Pumpkin is a real find. It contains a large amount of useful minerals and vitamins not only in the juicy pulp, but also in the seeds. Oil is prepared from the seeds, which has good anti-inflammatory and restorative properties. You can prepare a wide variety of dishes from pumpkin: children's cream soup, pie, salad, porridge and much more.
Having decided to grow this vegetable on their plot, gardeners ask themselves several questions: is it possible to plant pumpkin and zucchini together? Failure to comply with neighborhood rules can lead to loss of crop yields.
What vegetables does pumpkin go with?
Open ground and light areas with well-fertilized sandy loam soil are suitable for growing pumpkins. The plant loves feeding with potassium, phosphorus fertilizers, manure and compost. The seeds are soaked in water until they germinate, then placed in pots. Seedlings require moderate watering. It is grown until 3 true leaves appear, then planted in a permanent place.
Should I diversify one bed?
Pumpkin is cross pollinated. The developed root system of pumpkin consumes a large amount of moisture and nutrients from the soil, so in hot weather it is necessary to water the plants abundantly. Timely fertilizing will ensure a good harvest. The plant requires the formation of stems.
On a note! If female flowers are not pollinated, the ovaries die and require removal.
The compatibility of plants in the garden plays an important role in planting planning. Neighboring plants can have both positive and negative effects on each other. An important question to which gardeners are looking for an answer: what to combine pumpkin with in the garden beds.
- Pumpkin will harmonize well with corn, beans, radishes, onions or salad.
- Planting pumpkins between rows of corn will help keep them from overheating in hot weather.
- Beans, with the help of nodule bacteria, accumulate large amounts of nitrogen on the roots. This combination of vegetables will have a good effect on the growth and development of pumpkin.
- The lettuce neighbor repels the flea beetle, but requires a little shade, which large pumpkin leaves can provide.
But when planting squash next to a pumpkin, cross-pollination can occur and hybrids can grow. Patisson, or plate pumpkin, has a bush-like shape, large leaves with rough pubescence. The flowers have separate sexes (male and female flowers) and are orange and yellow in color. The vegetable has a flat shape, resembling a disk. The fruits are white or greenish in color, sometimes dark green and yellow-orange in color. Squash has juicy white or cream-colored flesh and large seeds.
Important! Corn, radishes, onions or garlic would be good neighbors for squash. Marigolds will help repel pests.
Zucchini is also a member of the pumpkin family. The plant is annual and loves warmth. They are grown by seedlings or by placing seeds in heated soil. Zucchini is afraid of frost. The plant takes root well in sunny areas and in partial shade. It needs good watering in hot weather. On cloudy days, watering can be reduced. The plant has spreading leaves, so zucchini requires a lot of space between plantings.
Good neighborhood
The pumpkin grows lashes 4-5 meters long, on which large rounded leaves and large fruits are formed. Not every plant can tolerate being in the shadow of its neighbor. The following crops will be able to develop favorably next to pumpkins.
Corn
This plant is large. The thick stalk of corn reaches a height of 2 meters. The root of the crop can grow to the same depth. A stable plant will not bend under the pressure of pumpkin shoots.
Sunflower
This is another powerful garden crop, reaching a height of 2.5 meters. The tap root goes deep by 2-3 meters. Thanks to him, the sunflower is firmly located in the garden bed.
Some gardeners even plant pumpkin and sunflower seeds in the same hole. Cultures require the same conditions, so their proximity is prosperous. The main thing is to move the pumpkin shoots away from the sunflower stem.
Radish
This is an early ripening plant. Radishes are sown in the garden in early spring. It requires a lot of light to develop. In shade, the fruits will grow small, bitter, with a dense peel.
Although the pumpkin grows large bushes, it will not be an obstacle to the growth of radishes. The root crop is removed from the garden in May, when the pumpkin crop is just beginning to grow powerful shoots.
Salad
Just like radishes, lettuce ripens early. The pumpkin does not have time to create a shadow for him. Greens are removed from the garden in the spring. Pumpkin, being the main crop, will continue to develop alone.
In order for the salad to grow in quality, it needs to be thinned out, otherwise it loses its taste and color.
Beans
The roots of the plant contain bacteria that fix nitrogen from the air. This substance is necessary for the development of pumpkin at the initial stage. To prevent the beans from being suppressed, they must be planted at a distance of at least 1.5 meters from the pumpkin.
Winter garlic
This crop is planted in the ground in the fall. In the spring, as soon as the sun warms up, winter garlic begins to develop. It releases phytoncides that repel pests from the pumpkin.
At the beginning of July, garlic is completely ready for harvest. The pumpkin crop does not have time to harm it, since during this period it still continues its development.
Black radish
The seeds of this crop are sown in the summer, after harvesting garlic, radishes and lettuce. Radish secretes substances that repel spider mites from pumpkins. To make the neighborhood prosperous, plants are planted at intervals of 1.5 meters from each other.
Horseradish
Horseradish grows quickly, occupying all available space, so it is usually planted along the fence. The center of the bed is reserved for more demanding plants.
Pumpkin, like horseradish, is planted around the perimeter of the site. Both cultures are powerful. Each of them occupies its own area without interfering with the development of each other.
Mint
Mint multiplies quickly, covering a large area, so it is planted around the perimeter of the garden bed. It tolerates partial shade well. Even if the mint bushes are shaded by pumpkin leaves, they continue to grow safely.
Onions on greens
First, onions are planted in the garden bed, then, when constant warmth sets in, pumpkins are planted. The greens will have time to ripen before the climbing crop takes up all the free space.
The main pest of onions is the onion fly. To prevent her from laying eggs, the soil in the garden bed is sprinkled with a mixture of lime and tobacco dust. Watering with a 1% solution of table salt also helps.
Is it possible to plant a pumpkin next to zucchini?
When to plant zucchini and pumpkin
Both plants spread their lashes far beyond the garden bed. In order not to thicken the plantings, it is not recommended to plant pumpkin and zucchini together. There is also the possibility of cross-pollination between zucchini and pumpkin. In this case, you can expect a harvest of hybrids of yellow round fruits on zucchini, and hybrids of oblong shape with pumpkin flavor on pumpkin. Therefore, each gardener decides for himself whether it is possible to plant a pumpkin next to zucchini.
Note! Pumpkin is a dominant plant, therefore, when cross-pollinated, it will retain most of its external and taste qualities.
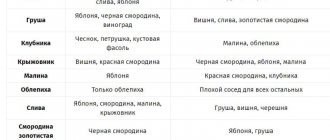
Culture compatibility table
The peculiarity of pumpkin is that it forms powerful shoots, so equally strong plants can grow next to it. It is also possible to plant early ripening crops nearby. They are harvested during the spring, leaving room for the development of large-fruited plants.
Compatibility table of pumpkin with other garden crops:
| Perfect | Neutral | Undesirable |
| sunflower | daikon | potato |
| corn | rhubarb | eggplant |
| radish | dill | pepper |
| black radish | fennel | tomatoes |
| winter garlic | turnip | White cabbage |
| beans | tarragon | Chinese cabbage |
| salad | beet | cucumbers |
| onions on greens | zucchini | |
| sorrel | squash | |
| spinach | melon | |
| parsley | watermelon | |
| mint | carrot | |
| basil | chard | |
| celery |
Pumpkin is an unpretentious plant. But it can be aggressive as it grows large bushes. Therefore, pumpkin neighbors must be early ripening or equally powerful. Then the gardener can harvest a good harvest of vegetables from the plot.
Other Pumpkin Neighbors
Watermelons are berries with tasty juicy pulp. This melon crop loves warm, sunny places without shade or trees. The soil should be sandy or sandy loam for better penetration of watermelon roots to moisture. Watermelons are grown as seedlings to get a quicker harvest, or the seeds are planted directly into the ground. The plant receives nutrition and moisture from internal waters, so it has a very powerful root system.
Watermelon seedlings
When to plant pumpkin and zucchini seeds in open ground
Watering should be moderate - 1-2 times a week. Good neighbors for watermelon will be: corn, peas. Beets, radishes, sunflowers.
Important! You should not plant a pumpkin next to a watermelon. Both plants are very climbing plants and can also cross-pollinate.
Melons belong to the cucurbit family due to their similar root system. They are thermophilic and do not tolerate waterlogging. It is better to choose a site on a hill to avoid water accumulation and get more sun. Parsley, cucumbers and pumpkin are not suitable for proximity. Corn and various greens growing nearby will have a good effect on the plant.
Cucumber is a tasty and healthy vegetable that is edible even when unripe. The plant is afraid of the cold; the optimal soil temperature for planting is 14 degrees. Cucumbers are not picky when choosing soil. Good development is achieved through the application of organic fertilizers.
Is it possible to plant pumpkin next to cucumbers?
Joint planting of these representatives of the melon family is undesirable. Cultures can carry the same diseases and interfere with each other through growing vines. A cucumber bush requires a lot of light and space to develop, and pumpkin leaves can thicken the plantings, which will reduce the yield.
Tomatoes, peppers, eggplants and potatoes are famous for their poor compatibility with pumpkins. As the pumpkin grows, it consumes a lot of nutrients from the soil, which will prevent nightshade representatives from developing well.
With cucumber
Pumpkin, squash, cucumber, melon and watermelon, all members of the Cucurbitaceae family, are crops that are cross-pollinated. In this case, pollen from the male flower is transferred to the pistil of the female flower.
Important! The close proximity of these plants of the pumpkin family will lead to cross-pollination between them.
To prevent cross-pollination, methods of covering plantings with material are not suitable. The diameter of pumpkin growth can reach 5 m. Also, the shelter will prevent the penetration of insects that help plants pollinate.
The most effective way to avoid over-grading is to pollinate manually. To do this, the unopened bud must be opened, pollen is collected from the stamens with a brush or a rod, and transferred to the stigma of the pistil. Then a gauze cap is put on to avoid repeated pollination by bees.
Note! Opened flowers cannot be used for hand pollination, as they can already be used up by insects.
There is nothing complicated or expensive about hand pollination. To obtain high-quality seeds, it is enough to pollinate a few flowers and trim the rest. Germination of seeds from the pumpkin family is 7-8 years.
Combined and compacted plantings
Combined (mixed) and compacted plantings require intensive use of land. With mixed crops, several crops are grown on one ridge throughout the growing season.
The simplest example of mixed sowing, practiced by our grandmothers: plant cucumbers in the garden along with dill . They grow well, and how convenient it is - I picked cucumbers for pickling, and here you have fragrant dill.
Also traditionally, garlic of strawberries (garden strawberries) , which repel weevils, slugs and other pests.
For almost all Celeryaceae (the second name of the Apiaceae family) - carrots, parsley, dill, celery, parsnips - the combination with alliums (all types of onions, garlic) is favorable. Onions are recognized as an excellent neighbor for carrots , which with their phytoncides repel the carrot fly, and carrots, in turn, repel onion flies.
Bulbs for feathers and turnips are planted between rows of carrots
The compact planting method is as follows: the main crop is temporarily supplemented with another that does not compete with it. As a rule, the compacting species is removed as it grows and matures, freeing up the space necessary for the main plant to fully develop. Compactors reduce heating of the surface layer of soil, improve the microclimate, maintaining favorable temperature and air humidity.
It is known that cucumbers love high humidity. corn and sunflower are used as compacting crops , which become a natural support for climbing cucumber shoots.
When growing early varieties of cabbage and potatoes , pumpkins are sometimes sown between rows . After harvesting early-ripening vegetables, pumpkin plants will be able to develop in the freed area until autumn.
It is convenient to sow radishes with zucchini , which will already have time to grow and ripen before the main crop grows.
Among green vegetables, spinach is good to use as a thickening agent. It is not yet in such demand among Russian gardeners as in Europe, but it is a nutritionally and medicinally valuable plant, rich in vitamins, minerals, organic acids, and antioxidants. Spinach can be used to “knock out” plantings of white cabbage , zucchini , beets , garlic , tomatoes , eggplants , and peppers .
Cold-hardy, fast-growing spinach grows up to 30 cm, producing a rosette of bright green, succulent leaves.
Many summer residents sow early greens in the following way: on one ridge they make several transverse or longitudinal rows, alternating lettuce , radishes , spinach , dill . This way they grow more actively, they turn out more beautiful, more magnificent. onions and beets with the same green crops . The greens are eaten in the first half of summer, and the bulbs and root vegetables continue to grow further.
Compacted plantings change the microclimate in the garden bed for the better, thereby increasing productivity.
In greenhouses with tall tomatoes, compaction is also done using greens - lettuces, onions, salad mustard.
Principles for selecting crops in the garden
In order for joint and compacted crops to bring maximum effect, certain botanical and agrotechnical rules must be followed:
- It is advisable that plants planted in one bed belong to different families. Representatives of the same group have the same preferences for nutrients obtained from the soil, common pests, and similar diseases.
- Neighboring crops should have different heights to prevent competition for light.
- Plants with root systems differing in length and location (surface, deep) are planted in the neighborhood.
- For compacted schemes, it is necessary to additionally take into account different growth rates, ripening and harvest dates.
When choosing potential neighbors, it is important to pay attention to the family affiliation of plants, the dimensions of the above-ground part, and the structural features of the root system
Advantages and disadvantages
Among the undeniable advantages of mixed and compacted sowing:
- maximum efficient use of land area;
- uniform depletion of soil resources without competition;
- the ability of neighboring plants to improve each other’s taste;
- creating a favorable microclimate for growing a particular crop;
- repelling insect pests;
- curbing weed growth and disease spread.
Gardeners who practice such plantings note as a disadvantage some difficulties in weeding and loosening the soil between the rows.
Secrets to growing a good pumpkin harvest
To grow a good harvest, you need not only to take into account what pumpkin goes with, but also to prevent the development of diseases and the appearance of pests.
Is it possible to plant zucchini and squash next to each other?
The most dangerous for pumpkins will be:
- Powdery mildew. Small white spots appear on the leaves, the leaf turns yellow and then dies. If treatment is not started, the disease will destroy the fruits.
- Olive spot. It is characterized by the appearance of small sores on the stems and brown spots on the leaves. Then the disease affects the fruits, and the vegetables lose their quality. Various drugs are used to combat diseases.
- Slugs that cause the most damage. They destroy fruits that are at the ripening stage. To combat slugs, use superphosphate or wood ash.
If rotting of the ovaries is detected, artificial pollination must be carried out. To do this, in the morning, all male flowers are cut off, the petals are pushed aside and several anthers are applied to the pistil.
If the pumpkin has spread its vines over the fence, the fruit must be suspended using a net to avoid damage to the plant.
A mandatory step in growing pumpkins is pinching. It is carried out to regulate the number of fruits.
Fact! The more fruits a plant produces, the smaller they will be.
If you leave one fruit on the vine, it will reach its maximum size. It is also necessary to trim the growing point. After the extreme ovary, 5-6 leaves are left and the lash is shortened. This will stop the growth of the lashes, and the plant’s forces will be directed to the ripening of the pumpkins.
A large pumpkin must be raised above the ground to protect the plant from moisture. To do this, several stones and a wide slab are placed under the fruit. These actions are performed when the fetus is still small. Transporting a large fruit may damage the stem.
Note. Proper watering of pumpkins is another secret to a good harvest. The amount of moisture depends on the weather; the plant requires rare but abundant watering at the root. During flowering, watering is reduced because moisture makes the pollen heavier and pollination becomes more difficult.
To extend the shelf life of the pumpkin, when cutting the fruit, a 5-centimeter stalk is left. Store pumpkin at a temperature no higher than 8 degrees.
Growing pumpkins in your garden is quite easy. Carefully selected seeds are soaked and, after biting, placed in a container with seedling soil. Having grown strong seedlings, the plant is placed in a permanent place.
0 0 votes
Article rating
Popular neighborhood: cucumbers and tomatoes
Any tomatoes and cucumbers in the same greenhouse are bad neighbors. This common tandem cannot be called successful. First, vegetables have different preferences in microclimatic conditions. Secondly, the suppression of cucumbers by tomatoes in greenhouse conditions can also be explained by agricultural cultivation techniques.
When alternating crops on a plot of land and when looking for an answer to the question of whether it is possible to plant tomatoes after cucumbers, you should familiarize yourself with the soil fertility conditions. So, a tomato will grow well after cucumbers. But it is recommended to wait for the season and plant something in demand from legumes at this time. Good nutritious soil will quickly deplete in the absence of proper planting. And even abundant fertilizers will not save the situation.
Preparing pumpkin seeds for planting
Seeds for planting must be young and large. They can be checked for germination in the following way:
- immerse the planting material in a saline solution;
- those seeds that have sunk to the bottom are considered suitable for cultivation.
Before planting, it is recommended to soak the seeds in a medium solution of potassium permanganate for 30 minutes and germinate.
The seed germination process should be carried out in a room with an air temperature of 22-23 degrees. To do this, the seeds are soaked for a day in a solution of potassium humate or sodium humate, and then kept in a damp cloth for another day.
Neighbors are pest protectors
There are plants that repel or lure vegetable pests. If you plant them nearby, you can eliminate or significantly reduce the use of chemical treatments.
Good neighbor-defenders in the garden are presented in the table below:
| Pests | Protective plants |
| Colorado potato beetle | Sage, medicinal wormwood, peppermint, nasturtium, tansy, thyme |
| Aphid | Radish |
| Cabbage caterpillars | Dill, basil |
| Cicada | Geranium, petunia |
| Ants | Castor bean, daffodils |
| Peach glass | Geranium, marigolds |
| Pumpkin glass | Garlic |
| Whitefly | Nasturtium, thyme, mint, wormwood |
| codling moth | Marigolds, calendula |
| Snails, slugs | Garlic, wormwood |
| scoop | Rosemary, garlic, parsley |
| Ants, aphids, hornworm | Basil |
| Wireworm, Colorado potato beetle | Vegetable beans |
| Carrot pests | Bulb onions |
| Aphids, caterpillars, cabbage cutworm | Leek |
| Onion fly | Carrot |
| Slugs | Parsley |
| Leaf beetle, spider mite | Radish |
| Earth flea | Salad |
| White butterflies, flea beetles | Celery |
| Aphids, caterpillars | Dill |
| Potato bug | Horseradish |
| Cabbage fly larvae | Lavender, wormwood, peppermint and spearmint |
| carrot fly | Radishes, sage, garlic, marigolds |
| Mice | Tobacco, sage, rosemary, leek, lettuce |
| Moles | Marigolds, garlic, onion |
| Rabbits | Coriander, horseradish, tansy, onion, catnip, nasturtium. |
Nuance No. 4. Diseases and pests
And as you know, representatives of the Pumpkin family have them in common. Among the diseases, these crops are most often affected by bacteriosis, powdery mildew, peronospora, anthracnose and various types of rot, and among pests - spider mites, melon aphids and sprout flies. Slugs will not disdain vegetables either. Vegetable crops of the same family planted nearby run the risk of simultaneously being exposed to any of the listed misfortunes. Therefore, if you have already decided that zucchini will look good in the company of pumpkins, promptly carry out disease and pest attack prevention with the help of fungicides and insecticides.
Planting pumpkin seeds in open ground
Planting holes should be prepared in advance with a size and depth of 40 cm:
- pour them with 1-2 liters of warm water;
- Place a layer of dry leaves and organic waste at the bottom of the holes;
- Place a mixture of compost with the top fertile layer on top, making a mound 10-15 cm high;
- Plant seeds into the resulting steam heaps.
The distance between the holes depends on the pumpkin variety and the length of the shoots:
- if the shoots are short, then the distance between plants in one row will be 70 cm, and between holes - 70 cm;
- if the shoots are medium, then 100 by 150 cm;
- if the shoots are long, then 150 by 200 cm.
It is recommended to plant seeds at the end of May or beginning of June to a depth of 4-10 cm, depending on the composition of the soil (the lighter the soil, the greater the planting depth).
Before planting, the seeds need to be soaked in hot water at 50 degrees for 3-5 hours. This will help them germinate faster and get rid of pathogens. 4-5 seeds should be placed in each hole.
After sowing, it is recommended to mulch the soil with grass, peat or cover the beds with covering material.
When the seedlings have several true leaves, you need to thin them out:
- if the pumpkin is large-fruited, then one of the strongest plants should be left in the hole;
- if the pumpkin is small-fruited, then 2 seedlings are left in the hole.
Other neighbors in the garden: table of flowers and herbs
In addition to the proximity between vegetables, the benefits of flowers or herbs growing nearby should also be taken into account. Such combinations in the garden provide protection from pests, improve taste and give the beds an attractive appearance.
The best flowers and herbs - neighbors of vegetable crops - are presented in the table.
Source of the article: https://ofazende.ru/blagopriyatnoe-sosedstvo-ovoshhej-na-gryadkah
What is crop rotation
Our ancestors also noticed that if the same plants are planted in the same place every year, the soil becomes depleted and ceases to produce a good harvest. It also matters which crops grew before a particular plant, and which will grow after it.
The alternation of agricultural crops, identified experimentally over many generations and systematized by modern agronomists and gardeners, is called crop rotation. With this knowledge in hand, even an inexperienced farmer can easily calculate what to plant next. Ideally, the planting site should be changed every season.
So what are the rules for pumpkin crop rotation? It is not recommended to repeat the planting location for this plant more than once every three to five years.
Do you know? In fact, pumpkin is not a vegetable, but a berry, only a very large one.
Advice from experienced gardeners
The experience accumulated over the years is always of great value. What advice do seasoned gardeners give on pumpkin crop rotation?
Inna: “On my plot, after pumpkins, I plant everything except other pumpkins (melons, cucumbers, watermelons). Although I’m sure that if the vegetables don’t get sick, you can leave them in the same place, including the pumpkin. For example, I have been growing zucchini in the same holes for many years, and they are of the same family. The only caveat is that it must be fertilized annually so that the land does not become depleted. I use humus. The permanent “place of residence” has not yet affected the quality of fruits and productivity, and I have not observed any diseases.”
Sergey: “From a biological point of view, a pumpkin will not harm its neighbors in any way. When choosing crops that will grow nearby, you need to take into account that the pumpkin bushes are powerful and the vines are long. The main thing is that it does not drown out neighboring crops. And after the berry itself, you can plant everything in the garden except its closest relatives. I like the result of planting tomatoes and potatoes after it.”
Lyudmila: “Pepper grows well after pumpkin, the soil after it is optimal! If you are growing peppers in a greenhouse, you can even transfer pumpkin soil under them. Yes, it's a hassle, but the results are worth it. Tomatoes or eggplants are also good on such soil.”
Favorable proximity of vegetables in the beds
There is a certain relationship between garden plants. Vegetables, greens, herbs and flowers can either help or hinder each other’s growth, development and pest control. The correct proximity of vegetables in the beds ensures a good harvest without unnecessary effort and the use of chemicals. Selecting neighboring plants is a whole science of garden planning, the basis of which is the organic farming method called “mixed plantings”. In this article we will look at the rules for joint planting of vegetables in the garden.