a week, one root needs 8-10 liters of water. If there is not enough of it, then the berries become bitter. With excessive watering, the root system rots. Therefore, you need to focus on the climatic conditions of your region.
If the weather is dry, increase the amount of watering; if it is rainy, reduce it. In autumn, the shrub is practically not watered. After irrigation, the soil must be loosened without damaging the roots.
Top dressing
Honeysuckle of this variety is fertilized three times. In the spring, products containing nitrogen are used, as the bush grows green mass. You can use ammonium nitrate, 15 g of product per plant.
The substance nitrophoska (25 g per 5 liters of water) will help restore fruiting of honeysuckle. If you don’t have it, then you can use phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. Organic fertilizers are added in the fall. To do this, manure is mixed with water in a ratio of 1:4. One plant needs 10 liters of mixture.
Trimming
Young seedlings do not need pruning; this event will not help them, but on the contrary will harm them. The first pruning is carried out in the 3rd year after planting the bush.
Broken, old and dried branches need to be removed. Sloping shoots should also be trimmed. There should be from 10 to 15 branches left on the plant, it all depends on the age of the bush. The more sunlight penetrates into the middle of the honeysuckle, the larger the fruits will become.
If the honeysuckle Bakcharsky Giant is already an old bush, then a rejuvenating procedure can be carried out; for this, all branches are removed at a level of 0.3-0.35 m.
Harvesting
The Bakcharsky Giant honeysuckle berries fall off very quickly, so they must be collected immediately after ripening. They come off the stalk well, the bush is wide - harvesting will not be difficult.
Preparing for winter
The variety’s homeland is the territory of Siberia; on its land, the shrub can withstand frosts of -50 degrees Celsius. There is no need to cover the plant. It should not be planted in the southern regions, because too warm a winter season can cause the plant to bloom again, which is useless.
Diseases and pests
The Bakchar Giant is not susceptible to disease. But the plant suffers from attacks by various pests. Therefore, in the spring season it is necessary to carry out preventive measures in the form of spraying. You can use the following drugs: Mavrik, Confidor and Inta-Vir.
Honeysuckle pests
This variety is practically disease free. But still, he has enough enemies. For example, aphids, roseate leaf rollers, moths, honeysuckle moths. It is better to save the Bakchar giant from each of them using preventive measures.
In the spring, even before the berries ripen, you need to spray the bush with insecticides. To prevent the solution from being washed off quickly, green soap is added to its composition, which in itself is an antiseptic and “fixes” insecticides on the surface of the leaves and shoots of honeysuckle.
Honeysuckle fingerwing - a threat to the plant
Tips: It will be useful to thin out the crown not only to make it easier to harvest, but it also contributes to the health of the plant.
Reproduction of honeysuckle Bakchar giant
Honeysuckle Bakchar giant can be propagated in several ways:
- Dividing the bush. In March, the entire bush is dug up to divide it into several parts. After which they all need to be seated.
- Seeds. Seeds taken from the berries are dried and placed in the cold for 2-3 weeks. After which they can be safely sown in boxes. Cover with film.
- By layering. In June, a healthy one-year-old shoot is selected from the bottom of the bush, bent to the ground and secured with wire. Covered with earth. The very next year this shoot will take root and can be separated from the bush.
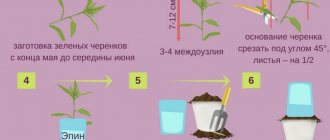
- Green cuttings. At the end of May, cuttings 10-15 cm long with three buds are cut from annual shoots. They are planted in pots under plastic bottles.
Honeysuckle Bakchar giant belongs to the self-sterile group of plants. And therefore it needs a pollinator. These are other varieties of honeysuckle. The best varieties for this are Nymph, Amphora, Lazurnaya, Pavlovskaya, and Pride of Bakchara.
Sweet berries will appeal to many people. You can eat them fresh, make jams and compotes, juices and wines, or you can freeze them to pamper your family with tasty and healthy berries in winter. Selected photos of honeysuckle Bakcharsky giant are the best review of this variety; they show that it is quite productive.
Yield variety of honeysuckle Bakcharsky giant
Honeysuckle willingly allocates space in its areas:
Moscow, Russia, on the website from 01/11/2017
Honeysuckle with moon-shaped fruits
Honeysuckle is increasingly gaining popularity in our country - it is highly productive and healthy. In addition, the crop has fruit varieties, and there are also decorative ones. Both of them bring us a lot of positive things. But it is worth noting that not all honeysuckle fruits can be eaten, but only those that are dark purple and blue. Today we will talk specifically about the edible variety. The variety is grown by many summer residents; we will be honest about its pros and cons and give advice on growing it. And today the reason for writing an article was the honeysuckle “Bakchar’s Pride”.
Good to know! Honeysuckle berry is a source of beneficial substances that have a beneficial effect on all organ systems. Ancient healers used all parts of the bush for their recipes, and it is also known that the culture helps in solving cosmetic problems.
Planting honeysuckle
| Stage 1. Preparation of planting material If you decide to grow seedlings yourself, then use one of three methods: Seeds. The most labor-intensive and time-consuming option, since you will have to prepare the seeds, scarify, germinate and replant first in small containers, and then in pots or open ground. It takes a lot of time. Cuttings. Honeysuckle shoots about 30 cm long are cut and placed in water. When roots appear on the lower part, it is transplanted into a pot or soil. About half of the cuttings take root. Layerings. The simplest and most effective option. Make several metal brackets as in the photo and press the lower branches to the ground. Over time, they take root, and you dig up the shoots and plant them in the right places |
| Stage 2. Choosing the time of planting and purchasing seedlings Step 1. If you decide to buy seedlings, then purchase them from nurseries and not from the market. This is the only way to ensure that you get the right variety. Plus, you can choose the best options from those offered. Step 2: Select a time to board. September-October is best, as the plant is dormant and takes root well. Spring planting is undesirable, since honeysuckle wakes up very early and does not take root well due to active sap flow and development |
| Stage 3. Selecting a site and preparing a hole for planting Step 1. Choose a place that is well lit by the sun for most of the day. The distance to the fence or neighboring plants should not be less than 2.5 m. It is advisable that the area be protected from the wind. Step 2. Dig a hole with a diameter of approximately 60 cm and a depth of 50 cm. In order to prevent stagnation of water in the root system, fill the bottom with a drainage layer 15 cm thick. Use crushed stone, gravel or broken brick |
| Stage 4. Planting honeysuckle Step 1. Prepare a nutrient mixture of 2 parts humus, 2 parts turf soil and 1 part sand. To enrich, add a little complex fertilizer or 100 grams. wood ash. Step 2: Fill the hole about 2/3 full and make a hole in the middle. Carefully remove the container from the root part so as not to damage the soil ball or disturb the roots. Step 3. Level the seedling and fill the hole completely with soil. Compact the surface well; you can make a small depression around the plant to collect moisture. |
| Stage 5. Watering the seedling Step 1. Immediately after planting, pour a bucket of water over the honeysuckle and watch how it is absorbed. If it’s fast, then add at least another bucket, and if it’s slow, then after absorbing the moisture, mulch the soil with peat or black soil. Step 2. Water the plant once every 5-7 days for a month after planting. If it rains, there is no need to water |
Varietal characteristics
A variety with very good returns
Honeysuckle “Pride of Bakchar” was bred by breeders of the Federal State Unitary Enterprise “Bakcharskoye”. If we talk about the shape of the bush, it resembles a stack of medium height. The branches are not located in the same tension - some grow upward, some fall, bend, like a willow tree. Not all summer residents like spreading bushes, so not everyone chooses this variety for landscape decoration. But the fruits of this honeysuckle are quite good, although they have a bitter taste. In more detail, we will get acquainted with the description below.
Varietal characteristics. "Bakchar's Pride":
- large-fruited shrub - fruit length reaches up to 5 cm, width - up to 1.5 cm, weight - up to 3 grams;
- the shape of the berry resembles a month;
- The fruits ripen closer to the third ten days of July, so this is more of a late variety;
- minus – high shedding of ripe honeysuckle. The collection must be carried out regularly;
- the color of the skin is blue-violet, there is a strong white coating;
- the taste is both sweet and sour, pleasant, but there is a bitterness. Taster rating is 4.8 out of 5 points;
- productive honeysuckle - up to 3.6-4 kg per bush. One hectare of plantings will bring up to 10.5 tons;
- grows up to 1.6 meters, in diameter can reach 120 cm;
- some of the branches are strong and do not bend, while others bend under the weight of their own harvest;
- edible honeysuckle pride “Bakchara” has a dessert purpose;
- well stored and easily transported, can be grown for sale;
- pollinator varieties are required;
- the berries can be frozen, made into jam, jam, compote, jam;
- is not afraid of cold weather, diseases, or insects. Seedlings are not afraid of return frosts down to -8 degrees;
- The advantage of this variety is that the crop can be harvested either manually or using machinery.
On a note! Experience has shown that honeysuckle is bitter if it grew in the sun and received little water. With sufficient moisture, the fruits are more tasty, and the percentage of vitamin C in them increases.
As you can see, there are many pros, few cons. We must also tell you that if you decide to plant this variety in your dacha, then do not forget to purchase pollinator seedlings. We have already mentioned this above in the description of the honeysuckle variety “Pride of Bakchar”. This could be “The Giant’s Daughter”, “Strezhevchanka”, “Delight”, “Bakcharsky Giant”.
We grow wonderful shrubs on the site
Selection of location
Seedlings need light and moist soil
As we have already said, this variety falls apart, if you don’t like it, then don’t make decoration your goal. The place should be sunny, which is important for any honeysuckle. It should be moderately humid, but not damp. We remember that light and good moisture as needed result in a tasty berry without bitterness and high quality. There should be enough space for both the “Pride of Bakchar” itself and its pollinators, while ensuring that no one interferes with each other - a minimum distance of 1.5 meters.
Planting can be done from autumn to spring, if the seedling was purchased in a pot; if with bare roots, then optimally - the end of August and September. Before planting, the area is dug up, ash is added, and weeds are removed. This variety prefers slightly alkaline and neutral soils that are well-permeable to air.
Important! Do not plant honeysuckle “Pride of Bakchar” where it is windy or in areas with high traffic. We remember about strong crumbling.
Feeding and planting
Organic matter is best suited both during planting for feeding and for annual application
We dig holes about 50 cm wide and 35 cm deep, but again we focus on seedlings. Here we put 3-5 kg of rotted manure, the soil that was dug out of the hole, mixed with 50 grams of potassium salt. We lay drainage at the bottom of the hole - sand or broken brick. We place the seedling in the hole, the root collar should be flush with the ground. We bury the honeysuckle, compact it and water it, shorten the branches by a third of the length. Then we lay out mulch - for the summer it can be decorative colored sawdust, straw, for the winter, rotted manure, spruce branches, peat.
Seedling care
There is no need to apply fertilizers for the first two years. You only have to water the area, loosen it, and remove weeds. In the spring, carry out sanitary pruning of all bad branches. When the shrub reaches the age of 6-8 years, rejuvenating pruning is done every year, removing all old trunks and shoots, allowing about five strong branches to grow. From the age of 3-4 years, feeding is carried out 2 times with organic matter per season - after awakening in the spring, and then after fruiting and with mineral preparations during flowering. Thus, you can grow honeysuckle pride of Bakchar without spending time, effort, or money.
Useful berry harvest
Advice! Choose feeding preparations that are based on biological substances. Markings can be seen on the packaging. Such supplements are safe for health.
If you have never grown honeysuckle, then we recommend that you plant it in the new season. The berry is really very healthy and worthy of your attention.
Moscow, Russia, on the website from 01/11/2017
Have you read it? Don't forget to rate
(
ratings, average:
out of 5)
Honeysuckle is a valuable berry in its chemical composition and properties, rich in vitamins B, A, C, P, as well as organic acids, glucose, phosphorus, magnesium, calcium, manganese and iodine.
One of the most popular varieties of honeysuckle is Bakcharsky Giant. This plant is distinguished by good resistance to diseases and frost, has fairly large berries and good yield. The description of the Bakcharskaya honeysuckle variety, the characteristics of the fruit and the rules of cultivation are discussed in detail in this article.
Description of the variety
Photo:
Bakcharskaya honeysuckle bushes are well developed, powerful, their height reaches 1.9 m and width - 1.3 m. The skeletal branches are straight and thick up to 60 cm long, the crown of large, matte, dark green leaves is oval, loose and spreading .
The berries are large, with an average weight of 1.8 g, but there is recorded data on a harvest with berries of 2.5 g. The length of the berries is about 5 cm, the diameter is 1.2 cm. They are located evenly on the branches. The shape is somewhat elongated, oval, asymmetrical, there is a slight tuberosity. The color of the fruit is dark blue, there is a strong waxy coating.
The pulp is tender, sweet and sour, and according to tasting characteristics it is rated 4.8 points out of 5. In general, the Bakcharsky Giant honeysuckle variety is classified as a dessert variety.
Important! The bushes bear fruit already from 2-3 years of growth, the harvest time is average, slightly extended - the first batch can be harvested at the end of June. Since this species is self-sterile, it is imperative to plant pollinators nearby.
The following varieties are best suited for this purpose:
- Azure;
- In memory of Gidzyuk;
- Amphora;
- Nymph;
- Bakchar's pride.
Productivity
With proper care during the growing process, Bakchar honeysuckle produces a good harvest. Depending on the specific region and conditions, on average 2-2.5 kg of berries can be removed from one bush, the maximum recorded is 4.5 kg.
Important! The fruits can be eaten fresh, frozen, processed into wine, juice, jelly, compote, jam. Also, the Bakchar giant honeysuckle tolerates transportation well.
Suitable region and climate
Honeysuckle Bakcharskaya can grow in different regions of Russia. But you need to take into account the fact that this is a winter-hardy variety, bred specifically for harsh climates.
Plants can withstand temperatures down to -50C. Therefore, in the southern regions, planting is carried out with caution, since repeated flowering is possible in the fall and it is difficult to lay fruit buds in the summer due to the intense heat. As a result, the ovary does not form the next year and the harvest is very meager.
Pros and cons of the variety according to reviews from gardeners
Everything that is indicated in the description of the honeysuckle variety Bakcharsky giant is also noted by gardeners who have evaluated the plants in practice. According to reviews, important advantages of this type:
- good dessert taste of large berries;
- high productivity;
- convenient collection due to the wide arrangement of branches.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Reviews from gardeners claim that there are many more good aspects of the culture than negative ones. Let's look at it in more detail.
Benefits of honeysuckle Bakcharsky Giant:
- regular fruiting;
- large and tasty berries;
- spicy taste of fruits;
- the harvest can be collected quickly and easily, because the branches are located at a distance from each other;
- excellent resistance to fungal diseases;
- high frost resistance, in winter honeysuckle can withstand temperatures of about -35 degrees Celsius;
- fruits can be transported from one place to another, the berries do not spoil, and the taste does not deteriorate.
Disadvantages of growing honeysuckle Bakcharsky Giant:
- crumbling of ripened berries. They must be removed immediately after full maturity, otherwise the entire harvest will be on the ground. Experienced gardeners quickly solve this problem - they spread a film onto which the fruits fall;
- low yield. Due to the fact that the berries are large, the bush cannot bear large quantities of them.
Watch a review of the honeysuckle variety “Bakcharsky Giant” in the video below:
Growing honeysuckle
When planting Bakchar honeysuckle, like any other variety of this fruit shrub, it is important to follow certain rules.
Landing dates
When to grow honeysuckle in different climates? For this variety, the period from the beginning of September throughout the month is considered more favorable.
Reproduction methods
Honeysuckle is propagated in different ways:
- layering;
- woody or green cuttings;
- seeds.
Important! The most convenient option is considered to be with layering.
Place on site
There are also special requirements for the landing site:
- lack of ventilation;
- neutral soil composition, possibly sandy or loamy;
- groundwater height - from 1.5 m;
- good illumination for the crown, but shade for the root zone.
Signs of good seedlings
The key to good plant health, their abundant fruiting and ease of care is high-quality planting material.
When choosing seedlings, pay attention to the following signs:
- 2-3 year old plants;
- well developed, massive root bundle;
- the cuttings have awakened buds and 4-5 leaves;
- dense shoots without damage.
Landing rules
- Prepare the area by marking planting sites at least 1.5 m apart.
- Dig holes measuring 0.4 m deep, 0.6 m in diameter.
- Place any drainage material at the bottom.
- Fill each with a bucket of water and add fertilizer in the following quantities: ash - 500 g, rotted manure - 1.5 buckets, superphosphate - 25 g.
- In the center of each hole, form a small tubercle and carefully place the roots of the seedling on it.
- Sprinkle more fertilizer on top of the roots in the same amount.
- Fill the holes, making sure that the root collar is no more than 2 cm in the ground.
- Water and mulch the tree trunk circle using wood shavings.
Features of cultivation
Required soil
The variety prefers fertile areas with chernozems and sandy loam soils. Such soils allow planted plants of this variety to quickly form a root system and begin intensive formation of young shoots. It is strictly undesirable to grow the variety on dry sandy soils, clayey and marshy areas.
Growing conditions
To create the best conditions for the growth of the above-mentioned variety, you need to select a site with the following indicators:
- The surface of the site should be as flat as possible. This requirement is explained by the fact that the smoother the soil surface, the easier it will be to water the honeysuckle plants and carry out weeding.
- Based on the fact that the variety is pollinated by wind and insects, it is necessary to place the honeysuckle plantation in relatively ventilated areas with a large number of wild and cultivated bees.
- Groundwater and melted spring water should not flood the surface of the site, even for a short time. Therefore, the optimal depth of groundwater is 3-3.5 m.
- To increase the number of berries set on a bush, you need to grow this variety at a distance of 45-50 m from other varieties of honeysuckle.
- It is very important that at a depth of up to 40 cm, the fertile layer of soil is not inhabited by such evil pests as the larva of the cockchafer, wireworms and false wireworms.
- Sunlight is very important for producing large honeysuckle berries. Insufficient lighting does not stop the growth of plant shoots, but leads to a decrease in the number and weight of berries.
Bush propagation
The variety is propagated using rooted cuttings and annual seedlings. High-quality honeysuckle planting material has the following characteristics:
- Annual plants take root the fastest.
- The height of plants should not exceed 1.5 m.
- The seedling must be healthy and free from fungal diseases and various pests.
- The root system should be very branched with a large number of small roots.
Landing time and method
The best time to plant seedlings is early September - mid-October. Planting is carried out as follows:
- A few weeks before planting, planting holes measuring 45 x 45 x 40 cm are dug using a bayonet shovel. The holes are dug so that the distance between the honeysuckle bushes in the row is 1.5-1.7 m. In this case, the distance between the rows should be from 2 to 2.5 m.
- 4-5.5 kg are placed in each pit. rotted manure and 75-80 g of superphosphate.
- To increase the amount of moisture in the soil, fill the fertilized planting hole with 8.5-10 liters. water.
- After waiting for the water to be absorbed, place the seedling in the middle of the hole and cover the roots with loose, fertile soil. There is no need to plant seedlings very deeply. The root collar can be no more than 5 cm below the ground surface.
- A furrow is made around the planted plant, and an additional 5-7 liters are poured into it. water.
- To preserve moisture and protect seedlings from weeds, the soil around the plants is mulched with straw, sawdust and dry peat.
Watering plants
Honeysuckle needs sufficient moisture especially during flowering and fruit growth. Lack of moisture leads to a sharp inhibition of shoot growth, a decrease in the number of flowers and ripe berries. Therefore, the variety needs timely watering, which is carried out in the following order:
- From the moment of autumn planting of planting material until the onset of the first frost, the plants are watered twice a week. It is enough to spend 9-12 liters on one honeysuckle plant. water.
- With the beginning of spring and the air temperature rising to + 10 degrees, watering should be done once a week with a norm of 15 liters. per plant.
- During the hottest period of summer (June - July), honeysuckle bushes need to be watered at least twice a week. At the same time, the watering rate increases to 18-20 liters. for one honeysuckle bush.
- From August to early September, it is enough to water the plants once for a week. In this case, the watering rate is 15-17 liters. per plant.
- Throughout the fall, honeysuckle is watered abundantly, but rarely. Therefore, it is advisable to water once a month with 20-23 liters. on the bush.
This irrigation scheme helps to provide honeysuckle plants with the necessary volume of irrigation water throughout the entire growing season.
Top dressing
The Bakcharskaya honeysuckle variety needs to be fed with the necessary nutrients to increase the number of shoots, size and number of berries:
- Before the buds begin to open, there is an urgent need to feed honeysuckle with ammonium nitrate. To do this, saltpeter is evenly scattered on the soil surface around the bushes and between rows in a dose of 33-37 g per 1 sq. m. m. In this case, it is very important that the soil surface is moist, which would facilitate the rapid dissolution of the applied fertilizer.
- In early April, honeysuckle bushes are fertilized with liquid mullein, which dissolves in water at the rate of 1-1.5 liters. fertilizers for 12-14 l. water. The solution prepared in this way is used to fertilize the soil around the honeysuckle bushes in a dose of 4.5-5 liters. per 1 sq. m.
- In order for the bushes to form a larger number of flower stalks, it is recommended to spray them with Vympel at a rate of 12-13 ml. for 7-8.5 l. water. This treatment will provide the plant with the necessary amount of microelements and helps to increase flowers and berries by 17-20%.
- During the period of formation and growth of honeysuckle fruits, it is necessary to fertilize the soil between the rows with a solution of chicken manure (1 liter of manure per 13-14 liters of water). For 1 sq. m. add 3.5-4 liters. the above solution.
Bush pruning
To create the best conditions for the growth and development of Bakcharskaya honeysuckle, proper pruning must be carried out in early spring:
- The outer shoots are shortened by 1/3 for better illumination of the central part of the plant crown.
- Dried and broken shoots will be completely removed.
- Frostbitten shoots are shortened to the first healthy bud.
- Cut out the above-ground parts of honeysuckle that are infested with pests or have signs of fungal diseases.
- The tops of annual shoots should not be shortened, since the main part of the flower buds are located on them.
- Unproductive shoots are systematically removed.
- For bushes older than 15 years, it is recommended to carry out anti-aging pruning.
Loosening the soil
In order for the root system to receive the required amount of oxygen and soil moisture, the surface of the site must be maintained in a loose state. This structure of the soil surface helps retain moisture and makes it possible to effectively fight weeds. The depth of soil loosening should be from 2 to 5 cm and should be carried out when the first weeds emerge and the soil surface begins to crack.
Disease Control
The variety can be affected by the following diseases:
Cercospora blight. Dirty green spots appear on the leaves. Subsequently, these spots acquire a light brown color. After some time, such leaves begin to dry out and crumble. The causative agent of this disease is the fungus Cercospora libicola. Control measures:
- Collect and burn diseased leaves.
- Sanitary pruning of honeysuckle shoots for better ventilation of the crown.
- Fertilizing honeysuckle plants with nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers.
- Before the buds begin to open, the plants are sprayed with the fungicide Cuprozan.
Tubercularosis. Honeysuckle bushes infected with this disease begin to dry out in early June. Shoots affected by the disease are covered with red-brown tubercles, which inside contain mature spores of the fungus - the causative agent. Control measures:
- Removing shoots affected by cercosporiosis using pruning shears.
- After flowering, honeysuckle is sprayed with Bordeaux mixture.
Powdery mildew. A sign of the disease is the presence of a white cobweb-like coating on the shoots and leaves of honeysuckle. Young shoots are the first to be affected, and later the disease affects all above-ground parts of the plant. Leaves affected by powdery mildew turn brown, dry out and fall off. Young infected shoots become deformed and their bark dries out. Control measures:
- Destruction of disease-infected leaves and shoots.
- Spraying honeysuckle bushes with the fungicide Oxyx.
Pest Control
The greatest damage to honeysuckle is caused by aphids and honeysuckle flies.
Aphids are located on the lower part of the leaves of young shoots. This pest multiplies quickly and can create entire colonies in a short time. Aphids feed on cell sap and, when shoots are heavily populated, cause leaves to curl. An effective way to combat aphids is to spray the shoots with insecticides BI-58 N and Komandor.
The honeysuckle moth causes damage during the caterpillar phase. This caterpillar is gray in color. The pest eats away the middle of the ovary along with the pulp and seeds. To combat it, insecticides Karbofos, Komandor or BI-58 N are used.
Plant propagation
To preserve certain properties, the variety must be propagated only vegetatively and using the following methods:
By dividing the bush:
- They dig up the bush and remove its root system from the soil.
- Using a shovel or wooden stake, divide the root system into several parts.
- The separated parts are planted in new areas for further cultivation.
Horizontal layering:
- Select a young, well-developed shoot from a honeysuckle bush.
- The tip of the shoot is placed in a furrow near the bush and sprinkled with fertile soil. To better fix the future cutting, a peg is driven into the soil near the top of the shoot and tied to it.
- The soil, which is located above the top of the shoot, must be constantly moist and free of weeds.
- When the top of the shoot, sprinkled with soil, has formed its root system, you can begin to separate it from the mother bush and transplant it to a new growing location.
By cuttings:
- From healthy shoots in the fall, cuttings up to 20-23 cm long are cut with at least 2-3 live buds.
- During the fall, these cuttings are kept in a moist sandy substrate.
- In spring, cuttings are planted in pre-prepared trenches 25-30 cm deep and 35-40 cm wide.
- During spring and summer, the cuttings are cared for, which consists of timely watering, fertilizing and weeding.
- As soon as primary roots appear on the cuttings, you can begin to transplant them to a permanent new growing location.
Harvesting
The first honeysuckle berries can be collected in early May. The entire cleaning process is recommended to be carried out based on the following recommendations:
- Due to the fact that the berry picking period is extended and can last more than two weeks, fruit harvesting should be regular at intervals of 2-3 days.
- Fruit collection is carried out only in dry weather without the presence of rain moisture or dew on the surface of the fruit.
- Only fully ripened berries without signs of rotting or the presence of fungal plaque can be harvested.
- It should be remembered that ripe honeysuckle berries tend to crumble. Therefore, delays in picking berries are unacceptable.
- The collected berries are sorted by size and placed in dried wooden plastic boxes or crates. The layer of honeysuckle fruits should not be more than 20 - 25 cm.
Preparing for winter
For better overwintering and replenishment of the amount of nutrients that went into the formation of the crop, it is necessary to carry out the following preventive measures after the end of berry picking:
- Sanitary autumn pruning of dried, broken shoots, affected by diseases or pests.
- Feeding honeysuckle bushes with chicken droppings (diluted with water in a ratio of 1:13) in a dose of 5-6 liters. for one bush.
- Controlling weeds and creating a loose layer on the soil surface.
- If necessary, spraying the aerial parts of honeysuckle in order to combat various diseases and pests of this crop.
Care
Proper care of honeysuckle variety Bakcharsky giant includes the following procedures:
- Watering. It must be in a suitable volume, since a lack of moisture deteriorates the quality of the berries and their taste, bitterness appears, and if there is excess, the roots can begin to rot. The recommended volume is 10 liters, which are poured in several portions. In autumn, watering is reduced to a minimum.
- Recharge. This variety requires nitrogen fertilizers in the spring - it is advisable to apply them before the leaves appear. The application of ammonium nitrate worked well - about 15 g per bush. In summer, an aqueous solution of nitrophoska of 25 g per 10 liters is suitable. In the fall, you can fertilize the soil with organic matter - a mixture of 100 g of wood ash and 5 kg of compost works well.
- Loosening. During each watering, it is necessary to thoroughly loosen the soil to ensure good air access to the roots.
Diseases
Honeysuckle in general is characterized by attacks from the following pests:
- scale insects;
- caterpillars;
- aphids;
- ticks.
But the Bakchar giant is a variety resistant to all diseases. Therefore, thorough measures and large dosages are not required; as a preventative measure, plants can be sprayed with Inta-Vir, Eleksar, Rogor, Confidor, Actellik, Mavrik, Tedion.
Honeysuckle Bakcharskaya is a very convenient and practical species. Its cultivation is especially beneficial in the northern regions, because this variety is specially adapted for such conditions. Follow the growing rules and enjoy beautiful plants and a rich harvest of valuable fruits.
Publication date: The best varieties
Growing
Only young plants need careful care in the first year after planting. An adult, well-rooted, healthy honeysuckle requires almost no attention from its owners.
Caring for a young plant
During the first months, honeysuckle needs to be watered regularly, the soil should be loosened for better oxygen supply to the roots, and weeds should be pulled out. It does not need regular feeding for the first three years if fertilizers were added during planting.
Honeysuckle grows slowly at first. First of all, it develops the root system, and then the above-ground part. The Bakcharskaya Yubileinaya variety differs from others in its early fruiting, so this period is reduced to 1-2 years.
At the beginning of autumn, sanitary pruning is carried out - all dry, broken and thickening branches of the bush are removed.
Caring for an adult plant
Starting from the third year, honeysuckle begins to bear fruit and needs additional feeding. In early spring, literally in the snow, nitrogen fertilizers are applied to each bush. At the end of summer, a liter jar of ash and a bucket of organic matter are embedded in the soil.
Further care consists of weeding, loosening tree trunk circles to a depth of 5-8 cm and periodic watering during dry periods.
Pruning and wintering
Until 15 years of age, honeysuckle is not pruned at all; it is limited to removing broken, dry, downward growing and thickening branches. Then the bushes are thinned out, cutting off the oldest branches at the base. At the age of 20 years, honeysuckle begins to age - while maintaining agricultural technology, the yield decreases. You can rejuvenate the bush by cutting it completely at a height of about 15 cm above ground level; next year it will recover and bear fruit for up to 10 years.
The Bakcharskaya Yubileinaya variety was created at an experimental station located in the Tomsk region. It tolerates temperatures lower than minus 50 degrees and does not need shelter.
Reproduction methods
Honeysuckle is not cheap; amateur gardeners can propagate it in one of the following ways:
- seeds;
- green or woody cuttings;
- layering;
- dividing the bush.
The most reliable way for non-specialists is to bury low-lying branches or divide a young, well-grown bush.