Honeysuckle Morena is a young berry crop that combines the qualities of an ornamental plant for open ground, as well as a source of tasty and healthy fruits. Such features have made the variety in demand among gardeners and summer residents, which is why it is increasingly found in personal plots.
Main characteristics
The hybrid variety is the result of breeding work at the St. Petersburg Research Center named after Vavilov. Elite varieties of honeysuckle, including the Kamchatka form, were used as mother plants, in light of which the new plant became characterized by high levels of winter hardiness. Today it can be grown everywhere, including the northern regions.
The name of the variety translated from Spanish means dark; in addition to the official name, the berry is sometimes called “The Little Mermaid”. The hybrid inherited from its mother forms not only frost resistance, but also its impressive size - the bush can reach 150-170 cm in height, with a similar width.
It is highly decorative, so it is often used as a hedge for single plantings in the garden. The crown of the crop has an oval and squat shape. The foliage is large, rich green in color, the shoots are quite flexible, curved, covered with brown bark.
Despite the fact that the berry can take its rightful place in the landscape design of the garden, most often it is cultivated for harvest. The hybrid is an early ripening one, so the first ripened fruits in the northern regions can be expected by mid-to-late June; in the south, the ripening period will occur several weeks earlier. Fruiting continues until September; some bushes are capable of bearing fruit until early October.
Honeysuckle Morena is large-fruited, the size of its berries reaches at least 3 cm in length with a diameter of 1.1-1.2 cm, the fruits are fleshy inside, and there is no bitterness in the taste. Their color will be blue, with a waxy coating, and their shape will be elongated. Weight varies from 1.5 to 3 g. The berries do not fall off and can remain on the branches for a long time.
Productivity directly depends on the place of cultivation and climatic conditions. Averages vary between 1.5-2.5 km of edible berries. The ability to bear fruit is inherent in crops from the age of two. Fruit ripening occurs every season.
Inherited winter hardiness allows the variety to remain viable even when the temperature drops to -40C. Flowers can withstand spring frosts down to -6C-7C.
In addition to frost resistance, the hybrid is distinguished by its durability; as a rule, the bushes of the variety are capable of bearing fruit for up to 20-25 years.
Description of the variety
Honeysuckle Morena was created by the Pavlovsk Institute of Genetic Resources named after. Vavilov from the species Kamchatka and Turchaninova. In 1995, it was accepted by the State Register and recommended for cultivation in all regions.
Specifications
The Moraine bush is oval and can grow 1.7 m in height. The shoots are thick, brown-green, with large green leaves, and form a loose crown. When planted in autumn and under favorable conditions, moraine can give an increase of 20 cm in the first spring.
The berries are one-dimensional, blue, and appear blue due to a waxy coating. Their shape resembles an elongated jug, and their weight is 1.0-1.2 g. The average yield of the Morena variety is 53 c/ha, up to 1.9 kg of berries are harvested from a bush.
The tasting rating of this honeysuckle is 4.5 points. The taste of Morena berries is sweet and sour, without bitterness, the pulp is tender, with a slight aroma. The variety is considered dessert, non-shattering, and in terms of ripening it is classified as mid-early.
Pollinators
Honeysuckle Morena is self-sterile. If there are no other varieties on the site, even after abundant flowering and timely pollination by bees and bumblebees, the bush will produce few berries. True, their number will be slightly greater than that of other honeysuckles under similar conditions, but this cannot be called a harvest.
Recommended pollinators for Morena are the Blue Spindle and Viola varieties.
Advantages and disadvantages
Morena has difficulty competing with the newer varieties of edible honeysuckle, but it is considered reliable and suitable for growing in all regions. The advantages include:
- Stability of fruiting.
- High winter hardiness.
- Non-shattering and large-fruited.
- Increased resistance of the variety to aphids.
- Low demands on growing conditions.
- Winter hardiness of the Morena variety.
- Good dessert taste without bitterness.
- The Morena variety is recommended for cultivation in all regions.
- High content of nutrients in berries.
Morena's flaws could include insufficient large fruit and imperfect taste, but do not forget that the variety is already more than 20 years old. At one time he was a real breakthrough. The Morena variety is self-fertile, but this is also characteristic of other edible honeysuckle.
Pollinators
Despite the many advantages of a hybrid crop, it is a self-sterile form, so it will not be able to bear fruit without pollinators growing nearby. For good annual yields, the gardener will need to root nearby honeysuckle varieties with a similar flowering period. Recommended neighbors will be:
- Amphora;
- Viola;
- Blue spindle;
- Kamchadalka, etc.
Amphora
Viola
Blue spindle
Kamchadalka
Pollinators should be planted on the windward side. There can be two landing schemes:
- Group - involves rooting plants near hybrid crops at a short distance.
- Alternation - when pollinators are planted directly between Moraine bushes.
Reviews from gardeners who have previously grown
According to reviews from gardeners involved in growing honeysuckle, Morena is one of its best varieties, suitable for cultivation in almost all regions of the country. The main advantage of Morena is its ability to produce a harvest of delicious sweet berries even under unfavorable weather conditions.
Despite the average yield, almost none of those who grow Morena are going to replace it with other, more productive varieties. Firstly, Morena is an excellent pollinator, and secondly, its stability in fruiting is captivating.
Considering the long productive life of Morena bushes, we can accurately predict that Morena will grow and bear fruit in our gardens for at least another quarter of a century. But I would venture to suggest that this period will be at least 1.5-2 times longer.
Breeders rarely manage to grow varieties like Morena. And until a replacement appears, Morena will delight us with both its unique beauty and its delicious fruits.
Selection of planting material
If you plan to plant a new plant in the garden, then it is better to purchase young seedlings from official representatives of berry nurseries.
When choosing a suitable seedling, you should pay attention to the following nuances:
- shoots must be elastic, with equal internodes;
- slight peeling is allowed on the bark;
- there should be no mold or rot on the root system;
- shoots should not be shortened.
Planting honeysuckle in open ground
Honeysuckle Morena does not require special planting and growing conditions. The main requirements for choosing planting material are a good root system and no signs of disease. In a temperate climate, the bush develops actively, but in hot and humid climates it may not grow to the usual varietal size.
How to choose a honeysuckle seedling for planting
Pay special attention to the choice of planting material. Because, even with very high-quality agricultural technology, a weak and infected bush will constantly get sick and produce little yield.
First of all, pay attention to the type of root system: open or closed. In the first case, the plant takes root more difficult and longer. A closed root system allows the bush to quickly adapt to environmental conditions. Honeysuckle is sold immediately in special pots with a lump of earth, with which it is planted in a permanent place of growth.
Also, the seedling must be free of signs of disease and pest damage. The root system is developed, but there should be little foliage and shoots, but the internodes are evenly distributed. The branches should be elastic and bend well.
Always purchase planting material from trusted nurseries or garden stores.
Where is the best place to plant honeysuckle on the site?
A lot also depends on the planting location, so plant the bush in a sunny place. But it should be slightly darkened and protected from drafts. In such a cozy place, honeysuckle will actively grow and bear fruit. It can also be planted near gazebos, along a fence or at home. The main thing is that the bush should be exposed to the sun most of the day, and at noon it should be protected from scorching rays.
Make sure that groundwater lies at a depth of at least 1.5-2 meters. Honeysuckle does not tolerate waterlogging and high humidity in spring and after rain.
As for soils, Morena prefers to grow in low acidic or neutral soils. They should be loose, breathable and nutritious. In general, the plant will grow in other types of soil, but this may affect the yield. To reduce acidity, add dolomite flour or limestone to the soil.
At what distance to plant honeysuckle
Morena grows as a bush with a dome-shaped crown. Its height is usually about 2 meters. To prevent plants from interfering with each other, they should be planted at a distance of 2-3 meters. Morena can be placed next to tall trees at a distance of up to 5 meters so that the root systems do not interfere with each other. Larger crops will provide shade and protect the bush from scorching rays.
There is no special planting scheme; each gardener decides on his own how to place honeysuckle bushes and other crops on his site. As for planting, the process is no different from other varieties of honeysuckle. The bush is planted in a hole 0.5 x 0.5 m in size and 0.6 m deep. If the soil is too acidic, then it is deoxidized with dolomite flour or lime. You can also add 50 g of phosphorus and potassium each to improve the growth of the seedling. Organic matter and ash will also help.
The best time to plant honeysuckle is autumn, when the plant is dormant. This is usually done in October, but the exact date depends on the growing region. In spring, the plant enters the active phase of growth and development very early, even before the snow has completely melted.
Choosing a place for rooting
For honeysuckle, it is worth selecting well-lit areas of the garden, since in shaded areas the yield will be sharply reduced.
It would be more correct to root it on the plain; it is recommended to avoid depressions and hollows in order to prevent stagnation of moisture in the soil, which will lead to rotting of the root system.
The variety can be planted at a distance of 4-5 meters from fences, buildings, tall trees on the site.
How to plant edible varieties of honeysuckle in the country?
Choosing a planting site for honeysuckle
The winter hardiness of blue honeysuckle is very high. The vegetative mass can withstand frosts down to -50°C, and the roots up to -40°C. Buds, flowers and young ovaries do not lose viability at -8°C. At the same time, it is better to place honeysuckle bushes in sunny areas, orient the rows so that most of the daylight hours the plants are illuminated by the sun.
Blue honeysuckle will grow in the shade, but the yield and taste of the fruit will decrease. The crop is not afraid of winds, so in an open sunny area it can be planted on the north side.
Honeysuckle is a cross-pollinated crop, so it is better to plant 3-4 different varieties nearby, coinciding in the flowering period.
The relationship of honeysuckle to soil conditions
The root system of honeysuckle cannot tolerate stagnant water close to the soil surface. The roots rot and die. At the same time, honeysuckle is moisture-loving and needs watering. Does well in regions with high air humidity. In acidic soils it slowly dies.
The best soils for honeysuckle are loams filled with humus or mature compost. It grows well in other soils, but requires sufficient addition of organic fertilizers.
Period of planting honeysuckle in the ground
Purchased or rooted honeysuckle seedlings are planted from August to mid-November. This is due to the early onset of the dormant period (late July) and early awakening for the next growing season (March). In some regions with the early onset of a snowless spring period, honeysuckle seedlings can be planted by transshipment in the spring, in early March. But starting from March 10-15, it’s better not to take risks.
In the second half of March, the dormant period of honeysuckle ends. The buds begin to swell and any actions with transplantation or planting will cause stress. The plants will begin to get sick and take root poorly. If the plot is small and there is no free space, you can plant honeysuckle next to black currants in the berry garden.
Planting edible honeysuckle
Planting honeysuckle
Planting holes for honeysuckle are dug according to the size of the root, but not less than 40x40x40 cm. This is especially necessary on sandy and depleted soils. Drainage is placed at the bottom of the pit, part of the prepared soil mixture is poured on top of it, consisting of the top layer of soil, 2 buckets of humus or compost, add 1 liter jar of ash and 60-70 g of superphosphate. Ash can be replaced with a 0.5 liter jar of dolomite or chalk. Instead of superphosphate, you can add ammophos in the same dose.
The soil mixture in the hole is filled with a bucket of water. A honeysuckle seedling is placed on a mound in the center, the roots are straightened and covered with the rest of the soil mixture, lightly crushed so that the soil adheres to the roots. A side is prepared along the edge of the planting hole (its circumference), another bucket of water is poured in, and after absorption, mulch with humus. When planting, the root collar of honeysuckle does not need to be buried. She does not form offspring. If it is deepened by 4-5 cm (no more), then adventitious roots will begin to form from the root collar downwards.
Landing rules
The rooting algorithm involves performing the following work.
- A few weeks before the expected date of planting the seedlings, the gardener needs to prepare the planting holes. The optimal size of the pits will be 45x45x40 centimeters. When planting in groups, the distance between bushes should be at least 2 meters.
- It is necessary to add nutrients to the planting hole that will provide the seedling with the necessary microelements for rapid adaptation. For one plant you will need 3-4 kilograms of rotted manure, 20 grams of potassium chloride, 45 grams of nitroammophosphate. In order for the fertilizers to dissolve better, one bucket of water should be poured into the planting hole.
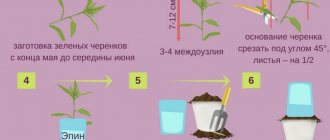
- Before planting, the shoots and ends of the root system should be shortened by 2-3 centimeters. Immerse in a container of water for a day. If necessary, you can add a growth stimulator to the liquid.
- After the soil has absorbed all the liquid, the young bush needs to be placed in the center of the hole, straighten the roots, sprinkle earth on top, and tamp it down.
- Then the plant is watered, and the trunk circle is covered with a layer of organic mulch.
Harvest dates and rules
Honeysuckle has a very short harvest period. Although Morena is characterized by low shedding, its berries will not hang on the branches all summer. The harvest can be harvested in 2-3 doses, visiting the bush every other day. Fresh berries cannot be stored for a long time - maximum 2-3 days in the refrigerator.
Honeysuckle fruits are good to eat fresh. Many people like to grind them with sugar and mix them with milk; they can be added to cocktails and fruit drinks. Jam made from this berry has a bright, memorable taste. Moraine can be frozen; after thawing, it does not flow and retains its shape. Dried berries are also added to tea.
Honeysuckle fruits are rich in pectin and tannins, organic acids and sugars. They contain magnesium, iron, iodine, copper, phosphorus, potassium, silicon, zinc, sodium and calcium. In folk medicine, honeysuckle is used for diseases of the stomach, intestines, liver, kidneys, and hypertension.
Harvest processing and storage
Morena, along with such edible varieties as Sinichka and Tomichka, is recognized as one of the best varieties of honeysuckle. Unfortunately, it has a very short harvest period. Although this variety is characterized as not prone to shedding, the berries cannot hang on it all summer. If you collect every other day, then in 2 or 3 doses you can remove all the berries. When fresh in the refrigerator, they are stored for a maximum of 3 days, but it is in this form that they contain the greatest amount of nutrients and microelements.
Fresh honeysuckle variety Morena can be consumed as follows:
- grind the berries with sugar;
- mix with milk;
- prepare fruit drink or cocktail;
- make jam;
- freeze in the freezer;
- dry.
Morena honeysuckle jam has a bright and memorable taste. They can not only pamper your family, but also surprise your guests. These berries contain a lot of tannins, sugars and organic acids. Honeysuckle is widely used in folk medicine due to its chemical composition.
Aftercare
Further agricultural technology concerns the following work.
Watering. An adult crop does not need frequent moisture, so natural precipitation will be enough for it. Plants are watered only during a prolonged absence of rain, as well as during the fruit-filling period and after harvesting.
In the first season, young seedlings are watered twice a week until the first frost arrives. In the next season, it is allowed to water once a week, increasing the volume of liquid introduced in the summer. From August to October, the crop can be watered once every 2 weeks.
Fertilizer. After planting, additional fertilizing will be required for fruit-bearing bushes in the third year of their life. Additional nutrition in the form of important microelements is carried out in 4 stages.
- At the beginning of the growing season after the snow has melted on the site. At this time, it is necessary to scatter nitrogen fertilizer in the root zone, which will have a positive effect on the growth of green mass and shoots.
- During the flower formation phase, root fertilizer is applied with humus and compost in liquid form.
- In the fall, after picking the berries, fertilizing is carried out with complex compounds, including nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus.
- Before wintering, the crop will require potassium-phosphorus fertilizers. This can be wood ash and superphosphate.
Trimming. Work related to the formation of bushes begins at the age of three. The gardener's task will be to remove damaged or diseased branches in the fall or spring, before the buds begin to bloom.
An adult crop, which will be more than 7 years old, needs to trim 2-3 old shoots, which will stimulate it to form young branches.
Bushes older than 20 years must be completely pruned in the fall; shoots no more than 20 centimeters long must be left on them. This haircut will help them rejuvenate and bear fruit for at least another 5 years.
Harvesting. Berries are collected in several approaches, depending on their ripening. The fruits are suitable for fresh consumption and contain a large number of useful microelements. The berries are also well stored in the cold and can be heat treated.
Agricultural technology
Because of its unpretentiousness, honeysuckle is suitable for cultivation by beginning gardeners.
Planting and caring for the plant are not particularly difficult. Important! The best place to plant honeysuckle is a slightly shaded area with diffused sunlight.
Selecting a location
Moraine can grow well even in poor soil with less than favorable conditions. But for the best harvest, you should choose an area with good lighting and no strong winds. It is better to choose a place away from the accumulation of underground groundwater, otherwise the root system of the plant may rot.
Planting and care
It is better to plant Morena in August-September or early spring, before buds begin to appear and swell on the plants. For planting, it is advisable to use a two to three year old seedling and adhere to the following work algorithm:
- Prepare a hole with a depth and diameter of about 50 cm. The distance between bushes in a row should be maintained at 2 m, and the same amount of free space should be left between the rows.
- Add 1 bucket of compost and humus to each hole, add 100 g of double superphosphate and 30 g of potassium sulfate.
- In the center of the hole, form a mound of soil, place a seedling on it, and carefully straighten its roots. Fill the hole with soil so that the root collar of the seedling is deepened by about 3 cm.
- It is good to compact the soil around the seedling, water it with a bucket of water and mulch it.
Morena should be watered only in dry and sunny weather, during the fruiting period, at the rate of 1–1.5 buckets of water per 1 bush. As for feeding, in the first 3 years of the bush’s growth, it only needs fertilizers added during planting. After this period, the bushes are fed in the spring, before the buds open, with ammonium nitrate at the rate of 15 g per 1 m² of area.
Please note what are the reasons for poor fruiting of edible honeysuckle.
Disease and pest control
In terms of disease resistance, Morena's Kamchatka roots allow it not to be afraid of the vast majority of infections that regularly affect other plants. One of the few diseases that can plague the bush is rust. It appears as a result of insufficient watering or poor feeding.
In this case, the Morena bushes need to be sprayed with Alto, Topaz or Folikur fungicides. It is recommended to carry out the treatment itself after harvesting or before ovaries begin to form on the bushes. Among the pests, Morena can be attacked by aphids, spider mites and whiteflies. The spraying preparations Actellik and Rogor are best suited to combat them.
Pruning and crown formation
In the first 4 years of ripening, it is extremely undesirable to touch the Morena bush in terms of pruning. This can lead to slower growth and poorer yields. Honeysuckle is not prone to dense vegetation and takes its spherical shape on its own, without the intervention of a gardener. After the 4-year period, it is recommended to carry out only sanitary pruning, removing old and diseased shoots and making room for new young growth.
Do not cut young branches under any circumstances! They are the basis for fruiting.
Features of pollination
The large-fruited Morena does not have the ability to self-pollinate, so other varieties of honeysuckle must be planted in the same area with it, which will become its pollinators. There are many such varieties: Blue Spindle, Amphora, Nymph, Blue Bird. For better pollination, they need to be planted on the windward side.
Frost resistance and wintering
Since honeysuckle itself is a frost-resistant crop, Morena in this regard does not require additional shelter for the winter. Even at a temperature of -30°C, you don’t have to worry about insulating the bush.
Did you know? In folk medicine, all parts of the plant are used, not just the fruits. Honeysuckle is used for the prevention and treatment of hypertension, indigestion, malaria, bleeding, etc.
Reproduction
The Morena variety can be propagated in several ways.
Dividing the bush. To independently obtain a new crop, you need to dig it out from the side where there are a large number of young shoots, separate the part with the root system and several branches. The resulting plant can be immediately rooted in the chosen place in the garden.
Layering method. You need to select a healthy young branch from the side of the plant, bend it to the ground, place it in a shallow groove, sprinkle it with soil, and you can additionally secure it with wire. After the roots have formed in the lower part, the cuttings should be separated from the mother bush and rooted in the garden.
The hybrid variety cannot be propagated by seeds and cuttings, since the seeds do not retain varietal characteristics, and the cuttings have an extremely low survival rate.
History of selection
The mysterious name of the Morena variety is interpreted in different ways. According to myths, this was the name of Kashchei’s wife and the goddess of death. Geologists use this term to refer to a cluster of rocks formed by the movement of ice. In Spanish this word is translated as brunette or dark-skinned.
The word "morena" has several meanings. In geology, this is the name given to a chaotic accumulation of stones formed as a result of the movement of ice. In Slavic mythology, Morena is the goddess of winter, illness, death, and the wife of Koshchei. And from Spanish morena is translated as dark-haired, brunette, dark-skinned. By the way, the second name of Morena honeysuckle is Little Mermaid.
Honeysuckle with the mysterious name Morena was bred at the end of the last century and is of Russian origin. The seedlings met the breeders' expectations: in cold climates, the bushes developed well and bore large berries with a dessert taste. Having passed variety trials, Morena spread to private gardens and stayed in them for a long time.
Honeysuckle variety Morena demonstrates increased cold resistance and excellent taste of the berries
Diseases
Honeysuckle Morena is immune to many diseases and rarely suffers from attacks by insect pests. But some climatic features, as well as errors regarding agricultural technology, can provoke the development of the following diseases.
Rust. Signs will be copper pustules on the leaves with powder inside. Treatment is carried out using store-bought formulations for treating the aerial parts. Poliram, Abiga-Pik, and Cumulus demonstrate high efficiency.
Powdery mildew. Signs of the disease are white spots covering the shoots and leaves. To overcome the disease, you can use Fundazim, Quadris, Topaz, Topsin-M.
Rust
Powdery mildew
Treatment of honeysuckle is carried out only after the ovaries appear in the spring or after picking the berries. If the fungus spreads strongly during the ripening period, treatment with biological fungicides, for example, “Gamair” or “Fitospirin” is allowed.
Problems during cultivation
Honeysuckle variety Morena is resistant to aphid attacks, but leaf roller butterflies and scale insects can annoy the plant. To neutralize them, insecticides or biological products are used. There should be 2-3 treatments, with an interval of 10-14 days. During the ripening of berries and harvesting, it is better to use only biological preparations or folk remedies.
Of the diseases, honeysuckle is most often affected by powdery mildew. This fungus appears as a whitish coating on the leaves. They fight powdery mildew with fungicides or Fitosporin.
Pests
The following insects pose a danger to the plant.
Aphid. The presence of pests is manifested by drying out of the leaves, the bush turns brown. The insect can be seen with the naked eye. Pests are destroyed by spraying the above-ground parts with Confidor or Actellik.
Spider mite. The pest settles on the underside of the leaf, so at first it remains hidden from the gardener. However, small white dots can be found on the top of the plate where the insect is attached.
When the tick moves to the surface of the green mass, it becomes covered with a white cobweb. It will be possible to destroy the insect with store-bought insecticidal compounds, for example, “Fitover” or “Aktofit”; folk remedies – spraying with a solution of laundry soap – will also be effective.
Leaf butterfly. Caterpillars that feed on its juice will be dangerous for honeysuckle. Signs of the presence of pests will be curled dry leaves covered with cobwebs. The fight against it is carried out with “Dimilin” or “Fitoverm”.
Shield. The pest is extremely rare on the plant and affects shoots under the bark. Signs of the presence of an insect will be bulges on the branches in the form of a comma. It will be possible to destroy the dangerous pest by treating the aboveground part with Fitoverm.
Aphid
Spider mite
Leaf roller butterfly
Shchitovka
During the period of fruit ripening, pests can be controlled only with folk remedies or biological products.
Review: Honeysuckle Gardens of Russia “Morena” - The first and long-awaited vitamin berries.
Good afternoon, everyone! Finally, the time has come for the first garden berries to ripen. And these berries are honeysuckle. I have five bushes growing. The very first, and now the largest bush, was planted in 2008. I don’t know what the variety is called, it’s a gift variety. By bending one of the branches, I got another bush of this variety. It's a smaller size for me. The third bush was given to me again. His former owner constantly trimmed the top of his head with a trimmer, and now I have him in a creeping shape. I bought another bush at the market, supposedly the Blue Spindle variety. But, as it turned out later, the bush turned out to be wild with small and bitter berries. I keep it not for its berries, of which there are very few, but as an additional pollinator. But I want to tell you in detail about the fifth bush. Previously, I wrote a review about (Russia, Shibanovo), with which I had some relations. It was there, in 2010, that I purchased a honeysuckle seedling of the “Morena” variety. I was attracted by the very good characteristics of the variety. Here are some of them: 1. Very early ripening of berries. Indeed, it is so. Of my four varieties, the first berries ripened on the third of June on the Morena bush. 2. Harmonious ripening of berries. Almost all the berries were ripe on June 8th. Since the bush is not large, we didn’t collect many berries from it, less than a liter mayonnaise bucket. There are only a few berries left on the bush, only on the lower branches.
3. Large berries. That’s right, the berries are large. Many are 3 cm long.
4. Berries are without bitterness and sweet. Of my four varieties, Morena berries are the sweetest. In terms of taste, I would compare them to blueberries. Other varieties have a sweet and sour taste. 5. Dry picking of berries. Yes, the berries come off easily and without leaking juice. I also like that the berries do not fall off spontaneously. Overripe ones, of course, may fall, but not a significant amount. There are varieties that involve harvesting by shaking off the bush. To do this, you need to put some material under the bush. Now about the seedling that I received from Gardens of Russia. I placed an order for autumn delivery. The seedling was very small. Compared to the currant seedling that I received along with honeysuckle, it was simply a dwarf. Having planted it in the fall, they began to wait in the spring to see if such a little thing would take root? Fortunately for us, the seedling took root, but the growth of branches every year was not large. This is what the bush looks like this year (which is lower).
The crown of the bush grows mainly in width, the structure of the bush is loose, the branches are thin and drooping.
I prefer pyramid-shaped bushes with strong branches looking up. When you look at a transparent bush with berries, it seems that it is strewn with them. In fact, there are not so many of them yet. My bushes are not spoiled with any special care. Sometimes I throw some mineral water under the bushes, it starts to rain. True, this year a bucket of manure humus was poured under all the garden shrubs in the spring. I think the plants are happy. Two days ago, we already collected 7 liters of berries from four of our honeysuckle bushes. Well, this is a photo of all my honeysuckle bushes.
During the ripening period, the bushes have to be protected from birds. Still can’t get around to buying a net. I remember her when the time comes. So we have to use the means at hand. I won’t write about the usefulness of honeysuckle berries; there is enough information on the Internet. I’ll summarize. I give the honeysuckle variety “Morena” from the Gardens of Russia a five-star rating.