To correctly determine the difference between seedlings of dina, zucchini and cucumbers, study the material below. The differences after this will be quite noticeable.
Planting material for zucchini, melon, and cucumbers can be confused. Moreover, if you have not previously owned a plot of land and are not an experienced gardener.
The slightly opened small leaves of these crops are almost impossible to distinguish. Moreover, when the shoots only appeared the other day. It is necessary to figure out what seedlings of cucumbers, melons, and zucchini should look like and how they differ from each other.
Comparison
Let's start the comparison with the appearance of the fruit.
The zucchini has an oblong, sometimes slightly curved shape. Its color can be either green or yellow, or almost white. Pumpkin fruits are round and often very large. Sometimes dark green specimens are found, but generally their color range varies from yellowish to bright orange. As for the pulp, when ripe it has the same rich sunny hue. Inside the pumpkin there is a loose seed cavity, as well as a hard shell layer located just under the skin. A similar one is present in melon and watermelon. The pulp of zucchini is white, its seed cavity is much denser. There is no armor layer. It is worth noting that zucchini is recommended to be eaten unripe. Such fruits can be eaten raw and directly with the skin; they have a number of beneficial properties. Pumpkin is included in the diet only when ripe, when the fruit reaches a very impressive size. By this time, the pulp becomes more tender, juicy and aromatic. Another difference between zucchini and pumpkin is that the latter plant forms powerful branched vines. Their length can reach several meters. Zucchini grows in small bushes, and if they form vines, they are very short. Their leaves are large, palmate, pentagonal in shape, while those of pumpkins are round, with teeth along the edges.
Special attention should be paid to the taste of the fruit. In the case of zucchini, it can be called quite bland
That is why this vegetable is often eaten in combination with other ingredients. Pumpkin has a very rich sweetish taste, slightly reminiscent of melon. It makes excellent cereals, juices and desserts. Despite the fact that zucchini is of great benefit to our body, pumpkin is significantly superior to it in this parameter. The pulp of the fruit contains many vitamins along with silicon, phosphorus, potassium, nicotinic acid, calcium, iron, etc. The seeds are used as an anthelmintic, and the oil obtained from them is rich in unsaturated fatty acids and is used for metabolic disorders, in order to speed up regeneration of liver tissue, mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, prostate gland.
Let's summarize what is the difference between zucchini and pumpkin.
| Zucchini | Pumpkin |
| Has an oblong shape | Produces round fruits |
| The color of the fruit is yellow, green or almost white | Pumpkins are yellowish or deep orange in color, sometimes dark green |
| White pulp | The flesh is usually yellow, orange |
| Dense seed cavity | The seminal cavity is looser |
| There is no armor layer | There is a hard shell layer |
| It is recommended to eat unripe | The pulp of ripe fruits is more juicy and tender |
| Grows as a small bush, sometimes forms short vines | Throws powerful branched lashes up to several meters long |
| Has a bland taste | The fruits are characterized by a rich sweetish taste, reminiscent of melon |
| Not suitable for preparing sweet dishes | It makes excellent cereals, juices, desserts |
| Provides great benefits to the body | Contains even more valuable substances present not only in the pulp, but also in the seeds, as well as in the oil obtained from them |
Climate-related challenges
Of course, it will not be possible to grow fragrant fruits throughout the entire territory of Siberia, especially in open ground. The short summer dictates its own conditions. Despite the fact that the upper layers of the soil thaw only in April, in May there are abnormal droughts, and the air temperature sometimes reaches +40 degrees. Such unpredictable weather surprises are associated with the predominance of northern winds - the culprits of frequent recurrent frosts. Closer to the south of Siberia and the Urals, the climate is much milder.
All the weather difficulties described above also apply to the Moscow region. Although in the middle zone favorable periods are longer in time, when choosing a sowing date, they pay attention not to calendar dates, not to lunar phases, but directly to the thermometer outside the window and long-term meteorological forecasts.
When growing in greenhouses, shoots of long- and medium-climbing bushes are usually tied to vertical supports, and not spread out, as in open ground.
Comparing the climatic conditions of harsh regions with melon growing technology, it becomes clear that it is not possible to obtain a melon harvest outside technically equipped industrial greenhouses. However, Siberian and Ural gardening enthusiasts claim that with a certain risk, but in amateur gardens this can also be done if the summer season is prosperous. Experimenters living in risky farming zones experimentally identify specimens with a short growing season (sometimes even contrary to the reference information of the State Register) that are resistant to typical diseases. At the same time, melons are grown both for personal consumption and for small wholesale sale. Although it is still wiser to focus on the most adapted and zoned varieties, tested by specialists for several years and included in official sources.
Early cucumbers
It’s important for me to get at least 4-5 early cucumbers to the table at the start. Then, when the bucket counts, it doesn’t matter anymore
But the first early greens are very valuable, especially when you have four grandchildren who go check the greenhouse every day.
This is interesting.
The word “cucumber” was preceded by the long-vanished “cucumber”, and it was borrowed from the Greeks: among them “aguros”, “cucumber” is associated with “aoros” - unripe, unripe. This is very interesting. Indeed, in fact, unlike their close relatives - watermelons and melons, which the riper, the tastier, cucumbers are valued until they turn yellow, that is, they are not completely ripe.
Watermelon and cucumber
The first differences are noticeable at the cotyledon stage. In cucumber they are smaller than in watermelon. A clear difference will be at the stage of formation of the first pair of leaves, and complete differences can be noticed when 3-4 leaves grow.
- In watermelon, the plates are more torn at the edges and have a characteristic shape. The cucumber has angular-heart-shaped leaves without a jagged edge.
- Another feature of watermelon seedlings is the light shade of the leaves. Despite the density of the leaf blades, they still look thinner than those of a watermelon and are never dark green.
- The third difference is the smell. If you rub a cucumber leaf, you immediately feel the characteristic aroma.
The similarity is manifested in flowering.
Definitions
Zucchini
Zucchini
- a herbaceous annual plant of the pumpkin family.
The fruits are oblong in shape and can be green, yellow or white. Zucchini came to us from America, where initially only its seeds were eaten. It was brought to Europe from the New World in the 16th century. Then no one even thought that the fruits of the strange plant could be eaten, and zucchini was grown in botanical gardens. Today it is difficult to imagine Mediterranean cuisine without this vegetable. It is believed that the Italians were the first to add unripe zucchini to dishes. This happened in the 18th century. Today, the vegetable is actively used in cooking. Young fruits are eaten raw with the skin, adding them to various salads. Larger zucchini is subjected to heat treatment: they are stewed, fried, baked. They are also good as a side dish for meat and fish dishes. Pumpkin
Pumpkin
– herbaceous annual plant, melon crop. Produces large spherical or oval fruits, predominantly orange in color. However, there are pumpkins of combined shades. Mexico is considered to be the homeland of the plant, because it was in the Oaxaca Valley that it first appeared about 8 thousand years ago. Initially, only nutritious seeds were eaten. A little later, the pumpkin spread north to the valleys of the Missouri and Mississippi rivers. The plant was brought to Europe by the Spaniards. In the 16th century it gained popularity in the Old World. The leading positions in pumpkin cultivation are occupied by Russia, India and China. Ripe fruits are eaten both boiled, fried and baked, and fresh. Juice is squeezed out of them, mashed potatoes, caviar, jam and marmalade are made.
Arrangement of the growing area
A lot of free space is allocated for melons, since the plants actively grow vines, have a powerful and developed root system, which is capable of reaching moisture at a depth of one meter, but some of it is located in the upper layers. The beds are located on the sunny, constantly illuminated side of the site. Poor lighting cannot be compensated for either by increased fertilizing, or by growth regulators, or by timely pinching.
Many gardeners use alternative greenhouse options - seedling greenhouses
In open ground and unheated structures, it is recommended to build warm compost beds made from plant waste, which generate heat during the process of decomposition. The roots are further insulated using heated stones, bricks and hot water bottles. The top provides reliable shelter. A film stretched over the arcs saves you from prolonged rains and, as a result, the appearance of fungal infections. In particularly hot weather, the ends of the shelter are opened slightly so that the seedlings do not burn from the stuffiness and heat.
In homemade greenhouses, when night temperatures are predicted to drop, tender seedlings are covered with inverted cardboard boxes or halves of plastic bottles to protect the above-ground part from cold dew and reduce the risk of various types of mycoses.
Soil enrichment
Melons are well suited to loose, biohumus-rich, light, medium-loamy soils mixed with sand. You should not get carried away with excessive addition of organic matter; it is used in limited quantities at the initial stage (before flowering). An excess of nitrogen will promote the growth of green mass to the detriment of fruit formation.
During the development of flower buds, the crop requires mineral supplements, which contribute to an increase in the number of female flowers and the rapid formation of ovaries
A large amount of minerals is necessary for accelerated ripening of fruits and increase their sugar content. There is no need to be afraid of contrived harm from the application of mineral fertilizers - these are the same natural components, only synthesized industrially. If they are introduced in accordance with the deadlines and in compliance with the instructions, they will only be beneficial.
Microelements are applied by the root method, combined with abundant watering, as well as foliar - by leaves. Alternating root feeding with spraying the tops every 10-14 days with complex preparations for melons and melons works well: “Nutrivat Plus”, “Kelik Potassium”, “Uniflor micro”, “Speedfol Amino”, “Universal”, “Potassium Lignohumate”.
Greenhouse preparation
When planning to plant seedlings in a greenhouse, the structure is checked in the fall for drafts, moisture leakage and heat loss. The cracks are sealed with punched tape and an end profile.
Protective perforated tape for polycarbonate acts as a membrane - it does not let anything into the honeycomb from the outside, and allows condensation from the inside to escape unhindered
It is better to seal the vertical sides with hermetic tape (solid). It is recommended to glue the metal arcs of the greenhouse frame with cork tape to create a thermal layer that protects the polycarbonate from heating and friction under wind load and expansion/constriction during temperature changes.
The holes in the places where the sheets are attached to the frame are additionally covered with thermal washers to prevent the ingress of rainwater and other precipitation. The walls and soil are disinfected. Treatment with special smoke (sulfur) bombs is considered effective. You can spill soil and wash polycarbonate with the environmentally friendly Percel 6 product - it and similar preparations are used in accordance with the precautions indicated on the packaging.
Recently, electrical soil disinfection systems have appeared on the market. But since the devices do not have the appropriate certificates, the effectiveness and appropriateness of using such disinfectants is highly questioned. The gardener risks not only being left without a harvest, but also receiving significant energy bills.
What crops cannot be combined with
Among the crops next to which it is undesirable to plant cucumbers, it is worth highlighting zucchini. This vegetable leads to excessive pollination of plants, as it belongs to the same species as greens. This will not affect the taste of the fruit, but the seeds will become unsuitable for further planting. The poor compatibility of these crops is also explained by the fact that the zucchini grows strongly, as a result of which the cucumber bushes do not receive enough ultraviolet radiation.
Basil, like cilantro or oregano, is incompatible with cucumbers. From such proximity, the fruits acquire an unpleasant taste and aroma.
Lettuce and spinach will prevent the soil from overheating and stimulate the growth of the root system of the crop. This is a bad neighborhood option. Plants need a lot of moisture, which they draw onto themselves. Cucumbers do not get enough of it.
Radishes and turnips also cannot be called good neighbors, as they make cucumbers taste bitter.
Pumpkin is the most undesirable neighbor, since cucumbers, along with it, are susceptible to identical diseases.
Fennel should not be planted. The plant has a powerful root system that will quickly take moisture and nutrients from the soil, especially if it grows in open ground.
Melon in a greenhouse
The greenhouse will help out gardeners living in cold climates. This option is also suitable for those who want to get an earlier harvest of fragrant fruits. The main task is to provide the melon with a sufficient food area, take care of a stable temperature, normal humidification and air exchange.
Small secrets of successful fruiting:
- successful cultivation will be ensured by varieties resistant to fungal diseases;
- plant the best prepared seedlings;
- do not forget that pollination is your concern, because bees do not fly in a greenhouse;
- Grow melon indoors only on a trellis.
A greenhouse is the key to a successful melon harvest in cold climates
Why do zucchini and pumpkins cross-pollinate and how to avoid it?
If these plants are planted in one bed, then... nothing will happen: good fruits will grow. But if you collect seeds from them, then next year pumpkins and pumpkin squashes will grow. For some reason they turn out worse than normal ones. That is, not sweet zucchini will grow, but tasteless, thick-skinned small pumpkins. Therefore, the first rule of a gardener if he is going to save his seeds: do not plant these relatives close to each other. To prevent cross-pollination from occurring, you need to grow pumpkins and zucchini (and their different varieties) at a far distance, ideally 80-100 m, that is, in neighboring fields. But in practice, the distance can be much less, 10-20 meters. Since summer residents do not even have this opportunity, it is better not to collect your own seeds, but to buy them every year. In this case, you can plant the seedlings very close, even in neighboring beds. So it’s not at all necessary to know in advance what is growing: the fruits will grow - look. And if the seeds of pollinated monsters are sown, you will never know. So you should not buy pumpkin seedlings, because you can easily be deceived. And yet, there are certain signs by which seedlings differ. So if you have sown normal, non-pollinated seeds and the cups with seedlings are mixed up, then there is hope of distinguishing similar plants.
It is necessary to grow pumpkins and zucchini at a far distance
When to plant melon in 2022 for seedlings and in the ground
Let's consider how the timing of planting melons differs depending on various factors.
Depending on the variety
Early varieties are well suited for cold climates with short summers. They can be planted under cover from mid-May directly into the ground.
Mid-season varieties take about three months to ripen, and they are able to withstand minor weather vagaries. Therefore, you can start sowing them from the end of May.
Late varieties are grown mainly for long-term storage and need a warm climate. They are planted in June, the first two weeks.
Depending on the region
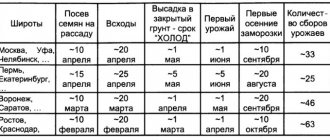
Weather conditions in Belarus, central Russia, as well as in the Volga region and Moscow region do not always make it possible to grow a full harvest of melons. But it is still possible, and the most favorable time here will be the end of May and the first days of June.
In Siberia, the Urals and neighboring Bashkiria, it is better to choose early varieties that can be grown in time under these conditions. The most ideal option would be a greenhouse. Planting dates here are in June.
In the Leningrad region it is also recommended to use early ripening varieties and a greenhouse. To get an earlier and better harvest, melon is grown here through seedlings, which are sown in mid-April.
In the southern regions, the choice of growing methods and varieties is richer. Here melon is planted from the beginning of May, depending on weather conditions.
Depending on the location and method of planting
To sow melon in the ground, it is enough that the air temperature is within +15-20ºС. But if spring is early, then it’s better not to rush anyway and wait until the last week of May. At this time, the main threat has passed. Sowing should be completed no later than the first ten days of June, or it simply may not have time to ripen.
They are planted in the greenhouse on the 2nd and 3rd weeks of May, if the temperature meets the above standards. Seedlings for this method are sown from the beginning of April.
Seeds for seedlings for open ground are planted from mid-April. It is replanted in early June, when 5-6 leaves have formed.
When to plant melon in 2022 according to the Lunar calendar
The Lunar calendar for sowing plants is extremely popular among gardeners. This is not surprising, since the influence of the Moon has long been known, and the recommendations from these tables are very useful.
Below are the basic recommendations for the time of planting melons according to the lunar calendar 2022.
| Favorable days | |
| February | 12-14, 21-23, 25-27 |
| March | 3, 6-8, 11-13 |
| April | 3-5, 7-10, 25-27 |
| May | 2, 5-7, 14, 15, 18-24, 27-29 |
| June | 1-3, 6-8, 10-13 |
In 2022, unfavorable days fall on the following dates:
- January – 2, 3, 17, 18
- February – 1, 2, 16, 28
- March – 1, 2, 18, 27, 28
- April – 1, 2, 16, 23
- May – 1, 16, 30
- June -14, 18, 29
- July – 13, 14, 28, 29
- August – 11, 12, 27-28
- September: 9-10, 26, 27
- October: 9, 10, 25, 26
- November: 1, 2, 7-9, 24, 25, 28, 29
- December: 7-9, 23-25
Zucchini and pumpkin: the difference
Zucchini and pumpkin are related vegetables, as they belong to the same species. The seeds and sprouts of these vegetables are almost impossible to distinguish.
Seeds
How to distinguish zucchini seedlings from pumpkin
To avoid getting a hybrid and tasteless zucchini harvest, they should be planted away from the pumpkin. Experienced gardeners plant seedlings of these vegetables at least 20 m from each other. This prevents cross-pollination of plants.
You can determine whether a young sprout belongs to a particular crop during the growing process by the following characteristics:
- Pumpkin seeds are large and round in shape, and the cotyledon leaves are identical in shape.
- Squash seedlings are lighter than pumpkin seedlings. It has a tall stem and looks weaker.
- Pumpkin leaves are larger and more rounded and lobed in shape. Less prominent than zucchini.
- Pumpkin sprouts are more powerful and squat than zucchini sprouts.
The following features are worth noting:
- Most varieties of zucchini have whitish or yellowish spots on the leaves. Pumpkin crop leaves are clean, without inclusions.
- Pumpkin flowers are placed at the base and rise higher along the stem. In zucchini, they are located in the center of the bush.
- Pumpkin vines cling to the soil and neighboring plants with tendrils. They take root where they touch the ground. This does not happen with squash. Even when placed in bushes, they never take root with tendrils in the ground.
Important! If you plan to save the seeds of both pumpkin and zucchini in the future, you should not plant them next to each other. Otherwise, there is a risk of being left with a modified harvest
If the seedlings end up in the same bed, they cannot be planted. It is unlikely that mature plants will survive transplantation.
If new seeds are purchased annually, this is not a problem. In addition, the fruits will change their size and shape.
In order not to confuse pumpkin and squash seedlings, you must follow the following rules:
- When the seeds are collected and dried from moisture, they must be placed in paper bags.
- Each of them must be signed: variety and year of collection. Pumpkin seeds can be stored for more than 8 years. But squash is not intended for long-term storage.
- Before sowing seedlings, you should purchase peat cups and make appropriate inscriptions on them.
Important! It is better not to buy ready-made seedlings grown by someone else. After all, there is a risk of not seeing the difference between pumpkin and squash crops
How to distinguish zucchini seedlings from cucumbers
- At the age of 4-6 weeks it is already possible to distinguish these cultures from each other. The cucumber sprout has a thinner and weaker stem. It is slightly shorter in length than a zucchini shoot.
- The cucumber leaf resembles its seed. It has an oblong shape with a rounded end. The leaves are soft to the touch. There is a slight shine, which is not typical for zucchini. Their leaves are dissected, rounded, with pointed tips.
- The cucumber will slow down its growth in the period 7-9 weeks, and the zucchini continues to actively develop.
These methods will help every gardener see the differences between zucchini and cucumber seedlings.
What to do
It is ideal if you determine the species of the seedlings before transferring them to a permanent place. But what to do if the mixed seeds were planted directly into the ground or you incorrectly differentiated the sprouts, and now young pumpkin and zucchini bushes grow together?
In this case, the sprouts need to be carefully transplanted into different beds, trying not to damage the delicate root system. It is not advisable to leave pumpkins and zucchini to grow together:
- Zucchini is very demanding of light, humidity and heat. Powerful pumpkin foliage, as well as spreading vines, can create unfavorable conditions for zucchini, in which they will not yield the desired volumes and may even wither.
- According to the rules of agricultural technology, zucchini and pumpkins should be planted at a distance of 80 meters. This is due to the fact that these subspecies actively cross-pollinate. If you collect seeds from ripe fruits, they will produce a defective harvest next year - sweetish zucchini and small, thick-skinned, tasteless pumpkins.
The last condition is almost impossible to implement on our small plots, so it is better not to prepare seeds, but to purchase seed material of the varieties you like every year.
Of course, there is a certain risk of repeating my deplorable situation, but the seedling method of planting will help you make sure of the species of the sprouts before transferring them to a permanent place in the ground.
Pumpkins and zucchini are close relatives. In terms of their biological characteristics (but not in taste, shape and size), they are no different; from a biological point of view, they are the same type of pumpkin plant (Cucurbita pepo), only its different subspecies. That’s why they are so similar, and gardeners need to distinguish between zucchini and pumpkin seedlings. Zucchini (a type of zucchini) is translated from Italian as pumpkin. One of Chekhov’s heroes even claimed that “ the Ukrainians call pumpkins zucchini.”
...”, although in the Ukrainian language there is a separate word for their name.
Pumpkins and zucchini are close relatives
The extensive, tasty and healthy pumpkin family also includes zucchini, squash, cucumbers, watermelons and melons, as well as all sorts of exotics (cucumber, watermelon, figoleaf pumpkin, giant and nutmeg).
Unlike other members of the cucurbit family, which never interbreed, pumpkins and squashes cross-pollinate easily. You end up with all sorts of round zucchini or unsweetened fruits, which is undesirable for a gardener. But cucumbers and melons, watermelons and zucchini do not cross-pollinate.
Selection of varieties and hybrids
Most often, early ripening fruits are characterized by small size, but this also has its advantage. Sugars, beneficial mineral compounds and vitamins accumulate faster in such pumpkins.
Small melons, as a rule, are well stored, having sufficient shelf life and transportability
As of 2022, 183 varieties and hybrids of melons are registered in the State Register of the Russian Federation, recommended for commercial production and amateur gardening. There are not as many of them as we would like for cultivation in unprotected beds in the central and northern regions, but the choice for planting in greenhouses is much wider:
| Regions | Varieties and hybrids | |
| For open ground | For protected ground | |
| All | “Augustino F1”, “Azovka F1”, “Al Halim F1”, “Amina F1”, “Anamax F1”, “Orange”, “Baghira F1”, “Bogatyr white / green”, “Vika”, “Cinderella”, “Zoryanka”, “Karotinka”, “Marquise”, “Honey gourmet”, “Honey cake”, “Turkish delight”, “Fairy tale”, “Sphinx F1”, “Seledyn F1”, “Timiryazevskaya early”, “Torpedo”, “Fiona F1”, “Fortune”, “Tsarskaya”, “Sherbet F1” | “Altyn F1”, “Assol F1”, “Indian Summer F1”, “Blondie F1”, “Galileo F1”, “Galina F1”, “Summer Resident F1”, “Gold of the Scythians F1”, “Snake Gorynych F1”, “Iroquois” F1", "Kapitoshka F1", "Moon", "Lyubava F1", "Margot F1", "Honeydew F1", "Millennium F1", "Extraordinary F1", "Ozhen F1", "Autumn Joy F1", " Rugby F1", "Sunny F1", "Tiger F1", "Fairy F1", "Huruma F1", "Chick F1", "Eldorado F1" |
| Ural | “Altaiskaya”, “Babor F1”, “Wintering”, “Collective Farmer 749/753”, “Lesya”, “Original”, “Temryuchanka” | |
| Siberia | “Altai”, “Collective Farmer”, “Lolita” (East Siberian), “Tender”, “Rosinka” | |
| Lower Volga region | “Mlada”, “Miracle Yudo”, “Ethiopka” and many others intended for commercial production | |
Signs by which you can distinguish seedlings of pumpkins and zucchini
When the first cotyledon leaves appear, you need to pay attention to their shape. They repeat the shape of seeds
Pumpkin seeds are always rounder and larger than zucchini seeds, which have more elongated seeds. The cotyledon leaves will be the same. Zucchini seedlings require better lighting. Therefore, if the plants are standing next to each other, the zucchini seedlings will look more elongated and lighter than those of the pumpkins, as well as weaker. At a young age, it looks more like cucumber seedlings. Pumpkin seedlings planted at the same time will be larger and more vigorous than zucchini seedlings. Zucchini leaves are smaller and more dissected, especially strongly cut in zucchini, while pumpkin leaves are more rounded and lobed. Some varieties of zucchini, especially zucchini, have yellow or white silvery spots on the leaves. This is not a disease, but a varietal trait. Pumpkins rarely have such spots. All pumpkins grow long vines, and zucchini almost always grow as a bush. But this symptom does not appear in seedlings. The plants have similar flowers: yellow, less often white, funnel-shaped. In pumpkins they are larger, since the whole plant is more powerful. The arrangement of flowers in plants is different: pumpkin flowers are distributed along the main stem, while zucchini plants grow from the middle of the bush. The fruits are located in the same way. Seedlings do not have fruits, but if the gardener could not determine what he was growing at the seedling stage, then he can at least try to correctly determine what kind of fruits he has. The pumpkin fruit is round and orange. And zucchini is white, yellow, green and elongated. Pumpkin vines cling to the ground and other plants with the help of tendrils. At the points where its creeping stems connect with the ground, the plant puts out additional roots. This does not happen with zucchini. Even if they do not grow as a bush, additional roots do not grow on the vines. And their lashes are thinner and shorter than those of pumpkins, but still much more powerful than those of cucumbers.
You can try to distinguish seedlings of pumpkins and zucchini, but not a single sign will give one hundred percent confidence that these are seedlings of pumpkins (zucchini). There are bush pumpkins and zucchini with long vines; some pumpkins and zucchini produce fruits of the same color and shape.
Not a single sign will give one hundred percent certainty that these are pumpkin (zucchini) seedlings.
How to distinguish melon seedlings from zucchini
What can you plant after zucchini next year?
The first thing you should pay attention to is the melon seeds. They differ from squash, have a narrow, elongated shape and a yellowish tint. The base of the melon sprout is thicker and slightly shorter. The leaves are almost impossible to distinguish, but there is one peculiarity. The leaves of melon seedlings have a richer green color and a smooth and shiny texture. If you tear off one leaf and rub it with your fingers, a subtle characteristic aroma of the fruit will appear. These characteristics are the key difference between these two cultures.
Melon seedlings
Is it possible to plant pumpkin and zucchini next to each other?
These are plants of the same genus and are easily cross-pollinated. If you accidentally planted them in the same bed, and during flowering and fruit formation you noticed that these are different crops, you should not plant them, since an adult plant is unlikely to survive transplantation.
Cross-pollinated pumpkin
Also, if you do not plan to collect seeds, but buy new ones every year, there is no need to worry - no changes will happen to them, the only thing is that they may change slightly in size and slightly change shape.
If you collect your seeds annually, if you are trying to preserve the variety, under no circumstances plant the crops nearby. Ideally, this distance between them should be more than 80 meters.
The common practice of gardeners - planting plants at a distance of more than 20 meters - has its advantages, provided that there is a third crop between the crops. You cannot plant them together in one bed.
If you grow these vegetables side by side and leave their seeds, the shape and taste of the fruit will change next year. The zucchini will become rounder, with a harder skin, and the color of the flesh will change. Pumpkin, on the contrary, will become more oval, lighter, and will lose its taste to a neutral one.
The seeds will change and lose their external differences. Vegetables will become something in between, between one and the other. Such “selection” is undesirable, as it leads to a complete loss of culture as such.
Cross-pollinated zucchini
If you want to preserve the variety, follow the planting rules and avoid crossing. And you will always have healthy vegetables with their original taste and color.
If you buy seeds every year, there is no need to worry about this as there will be no change in your favorite vegetables in one year.
How to grow melon through seedlings
Melon is a heat-loving crop, so the seedling growing method is an excellent solution for regions with cold climates and for those who want to get the harvest earlier.
But for this you need to know the technology and correctly go through all stages of cultivation.
Preparing seeds and soil
The first step is to select the best seeds. First, empty and small ones are removed, and the remaining ones are immersed in a saline solution. Those that float are also not suitable for landing.
In stores, seeds are often sold already prepared, but if they are your own, then they need to be disinfected. To do this, they are placed in a manganese solution for 20 minutes, after which the seed is soaked for another 10 minutes in a soda solution.
Before planting, it is better to germinate the seeds on a damp cloth.
Melons do not tolerate diving, so they are initially sown in separate containers with a diameter of at least 10 cm.
Soil preparation
It is better to buy soil for pumpkin plants with neutral acidity. If you cook it yourself at home, then mix:
- 9 parts peat
- 1 part river sand,
- 200 g of ash.
You can use a different soil composition:
- 3 parts humus,
- one part each of garden soil and peat.
The container for seedlings is not completely filled with the soil mixture, so that it can be added later when the seedlings grow.
Planting melon seedlings
Seeds are sown in moist soil, buried 2 cm, 1-2 seeds are placed in each container. Before emergence, the seedlings are covered with film or glass. They appear in 1-1.5 weeks, and if you plant sprouted melon seeds, they can sprout on the fourth day.
For seedlings at home, you need to choose a warm, lit place where they will develop well. The optimal temperature is about +26ºС during the day, and at night +18ºС..20ºС.
How to care for seedlings
For the first two weeks, watering is carried out every other day; it should be moderate to prevent waterlogging. In this case, water should not get on the stems and leaves. The length of daylight should be 10-12 hours; if it is shorter, then additional lighting must be provided.
When the first two true leaves appear on the seedlings, the first feeding is carried out. Repeat after 14 days. For this purpose mineral fertilizers are used:
- Superphosphate;
- Potassium chloride;
- Ammonium nitrate.
A week before planting, the seedlings are hardened by lowering the temperature during the day to +15ºС and at night to 12ºС. It is also periodically taken out into the fresh air or the room is ventilated more often and longer.
Video from Yulia Minyaeva: How to grow melon through seedlings
How to distinguish between zucchini and pumpkin seedlings
Preparatory manipulations with seeds are the same for all pumpkin crops. They need to be calibrated, warmed up, disinfected, and soaked. Dressing occurs in a solution of fungicide or potassium permanganate. The seeds are placed in a fabric bag and dipped into the mixture for 20-30 minutes. For soaking, use clean water or a solution of a growth stimulator. The swollen seeds are planted in separate pots or cups with a volume of 200-250 ml. Place 2 seeds in each container, deepening them 2-3 cm.
The soil for seedlings should be loose and fertile. Its components are:
Advice. To make seedlings appear faster, the pot is placed in a plastic bag to create greenhouse conditions.
The first shoots appear after 3-5 days. If both seeds germinate, the stronger sprout is left, the second one is removed. For the first week they should be kept in cool conditions with temperatures of 18-20°C during the day and 15-16°C at night. This environment prevents the stems from stretching. Then the seedlings are placed in a permanent place. She needs to be provided with good lighting for 12-14 hours a day. The optimal temperature for growth is 22-24°C. Detailed instructions in the article “The key to the harvest is the correct cultivation of zucchini seedlings. What do we recommend?
As the soil dries, the plants are watered with warm water and fed with fertilizers 2 times. They use “Nitrophoska”, urea, mullein solution. Seedlings are transplanted into open ground at the age of 25-30 days. It is impossible to keep it longer; overgrown seedlings do not adapt well in open ground; some die without taking root.
With the appearance of leaves, it’s time to figure out what pumpkin and zucchini seedlings look like. The seedlings appear similar, but upon careful comparison the differences are noticeable.
Zucchini seedlings
Description of zucchini seedlings:
- The cotyledon leaves are elongated and light green.
- The first true leaf (and the rest) have raised venation and jagged edges of the plate.
- As it grows, the stem becomes long and thin, the color is pale green.
With a lack of light, seedlings stretch out and become unsuitable for planting. To avoid the problem, plants are placed on the windowsill under the sun's rays. The lack of lighting on the north side is compensated by installing fluorescent lamps. One reason for stretching is placing containers close together. More space should be allocated for seedlings.
Pumpkin seedlings
What pumpkin seedlings look like:
- The cotyledon leaves of the pumpkin are wide and round in shape. The plate is painted in a rich green color, the veining is light.
- The stem is short and strong.
- The structure of the leaves is dense and rough; very quickly they overtake zucchini in size.
Advice. If seedlings are grown in transparent cups, then it is worth considering the root system. In pumpkin it is more voluminous and developed.
After planting in open ground, the crops will begin to actively grow. As the plant matures, a compact zucchini bush or long vines of pumpkin are formed. This stage is not always the final one, because there are climbing varieties of zucchini. Only the appearance of fruits will confirm the guesses. Round yellow or orange vegetables are pumpkins, oblong, green or white ones are zucchini.
But not only can the two pumpkin crops be confused; sometimes novice farmers have to figure out how the seeds of zucchini and melon differ. The heat-loving melon crop is grown in open ground only in the southern regions. Its seeds are narrow and long, yellow-brown in color. More often than not, plants get confused in the seedling phase. Having planted seeds in identical pots without a signature, it is difficult to discern where each crop sprouted. How to distinguish zucchini seedlings from melons? It's worth waiting for the real leaves to appear.
The cotyledon leaves are narrower and longer than those of zucchini. The surface is smooth without obvious veining. Real leaves have a curved plate and are wrapped in a bowl shape. Also, melon seedlings are characterized by an edge of short, thin hairs. It covers the petioles and the underside of the leaves.
How to grow zucchini
For a high-quality harvest, it is necessary to carefully select varieties, since fakes may be found on the market. Selection criteria depend on cultivation in certain climatic conditions. When the choice is made, it is necessary to begin preparing the seeds for planting. When using your own seeds, you need to treat them against fungus.
The seeds are poured with hot water at a temperature of 50 degrees Celsius. Soak for a day. Then it is necessary to create a stressful environment; for this, the seeds are immediately placed in cold water for several minutes. Prepare the soil yourself. Sand is added to the soil from the summer cottage. For better thermal insulation, dilute with humus. You can also buy ready-made soil, this will make the process easier and save time.
Early ripe vegetable
The time range when a gardener begins to plant seedlings is very wide. Zucchini is an early-ripening vegetable, so its sprouts can be planted in open ground at two weeks of age. You can plant zucchini seeds in separate pots or in a common container. Peat pots are best suited for this purpose. They will prevent damage to the root system when transplanting to the garden bed.
Important! If you transplant seedlings from a common container, there is a possibility of destroying the rhizome. This will be very stressful for the plant and can slow down its growth for a long time.
It is best to place the seedlings on the sunny side of the house. This will allow her to develop correctly and quickly. The soil must be loosened and young zucchini seedlings regularly watered. It is important not to forget to feed with light fertilizers.
Some time before planting on the site, the sprouts begin to harden, increasing the time spent in the open air. This is done so that the plants better adapt to different climatic conditions. Relocating seedlings is not difficult. Seedlings are planted in dry soil to a depth of 4-5 cm and watered with sufficient water.
Growing zucchini is not a difficult or time-consuming process. You just need to understand the varieties and basic rules for growing seedlings. You should also learn to distinguish seedlings of different crops so as not to confuse zucchini with other vegetables.
0 0 votes
Article rating
Varieties of zucchini and their hybrids
- Variety Gribovsky 37. This type of zucchini evokes a special attitude among experienced gardeners. It is unpretentious to soil types and tolerates planting easily. In terms of herbal and taste qualities, it is a leader among its fellows. Variety Gribovsky 37 has a round shape and short fruit. Zucchini is resistant to various bacterial manifestations - this is another advantage. But there is also a minus - these are vigorous bushes. It will take a lot of space to grow this type of zucchini. The vegetable can be stored all winter. It tolerates transportation well over long distances.
- Variety Iskander F1. This is an early ripening variety. The ripening period is 40-46 days. It has high productivity. Even at low temperatures it is able to set fruit. A very compact bush plant. An excellent choice for summer residents with limited land area.
- Variety Tsukesha. Also refers to early ripening. Unpretentious to climatic conditions, high-yielding. Transports well. The fruits can be collected after 50 days from planting. This variety absorbs little moisture, so it can be stored for a very long time and is widely used in cooking.
- Variety Aeronaut. This is a compact bush plant. It takes about two months before the first harvest. It is popular among gardeners because it has a wide range of advantages. These include long storage, high yield, taste and ease of care.
- Variety Medusa. It is an early ripening hybrid. The ripening period of the first fruits is from 35-37 days. The yield is slightly lower than that of the above-mentioned counterparts. But this variety is resistant to strong temperature changes, for which it is valued by summer residents.
Types of zucchini
Most popular:
- Kruknek. In everyday life it is called the tortuous pumpkin. It has a rounded voluminous base and a thin curved top. Color: bright yellow. The coating of the peel may vary depending on the variety. They are found both with a smooth coating and with convex inclusions.
- Hybrid Delicate marshmallow. This subspecies of zucchini has an interesting color: the fruit is half yellow and half green. The pulp is very dense, like squash. Therefore, this hybrid is great for baking and stewing.
- Squash. This type of zucchini is the easiest to distinguish from others. It has an unusual shape and dense flesh. Color varies from pale green to bright yellow. Tolerates treatment at high temperatures well.
- Zucchini. The closest relative of zucchini. It differs from other types by its thin green crust and delicate white flesh. Zucchini belongs to the early ripening subspecies, and the ideal size is considered to be a fruit of about 15 cm. It is well absorbed by the body and is even recommended for the first baby food.
- Round zucchini. These small fruits, shaped like spheres, come in green and yellow. These zucchini are popular with chefs. For cooking, the pulp of the fruit is removed, and the remaining part is used as a container for interesting dishes.
It is well absorbed by the body and is even recommended for children’s first complementary foods.
Interesting! About 140 different varieties of zucchini are registered in Rosreestr.
Let's talk about growing Zucchini, Pumpkin, Watermelon, Melon in our area
Seedlings of zucchini, pumpkin, watermelon, and melon should be grown in large pots, one plant in each. For zucchini and pumpkin, the temperature should be 2-3°C lower than for cucumbers, for melon and watermelon - the same as for cucumber.
Seedlings of cucumbers and pumpkins can be successfully grown in film greenhouses or tunnels between rows of cultivated crops.
To do this, pots with sown seeds are placed in boxes or on film placed between the rows. After 20-25 days (in the first ten days of June), the seedlings are planted in open ground.
To grow melons or watermelons in our area: in early April or a little later, you need to sow the seeds in pots with sufficiently nutritious soil. To do this, you can suggest adding AVA fertilizer to the soil in powder form at the rate of 1-3 g per kg of soil mixture. In April, it is advisable to supplement the seedlings with a fluorescent lamp. In the 2nd half of May, or rather 40-45 days after germination, the seedlings can be planted in the garden bed, but under a film cover.
Features of growing melons and watermelons. When planting in a permanent place, the root collar of the seedlings must be left above the ground. If possible, plant in a specially prepared bed (with manure and plant waste, preferably in the fall), for example, prepared for cucumbers. The film should be stretched so that at the ends of the bed it can be opened for ventilation. From June it is advisable to start liquid fertilizing and watering. As fertilizers you can use azofoska, Kemira, Baikal EM1. Before flowering, it is enough to feed once every 2 weeks. At the beginning of flowering, as well as during the period of intensive fruit set and before their ripening, it is necessary to increase phosphorus nutrition, for which it is advisable to fertilize with superphosphate extract (2 liters of water per 1 kg of superphosphate. It is infused for 3 days. The resulting blue solution is diluted with water to a concentration of 1 .5 or 2%) or AVA fertilizer (2 G/l, leave for 2 days). If it is possible to make a wooden frame, make a crossbar at a height of 40 cm to ensure maximum illumination and minimal spreading of the tops over the area.
Growing methods
There are many ways to grow a juicy dessert. From traditional ones - spread out or on a trellis, to unusual ones - in a bag or barrel.
Melon in a barrel without a bottom
This method is perfect for central Russia, where summer is not very warm. For melon, a simple barrel is not entirely convenient. There is too little space, because it is advisable not to let the lashes outside, since the temperature difference can negatively affect the harvest. And in case of bad weather, the sissy can easily be covered with film or other covering material. Therefore, sheets of iron connected together or a large container are just right.
Install such a bed in advance:
- All remnants of vegetation are placed at the bottom of the container: branches, dry parts of plants. They will not only serve as drainage, but heat will be generated during decomposition.
- Then fresh grass, hay, humus and fertile soil are laid on top.
- Everything is watered with water or Baikal fertilizer, which will help the plants to rot better.
- The structure is covered with cellophane on top and left until the beginning of May.
- You can plant soaked seeds in the second half of April or seedlings in mid-May, but always under cover.
Video: garden melon
In the bag
This method is useful for those who grow melon on the balcony. But, if you take a larger bag, then it is quite possible to get a harvest in a small area. Of course, thin cellophane bags are not suitable as a material. You need large ones, made of durable polyethylene. Fertile universal soil is suitable for balcony culture. Don't forget to install a trellis. In a garden structure, you can fill the volume in the same way as when growing in a barrel.
Video: growing melons in bags
On a warm bed
This design is an exact copy of the barrel growing method described above. The only difference is that the box is constructed not from metal, but from boards.
Raised beds are an excellent opportunity to grow heat-loving crops
On the trellis
The method is used when growing crops on a balcony or in a greenhouse. It allows you to significantly save space and provides plants with high-quality care, which will definitely result in high yields and low disease rates.
- The method involves the construction of a U-shaped frame - the columns are buried in the ground so that they rise 2 m above ground level, their tops are connected with planks for greater stability.
- The distance between columns in a row is at least 2 m.
- Then a soft wire is tied to the crossbar.
- One end is attached to the crossbar, the lower end is lowered to the growing melon and secured to the plant.
- Subsequently, the growing lash is carefully wrapped around the wire and tied.
When growing melons using a trellis method, you can stretch a coarse, strong mesh between the supports.
Melon grown on a trellis is easy to care for.
Spread method
This method is considered the most natural and simplest. It is used when growing sweet fruits in open ground. Planting scheme for this method: the distance between plants in a row is at least 60 cm, row spacing is 1 m. The stems of the plant should not be intertwined. To prevent the shoots from being blown away by the wind, pin them to the soil using wire staples.
Growing melons spread out - the easiest and most natural way
Are pumpkin seeds healthy?
Pumpkin is a storehouse of vitamins and nutrients. It contains: amino acids, pectin, saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, vitamins, minerals, dietary fiber. In this way it is not very different from zucchini. The most valuable thing about pumpkins is the seeds. Eating them relieves constipation, reduces bad cholesterol in the blood, helps with depression, stress, heals wounds, improves metabolism, normalizes blood pressure, acts as a diuretic, laxative, and fights parasites. It is recommended to include pumpkin seeds in the diet of children, adolescents, elderly people, pregnant women, and athletes. To avoid motion sickness when traveling in public transport, you can chew pumpkin seeds.
People prone to allergies should use the seeds with caution. Not recommended for hyperacidity, obesity, and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Pumpkin seeds are very high in calories; the daily intake should be no more than 100 grams per day. If the product is abused, a stomach ulcer may worsen. For men, pumpkin seeds are good for the genitourinary system, prevent the development of osteoporosis, prevent the deposition of salts in the body and the formation of stones. Arachidonic acid in pumpkin seeds restores memory and helps strengthen blood vessels. And pumpkin pulp has a softening effect on the skin.
What varieties of melons are similar to pumpkins?
Among the variety of types of melons and melons, there is a melon like a pumpkin, which successfully combines the best qualities of these fruits. Therefore, many gardeners who prefer to grow unusual plants on their plots give it preference. There are several crop varieties that meet these characteristics. But you can also get a hybrid by grafting one crop onto another.
Criteria for selecting cucumbers for seeds
There are several rules to follow when collecting seeds if you are interested in the quality of the seed. You need to choose only female fruits with a dried tail: they have already absorbed all the nutrients necessary for the seeds. Female fruits have four chambers, and this is noticeable to the naked eye: they are not triangular in cross-section, like the three-chambered male fruits, but square.
TOP pumpkins by sugar content
Gourmets often argue about which type of pumpkin is the sweetest, since everyone's tastes are different. An objective criterion is the percentage of natural sugars in pumpkin pulp.
So, the sweetest varieties of pumpkin:
Winter dining room A 5
This is a climbing Krasnodar variety, bred back in the 40s of the twentieth century. Used in further selection. Sugar content 9–13%. Ripening time is medium (in the North Caucasus) or medium-late (in temperate climates, through seedlings).
Pumpkins are flattened, weighing up to 7 kg, gray on the outside. When cut, there is dense orange pulp. The keeping quality is excellent.
Winter sweet
Sweet Winter pumpkin is a popular modern variety that is not prone to nitrate accumulation. Depending on the region and weather, mid-season or mid-late. Resistant to anthracnose disease. The stems are quite long.
Fruit weight 4 – 7 kg (sometimes twice as much); The outer color is spotted gray, the inner color is orange-yellow. The consistency is not loose. The taste fully justifies the name (about 8% sugar). Long-term storage.
Chit
It ripens 4 months after germination, filling up to 2 – 3 kg. Easy to grow, not affected by anthracnose. Pumpkins are soft gray on the outside and deep orange on the inside. The seed chamber is small.
The pulp is not watery, slightly crunchy; sugar content over 9%, even in temperate climates.
Michurinskaya
The pulp is thick, bright orange, fiberless; accumulation of sugars – up to 10%. Storage is long, and the sweetness increases 1 – 2 months after harvesting.
Marble
Mid-late, climbing pumpkin. It got its name Marble because of the contrasting spotted pattern on the skin. There are no cracks or white rot on the fruits; they are stored excellently. Weight 4 kg; the shape is spherical-flattened, with small ribs.
The average sugar content is 9%, the maximum is 12%. The pulp is not mealy, juicy and tender.
Orange honey F1
Climbing hybrid of medium ripening period, weighing 1.8 – 3.7 kg. Pumpkins are flattened and striped. From the inside they are very bright - red-orange.
The consistency is balanced in juiciness and density, the taste is excellent. Shelf life - about 5 months.
New
The stems are long and need pinching after the ovaries form. This mid-season (120 days) butternut squash produces club-shaped fruits. Can be stored for 8 months. When fully ripe, the skin is pinkish-orange.
The pulp is very juicy, orange in color; sugar content – 10%.
How to dry seeds
The planting material is dried by spreading it in a thin layer on paper or a piece of fabric; you can also use plastic film; well-washed grains do not stick to it at all.
Place the container in a warm, dry place. It will take about a week to dry completely.
There is no need to rush; it is best if the planting material dries naturally. The ideal place is a sunlit window sill.
Collecting cucumber seeds
The pulp of cucumbers near the tail is always bitter, and the seeds located in this part are not suitable for propagation: they can pass on the bitterness by inheritance. Therefore, we cut off the end of the cucumber with the dry tail and throw it away, and then cut the cucumber and scrape out the seeds along with the pulp into a jar with a spoon.
Each cucumber seed is in a transparent shell, which must be removed so that the seeds can be stored for at least 3-4 years. In order for the shell to peel off, you need to leave the seeds in the jar for 2-3 days for fermentation. During fermentation, the shell breaks down and is easy to remove: pour water into a jar and shake the contents well, then let it sit.
During the settling process, empty seeds will float to the surface, and you can scoop them up with a spoon and throw them away, while full-fledged seeds will settle to the bottom. Place them on a sieve and rinse thoroughly under running water to remove any remaining pulp and loose shells.
Place clean seeds in one layer on oilcloth or an old file to dry. I usually use a file that the seeds don't stick to and is very easy to collect later. The seeds are glued to the paper. Don't forget to label the file so you don't forget which variety the material was collected from.
Pumpkins with an interesting taste
The typical pumpkin smell can attract or, conversely, repel - and then “camouflage”, the vegetable’s tendency to taste variety, helps out. This usually refers to the aroma and feel of the consistency.
For some, the most delicious variety is mealy with a nutty smell, while others prefer nutmeg notes. The palette is really large.
Sweet pumpkin varieties have different tastes. Variants of taste and aroma of the pulp:
Muscat
This is a special spicy aroma, subtle and pleasant. Inherent in many varieties bred on the basis of nutmeg pumpkin. Its intensity depends on the variety, degree of ripeness, and growing conditions. The most plump club-shaped forms:
Arbatskaya
Climbing, late (bred in Crimea), weighing 6 - 20 kg, orange inside and out. One of the most fragrant!
Pineapple F1
A productive mid-season hybrid weighing about 2 kg. The skin is beige, the flesh is dark yellow; sugar content up to 10%. During storage, the odor increases.
Old French varieties also have a classic nutmeg aroma, the most famous of which is:
Muscat de Provence (Muscat de Provence)
It grows excellently in the Russian climate - from 3 to 8 kg (or more). The timing is medium late. Pumpkins are beautiful - round, flattened, ribbed, brownish-red. The pulp is bright orange, not too watery; The sweetness is moderate, but the aroma is intense.
Vanilla
In relation to pumpkin, it is considered a type of nutmeg flavor.
Pastila-Champagne
A popular variety without a “vegetable” pumpkin smell, very sweet and long-lasting. The taste is excellent both raw and after cooking. Weight 2 – 4 kg (up to 10 kg). The shape is oval, the skin is pinkish, the flesh is orange. Reviews about the aroma are varied: in addition to vanilla, you can smell watermelon and melon.
Dacha
An early compact variety belonging to the hard-bark pumpkin species. It ripens steadily in temperate latitudes, filling up to 3–5 kg and accumulating 6% sugars. The consistency is tender and juicy. The shape is oval, smooth. The outside of the fruit is striped, the inside is orange. Stored until January.
Melon
Pumpkin and melons are close botanical relatives. It is not surprising that breeders managed to obtain a pumpkin with the taste of melon and its slightly sugary aroma.
Smile
It has unique characteristics: almost bush (1 meter), cold-resistant, early ripening (85 days), with a sugar content of 8%. The plant produces 5 – 7 orange “balls” weighing 700 – 980 g.
Ethiopian
This variety of melon, like a pumpkin, forms compact bushes with vines up to 4 m long. The leaves of the Ethiopian are large, heart-shaped. They reliably protect fruits from sunburn. The first harvest of this variety ripens 70-80 days after emergence.
Melons are flattened and round, divided into segments in the form of large lobes, which makes them similar to a pumpkin. The peel is bright yellow. There is a continuous mesh pattern on the surface. The pulp is light beige in color, very juicy, with a honey taste and rich aroma.
The Ethiopian melon produces a lot of seeds. The average fruit weight is 3-4 kg, but by limiting the number of ovaries, the weight of individual specimens can be increased to 7 kg.