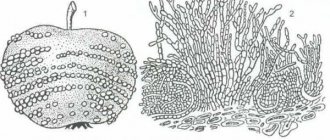
Spider mites are small insects invisible to the eye; they feed on the juices of the plant and weave it with thin webs, along which they move very quickly. They have amazingly high fertility and can be a real challenge for the gardener. What to do if these small, but not at all remote pests suddenly settled on the site?
Spider mites love to settle on apple trees, but they can also move to other fruit and berry crops. Their omnivorous nature easily turns a small pest into a gardener's nightmare. The dominance of spider mites quickly reduces the immunity of a crop and makes it vulnerable to secondary infections of various origins. How to overcome an insect? Let's look at this issue in more detail.
Spider mite: features
Spider mites are a group of insects of various species from the arachnid family. They affect not only apple trees, but also many other plant species. The infestation of such insects leads to a decrease in the yield and immunity of trees, making them vulnerable to various infections.
Spreading
Spider mites are ubiquitous because many of their species are omnivores and feed on any plant. Some species prefer more southern or northern regions, but in general their habitat covers any area where there are green plants.
What does it look like
The appearance of the pest depends on its species. In general, these are small ticks, most often no more than 5–7 mm in diameter, but larger individuals are also found. The most common unwanted guests on apple trees are:
- red fruit mite – an oval small mite of bright red color, 0.4 mm long;
- brown fruit mite - insects 0.4–0.6 mm long, flat, brown or reddish in color;
- gall mite is an extremely small insect no more than 0.25 mm long, the characteristic feature of which is the formation of swellings on the leaves;
- kidney mite – arachnid 0.5–0.7 mm long, bright brick color;
- Schechtendahl's mite is a yellow-brown insect 0.2 mm long, characterized by high fertility;
- The common spider mite is the most common type, length is about 0.4 mm.
Life cycle
The life cycle of any spider mite includes 4 stages: egg, larva, nymph and adult, or adult insect.
- An egg can be either fertilized or unfertilized, depending on the species and the ability for parthenogenetic reproduction. One female can produce from 150 to 350 eggs per year over 8–10 generations. The eggs are small, most often no more than 0.2 mm long. They develop depending on the air temperature.
- The larva is a small insect about 0.1 mm long with three pairs of legs. Actively moves and feeds. It develops within 8–20 days, depending on weather conditions, and feeds on the juice of leaves, fruits and shoots.
- The nymph is an intermediate stage between the larva and the adult. The body shape resembles that of an adult insect.
- Imago is an adult insect ready for reproduction. Actively moves, feeds and looks for a partner for mating. Females can lay parthenogenetic eggs and the cycle begins again.
How to detect
This variation has a color suitable for camouflage and is small in size. They blend in with the foliage, which helps them stay in the shadows for a long time and go unnoticed.
It is much easier to detect its presence by the symptoms of the foliage. If there are few of them on the bush, then the leaves are simply covered with white spots, but if there is a large arch, the plant is enveloped in an almost imperceptible web, hence the name mite.
You can verify this by looking at photos of the flowers on which it started. The females of these creatures die about a month after birth, but during this time, unfortunately, they can lay over a hundred eggs.
Fighting methods
All methods of combating spider mites can be divided into 4 main groups:
- chemical;
- agrotechnical;
- biological;
- folk
Let's look at each group in more detail.
To increase the overall resistance of trees, it is necessary to carry out regular root and foliar feeding with complex fertilizers.
Agrotechnical techniques
Agricultural methods mostly relate to preventive measures, but they can help eliminate mites in combination with other methods and speed up the tree’s healing process.
- To reduce the number of mites and eggs overwintering in the soil, gardeners and agricultural technicians recommend plowing the tree trunk in autumn and spring. In autumn, it is necessary to remove and burn leaf and fruit litter to reduce the number of wintering sites for insects.
- Sanitary pruning should be carried out regularly, removing weak, damaged or thickening branches. Removed shoots must also be burned to prevent spider mites from spreading throughout the area.
- It is necessary to monitor the condition of the bark, treat all cracks and frost holes, since they can easily become entry points for the pest. You should not be lazy in removing loose bark from skeletal branches, as mites can overwinter under it.
Biological methods
Biological control methods include the use of biologically active drugs, as well as the reproduction of spider mites in the area of natural enemies.
One of the most popular biological preparations is Fitoverm. This is an extract from the waste products of some fungi, which, due to their properties, exhibit a toxic effect on adult spider mites. "Fitoverm" is active at temperatures from +18 degrees. In addition, it does not decompose at temperatures above +25 degrees, unlike most chemicals. The disadvantage of the product is that it does not act on insect eggs and larvae, therefore it requires regular repetition of treatment - at least 2 times per season. The danger of “Fitoverm” lies in its toxic effect on aquatic organisms and fish, therefore, if there is an open body of water near the site, the drug should be used with extreme caution. When working with it, it is necessary to remove pets and children from the area, and carry out the treatment with gloves and a protective mask.
To prevent ticks from developing resistance to the drug, it must be alternated with other groups, such as acaricides.
The natural enemy of the spider mite is the phytoseiidae, a small arthropod that can destroy about a hundred individuals per day. It is bred artificially and planted on affected trees.
Traditional methods: methods without chemicals
Supporters of traditional methods and opponents of chemicals should remember that this group of measures in case of tick infestation is ineffective due to the high rate of reproduction of the pest.
Treatments must be carried out frequently and regularly according to the insect's life cycle. Most popular recipes:
- Spraying with garlic solution. The working mixture is prepared from 50 g of cleaned heads, filled with 10 liters of water. The product is infused for 24 hours in a dark place, then 2 tablespoons of liquid laundry soap are added until completely dissolved and the crown is treated with the resulting composition once every 7-10 days.
- Sulfur-tar soap. Dilute 100 g of grated tar soap in 10 liters of water until completely dissolved and spray the crown once a week until the insects are completely exterminated.
- Onion infusion is prepared from 200 g of fresh onion peels, infused in 10 liters of water for an hour. After this, the solution is filtered and the crown is sprayed with it once a week.
- Horseradish root infusion. 400 g of fresh chopped root is poured into 10 liters of water and left in a dark place for 2–4 hours. The resulting infusion is sprayed onto the crown every 7–10 days.
- Black henbane infusion should be used with extreme caution. To do this, 1 kg of fresh henbane is poured with water and boiled over low heat for 5–6 hours. Then the broth is diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 1 and the trees are treated with it.
Causes of the parasite
How and where does the parasite get to the plant? There may be the following reasons for this:
- With an infected plant brought from a nursery or store.
Important! When purchasing a new flower, you should immediately examine your pet thoroughly. If there are white or yellow spots on the leaves, you should refuse to purchase.
Advice! Immediately place the new plant for 2 weeks in a separate place, away from other plants. If problems suddenly arise with mites or other insects, other plantings will not be affected.
- With purchased or street soil substrate, humus. Under unfavorable conditions, an insect can hibernate and not reveal itself in any way. At high temperatures and low humidity, the tick wakes up and becomes more active.
Advice! Before using such soil, it must be disinfected using hot temperatures, for example, calcination.
- With the wind, which carries ticks through the air. On an open balcony, the likelihood of picking up a parasite increases.
- With gardeners' clothes. Clinging to a shirt or trousers, an uninvited guest ends up in a garden, greenhouse, or house.
- From plants adjacent to the dacha plot already infected with mites.
Chemicals to combat spider mites
Chemical control methods should be considered in more detail, since they include different groups of drugs that differ in their mechanism of action.
Preparations with a wider spectrum of action are called insecticides, and a narrow-spectrum group aimed at eliminating ticks is called acaricides. There are a large number of different drugs available in different forms. These can be concentrates, emulsions, aqueous solutions, powders, tablets. It is necessary to prepare working solutions in strict accordance with the instructions, since too low or high concentration will not give the desired positive effect.
Too low a solution concentration will not affect insects and, moreover, may provoke population resistance to this drug. Excessively high concentrations can have negative chemical effects on the plant itself.
Insecticides
Of the wide group of drugs, the most effective have been shown:
- Carbofox;
- Fufanon;
- Ditox;
- Clipper.
In addition to spider mites, they also act on other pests - caterpillars, scale insects, weevils and many others. The use of such drugs provides comprehensive plant protection.
The most popular drug is Fufanon. It is distinguished by the speed and severity of the effect, affecting both adult forms and larvae. However, the last treatment with the drug should be carried out no later than 30 days before the expected harvest. No more than two treatments are allowed per season.
Acaricides
Specific narrowly targeted drugs with contact-intestinal action. They require careful treatment of the entire surface of the plant. The most popular in this group are:
- Zolon;
- Apollo;
- Demitan;
- Sunmite;
- Omite.
The most pronounced effect in terms of duration is provided by the drug Omite and its analogues, the active ingredient in which is propargite. It provides up to three weeks of protection against spider mites. However, it is considered the most toxic to animals and people.
The main advantage of acaricides is their narrow focus and harmlessness to other insects and natural enemies of spider mites. They do not destroy beneficial insects or affect pollinators.
Technology for treating trees against pests
It is not easy to destroy a spider mite, and its small size practically eliminates mechanical treatment. Even regular spraying every two weeks may not give the desired result due to the high rate of reproduction of the pest.
Many drugs do not act on mite eggs, so regular re-treatment is required.
The main method for combating spider mites is spraying with various infusions, decoctions or working compositions of chemicals. The consumption of chemicals largely depends on the drug. Consumption in folk wrestling recipes is 10 liters per tree.
Treatment is carried out using a sprayer. It is necessary to thoroughly treat all areas of the tree, especially when working with acaricides of the contact-food mechanism of action. Not only the foliage is sprayed, but also all branches, including lateral ones, and the main trunk. For prevention, some gardeners also water the tree trunk circle - in case some of the insects may have fallen off the foliage at the time of spraying.
Prevention
It’s better to prevent pests from appearing so you don’t have to deal with them. To do this, procedures are carried out to destroy other pests, as well as to increase immunity.
Preventive measures include:
- spring pruning and spraying;
- use of insecticides before flowering;
- cleaning damaged branches;
- cleaning the bark and whitewashing it;
- cleaning the trunk circle.
If you keep your garden healthy, the likelihood of spider mite infestation is minimized. But don’t think that care will provide a 100% guarantee. Ticks are small and mobile, easily transported by wind from neighboring areas.
Time of processing
To protect plantings from attacks by spider mites, it is necessary to carry out timely treatment during the season.
In spring before flowering
The first treatment is carried out to destroy females that have overwintered in the soil and bark and to prevent the deposition of eggs.
The soil and branches are sprayed with a 3% solution of iron or copper sulfate before the leaf buds open. After the leaves bloom and before flowering begins, it is possible to treat with any insecticide or acaricide that has an effect on the insect. At the time of flowering, treatment only with acaricidal preparations is allowed!
After flowering
After the formation of the ovary at the very beginning of fruit growth, the treatment preparation is changed to avoid addiction and the formation of a stable population of insects. The use of both broad-spectrum and narrowly targeted drugs is allowed.
During the period of fruit ripening
During the period of active fruiting, treatments are undesirable. If necessary, spray with infusions and decoctions prepared according to traditional methods. If there is a need for treatment with chemicals, it should be taken into account that the last treatment must be carried out no later than a month before the expected harvest.
Dates in autumn
The final treatment is carried out after harvesting before the leaves fall. This will reduce the number of wintering insects. Broad-spectrum insecticides, as well as urea or a 3% concentration of copper sulfate solution are suitable for treatment. After the leaves fall, all litter is collected and burned. The soil around the tree trunk is treated with a 3% solution of copper or iron sulfate and carefully dug up.
Processing frequency
The frequency of treatment largely depends on the chosen method and the active drug. Traditional methods require regular spraying at least once every 7–10 days. Chemically active preparations usually require two or three treatments per season (depending on the active substance).
Processing times in regions
Processing times depend on the region, since warming occurs differently in different areas:
- Central Russia - primary treatment in the second or third decade of March, then as leaf buds and ovaries form;
- South – first ten days of March;
- Ural and Siberia - the first ten days of April;
- Far East – second and third ten days of April.
Spider mites are an extremely unpleasant scourge. They have a high reproduction rate, are invisible to the naked eye, and quickly spread from a diseased tree to a healthy one. To avoid problems with the pest, it is necessary to follow the rules of agricultural technology when caring for apple plantings and do not forget about regular preventive treatment, if possible with broad-spectrum chemicals.
Previous
Pests