History of origin and distribution of the variety
Osennyaya Yakovleva pear is an autumn-ripening variety that was bred by crossing the varieties Daughter of Blankova and Esperen's Bergamot . The work was carried out by breeders P. N. Yakovlev, S. P. Yakovlev and Z. N. Tsvetaeva - employees of the All-Russian Research Institute of Genetics and Selection of Fruit Plants named after. I. V. Michurina.
The first tests were carried out in 1949. The variety has been approved for cultivation since 1974 in the Voronezh, Kursk, and Volgograd regions and is most widespread in the regions of the middle zone.
Description and characteristics
The trees are tall (about 15 m) and fast growing . The crown is sparse and spreading. The branches droop slightly as they grow. The shape is highly rounded or broadly pyramidal.
The shoots are curved, dark brown, of medium thickness, lentils are few . The leaf blade is wide, slightly curved, medium in size, pointed at the tip. The base of the leaf is wedge-shaped, directed upward. The edges are jagged. The petioles are long, the stipules are subulate.
The variety is distinguished by its high ability to shoot - after pruning, the crown thickens greatly.
The fruits are formed on fruit rods and ringlets , and have a ribbed, broadly pear-shaped or irregular rounded-diamond shape. Average weight - 130-150 g, maximum - 250 g.
Fruits of medium ripeness are green, with a slight blush on the sunny side . Fruits of technical ripeness have a green-yellow color. The top coat color runs along a narrow part in the form of a vague carmine blush. Large brown dots are visible on the skin.
The stalks are of medium thickness and length, straight. The funnel is wide, without rust. Open cup. The saucer is shallow, wide, ribbed. The heart is oval, wide.
The seeds are large, ovoid, light brown in color , with closed seed chambers.
The pulp is oily, dense, non-grainy .
The aroma is weak. The taste is melting, juicy, tender, sweet, without astringency, with a slight aftertaste of nutmeg. Tasting score - 4.8-4.9 points on a five-point system. Biochemical composition of the fruit :
- sugar - 9%;
- acidity - 0.08%;
- vitamin C - 12 mg;
- catechins - 38.8 mg.
The fruiting period begins 5 years after planting , but there is information about later dates. The fruits are used universally: wines, preserves, jams, marmalade, compotes, candied fruits. The harvest is harvested in the second half of August and stored in the cellar until the end of October. Productivity - 30-35 kg per tree.
The level of winter hardiness is low - up to -25°C . Drought resistance is high. The variety is prone to fruit scab.
Autumn Yakovleva is used in breeding work . With her participation, the Debutante pear variety was developed, zoned in the Middle Volga region.
Interesting things on the site:
Step-by-step instructions for planting cherry plum in autumn
How should grapes be planted in the fall?
When and how to prune raspberries correctly in the fall
Description of the Autumn Yakovleva pear with photo
The Autumn Yakovleva pear is a successful hybrid that has inherited mainly positive qualities. The fruit tree is fast-growing, producing a considerable harvest, ripening by mid-autumn.
Tree
Autumn Yakovleva pear is characterized by tall trees. The crown is voluminous, drooping under the weight of the fruit, its shape can be round and pyramidal. The branches are curved, medium in thickness and firmly fused with the main trunk. The shoots are brown with numerous lentils.
Attention! The shoots develop quite quickly, which, if severely pruned, can cause thickening of the crown.
The green mass is dense, with leaf blades of medium size. Their shape has a wedge-shaped base, slightly pointed at the end, and jagged edges. The stipules are subulate, the petioles are quite long.
Fruit
Fruit ovaries are formed on ringed twigs. Their number can reach 150 kg per tree. The fruits themselves are small, and their weight varies from 130 to 180 g, some specimens can reach up to 200 g. The shape is asymmetrical, broadly pear-shaped, with a ribbed surface.
The color of the fruit at technical maturity is green with a pinkish-yellow tint. When fully ripe, their color changes to yellow with a blurry red blush. The points characteristic of pears are pronounced and large.
The fruits are small in size, but their taste is pleasant, sweet with a slight sourness.
The peduncle is strong, thickened towards the base, and of medium length. The section shows an oval-shaped heart, where the closed seed chambers are located. The seeds are drop-shaped, brown.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of the variety:
- high taste qualities;
- drought resistance;
- productivity;
- stable fruiting;
- keeping quality;
- vitamin content.
Flaws:
- susceptibility to fruit scab;
- tallness;
- late fruiting;
- the need to trim the crown.
Characteristics
This pear variety is high-yielding. It bears fruit consistently . Harvesting takes place in the second decade of August.
When storing fruits in cool pear storage facilities, the consumption period can last up to 75 days.
The variety begins to bear fruit 5 years after planting the cuttings.
Winter hardiness is average.
Withstands frosts down to minus 25 degrees Celsius.
In winter, it requires shelter for the winter.
The drought resistance of the variety is very high.
Preparation of planting material and soil
When cultivating the variety, standard pear farming techniques are used . It is preferable to plant in the spring. When planting in autumn in the regions of the middle zone, there is a high probability of unrooted seedlings freezing in winter.
The site is chosen on the sunny side, without drafts, with deep groundwater . On the north side, trees should be protected from piercing cold winds by the dense crown of neighboring trees or the wall of the house. At the same time, it is not recommended to place seedlings in close proximity to fences or trees so that they do not end up in the shade.
The soil must be moisture- and breathable, fertile . Black soil or loam with an acidity level of pH 5.5-6 is best suited. The plant does not develop well in alkaline soil.
Seedlings can be purchased in the spring, but in the fall the choice is much wider . This is explained by the fact that nurseries dig up seedlings en masse in the fall. In the spring, unsold copies that were left for storage go on sale.
A high-quality seedling has a well-developed root system, smooth bark without cracks . The optimal age is 1-2 years. Old seedlings do not take root well; later they begin to grow and bear fruit.
Seedlings purchased in the fall are buried in the ground until spring for better preservation . In the garden, they dig a rectangular hole, up to 30 cm deep, pour river sand on the bottom and lay the plant with the rhizome down. The top is placed on the edge of the pit. Before this, the roots are dipped in a solution of mullein and clay, then covered with sand and watered. With the arrival of cold weather, the hole is filled with soil.
Seedlings can be stored in the basement at a temperature of 0…+5°C.
Pear needs feeding
You should not feed the pear in the first year of planting. The tree should take root and develop good roots. It is recommended to treat pear seedlings with anti-stress drugs, such as: Epin Extra, EcoFus, Cytovit.
From 2-3 years old, pear trees need to be fertilized. It’s worth starting when the snow melts. Nitrogen fertilizers are applied according to the dosage indicated on the package. For a 3 m pear, 5 liters of solution will be enough.
The next feeding is carried out two weeks after the first. Here the appearance of the plant is already assessed. If growth progresses poorly, then there is a need for pure nitrogen fertilizing. Or complex fertilizers are applied. During the season it is worth carrying out 3-4 such procedures.
In the second half of summer, pears are transferred to phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. This prepares the plant for winter and the formation of new fruit buds.
Landing technology
Tall trees with spreading branches need space for full development. Recommended planting pattern: 4-4.5 × 5-6 m .
The pit for planting trees is prepared in the fall . Its size depends on the fertility of the soil. The lower the soil nutritional value, the larger the hole. On loam, a depression is formed with a diameter of 80 cm and a depth of 70-80 cm. On sandy soil, a hole is dug with a diameter of 1 m and a depth of 2 m.
The bottom is compacted with crushed stone, broken brick, expanded clay to prevent water stagnation . The thickness of the drainage layer is 10-15 cm.
A nutrient mixture of peat, chernozem, sand and humus (1:1:1:1) is added to the hole , 300-400 g of superphosphate and 3-4 liters of wood ash are added. The pit is covered with roofing felt, slate or thick film to prevent the nutrient mixture from being washed out by melt water in the spring.
In the spring, seedlings are dug up or taken out of storage, carefully examined and the roots are immersed in a solution of “Kornevin”, “Heteroauxin”, “Epin” to stimulate the formation of new roots .
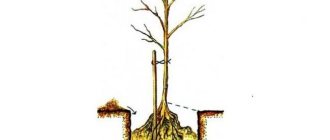
The cover is removed from the pit, a depression is formed in the center according to the size of the rhizome and a small elevation is made . A stake 1-1.3 cm high above the ground level is driven in 15 cm from the center.
The seedling is lowered onto a hill with its root collar, and the roots are spread along the slopes . Soil is poured on top. Each new layer is compacted. The root collar should be at ground level.
After filling the hole, the seedling is tied to a stake with an elastic rope . It is important not to squeeze the bark.
A shaft 25-30 cm high is formed around the hole to retain water during irrigation.
After planting, the seedling is watered abundantly so that air bubbles come out and the soil adheres tightly to the roots. After the soil has dried, the top layer is loosened and covered with sawdust, spruce branches, compost, and straw. Mulch layer - 6-8 cm.
The central conductor of a young tree is pruned to a height of 60-80 cm , the branches are shortened by 50%.
Pear "Hera"
This variety is medium in height, its crown is small, narrow-pyramidal. Fruits are formed on both annual and perennial branches. The plant tolerates frost well and produces a magnificent harvest. The foliage has an oval, slightly curved shape, and is colored in a rich dark green color. The shoots are quite thick, straight, with a small number of lentils. The buds are medium-sized, round, tightly adjacent to the trunk.
Fruit:
- enlarged, weighing on average 230 grams;
- have the correct shape characteristic of pears;
- their skin is rough, of medium thickness, a little dry;
- painted green, with a reddish outer tint and a rusty mesh;
- the pulp is cream-colored, fine-grained, has a weak aroma and contains a lot of juice;
- The taste of pears of this variety is sweet and sour;
- are stored for up to six months.
Varietal features
Harvesting begins towards the end of September, and active fruiting of plants begins 4 years after planting. Remarkably withstands severe frosts up to 39 °C.
Planting and care
Trees are planted in the fall, in advance, before the onset of frost.
When planting, it is important to maintain a distance of at least 3 meters between pears and other trees or buildings. There is poor survival rate of plants due to the characteristics of the root system
Landing is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- a hole is dug a meter deep and 80 centimeters in diameter;
- humus, potassium sulfate, sand and peat are added to it;
- fertilizers are poured into two buckets of water, and the hole is left for a week;
- At the end of the period, the tree is planted.
You need to water the pear regularly:
- first watering - immediately after planting;
- in the first year - before the tree takes root;
- subsequently - during drought and three times in the summer: before the flowers appear, during the appearance of fruit ovaries and in October.
The plant needs pruning - thinning (removing thick branches that interfere with the sun's rays), shortening the top (so that the plant does not grow too much), removing diseased, old and branches growing at right angles. The cut must be treated with a specialized garden varnish to prevent loss of juice and death of the pear. The cutting itself is carried out near the trunk, so that no stumps remain.
Mature trees do not need shelter for the winter, but young trees just need to be covered with spruce branches and fallen snow. Trees are susceptible to diseases and pests, so timely treatment should be carried out in spring, summer and before wintering.
Growing and care
Agricultural technology for pears is standard : watering, pruning, fertilizing, disease prevention.
Watering is carried out regularly - once every 25-30 days . The first time the pear is watered is before flowering, the last time - in October. The soil is spilled to a depth of 25-35 cm. The trunk is hilled to prevent direct contact with water. This way it is possible to protect the root collar from rotting.
The soil is loosened after each watering and rain to better saturate the root system with oxygen.
Mulching retains moisture and reduces the frequency of watering and loosening . The mulch layer is regularly checked and updated - this is an ideal environment for the accumulation of beetles and slugs.
The nutrient mixture in the planting hole is depleted 3-4 years after planting. Fertilizing begins annually, using organic matter and minerals.
Feeding scheme:
- Compost, peat and humus are added in the spring for digging every 2-3 years. For 1 m² of tree trunk circle use 5-7 kg.
- Nitrogen-containing fertilizers (ammonium nitrate, urea, Nitroammofoska) are applied annually in an amount of 20-30 g/m².
- During the period of active growth of shoots and fruits, trees are fed with potassium sulfate or monophosphate in an amount of 10-20 g/m².
- Superphosphate is added in the fall for digging - 20-30 g/m².
- To support fruiting, trees are fed with a solution of mullein or chicken manure: 2 liters of liquid fertilizer are poured into 10 liters of water and left for a week in a warm place to ferment. Fertilizer consumption is 10 liters per 1 m² of tree trunk circle. Instead of mullein, green fertilizers are used (infusion of nettles, weeds, tops, any grass): 5-7 kg of raw materials per 10 liters of water.
In March, the crown is trimmed . This procedure is performed to delay the growth of branches and stimulate the growth of buds and fruits.
Important! At the end of April, trees are sprayed with Fury and Inta-Vir to prevent fungal diseases and the spread of pests.
The standard crown formation for tall trees is sparsely layered . An annual seedling is pruned to 70 cm. In the next season, a first tier of 3-4 shoots 45-50 cm high is formed. Over the next two years, a second tier of 2-3 frame branches is laid at a height of 35-40 cm from the outermost branch of the first tier. If necessary, form a third tier of 1-2 branches. After 5 years, you should get a crown of 6-8 frame branches.
There are other types of pruning:
- sanitary (removal of dry, diseased and damaged branches);
- regulating (thinning);
- supporting (shortening the length of branches to stimulate fruiting).
The last type of pruning is performed by the chasing method (shortening young shoots by 5-10 cm) or by forming shoots that replace fruiting branches.
General pruning requirements:
- The pruning tool (hacksaw, pruning shears, lopper, knife) must be sharp.
- Before starting work, the instrument is disinfected with a 1% solution of copper sulfate, 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide, 3% solution of potassium permanganate, alcohol (optional).
- After pruning, hemp and branches should not be left open - after drying, putrefactive processes develop and a fungal infection occurs. Experienced gardeners advise using the “ring” technique. The branch is cut with a hacksaw from below to 1/3 of the thickness, 25 cm away from the ring. Next, the tool is shifted 2-3 cm to the side and sawed from above. After removing the branch, the stump is sawed off along the top of the ring. A torn, uneven cut is cleaned with a knife - a smooth one heals faster. The saw cut is disinfected with brilliant green or the biological preparation “Farmayod” and covered with wood paint based on lanolin or beeswax.
Diseases and pests - main representatives and control measures
Along with performing basic agrotechnical measures, you need to remember that pears can be affected by some diseases and pests. Therefore, you should not expect such misfortunes, but carry out sanitary and preventive work in a timely manner.
Prevention
Work on the prevention of diseases and pests in most cases helps to avoid infections with fungal diseases and resist insect infestations.
Table: types of preventive work in the garden
| Types of jobs | Methods and techniques of implementation | Deadlines | What effect is achieved |
| Pre-winter garden cleaning. All fallen leaves, weeds, branches, etc. are collected. All this is burned, and the resulting ash is stored for further use as fertilizer. | October November | Destruction of fungal spores and wintering pests | |
| Whitewashing trees | Dilute slaked lime in water, add 3% copper sulfate or Bordeaux mixture. This solution is used to whiten the trunks and skeletal branches of a tree. You can use special garden paints for these purposes. | Preventing bark burns. Creating obstacles for insect pests. | |
| Digging tree trunk circles onto a spade bayonet. At the same time, layers of earth are turned over in order to raise insects to the surface, which spend the winter in the upper layers of the soil. | November | Overwintering insects raised to the surface die from subsequent frosts | |
| Copper sulfate treatment | Spray the crown of the tree and the soil around the tree trunk with a 3% solution of copper sulfate. | November, March | Prevention of fungi and pests |
| Treatment with strong pesticides | Once every three years, the tree crowns are sprayed with DNOC. In other years - Nitrafen. | March | |
| Installation of catch belts | Hunting belts, which can be made from available materials - roofing felt, film, burlap, tarpaulin, etc., are installed on tree trunks 30-40 centimeters from the surface of the ground. | Belts prevent weevils, ants, caterpillars and other pests from crawling onto the crown | |
| Treatments with systemic fungicides | For regular spraying, proven preparations Skor, Horus, Quadris and others are used. Treatments are started after flowering and subsequently repeated at intervals of 2-3 weeks. It must be remembered that all antifungal drugs are addictive and usually lose effectiveness after three treatments. Therefore, drugs should be alternated. Immediately before harvesting, those with minimal waiting periods are used. For example, for Horus the waiting period is 7 days, for Quadris it is 5 days before consuming the fruits. | Prevention and treatment of fungal diseases | |
| Insecticide treatments | In spring and early summer, during the flight of butterflies and flies, Decis and Fufanon are used. Later they switch to biological products such as Iskra, Iskra Bio and others. | Prevention and destruction of insect pests | |
Diseases to which pears are susceptible
The Memory Yakovleva pear has a high immunity to scab, and the Osennyaya Yakovleva and Lyubimitsa Yakovleva varieties are prone to this disease . Pears can also be affected by other fungal diseases. As a rule, the implementation of the described preventive measures prevents infections, so we will briefly introduce the gardener to the main representatives, without going into unnecessary details.
Scab
This is the most common disease of pear and apple trees. It manifests itself in the formation of olive-brown spots on the underside of the leaves. Then the spots appear on the fruits, gradually turning putrefactive. The skin begins to crack, and hard, rocky areas form in the pulp. The fruits become unfit for consumption.
Pears Osennya Yakovleva and Lyubimitsa Yakovleva are often affected by scab
Moniliosis
Moniliosis is a fungal disease that affects not only pears, but also other fruit trees. Most often, infection occurs during flowering - bees bring pathogen spores along with pollen on their legs. It is clear that the flowers are affected first. The fungus then spreads through the pistil and stalk to the shoots and leaves. All these parts of the plant receive the so-called Monilial burn. The affected parts of the pear droop, wither and turn black. Having seen this phenomenon, you should immediately cut off the diseased shoots, including healthy parts 20–30 centimeters long. After this, fungicide treatments begin. In summer, the fungus attacks the fruits, causing a disease such as gray or fruit rot.
Recent Entries
Lilac perennials that are beautiful, compact and do not crowd out other plants Why when buying seedlings you should not take the sellers’ word for it and how to determine the age of the plant using 3 signs Tomato seedlings have turned purple or whitish: why the color has changed and how to save the plants
In summer, moniliosis affects pear fruits, causing a disease such as gray or fruit rot
Sooty fungus
In the second half of summer, when aphids often appear on plants, the pear tree may be affected by sooty fungus. This is due to the fact that the sweet secretions of aphids are a breeding ground for this fungus. A grayish-white coating appears on the leaves and fruits of the pear, which subsequently turns black, resembling soot. First of all, you should fight aphids, and fungicides will help deal with the emerging fungus.
On the leaves and fruits of pears affected by sooty fungus, a grayish-white coating appears, which subsequently turns black, resembling soot
Possible pests of pears
As already indicated, preventive measures are the most effective in pest control. And indeed, it is too late to fight the butterfly when the caterpillars have already crawled out of its eggs and penetrated the fruits. Let's get acquainted with the main “lovers” of eating pear fruits and leaves.
Aphid
It is well known that aphids are brought to the crowns of trees by ants, which, like sooty fungus, love to feed on the sugary secretions of these small insects. As a rule, they are located on the underside of leaves and feed on their juice. Subsequently, the leaves curl and by this sign you can recognize an aphid attack. After this, treatments with contact insecticides lose their effectiveness, since the solution does not get inside the curled leaves. All that remains is to pick off the affected leaves. It is clear that by driving ants away from the site, the gardener also gets rid of aphids.
Ants carry aphids onto the crown of a pear tree.
Pear moth
A small, brownish butterfly lays eggs in the soil. The caterpillars that emerge from them crawl onto the tree, penetrate the fruits, after which they can be detected by the appearance of holes with droplets of gum. Such fruits lose their marketable value - they can only be used for processing, cutting out the affected parts.
The pear moth caterpillar penetrates the fruit
Pear flower beetle
This pest is a representative of the galaxy of weevil beetles. It overwinters in the soil of the tree trunk and fallen leaves. If the beetles have overwintered safely, with the onset of spring they crawl out of the ground and climb to the crown of the tree. At this time, usually the leaves and flowers have not yet blossomed, so the beetles begin to feed on the pulp of the flower buds, gnawing out the inside of the buds. In the future, they can feed on leaves, flowers, and young shoots. An attentive gardener has already understood what preventive measures will help him prevent this invasion. If the beetles do end up on the tree, then in early spring, when it is still cold, the problem can be solved simply by collecting the beetles by hand. To do this, they use the ability of beetles to be in a state of torpor at low air temperatures. In the morning, when the air has not yet warmed up, you can spread some fabric under the pear and shake off the beetles on it.
With the onset of spring, flower beetles crawl out of the ground and climb to the crown of the tree.
Pollinator varieties
The level of self-fertility of the variety has not been studied . Some sources mention partial self-fertility, so the Avgustovskaya and Lada varieties are planted next to the Osennyaya Yakovleva pear.
Cross-pollination occurs during the period of full opening of flowers . The flowering and ripening periods of different varieties often do not coincide. Flowering of Autumn Yakovleva can occur simultaneously with late summer and late autumn varieties. Trees growing at a distance of 50-60 m can cross-pollinate, so in practice the number of pollinators increases due to specimens located nearby.
Planting pear variety Simply Maria
To plant a pear, you first need to find a suitable place for it. Only by creating favorable conditions for the life of a tree can one expect high and stable yields from it. Pear does not like cold northern winds, drafts and deep shade. It will completely refuse to grow in wetlands and flooded areas, and on soils with a high alkaline reaction it will hurt.
Better results can be achieved by planting Simply Maria on a slight slope in a south or south-west direction with natural protection from the north or north-east in the form of a building wall, fence or dense trees. In the absence of such protection, you can initially install special shields painted white. This color reflects the sun's rays and creates additional heating and better illumination of the crown. The soil needs to be loose, well-drained with a neutral or slightly acidic reaction. The pH level can range from 5.5-6, but 4.2-4.4 is also possible. In the latter case, as some sources note, the incidence of scab is practically eliminated.
It’s good if there are dense trees to the north or northeast of the planting site, protecting the young tree from cold winds
Although you can plant a pear in the fall, in this case there is a high risk that the weakly rooted tree will not tolerate winter frosts well. This is especially critical for the northern regions. Therefore, early spring planting is recommended, when the buds have not yet blossomed and sap flow has not begun.
It is advisable to purchase seedlings in the fall - at this time they are massively dug up in nurseries, which provides a large selection of varied, high-quality planting material. The age of the seedling should not exceed two years, it is better even if it is one year old. This age is optimal for the tree to survive. It will grow quickly and begin to bear fruit earlier. When purchasing, inspect the condition of the seedling - its roots must be healthy, well developed, without growths and cones. The bark is clean, smooth, without cracks or damage.
When purchasing, inspect the condition of the seedling - its roots must be healthy, well developed, without growths and cones.
In order for the seedling to be well preserved until spring, it should be buried in the garden. To do this, you need to dig a small hole 30–40 centimeters deep and about a meter long. A small layer of sand is poured onto the bottom, the tree is laid with its roots on the bottom, its crown on the edge of the hole, the roots are sprinkled with sand and watered. First, the roots need to be dipped into a clay mash with the addition of mullein and water. This will prevent them from drying out. With the onset of the first frosts, the hole is filled to the top with earth, leaving the upper ends of the branches on the surface.
In order for the seedling to be well preserved until spring, it should be buried in the garden
If there is a basement or cellar in which the temperature is maintained between 0 °C and +5 °C, then you can save the seedling there. Just don’t forget that the roots need a moist environment, so cover them with moss or sawdust, moisten them and place them in a plastic bag. You need to make several small holes in the bag for ventilation. After this, you can begin to carry out planting activities.
Reviews
Reviews about the Autumn Yakovleva pear are mostly positive. Gardeners note high yields and excellent taste .
Evgeniy, Nizhny Novgorod : “I grow several varieties of pears in the garden, including Autumn Yakovleva. I don’t bother too much with pruning, I just trim off thickened branches. The trees began to bear fruit 7 years after planting. Withstands frosts down to −40°C. In dry years it produces small fruits, but just as tasty.”
Vasily, Borisoglebsk : “This variety of pears has been growing in my garden for 15 years and is actively bearing fruit. I don’t have any particular complaints, except that the tendency to scab spoils the picture a little. Knowing this feature, I carry out preventive treatment with Bordeaux mixture and spray it with “Skorom” before flowering. Pears are very tasty, sweet and easy to eat. Pulp without grains. The aroma is not bright, but for me the taste is more important.”
Peculiarities
The “Osennyaya Yakovleva” variety has positive and negative qualities that are recommended to be taken into account when growing pears.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Excellent taste of the fruit. | Large tree size. |
| High yield. | The variety does not have good resistance to frost. |
| The variety is unpretentious in care. | The variety is susceptible to scab infection. |
Osennyaya Yakovleva pear is a high-yielding variety with stable fruit formation. Based on the description and photo, the harvest has a long shelf life and is suitable for transportation. With proper agricultural technology, the fruit crop rarely gets sick and is attacked by pests.
Harvesting, transportability and storage of crops
As a rule, experienced gardeners try to harvest pears before the fruits reach full biological ripeness. The fact is that such pears are stored much better and, in addition, as they ripen, the fruits often do not stay on the stalks and fall off, and the so-called carrion spoils very quickly. However, the Pamyati Yakovlev variety is a rare and pleasant exception to the rule. Its harvest can be harvested both at the stage of technical ripeness and after full ripening.
In both cases, the pears are perfectly held on the tree and subsequently stored equally well. The optimal place to store the pear harvest is a cellar, the optimal container is wooden or cardboard boxes. It is best to place the fruits in them in one layer, placing the pears vertically, with the stalk facing up. This way they will deform less, which means they will remain usable longer. If these requirements are met, the Yakovlev Memory harvest harvested in October can be stored until March without any problems.
In Memory of Yakovlev is a well-tested classic. Having planted such a tree on your site, you don’t have to worry about encountering unpleasant surprises that are typical of newfangled products. Of course, this pear also has disadvantages, but still, for a novice gardener, an unpretentious variety that is resistant to various diseases is perfect.