Gooseberry Grushenka: variety description, reviews, photos, cultivation, pruning, planting and care
Quite a lot of gooseberry varieties have been bred, but how to choose among this variety one that does not require special care, is not affected by diseases and gives good yields?
The answer is simple - gardeners should pay attention to the gooseberry variety Grushenka
. Its main characteristics, care rules, main advantages and much more will be discussed in this article.
The content of the article:
1. History of the variety 2. Description and characteristics of the Grushenka gooseberry 3. Productivity of the variety 4. Advantages of the gooseberry variety 5. Diseases and pests 6. Agricultural technology for growing Grushenka gooseberries 6.1 Planting gooseberries 6.2 Further care 6.3 Feeding rules 6.4 Pruning gooseberries 7. Reviews of the Grushenka gooseberry variety Enka
Harvesting
The first berries from the Grushenka gooseberry can be picked at the end of June. The harvest period can last until the beginning of August, and all this time you will be provided with fruits of excellent quality. You can remove 6–7 kg of berries from one bush.
The berries themselves have a set of useful and nutritious substances necessary for the human body. There is ascorbic acid, vitamin E, beta-carotene, PP vitamins, and B vitamins - riboflavin, thiamine and folic acid. As well as microelements such as zinc, nickel, molybdenum, manganese, magnesium, calcium, phosphorus and others. This amazing combination of components makes it possible to use gooseberries in the treatment of hypertension, anemia, obesity and other diseases.
The harvest on a gooseberry bush is sometimes so large that the leaves are hidden behind the berries
Thanks to their excellent taste, Grushenka berries are good not only when freshly picked, but also in all kinds of preserves, jams, compotes and other preparations.
History of the variety
Gooseberry Grushenka was bred by breeders from the All-Russian Breeding and Technological Institute of Horticulture and Nursery Growing in the 80s of the last century
. Specialists, by hybridizing the gooseberries Northern Captain, Moscow Red and GF 595 33, obtained a new thornless variety. At the same time, the goal of the breeders was to develop a variety of this berry crop that would not have thorns, would not be demanding on certain types of soil, and would have high resistance to diseases.
And their efforts were crowned with success - the bred gooseberry Grushenka meets all the above requirements. Although this berry bush has not yet been included in the State Register of Russia, over the past decades the Grushenka variety has been appreciated by Russian gardeners from many Russian regions.
Gooseberry Grushenka - photo
The thornless gooseberry Grushenka is recommended by experts for cultivation in the Moscow region, central Russia and other regions with similar climatic conditions
.
Gooseberry variety Grushenka: description and characteristics
The bushes of this variety are quite tall; in young plants, the shoots practically lie on the ground. But as the bush “matures,” its stems become stronger and more powerful, so Grushenka’s bushes become semi-spreading.
On a note!
In this shrub, young shoots grow quickly and in large numbers, contributing to the strong thickening of the plant. Therefore, experts recommend regularly pruning gooseberries of the Grushenka variety in order to remove excess branches growing inside the bush.
Annual stems branch well and have virtually no thorns, which makes caring for and harvesting this berry perennial much easier. Internodes are shortened, shoots are heavily leafy. The foliage is the usual size for a gooseberry, round in shape with five lobes, the outer leaf plates are smooth, with a glossy sheen, rich emerald color. The middle blade is higher than the others. The tips of the blades are extended upward, the teeth do not bend.
The flowers are collected in inflorescences, each of which can contain from one to three flowers, and are borne on last year's and two-year-old shoots. A large number of inflorescences form on each branch, as a result, by the time the fruits ripen, the entire bush is literally covered with berries.
Gooseberry Grushenka - video
The fruits of the gooseberry Grushenka have an elongated pear-shaped shape (hence the name of the variety)
. The skin of the berries is thickened, quite dense, smooth to the touch, with a characteristic bluish waxy coating. As the fruits ripen, their color changes from reddish to dark purple, almost black.
The berries on the shoots can ripen in different sizes - from large to small, weighing from 4.2 to 8 g. The taste of ripe Grushenka gooseberries is sweet with a characteristic sourness.
Interesting!
Tasting assessment by specialists of the taste qualities of Grushenka gooseberries ranges from 4 to 4.9 points.
The juicy pulp with a pleasant aroma contains an average number of small seeds. This gooseberry variety is characterized by a high content of pectin and anthocyanin in ripe berries.
Photo of gooseberry bushes Grushenka
Ripe fruits hold tightly to the stalks without falling off and are not prone to cracking
. The harvested Grushenka variety tolerates transportation well over long distances without losing its presentation and taste. Gooseberries can be stored in appropriate conditions (high humidity and 0 degrees Celsius) for 25-30 days.
Ripe berries are universally used; they can be eaten fresh, cooked in compotes, canned, or frozen for the winter.
Excellent variety!
Gooseberry Malachite
The first harvest from this berry bush is obtained 2-3 seasons after planting the seedlings, so the gooseberry Grushenka is considered early-fruiting
. If gardeners plant two-year-old plants, then the next year the bushes produce their first small harvest. In one place, this berry bush can grow and not reduce productivity for up to 16-19 years.
Important!
Gooseberry Grushenka is classified as a mid-late variety; the berries begin to ripen in the last ten days of July, but mass harvesting can be carried out in the first or second ten days of August.
Gooseberry Grushenka is not afraid of spring frosts
, which do not have a negative effect on the flowers of this shrub that bloom in May. It should also be noted that it is highly resistant to frost - even in winters without snow, this gooseberry without shelter can tolerate cold temperatures down to -28-29 degrees Celsius. Also, the Grushenka variety is resistant to hot summers and is resistant to periods of drought.
Gooseberry Grushenka has high immunity, so it is practically not affected by the main diseases characteristic of other varieties of this berry crop, and is not attacked by pests.
Possible problems
Gooseberry Grushenka amazes many gardeners with its immunity to diseases if the owners properly care for their plantings. With normal watering, timely feeding, and mandatory pruning so as not to thicken the bush, Grushenka will not get sick.
Diseases
But sometimes little depends on us. During periods of severe waterlogging, it is difficult to avoid spores of fungal infections and the development of putrefactive diseases.
It is important to decide what is wrong with your gooseberry and how to deal with it correctly:
- Anthracnose - affects the leaves, which become covered with rusty spots, then rough, dry crusts appear, growth processes are disrupted, and fruiting stops. Before and during the flowering period, you can treat with a 3% solution of copper sulfate. After picking the berries, the bush and the ground under the crown are well watered with the same solution.
Prevention of the disease is expressed in pruning, burning leaves that have fallen during leaf fall and treating the plant and soil in early spring before the leaves appear with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture;
- Drying out - cracks on the bark of branches, in which small beads are visible - fungal spores. The bush is gradually drying out. Control and prevention are similar to those listed above;
- Columnar rust - reddish formations similar to pads appear on the underside of the leaves, as well as on the ovaries. Later, the plant becomes covered with a fluffy coating and withers. The fight is expressed in the use of Bordeaux mixture 1% three times (at the stage of leaf opening, bud swelling, after flowering), additionally using Fitosporin according to the instructions. Prevention is similar to that described above;
- Spheroteca (Powdery mildew) - a fungal infection affects all parts of the plant; a felt coating is clearly visible on the fruits, initially light, then turning brown. An excellent result is shown by using soda ash, which is taken in the proportion of 50 g of powder per 10 liters of water. Grated laundry soap is also added. Treatment is carried out twice with a break of 10 days. Prevention is similar to that described above.
Columnar rust
Pests
Gooseberries have good immunity, which protects it from most fungal diseases, however, like any other variety, it is not protected from parasites. The main parasites that can cause problems when growing Grushenka are:
- Spider mite. In early spring, this parasite very often settles on gooseberry bushes. The spider mite weaves a small web on the leaves of the plant, which is difficult for the human eye to detect. This causes the leaf to begin to dry out. If no measures are taken, the bush may even die. People most often use wormwood tincture to combat spider mites. To do this, take half a bucket of chopped flowering wormwood and fill it with 10 liters of water. All this is insisted for 24 hours. Then it is boiled for 30 minutes, allowed to cool and strained. Afterwards, the infusion is diluted with water (1:1) and 40 g of laundry soap is added.
Prevention is expressed in the collection of fallen leaves, autumn digging of the soil under the crown, weekly treatment of the plant with a two-day infusion of onion peels;
- Shoot aphid. Another parasite that likes to settle on gooseberry bushes. In the spring, colonies of aphids move to the petioles of leaves, sucking out all the juices from them. This causes the leaves to curl into lumps. Hot water is used to combat these parasites. Boiling water is poured over the bush, and then it is treated with special insecticides, such as “Iskra”, etc.
Preventive measures include fighting ants, weeds, and planting herbs around.
- Moth - if early pigmentation of the fruit occurs, this is the main sign of damage by caterpillars. The means of control is to use before the leaves bloom and after flowering such products as Actellik, IskraM.
Prevention is expressed in autumn digging and manual collection of spider nests. Many gardeners place sheets of roofing felt under bushes to prevent the passage of caterpillars;
- Gooseberry moth. This is a butterfly that lays larvae on the back of leaves. The larvae form caterpillars that eat the leaves of the crop with incredible appetite. To combat moths, they use special pesticides, and also collect fallen leaves in a timely manner and dig up the soil near the bush.
Preventative treatment
If not properly cared for or in unfavorable weather conditions, gooseberries can suffer from pathogenic microorganisms and be attacked by pests. Therefore, in the spring, bushes are sprayed with insecticides and fungicides for prevention.
Advantages of gooseberry varieties
The main advantages of gooseberry Grushenka include:
- good yield;
- stable fruiting;
- high resistance to frost;
- versatility of the harvested crop;
- good taste of ripe fruits;
- Grushenka gooseberry berries do not fall off the bush even after ripening;
- the variety is heat-resistant and easily tolerates periods of drought;
- the harvested crop tolerates transportation well and has good shelf life;
- This gooseberry is highly resistant to most diseases.
Pest and disease control
To combat fungal diseases, use a solution of ammonium nitrate with a concentration of 0.5%. Good results are obtained by spraying the bush with whey diluted with water 1:10. Chemicals are used with caution. The drugs Topaz and Oxychom are effective against fungal diseases.
The most dangerous pests of gooseberries are moth and sawfly caterpillars. To scare away butterflies that lay eggs, tomato tops or elderberries are laid out next to the bush. For prevention, dig up the soil in the fall. Lepidocide and other biological preparations are effective against pests.
Gooseberry Grushenka: agricultural cultivation techniques
Seedlings of the Grushenka variety should be planted in the spring, when the snow melts and the soil warms up.
. Typically, the timing of planting gooseberries depends on weather conditions in specific regions and ranges from mid-April to mid-May.
Photo of gooseberry Grushenka
If autumn is warm in specific areas, then you can plant this berry bush in early September
so that the plant has time to take root before the onset of cold weather.
Planting gooseberries Grushenka
The place for planting gooseberry seedlings Grushenka should be sunny and not in a lowland
. This berry perennial grows best on loamy or chernozem soils with a neutral or slightly acidic pH. If the garden plot has heavy soils, then you must first add compost (or humus) and river sand.
Useful article:
Planting gooseberries in spring - rules and terms
To protect the bush from gusts of cold wind, it is better to plant it next to the country house. You should not plant gooseberries in the shade of fruit trees or next to other berries - raspberries or currants (or after them).
Important!
The best predecessors for gooseberries are potatoes, peas, beans, beets or lupine.
Before planting gooseberries, planting holes with a depth of 0.5 m and a diameter of 0.4 m are dug in the area. A layer of nutrient substrate made of compost, humus, ash, superphosphate and potassium fertilizer is laid on the bottom.
5-7 liters of water are poured into each hole and left for a couple of weeks for the soil to settle. Then soil is poured into the center of the hole in the form of a mound, on which the seedling is installed. Its roots are carefully spread along the edges of the hill, the hole is filled with soil, compacted and watered again.
Planting gooseberries
Reproduction methods
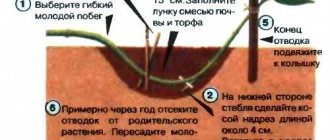
Grushenka is propagated, like other varieties of shrubs, vegetatively - by cuttings and layering. To take cuttings from an adult plant, in July–August, branches about 15–20 cm long are cut, and the cuts are treated with “Heteroauxin” or “Kornevin.” The cuttings are buried in loose nutritious soil, leaving 2-3 buds on the surface. The sprouts are watered regularly until new shoots begin to grow from the buds.
Reproduction by layering is a more common and gentle method of reproduction. The annual shoots located in the lower part of the bush are bent to the ground and secured with a bracket approximately in the middle. The bracket should fix the stem firmly. The attachment point is sprinkled with soil, leaving the end of the branch free, and watered regularly. After rooting and the appearance of young shoots, the cuttings are cut off from the mother plant and planted in a permanent place.
Pruning gooseberries Grushenka
Every year you should carry out sanitary pruning of Grushenka gooseberry bushes, removing dried, broken and weak branches
. You also need to remove most of the branches that grow inside the bush to prevent it from thickening.
It is important to know!
Pruning of the Grushenka gooseberry is carried out in early spring before the sap begins to flow or in the fall after all the foliage has fallen.
In the fall, be sure to carry out moisture-recharging watering of the Grushenka gooseberry and add a layer of mulch at least 10 cm thick. Humus or dry leaves can be used as a mulching material.
Pruning gooseberries in spring - video
Pruning gooseberries in autumn
Preparing the bush for wintering
The cold-resistant qualities of this variety allow it to winter quietly without shelter. Therefore, if the crop is grown in regions with a temperate climate, then you don’t have to worry about winter shelter at all.
We also recommend reading: Description of the gooseberry variety Ural emerald
At the same time, before the onset of winter, the following preparatory work is carried out:
- Remove old, diseased or damaged branches.
- The bushes are treated with Bordeaux mixture to rid it of parasites.
- Remove fallen fruits and leaves, as well as mulch, if any.
Gooseberry Grushenka: reviews from those who planted
Below are some of the reviews from gardeners who grow the thornless gooseberry variety Grushenka on their plots.
Elena, 40 years old: There are several bushes of this variety of gooseberry growing at our dacha. Although for my taste the ripe berries are not too sweet, the harvested fruit produces aromatic and tasty jam, and we also add the collected berries when cooking compotes. The Grushenka gooseberry does not require special care; I regularly water the bushes and add a couple of fertilizing treatments during the season - that’s all the work.
Olga, 39 years old: Gooseberries appeared in my garden several years ago. I planted the Grushenka variety, which was recommended to me by my neighboring summer residents. And I have never regretted it - the variety is resistant to diseases, I water it, feed the bushes and at the beginning of August I harvest good harvests. Another advantage of the variety is the absence of thorns, so picking berries is very easy. I would like to note one drawback - the berries disappear quickly, literally in a few days.
Good decorative appearance, excellent yield and ease of care - these are the main positive qualities of the Grushenka gooseberry
. The variety is quite promising; due to its resistance to frost, heat and drought, this shrub can be grown even in conditions unfavorable for other gooseberry varieties.
Recently searched:
Plant care
Gooseberries are easy to care for, so don’t be lazy to devote some time to them, because without good care, any variety will not be able to show its best qualities. Gooseberries love loose soil around them, so try to maintain it in this condition from time to time. The depth and intensity of loosening depend on the type of soil. On heavy soil, it is better to dig deeper than on light soil, where surface loosening will be sufficient. To till the soil, use a fork or a shovel with a ripper.
Don’t forget to “take care” of weeds - their presence in the tree trunk is undesirable, since they take away nutrients from the bush and retain moisture, which is fraught with the appearance of viral infections. Although the Grushenka variety is resistant to many of them, it is better not to take unnecessary risks.
Of course, gooseberries will only be happy with periodic feeding. It is carried out twice a year - in spring and autumn, and it includes a standard complex of nutrients: 20 g of potassium chloride, 40 g of saltpeter, 80 g of superphosphate, 7-10 kg of compost or manure.
At the age of 5-6 years, all young shoots of the gooseberry begin to be cut out
Timely pruning is also important, carried out in the fall in order to form a bush and remove old and improperly growing branches. In the first seasons, the root shoots are removed, and then the young shoots are cut out.
To prevent the bush from becoming thickened, it is necessary to carry out periodic pruning