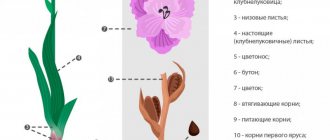
What seeds need preparation?
The quality and quantity of the future harvest depends on the proper preparation of cucumber seeds for sowing. To sprout and form strong and healthy plants, some effort must be made.
Varietal seeds, purchased in a store or collected independently, must undergo preliminary preparation.
The procedure for preparing seeds for sowing for seedlings, in a greenhouse (greenhouse) or open ground is not fundamentally different. But in greenhouse conditions there is a special microclimate, high humidity, special temperature conditions and crowded plantings.
Infectious and fungal diseases spread faster in a greenhouse than in other conditions, so the most important technique in such conditions is seed preparation, including disinfection.
For hybrid seeds indicated on the packaging as F1, it is not necessary to perform any manipulations to prepare them. They have already been calibrated, heated up, treated with fungicides and stimulants, and have an uncharacteristic color. Such seeds can simply be germinated or directly planted in the ground.
Soil preparation
To sow cucumbers, you can purchase a ready-made soil mixture in the store or make it yourself from:
- 1 part sifted turf or leaf soil,
- 1 part peat
- 1 part humus
- 1 part sifted river sand.
Instead of peat, you can take steamed (spilled with boiling water) sawdust. Per 10 liters of mixture, 100 grams of wood ash and 20 grams of superphosphate are added. The mixture is thoroughly mixed.
How to properly prepare seeds for sowing seedlings
Properly carried out measures for calibration, disinfection, heating, hardening and germination of seeds help to obtain strong seedlings, and then a good harvest of cucumbers.
Calibration
Seed preparation should begin with selection and calibration.
Add a tablespoon of salt per liter of water and stir. The seeds are immersed in the solution for 15-20 minutes. Floated, as well as dark, stained, deformed, damaged seed material is removed.
The remaining seeds are washed under running water and dried on a napkin. After this, calibration is carried out. Small seeds are separated from large ones. When planting, they are planted to a depth of 1 centimeter, and large ones - 1.5-2 centimeters. If there are a large number of seeds, small ones may not be planted.
Disinfection
To protect seeds from diseases such as bacteriosis, root rot, viral mosaic, powdery mildew and tracheomycosis wilt, you need to undergo a disinfection procedure.
The seeds are placed in a gauze or fabric bag and dipped in a strong (purple) solution of potassium permanganate for 20 minutes. After which they are washed with running water.
Small seeds can be disinfected under an ultraviolet lamp for 2-3 minutes.
Instead of potassium permanganate, you can use a solution of wood ash, a hot solution of nitrophoska and copper sulfate, boric acid (a teaspoon per liter of water) or a solution of Fitosporin-M. Seeds are placed in any of the solutions for 12 hours.
Seed disinfection can also be carried out in garlic peels. To do this, the husk is poured with boiling water for 2 hours and filtered. The seeds are placed in the infusion for an hour, then washed.
To increase immunity, the seeds can also be placed in aloe juice, diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio for 6 hours.
Warming up
To increase the germination of seeds, before planting they are heated in the oven for 3 hours at a temperature of 50-55 degrees.
If you have time, the seeds can be warmed up in advance, a month before sowing. For this purpose, they are laid out next to the heating device at a temperature of 25-29 degrees. This gradual heating dries them evenly, increasing their germination.
Bubbling
Enrichment of cucumber seeds with oxygen (bubbling) is used for seeding material that has reached 6-7 years of age. This procedure increases germination energy and increases the number of seedlings. Young seeds do not require this procedure.
The seed material is placed in a gauze (fabric) bag and sent to a container with a warm solution of a growth stimulator, for example, Zircon, Kornevin, Epin, Cytodef, sodium humate (5 drops of solution per 1 liter of water). Then, using an aquarium compressor, a stream of air is supplied to the seeds. The filter on the compressor is removed. The tube is located under the seed bag. Air bubbles surround the seeds on all sides. They are kept in water for approximately 18-24 hours. If there are a large number of seeds, in the middle of the cycle (after 9-12 hours) the water is replaced with new one.
In the absence of a compressor, the seeds are poured into a container with a growth stimulator for 12 hours and mixed regularly with a wooden spoon. To further saturate the air, the water can be partially replaced with new water every 2-3 hours. It should be warm (20-25 degrees).
After bubbling, the seeds are poured onto a paper napkin to dry.
Germination
The seeds are laid out in a damp cloth and sent to a transparent bag or on a saucer and placed in a bright, warm place for 1-2 days. When the fabric dries, it is sprayed with water. The seeds will swell and begin to germinate. The length of the roots should not exceed 2 millimeters. Otherwise, they may break off when landing.
Sprouted seeds can be planted, but it is better to harden them first.
Hardening
Hardening of seeds increases the resistance of future plants to any unfavorable environmental conditions.
The seeds are hardened in the swollen or hatched state. They are placed in a damp gauze bag on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator (on the vegetable shelf) for 2 days.
Also, seeds can be hardened for 3-5 days, alternating heat and cold. In this case, the seeds are placed in the refrigerator at night, and warmly for the day.
The bag should not dry out during hardening. To reduce moisture evaporation from the bag, it must be wrapped in polyethylene.
Hardening makes plants stronger, resistant to diseases and temperature fluctuations.
Selection of the best specimens
Those who grow seeds themselves or purchase planting material from other farmers will have to undergo a calibration process. Store-bought products are usually processed before sale.
Seeds of irregular shape and color are eliminated: dark and spotted. For planting, the farmer chooses large, straight white specimens. In order to optimize the process, salt calibration is recommended:
- 3 g of salt are mixed in 100 ml of water (30 g per 1 l);
- the seeds are dipped into the solution and stirred until the bubbles disappear from their surface (usually it takes no more than 10 minutes);
- The floating seeds are discarded, the remaining ones are rinsed and dried.
Such a test is only suitable for young seeds (no older than 2 years). The old ones will most likely pop up.
Proper care of cucumber seedlings
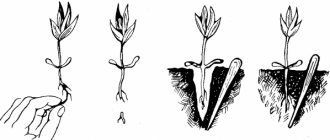
To sow seeds, take separate peat pots or cups without a bottom, with a diameter of at least 8 centimeters. Peat pots allow you to plant grown seedlings directly into the ground without removing them and without damaging the roots. They easily grow through the walls, and the peat structure serves as additional fertilizer for them. You can also use peat tablets, which are then planted in separate containers.
The pots are filled with soil mixture and spilled with a warm solution of potassium permanganate. After the moisture has drained, the seeds are placed in the soil to a depth of 1.5-2 centimeters. Then they are watered with warm water and sprinkled with soil. The containers are covered with glass or transparent plastic film.
When to plant cucumbers for seedlings
After the first shoots appear, the seedlings are placed on a well-lit windowsill on the south side. The air temperature in the room during the day should be 20 degrees, at night it should not drop below 15 degrees.
Young plants need good lighting for 10-11 hours a day. In the absence or lack of natural light, additional illumination with a phytolamp is required.
Watering plants is carried out with warm water. Before the first leaves appear, the ground is irrigated with a spray bottle. After the first leaves form, the seedlings need to be watered using a syringe or a teaspoon. Water should not fall on the stems and leaves, but should saturate the soil.
Fertilizing cucumber seedlings is carried out after the appearance of one main leaf. Then it is repeated once every 10 days. For a bucket of water, take a liter of mullein, 20 grams of urea or ammonium nitrate.
A few days before planting the plants in the ground, they are fertilized with a solution of ammonium nitrate (5 grams of fertilizer per bucket of water).
Fertilizing should be done in the evening, after watering. The solution should not get on the leaves. If the fertilizer does get on the foliage, it is immediately washed off with water from a spray bottle or watering can.
The period for growing seedlings is 25-30 days. Plants ready for planting have dark green, well-developed leaves, a strong, dense stem and strong roots.
A week before planting seedlings in unprotected soil, seedling hardening begins. Her time in the open air increases gradually.
When planting, the soil should warm up to 15 degrees, and the air to 18ºС.
Grown plants are planted in prepared beds. They are placed in the center or in a checkerboard pattern, on average there are 4-6 seedlings per 1 square meter. The distance between rows should be about 50 centimeters, in a row 30-40 centimeters, when planting in 1 row - 20 centimeters.
After planting, they are thoroughly watered with warm water. If necessary, non-woven material is stretched over the top for acclimatization. When the plants begin to grow, the shelter is removed.
In the future, the plants are provided with proper care, which guarantees a good harvest.
After what to plant cucumbers? What to plant after cucumbers?
Disinfection
Dried cucumber seeds must be processed before planting.
In a solution of manganese
The seeds are immersed in manganese tincture for 25-30 minutes, after which they are thoroughly washed. To prepare the mixture, you will need 1 tsp. for 2.5 cups of liquid. The color of the finished mixture is ideally bright purple. If the liquid is translucent, the solution is not suitable for disinfection.
The method is suitable for removing bacteria from the surface layer of seeds. If you pre-treat them, the effect obtained is reduced.
Drugs
Fighting diseases that form in the seed embryo is much more difficult. Modern gardeners use bacterial preparations for baiting. Such means are a double-edged sword. In addition to destroying bacteria, they also tend to suppress beneficial microflora.
Tracheomycosis and other infections are eradicated with the help of Baksis and Fitosporin. Cucumber seeds are soaked in a solution of a bacterial preparation for 1.5 hours, then dried.