Why do tomato seedlings die?
When growing tomatoes at home, the gardener tries to provide the seedlings with light, warmth, moisture and nutrition. But the dry air of the apartment, tap water and scanty spring sun do not create comfortable conditions for the culture.
Tomato seedlings most often die from errors in care or disease. Even harmful insects can annoy seedlings if they enter the room (for example, with purchased indoor flowers).
Diseases
The death of seedlings is caused by fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases. Diseases caused by improper care also contribute to the list of losses.
Bacteria and viruses are introduced with soil and planting material. Fungi develop in a waterlogged environment, at low temperatures of the substrate and air.
Non-infectious diseases arise due to a lack of one or another element in the soil, its incorrect acidity.
Blackleg
Leads among diseases that damage tomato seedlings. Blackleg in tomatoes is caused by fungi that persist in the soil for a long time. Additional risk factors: excess moisture in the ground, watering with cold water, room temperature below +16 degrees.
Signs of the disease appear on seedlings soon after germination. A constriction (thinning) appears at the base of the stem; later the stem turns brown or black. Tomato seedlings fall and wither at the root.
There is no cure, you can only prevent the disease. To do this, treat the soil before planting with fungicidal preparations (Fitosporin, Fundazol, potassium permanganate). Water the tomatoes only with warm water, sprinkle the soil with wood ash after moistening.
Late blight and fusarium
Fungal diseases that appear when the soil is over-moistened and seedlings are planted closely. Sick tomatoes wither, turn yellow, leaves dry out and die. Tomatoes can be saved by transplanting them into loose, disinfected soil.
Before the procedure, tomatoes are kept in a solution of potassium permanganate or Fitosporin for half an hour.
Viral diseases (spotting)
They are manifested by a change in the color of the leaves, followed by their drying out. Dried leaves fall. The virus is transmitted through infected seed material. The dead seedlings are thrown away, the soil in which they grew is spilled with boiling water and a raspberry solution of potassium permanganate.
As a preventative measure, tomato seeds are treated with Maxim before sowing.
Lack of elements in the soil
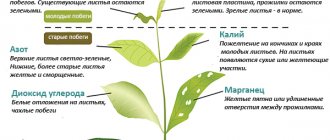
A lack of potassium, iron, magnesium, sulfur, zinc and other substances necessary for tomatoes leads to the appearance of white, yellow or brown spots on the foliage. Gradually, the plant itself begins to wither and dry out. Treatment of seedlings consists of urgent feeding with necessary microelements.
Other reasons
When growing seedlings, the room temperature and relative air humidity are constantly monitored.
Lighting and heat
Sharp changes in day and night temperatures contribute to the development of infection . In low light conditions, seedlings are more susceptible to disease as they stop absorbing nutrients.
Blackleg develops at a temperature of 18 ºC and waterlogging of the soil.
Humidity
Seedlings get sick if the relative air humidity in the seedling room is below 60 and above 70%. Dense plantings and insufficient ventilation also contribute to the development of diseases. Avoid overmoistening the stems and leaves .
Seedlings are watered no more than 2 times a week; as the soil dries out, frequent and abundant watering leads to putrefactive diseases.
It is not recommended to spray grown seedlings with a spray bottle - this will keep the soil layer with roots dry, and create conditions for the development of rot in the wet top layer. Waterlogging of the soil in combination with low temperatures leads to the development of diseases.
Soil problems
If the soil mixture for seedlings is prepared incorrectly - too dense, water- and air-tight, with high acidity - favorable conditions are created for the development of pathogens.
Pathogens persist in peat and plant debris. Before planting, the soil, prepared independently or purchased in a store, must be disinfected with steam.
In what substrate should you not plant tomato seeds?
- with an unpleasant musty odor;
- sticky or very dense;
- with a large amount of remains of undecomposed plants;
- with excessive sand content;
- with traces of mold on the packaging.
Important. Tomatoes should not be sown in peat soil that has expired - it can spontaneously heat up, which is dangerous for young roots.
Errors in the preparation of soil mixtures that lead to seedling diseases:
- You cannot add fresh manure, unburnt leaves and tea leaves - organic matter begins to decompose and the soil temperature rises.
- If the mixture contains clay, which compacts the substrate, the access of oxygen to the roots is limited.
A high concentration of nutrients in seedling soil can cause seedling diseases. Moderately fertile soil is prepared for seedlings, and nutrition is provided evenly during watering.
Seedlings die from an excess of fertilizers . In this case, the substrate with seedlings is washed with a large amount of clean water, which should flow freely through the drainage holes.
Lack of additional lighting
Tomato seedlings planted early (January - early March) need additional lighting.
Natural light (even if the seedlings are standing in the brightest window) is not enough for normal photosynthesis. Experiencing a lack of light, seedlings begin to:
- turn yellow;
- stretch out (stems lean towards the light);
- become sluggish and thin.
Additional lighting will help correct the situation. Fluorescent or phytolamps with a special spectrum of rays are installed above the seedling containers.
The distance from the lamps to the plants is 30-40 cm. The total daylight hours are at least 10 hours.
Growing in a cold place
Growing in a cold room is one of the reasons why tomato seedlings wither. When the air temperature in the room is below +16 degrees, tomatoes stop growing. Their leaves curl with their edges down, and the color changes from green to a leaden hue.
Combined with high humidity, fungal diseases develop rapidly. They contribute to withering.
Drafts are also dangerous for delicate plants, especially for seedlings standing on the windowsill. Icy air coming from window cracks inhibits the development of roots, and they are less able to absorb nutrition from the soil.
The opposite situation, when the room is too hot, also harms pets. Tomatoes may turn yellow and wilt.
The optimal temperature for tomato seedlings should be between +22 +24 degrees during the day and +18 degrees at night.
Poor quality soil
For tomatoes, loose, nutritious soil with a neutral and slightly acidic reaction is suitable. The standard composition of seedling soil includes humus, peat, sand and turf soil in equal parts.
Shortages or excesses of any component lead to the fact that seedlings begin to hurt immediately after germination:
- In dense soil, tomatoes grow slowly and wither;
- if the substrate is acidic, the seedlings turn yellow;
- in sandy soil poor in nutrition, tomatoes dry out or die at an early age.
Why do tomato seedlings fall if the soil is composed according to the rules? If the substrate is not treated with fungicides or steamed at high temperatures before sowing seeds, pathogens and insect eggs may remain in the soil.
Purchased soil is not a guarantee of the purity of the substrate. It is also pickled before use.
What happens to the seedlings after the dive?
In order to answer this question and understand what kind of care such plants require, let's define what picking is?
Reference . Transplanting seedlings from common containers into separate pots or from a smaller container to a larger one is called picking.
According to gardeners, diving promotes root development . After a correctly carried out procedure, the tomatoes feel good, but experience stress. Some of them may not take root in the new place. The sprouts have a weak root system, and picking must be done very carefully. Minor damage to the roots leads to the death of the young seedling.
Therefore, the time from picking to planting in the ground should be used to strengthen the immunity of seedlings, give them strength to grow and take preventive measures against diseases of tomato crops.
Thickening of plantings
Dense sowing of tomato seeds has a detrimental effect on the development of seedlings. They interfere with each other, blocking the sun and preventing the absorption of nutrition from the soil.
Tomatoes in thickened plantings become thin and sluggish, they stretch upward. Such seedlings will eventually fall due to their thin, weak stems.
Recommended distance between tomato seedlings: 2-3 cm before picking, 4-5 cm after transplanting.
Lack of moisture
Tomatoes can withstand short-term drought; excess moisture is worse for them. But for full development, the watering regime is every 3-4 days. Signs of lack of fluid:
- the leaves on the tomato are curled into a “boat”;
- the seedlings wither;
- the stems may fall to the ground.
Moisten the tomato with soft water at room temperature. It is necessary to wet the entire earthen lump in the boxes so that excess water pours into the pan (it must be drained).
Improper watering
Young seedlings really need sufficient moisture and light. They need to be watered regularly with a spray bottle. The soil in the box with seedlings should be moist and loose. It is necessary to water so that the soil in the container does not turn into a swamp. In such conditions, the roots of the plants will begin to rot and the sprout will wither.
Important! If the leaves on the seedlings have withered and faded, you need to check whether the drainage holes in the pots are clogged. Perhaps excess water accumulates in the container and its excess has caused the sprouts to wilt
If the soil in the pots is constantly wet, you need to increase the size of the drainage holes and reduce the number of waterings.
How to save seedlings
When tomato seedlings fall, only experienced gardeners know what to do. First of all, inspect the soil and the plants themselves. The soil should not be cold and waterlogged, and there should be no constrictions on the tomato stems. If there are no signs of disease, the reason for the death of tomato seedlings lies in improper care and soil composition.
Sluggish, but apparently healthy seedlings are transplanted into a new, clean substrate. To prevent elongated seedlings from falling after transplantation, they are buried down to the first pair of leaves. Additional roots are later formed on the stem immersed in the ground.
Seedlings may disappear after improper transplantation. If you press the seedling stem tightly with soil when diving, it will be difficult for nutrients to flow from the roots to the leaves. The tomato will wither and fall.
If there is a clear lack of lighting and it is impossible to install additional lamps, the tomatoes are transferred to the brightest window. Reflective screens (mirror, piece of foil) are installed behind the plants. This trick allows you to increase the lighting of seedlings by 20%.
Prevention of falling and wilting of tomatoes
Plant death can be avoided using preventive measures:
- Careful selection of varieties, study of all its properties and features.
- Selection of quality land.
- Carrying out high-quality disinfection of seeds and soil and tools.
- Carrying out careful picking and landing.
- Setting up irrigation.
- Controlling air humidity.
- Timely fertilization and feeding.
- Preventing insects from getting on seedlings.
- Shelter from direct sun rays.
Proper care and careful attention to seedlings will ensure you a good harvest of tomatoes.
It is important to ensure complete safety of tomato seedlings from external factors and to provide high-quality and timely care. Tomatoes are unpretentious, but they have their own characteristics in growing. Proper agricultural technology is the key to healthy and strong seedlings, which in the future will bear fruit well with large, juicy and tasty syncarpous berries.