Crispy cabbage has firmly established itself in our diet for a reason, because among the widest variety of garden crops, this low-calorie product is a real storehouse of vitamins and microelements. It has been known since time immemorial, and received its name from the ancient Roman word “caputum”, meaning “head”. And in Rus' this vegetable had a figurative nickname - “garden head”. Today it is difficult to meet a gardener who does not grow cabbage - white heads can be seen behind almost every country fence. Growing this beauty so that the forks are dense and the leaves are juicy and crisp is actually not difficult if you know some rules.
What kind of soil does cabbage like?
The white-headed lady is demanding in terms of light, high humidity, as well as the composition and quality of the soil, so it is important to choose the right place for planting it.
Taking into account the acidity of the soil
Cabbage prefers fertile soils with a neutral or alkaline reaction. The optimal acidity level is 6.7–7.4 pH. Acidic soils are not suitable for cabbage, increasing the risk of clubroot disease. Such soil can be improved by liming using:
- dolomite flour;
- fluff lime;
- powdered chalk;
- wood ash.
Dolomite flour contains calcium, which reduces acidity, as well as magnesium, which improves the quality of vegetable products. That is why it is considered the best of deoxidizers.
This procedure is carried out in the fall. One of the listed substances is added to dry soil at the rate of 1–2 cups per 1 square meter. m, the garden is immediately dug up and left until spring.
Selecting and preparing a site for planting
Cabbage grows well on open southern or southeastern slopes, with the possibility of an abundant supply of water. The soil must be characterized by high air and water permeability. When the soil is excessively moistened, the plant suffers from a lack of oxygen, and therefore develops poorly and grows slowly.
The best option is loam, which has the ability to retain moisture in its particles. Sandy soils do not retain enough water and nutrients. To improve their properties it is necessary:
- Remove the top layer of soil from the area (40–50 cm).
- Place a 10–15 cm layer of clay on the bottom.
- Mix the initially collected soil with peat, manure and mineral fertilizers and pour it onto the clay layer.
Loams are ideal for growing vegetables as they provide good drainage and water-retaining properties.
You can increase the moisture capacity of the soil if, during autumn digging, you add sawdust moistened with urea, peat or turf soil. It is recommended to dig the bed as deeply as possible without breaking large clods. The wavy surface of the area will freeze better in winter and accumulate more moisture.
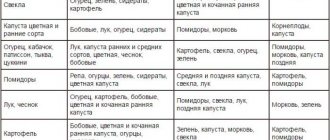
An important factor when placing cabbage beds in the garden is plant compatibility. When planting cabbage next to bad neighbors, the likelihood of them being affected by common diseases or being oppressed by each other increases.
Table: predecessors and neighbors of white cabbage
| The best predecessors |
|
| Bad Predecessors |
|
| Ideal neighbors |
|
| Incompatible neighbors |
|
By planting cabbage next to celery, you can ensure the destruction of flea beetles, and proximity to aromatic herbs will scare off oviparous cabbage butterflies
Do not forget to follow the rules of crop rotation: do not plant cabbage in the same place for more than 2-3 years. This depletes the land, increases the risk of disease, and affects productivity.
Methods and technology for growing cabbage
Cabbage can be grown either through seedlings or without seedlings. The choice depends on the climatic conditions of the region - in the middle latitudes and in the north the vegetable is grown mainly by seedlings, in the south - by sowing seeds directly into open ground.
Sowing cabbage seedlings at home
By observing a number of requirements, white-headed seedlings can be grown at home. The first step is to decide on the planting time. They will depend on the cabbage variety:
- early varieties are sown for seedlings from March 5 to March 25;
- mid-season - from March 20 to April 20;
- late - from April 1 to April 25.
You can calculate the exact sowing time yourself, taking into account that 60–70 days pass from the moment the seeds are immersed in the soil until the sprouts are planted on the site. For sowing, it is better to use large but low containers - trays or containers with drainage holes.
Cabbage requires a fertile, loose substrate. The best option is a mixture of humus and turf soil in a 1:1 ratio with the addition of wood ash (at the rate of 1 tbsp per 1 kg of soil mixture).
The seeds are placed in pre-moistened soil in rows quite close to each other. With the emergence of seedlings (on the 5th–6th day), the planting should be thinned out. After 3 weeks, when two leaves grow, the seedlings need to be picked.
When thinning, keep in mind that each sprout requires 2 square meters for normal development. cm soil
A prerequisite for the normal formation of cabbage seedlings is supplementary lighting. At the beginning of spring, there is not enough sunlight, so in addition to the daytime period, another 7–8 hours of illumination will be required. To do this, you can use a regular fluorescent lamp.
Watering is carried out as the soil dries, followed by obligatory loosening of the soil. Feeding of seedlings is carried out three times:
- 2 weeks after emergence. Plants are watered at the root with a solution per 1 liter of water:
- 2 g ammonium nitrate;
- 4 g superphosphate;
- 2 g potash fertilizers.
- 12–14 days after the first; the same composition, but 2 times more concentrated.
- 2 weeks before the expected planting in the ground. Dissolve in 1 liter of water:
- 3 g of saltpeter;
- 5 g superphosphate;
- 8 g of potash fertilizers.
Before planting on the site, seedlings need to be hardened off. First, open the window (without drafts), then take the plants out into the air for several hours, and in the last week move the seedlings to the balcony.
Video: how to grow cabbage seedlings
Picking seedlings
Picking is an agrotechnical technique that involves transplanting plant seedlings from a common box into individual containers. As for cabbage seedlings, there is friction among gardeners regarding the need for it. Some believe that picking allows you to get an earlier and higher-quality harvest. Others believe that in the process of moving the sprouts, their root system is damaged, and this delays the development of the plant.
Table: advantages and disadvantages of picking cabbage seedlings
| Advantages | Flaws |
|
|
Cabbage seedlings are picked when two or three true leaves are formed on the sprouts. The seedlings are transferred to separate containers: plastic or paper cups, film cylinders, pots, peat tablets.
Frequent mistakes when picking are incorrect placement of the root and insufficient depth of the seedlings: 2 - the root is bent, 3 - the root is not in contact with the soil, 4 - the seedling is planted shallowly, 1 - correct planting
It is important to ensure that when transplanting sprouts, their roots are positioned strictly vertically. The soil around them needs to be carefully compacted, and then the substrate should be added right up to the cotyledons and lightly moistened.
One pick is enough for cabbage. But if you were unable to move the seedlings to the garden bed in a timely manner, then you can do a second one.
Video: how to pick cabbage seedlings
Growing cabbage in open ground
Seeds are sown in open ground from mid-April after the threat of frost has passed. It is better to plant on a sunny, warm day in pre-moistened soil. It is important to choose the sowing time so that the daytime temperature does not rise above 20 °C. Cabbage doesn't like heat.
If you sow dill between the main plantings, this will repel many insect pests.
- The holes are made at a distance of at least 40 cm.
- A fertilizer solution is added to each and 1-2 seeds are placed.
- Fall asleep and lightly compact.
Video: how to sow cabbage in the ground
Features of growing cabbage in a greenhouse
The greenhouse method for growing white cabbage is rarely used, because this vegetable is quite frost-resistant - it can tolerate short-term frosts down to –8 °C. Nevertheless, its advantages are obvious: thanks to the ability to regulate temperature and extend daylight hours, greenhouse conditions allow you to harvest early ripening varieties as early as June.
Seeds for seedlings are sown in a greenhouse in February, and already in mid-April the plants can be planted in a bed in a greenhouse. To grow cabbage seedlings you need:
- Prepare a greenhouse: dig a trench in the ground up to 30 cm deep and 100–120 cm wide. Place biofuel on the bottom, cover it with a substrate of turf soil, peat and sand in equal parts.
- Plant cabbage seeds, deepening them 1 cm into the soil.
- Place a frame with a film at least 30 cm high on top.
In a biofuel greenhouse, optimal conditions are created for the development of seedlings - When the first shoots hatch (after 4–5 days), open the greenhouse during the day to harden the crops.
- Raise the temperature to 10–12 °C after the first leaf has formed.
- Thin out the seedlings and begin active watering when 1–2 true leaves appear.
- At the same time, carry out the first fertilizing with a nitrogen-potassium-phosphorus mixture. The second - if there are 3 leaves, with only nitrogen fertilizer, the third - before planting in the greenhouse with the original composition.
Do not forget to provide additional lighting in the greenhouse - cabbage requires at least 14 hours of daylight.
The main signs that seedlings are ready for planting are the presence of 4 leaves and a green-purple color. Transplantation should be carried out using the transshipment method, i.e., together with a lump of earth without shaking off the roots. Water is poured into pre-prepared holes, fertilizer is placed and the seedling is lowered, compacting the soil tightly. The minimum distance between the holes should be at least 30 cm. The first watering is carried out after a week.
Popular varieties of different types of cabbage
There are about 38 different types of cabbage, differing in appearance, taste and quality characteristics. Among them, it is worth highlighting several of the most common among gardeners.
Red cabbage
Varieties of this species are characterized by unusual, bright colors of heads of cabbage.
The TOP 5 red cabbage varieties include:
- Vorox – ripening 95 days, productivity 6 kg/m2, weight up to 3.5 kg, purple color with waxy coating. Recommended for processing and fresh consumption.
- Lyudmila – growing season 130 days, purple color with a green tint, weight 2 kg, yield 5 kg/m2. Excellent taste, transportability, long-term storage.
- Rebecca – mid-ripening, weight 3 kg, productivity up to 7 kg/m2. Purple color, presence of a strong waxy coating. High density, excellent taste.
- Juno – ripening 160 days, weight 1.2 kg, yield 4 kg/m2, dark purple color, recommended for fresh consumption.
- Faberge - growing season 110 days, weight up to 3 kg, productivity 8 kg/m2, pronounced purple color, rich taste. Resistance to cracking and numerous diseases.
Colored
Cauliflower is characterized by a high content of vitamins, soft texture and delicate taste. Its best representatives:
- Cauliflower Dacha - ripening 100 days, weight 1 kg, transportability, possibility of long-term storage without loss of quality.
- Snow globe - early ripening (about 60 days), resistance to diseases, the ability to harvest up to 2 times in 1 season.
- Movir – early ripening, weight up to 1.2 kg, ability for simultaneous germination, excellent taste characteristics.
- Express – growing season 62 days, weight ½ kg, high immunity to bacteriosis, excellent taste.
- Guarantee - ripening 100 days, weight up to 1 kg, high yield, unpretentiousness, excellent taste.
Beijing
This annual crop is very popular. Among its many varieties it is worth highlighting:
- Chinese cabbage Manoko - ripening in about 50 days, weight 1.5 kg, high yield, excellent taste, immunity to internal necrosis and fusarium, not susceptible to bolting, resistance to hot conditions.
- Cha-cha F1 – ripening 60 days, weight 2.5 kg, high yield, resistance to pathogens of major diseases, ability to fully develop in hot climates.
- Hydra F 1 – growing season 60 days, non-susceptibility to bacteriosis and clubroot, high quality characteristics.
- Custar F1 – ripening in about 70 days, weight 1.5 kg, high productivity, excellent taste.
- Miraco F1 – medium early ripening, weight up to 1 kg, unpretentiousness, low maintenance, good taste.
Broccoli
Broccoli is an annual crop characterized by cold resistance and a need for a humid environment. The TOP 5 best varieties of broccoli include:
- Green Magic - ripening 65 days, weight 700 g, excellent taste and product characteristics, immunity to peronosporosis.
- Fiesta F1 - ripening 80 days, weight 0.6-1.2 kg, high yield, excellent taste, heat resistance.
- Naxos F1 - ripening in about 80 days, weight 0.5-0.8 kg, excellent product and taste characteristics, resistance to heat and major diseases.
- Batavia F1 – growing season 95 days, weight 0.7 kg, high productivity, possibility of long-distance transportation without loss of original properties, heat resistance, non-susceptibility to fusarium.
- Heraklion F1 - ripening 75 days, weight from 0.5 to 2 kg, unpretentiousness, good yield, resistance to heat.
Savoy
Heads of Savoy cabbage are bubbly and loose. This type is indispensable when preparing vegetable cutlets and cabbage rolls. The TOP 5 best varieties of Savoy cabbage include:
- Golden early - ripening 110 days, weight 800 g, productivity 34 kg/10m2. Resistant to drought, cold temperatures and cracking.
- Moscow lacemaker - growing season up to 95 days, weight 1.2 kg, yield up to 40 kg/10m2. Low susceptibility to bacteriosis and fusarium.
- Petrovna - ripening 110 days, weight 1.2 kg, productivity 40 kg/10m2.
- Melissa F1 – growing season 120 days, weight about 3 kg, productivity 43 kg/10m2. Resistance to many diseases. as well as drought and cooling. Possibility of storage up to 5 months.
- Vertu 1340 – ripening 130 days, weight 3 kg, productivity 80 kg/10m2, pleasant and delicate taste.
Brussels
Brussels sprouts contain a large amount of protein, folic acid, nutrients and vitamins A, B, C. Due to this, the vegetable is often included in the diet.
The most popular varieties of Brussels sprouts:
- Perfection – medium-late ripening, yield 5 kg/m2, excellent taste.
- Curl - ripening after 160 days, the weight of small heads of cabbage is 10-15 g, high yield, since up to 35-40 heads of cabbage can form on one plant.
- Boxer F1 – mid-season. productivity up to 16 kg per hundred square meters. Resistance to pests and major diseases.
Kohlrabi
This unusual cabbage is similar in appearance to a root vegetable. Almost all varieties of kohlrabi are distinguished by excellent taste, high productivity and early ripening.
The most common varieties of kohlrabi:
- Vienna white 1350 – growing season up to 75 days, simultaneous ripening, drought resistance, cold resistance, tender and juicy fruit pulp.
- Sonata F1 – ripening 65 days, weight 0.75 kg, frost resistance, recommended for processing.
- Smak – ripening 80 days, weight 700 g, dark purple color, can be stored for up to 3 months.
Decorative
This type of cabbage is considered a vegetable crop, despite the fact that it looks like a beautiful flower. Popular varieties of ornamental cabbage:
- Tokyo - height 35 cm, burgundy-red color.
- Osaka – burgundy-red or pink color, height 55 cm.
- Nagoya – height 60 cm, color options: pink, white, purple-red.
Non-standard growing methods
In pursuit of a good harvest, inventive summer residents come up with original techniques and devices for growing vegetables. And cabbage is no exception.
Under plastic bottles
This method is used for growing cabbage from seeds in open ground. The plastic container acts as a mini-greenhouse with a stable microclimate where the seedlings feel comfortable.
Planting seeds for bottles is carried out in early to mid-May as follows:
- Place beds 10–15 cm high and 35–40 cm wide. The day before sowing, they are filled with water.
- Shallow holes are formed at a distance of 30–40 cm from each other. To make the recesses perfectly even, you can squeeze them out with the bottom of a glass bottle.
- Place several cabbage seeds in each hole, sprinkle with a tablespoon of humus and cover with a plastic bottle with a cut bottom and screwed on lid.
Watering of crops is carried out as needed through the neck. The lid is finally removed when 2-3 true leaves appear. The bottles are removed with the onset of stable heat.
Use containers made of light plastic. This way you can monitor the development of the crops.
Video: planting cabbage under bottles
In bags
Gardening in bags is becoming increasingly popular for several reasons:
- compactness;
- mobility;
- productivity does not depend on the quality of the land on the site;
- no weeds;
- reducing the likelihood of diseases and pest damage.
To grow cabbage in this way, use polyethylene or propylene bags with a volume of 100–120 liters. Organic residues, compost, sawdust are placed at the bottom of the container and covered with a layer of earth. Several small holes are made in the bag for drainage. Cabbage can be planted either from seeds or seedlings. One of the disadvantages of this method is the need for frequent watering.
Video: growing cabbage in aquarium bags
Behind a plastic wall
This planting method means that the cabbage will grow behind a makeshift plastic wall. According to the authors of this idea, this way you can protect the seedlings from the wind, mole crickets and partly from direct sunlight.
“Building” such a fence is not difficult:
- Rings 15–20 cm high are cut from two or five liter bottles and immersed in the ground.
- Seedlings are planted in the center.
Planting seedlings in plastic rings causes controversy among gardeners: some claim that this saves cabbage from mole crickets and slugs, others are convinced that the method is of little benefit - The plastic is removed when the leaves begin to fall over the top of the wall so that they are not cut off by the edges of the rings.
Rules for caring for cabbage
Caring for cabbage after moving to a permanent place of residence will not cause much trouble if you follow the principles of care.
Watering
The white-headed lady is capricious regarding water. If you do not provide sufficient irrigation, the formation of rosettes stops. And excessive stagnation of moisture for 10 hours will lead to the death of the roots. In mid-latitudes, cabbage is watered 2-3 times a week.
With drip irrigation, the maximum effect is achieved: moisture goes directly to the cabbage roots with little labor input
Features of watering cabbage:
- The optimal water temperature is 25 °C.
- The best time to water is early morning or evening in clear weather and all day if it is cloudy.
- The approximate volume is 20 liters of water per 1 m2.
- 20–25 days before harvesting the forks, watering must be stopped - this will protect the heads of cabbage from cracking.
Loosening and hilling
Loosening and weeding are measures that allow you to get rid of weeds and saturate the soil with oxygen. Must be carried out systematically after precipitation and watering.
Hilling is required to maintain the thin stem of the plant, protect it from the wind, and also to retain moisture in the soil. Carried out twice during the growing season:
- 7–10 days after transplanting the seedlings.
- After a month and a half.
When hilling, soil is raked to the outlet within a radius of 30 cm
Fertilizer
Cabbage consumes a large amount of different nutrients from the soil, which it needs to grow green mass. Moreover, some of them are used by the plant in large quantities (they are called macroelements):
- nitrogen;
- phosphorus;
- potassium;
- sulfur;
- magnesium;
- calcium;
- iron.
Consumption of other substances is kept to a minimum, but is also vital (these are microelements):
- boron;
- manganese;
- copper;
- molybdenum;
- zinc;
- silicon;
- cobalt;
- sodium;
- iodine.
For this reason, it is recommended to feed cabbage with complex fertilizers - both organic and mineral.
After fertilizing the soil, watering is necessary. This way the substances will dissolve better and be more efficiently absorbed by the plant.
It is important to know that at different stages of the growing season, cabbage consumes different amounts of substances.
- During the seed germination stage until the leaves form, the plant needs more phosphorus.
- At the next stage, intensive development of the root system occurs and the sprouts need more nitrogen and potassium.
- At the ripening stage, the need for phosphorus, nitrogen, and potassium increases.
Therefore, there should be at least two feedings:
- 2–3 weeks after planting the seedlings for intensive growth of the rosette, on which the future harvest depends. Norm per hectare:
- 40–80 kg of ammonium nitrate or 50 kg of urea;
- 100 kg of superphosphate;
- 50–100 kg of potassium salt.
- At the beginning of head formation:
- 100–150 kg of ammonium nitrate;
- 50–100 kg of potassium salt.
Cauliflower varieties
Late varieties of cabbage
The variety of crops in the modern world has a huge number of varieties. Its varietal feature is the difficulty of growing. But a lot of vitamins and minerals make it simply an irreplaceable product in the menu of adults and children. Crops must be planted in seedlings, just like cabbage. But she requires a lot more attention.
Cauliflower varieties
The main varieties cultivated in Russia and the post-Soviet space are: Pionerka, Opal, Beautiful Vecha and Francoise. Cauliflower Guarantee is popular.
The main condition for success is the correct choice of variety for cultivation in a particular climate zone. For example, the Francoise variety is perfect for agricultural technology in central Russia.
Features of growing cabbage in the regions
Cabbage is cultivated almost everywhere. Thanks to the centuries-old work of breeders, it became possible to choose zoned varieties: for the northern regions - frost-resistant, for the southern regions - drought-resistant. Planting methods and timing may vary in different climates.
In the Urals, Siberia, Altai
In these regions, cabbage is grown through seedlings. Sowing is carried out in late March - early April.
Stronger seedlings are planted in open ground somewhat later than in the southern regions:
- early varieties - in the second half of May;
- varieties of medium ripeness, medium late - in early June.
Late varieties are practically not planted in these regions, since there are already frosts in August, and the first snow falls in October.
Table: popular varieties and hybrids of white cabbage for Siberia, the Urals, Altai
| Early ripening |
|
| Mid-season |
|
| Mid-late |
|
Another feature of growing vegetables in cold climate zones is the need to treat seedlings with growth activators that stimulate their development:
- Gumat-7,
- Stimulus,
- Epin-extra.
In outskirts of Moscow
The climate of the Moscow region allows you to sow cabbage seeds not only for seedlings, but also directly into the ground, provided they are protected with film coverings, using greenhouses or warm beds. Sowing time in middle zone conditions:
- early and mid-early varieties - from April 20 to May 10;
- medium, medium-late and late - from May 10 to May 30.
Seedlings are planted in open ground at the age of 35–40 days.
Table: the best varieties for growing in the Moscow region
| Growing methods | Variety name |
| In the open ground |
|
| In the greenhouse |
|
In Ukraine
The mild climate of the country creates comfortable conditions for the growth of white-headed fish in all areas. Early varieties are cultivated in greenhouses and warm beds, mid-season and late varieties are sown with seeds in open ground. In the southern regions of Ukraine, even the latest varieties with a ripening period of more than 190 days have time to ripen.
Table: the most common varieties of white cabbage in Ukraine
| Early |
|
| Mid-season |
|
| Late |
|
So, now you are armed with knowledge about the features of planting and caring for cabbage. You can safely get to work and, undoubtedly, the white-headed one will delight you with a rich and crunchy harvest.
Grow, “garden head”: how to grow cabbage wisely from yagodka.club.
Rating of the best varieties of WHITE cabbage
White cabbage is the most common among gardeners. Today, many varieties of this species have been bred, differing in quality characteristics. The best of them are presented in the ranking.
Most Popular
TOP 7 most popular varieties of white cabbage with descriptions and characteristics:
- Slava - medium-late ripening, weight of round heads up to 4.5 kg, resistance to most diseases and low temperatures, lack of tendency to cracking. High taste, juiciness, versatility in use, yield up to 12 kg/m2.
- June - early and simultaneous ripening of heads of cabbage, resistance to cold and cracking, weight 2.4 kg, high content of vitamins, excellent taste. Productivity 6.4 kg/m2, suitable for widespread cultivation, the variety is recommended for fresh consumption.
- Rinda F1 - medium maturation, weight up to 8 kg, high content of vitamins and nutrients, resistance to disease and cracking, good transportability. Juiciness, suitability for pickling, yield up to 10 kg/m2.
- Russian size - average ripening period, weight 15 kg, sufficient density of heads of cabbage, allowing long-term transportation without loss of commercial qualities. Productivity 700 c/ha, unpretentiousness, excellent taste, universal use.
- Moscow late - late ripening, weight up to 4.5 kg, yield 12 kg/m2. Excellent taste, high content of ascorbic acid and vitamin C. Can be used both for preparations and fresh.
- Aggressor F1 – medium-late ripening, unpretentiousness, resistance to sudden temperature changes, ability to easily tolerate short-term frosts (down to -5ºC). Resistance to cracking, good transportability, yield up to 600 kg/ha. High taste, versatility in use.
- Univers F1 – ripening 130 days, weight 5 kg, yield up to 800 c/ha, suitable for growing without seedlings. Resistance to cracking, excellent product and taste qualities.
The most productive
The TOP 7 varieties with the highest yield include:
- Dumas cabbage F1 - ultra-early ripening (up to 55 days), good yield (9 kg/m2) even in unfavorable growing conditions: drought, excessive planting density, shade.
- Golden hectare – early ripeness, weight up to 3.5 kg, yield 8 kg/m2. Sufficient density of heads of cabbage, lack of tendency to cracking, resistance to major cruciferous diseases.
- Marshmallow F1 – mid-ripening, simultaneous fruiting, weight 1.5-2 kg, exquisite taste, crispy and juicy texture, yield up to 8 kg/m2. Resistance to cold and infectious diseases.
- Transfer F1 – ultra-early ripening, yield 6 kg/m2, weight 0.7-1.5 kg, resistance to spring frosts (down to -5ºC). Excellent taste and commercial qualities, increased immunity to many diseases, unpretentiousness, transportability.
- Three heroes - late ripening, productivity 17 kg/m2, weight 15 kg, possibility of long-term storage. Excellent taste, increased juiciness, suitability for fermentation.
- Mother-in-law F1 - average ripening period, weight up to 8 kg, productivity up to 650 c/ha. Increased content of microelements and vitamins, excellent taste and commercial qualities, resistance to major diseases, universal use.
- Sugar loaf - late ripening, yield 550 c/ha, storage duration up to 1 year, possibility of long-term transportation. Excellent taste, high content of vitamins, resistance to diseases: bacteriosis, fusarium, clubroot.
New varieties
The TOP 5 modern varieties of white cabbage include:
- Grandmother's pickle – medium ripening, weight 4 kg, yield 10 kg/m2. High taste, juiciness, suitability for pickling, good keeping quality.
- Vityaz F1 – late and simultaneous ripening of heads of cabbage, weight 4.5 kg, productivity up to 10 kg/m2, storage up to 7 months. Resistance to white rot, fusarium, mucous and vascular bacteriosis. Good taste, versatility in use.
- Orient Express F1 – early ripening (up to 90 days), yield 4 kg/m2, weight 0.8-1.2 kg. Excellent taste, non-cracking, disease resistance, transportability.
- Kulikovsky F1 – early ripeness, productivity up to 870 c/ha, weight 5.4 kg, excellent taste. The variety is recommended for fresh use.
- Found in a garden bed – early ripening, weight 1.2 kg, yield 5.3 kg/m2. Sufficient density of the head of cabbage, high taste, juiciness.
The best hybrids
TOP 5 best hybrid varieties of white cabbage:
- Zarya F1 – ultra-early ripening (up to 45 days), weight 1.5 kg, high yield. Excellent taste, suitable for fresh consumption.
- Cossack F1 – early ripeness (up to 55 days), weight 1.2 kg, high productivity. Immunity to clubroot and blackleg diseases. Good taste, rich in ascorbic acid.
- Malachite F1 – early ripening (up to 60 days), weight 1.5 kg, productivity 6.7 kg/m2. Excellent taste, resistance to cracking and many diseases.
- Midor F1 – ripening period up to 105 days, productivity up to 7.5 kg/m2, immunity to gray rot and clubroot, unpretentiousness, frost resistance. Excellent taste, the ability to be transported without loss of commercial qualities.
- Geneva F1 – ripening period up to 140 days, weight 5 kg, storage duration up to 8 months, resistance to fusarium and drought, yield 90 t/ha. The main purpose is pickling and fermentation.
Varieties for growing in a greenhouse
Planting cabbage in greenhouses and greenhouses has many advantages and is becoming increasingly widespread. However, this method is characterized by a number of features. First of all, it is important to choose the most suitable variety.