Is it necessary to trim the leaves of cucumbers in a greenhouse and why?
Pruning leaves and forming bushes is an expedient and effective procedure for improving the quality of the crop. With uncontrolled growth of the plant, many empty flowers (male inflorescences) are formed, the cucumber vine begins to branch, making care difficult.
Benefits of forming cucumber bushes
Trimming the leaves increases the yield and taste of the fruit, because the plant does not waste energy on the growth of vines:
- new ovaries form faster;
- bitterness disappears from cucumbers;
- fruits of the correct shape are formed;
- less water is required to water the bush;
- air circulation improves;
- improved access to plant roots for weeding and loosening;
- makes harvesting easier.
By trimming excess leaves, they reduce the density of the bushes - the plant receives more light and is better ventilated, which reduces the likelihood of fungal diseases.
The choice of method for forming a cucumber bush depends on the method of pollination of the variety (parthenocarpic and bee-pollinated), the timing of ripening (early ripening, mid-ripening, late ripening), the method of planting (row, checkerboard) and garter (vertical, horizontal or net).
Reference. When growing cucumbers in greenhouses, the bush is formed into one stem, in open ground - into two or three vines.
Important Rules
Based on the experience of gardeners, whether it is necessary to prune cucumbers, we can say that this procedure is simply necessary
It is important that the top is always in the light. Therefore, the stem must be directed all the time
Pruning cucumbers in a greenhouse must be carried out in compliance with all rules.
- It is necessary to cut not the entire branch, but only to the growth point, otherwise the entire branch will dry out.
- The procedure for getting rid of leaves from cucumbers in a greenhouse cannot be postponed until later, otherwise the vines will become intertwined and the stem will become thinner.
- Leaves need to be trimmed with special, sharp, sterile garden scissors early in the morning. During the day, the wound will heal and dry out. If the stepsons are broken and torn off manually, the plant will suffer for a long time and the yield will decrease.
- Is it possible to remove the lower leaves of cucumbers? Some vegetable growers advise removing the lower leaves to prevent excessive soil moisture. The risk of spreading fungal infection and root rot is reduced. But you can only pick off the lower leaves of a bush rich in greenery. If the bush has sparse leaves, it can harm the growth and development of the plant.
- It is recommended to pluck off excess mustache, which takes away a lot of nutrients. They cannot be directed horizontally along the trellis, otherwise a shadow will be created.
- Cotyledon leaves should not be removed. These leaves are formed in almost all plants at the very beginning of seedling growth. Cotyledons grow in 7-8 days. This is an elongated single leaf, without a pair. When the plant no longer needs it, the cotyledon leaf itself dries up and falls off.
What leaves should be removed from cucumber bushes? Pick off yellowed, dry leaves. You should not leave those leaves that are covered with spots or pests have settled on them. Such leaves do not allow light to pass through and promote rotting. When is the best time to pick? The procedure is carried out every 7-10 days in the morning.
From reviews of experienced vegetable growers: “Unpruned cucumber vines often begin to turn yellow and curl their leaves. The plant becomes weak, and the fruits begin to ripen later and do not taste as sweet and crunchy. In recent years, I have been making sure to cut off all the side branches with leaves, and I also get rid of diseased, yellow leaves. The harvest pleases with its taste and quantity.”
Do not remove large leaves if they are healthy and rich green in color. Leaves participate in the process of photosynthesis and nourish the entire plant. Large leaves can be a result of an excess of nitrogen or simply because this variety was chosen.
If there are a lot of barren flowers on the bush, there is no need to rush to tear them off. Perhaps by changing the conditions of care, the situation can be improved. Often the cause of the formation of barren flowers is excessive watering and excess nitrogen. Greenhouse soil may also need some microelements.
Basic principles of pruning in a greenhouse
Seedlings in a greenhouse quickly increase their vegetative mass - stems, leaves, inflorescences and ovaries. Nutrients are evenly distributed throughout the vine - cutting off excess shoots and leaves contributes to better nutrition of the ovaries.
Experienced gardeners recommend adhering to general principles when pruning greenhouse cucumbers:
- The bush is formed no earlier than a week and a half after planting.
- The formation of bushes begins with a garter.
- Pruning is carried out only with sharp sterilized instruments (boil for 5-10 minutes) - breaking off the stepsons with your hands can damage the plant.
- The shoots are trimmed close to the stem, without leaving any protruding “stumps”.
- Pruning is done regularly as the bush grows - at least once a week.
- The procedure is carried out in the morning so that by evening the “wounds” heal and the plant does not catch an infection.
- The air temperature is at least 20°C.
During any manipulations with the plant, carefully handle the central stem - if it is damaged, the plant dies.
Methods for tying bushes before shaping
A garter is the securing and guiding of a cucumber vine along a guide. In a tied plant, it is easy to identify the main stem and lateral shoots.
Cucumbers are gartered when 4-6 leaves form on the vine, and the plant itself grows more than 30 cm long. A special structure is built for gartering, which will help the bush form and free up space in the garden bed.
Attention! The supports are installed before planting the cucumbers.
Prepare materials for making supports:
- two-meter posts made of wood or metal;
- twine or cord;
- plastic mesh;
- hooks for fastening;
- fixing pegs;
- strips of soft fabric (cotton, knitwear) 3-4 cm wide;
- tools – hammer and pliers;
- nails.
It is not recommended to use thin wire for gartering - it can injure the plants.
There are several methods for gartering cucumbers - let's look at each in more detail.
Vertical
This method is convenient because each plant will have an individual support along which it can climb:
- Inside the greenhouse, along the edges of the bed, a U-shaped structure 2 m high is placed - if the bed is long, you can put an additional support in the middle of the P.
- One end of a rope or twine is attached to the upper horizontal bar, the number of which depends on the number of cucumber seedlings.
- The second end is lowered down, pulled and secured in the ground with pegs or pins next to the bush.
- The cucumber stem is carefully wrapped around the support, directing it clockwise.
- The plant is carefully secured with strips of fabric.
Horizontal
This method is used in open ground or low greenhouses:
- On both sides of the beds, supports 1.5-2 m high are dug in - there are two pillars for each row of cucumbers.
- Between them, at a distance of about 30 cm from the ground, stretch the first row of cord or twine.
- Parallel to the first, several rows of cord are pulled at the same distance (25-30 cm) from each other to the very top.
- Young shoots are carefully directed to the lower tier of the structure; they can be secured with strips of soft fabric so that they do not fall; then they themselves will begin to crawl along the rows of the support and form.
The disadvantage of this method is that as soon as the cucumber vine reaches the upper level, it will no longer be able to continue to rise further and will begin to hang down, shading the lower part of the plant and interfering with the care of the bush.
Mesh
The stores offer a large selection of nets for weaving plants - they are easy to install, have large cells and are made of durable, non-rotting materials:
- Two supports up to 2.5 m high are dug in on both sides of the bed.
- The mesh is stretched and firmly secured between them.
- The bushes are directed onto the net and, if necessary, secured with strips of fabric.
- The cucumber vine itself is woven into the mesh and formed.
When gartering, the lashes are tied loosely, without tension, so as not to tear the plant out of the ground. The top is left free, otherwise the plant will begin to turn yellow and wither.
Garter of cucumbers: step-by-step scheme of work
Tying cucumber vines in a greenhouse is just as important as shaping them. Durable polypropylene twine is suitable for this purpose. But it is not advisable to use thin wire or fishing line. They can cut juicy and fragile shoots. The bushes are tied at the age of 1 month. At this time, the height of the plant reaches 30-35 cm. There is no need to hesitate with tying it up. When the plant begins to mature, the shoots lose flexibility and become harder. They are easily damaged when fastened to a support.
Step-by-step instructions for gartering cucumbers look like this:
- Tie a garter loop . It is done under the first or second true leaf. The loop should be free. The stem needs space. After all, when it grows, it will begin to thicken. A loop that is too tight can tighten the tissue and crush the stem.
- Secure the twine at the top to a horizontal support . Make a regular knot. The rope should not be pulled too tight; it should be loose. A cord that is pulled too tight can damage the whip.
- Twist the rope around the plant . Twist the stem clockwise. Do not change direction while twisting the barrel. Otherwise, the stem will unwind itself during the growth process. As the stem grows, the twine must be twisted, wrapping around the trunk under each internode, under each leaf. If this is not done, the whip will break under the weight of the filling fruit.
Tie a garter loop
Attach the twine to the horizontal support at the top
Twist the rope around the plant
Trimming schemes
The choice of pruning scheme depends on the group of cucumber varieties.
Parthenocarpic
Parthenocarpic cucumbers are hybrids that form fruits without pollination. About a third of the harvest is produced on the central stem, the rest is formed on the side shoots.
Cutting leaves and shoots is done in this order:
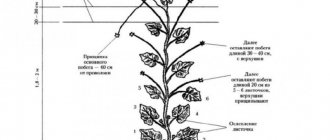
- The stem is conventionally divided into four zones, pruning begins from the bottom.
- The first conditional zone is to remove the first side shoots and flowers in the axils between the second and fourth leaves, without touching the leaves themselves.
- The second conditional zone is when the stem reaches a length of approximately 70 cm and four new leaves appear, only the side shoots are cut off (leaves and flowers are not touched), and one ovary and one leaf are left on the stem.
- The third conditional zone is at a height of 120-130 cm, when the tenth leaf appears, the shoots that form above it are removed. Here two flowers and two ovaries are left in three nodes.
- The fourth conditional zone - in it, after the appearance of the twelfth leaf, all ovaries and leaves are cut off, three ovaries are left on the side shoots and three leaves are left on the stem every half meter.
- After this, the top of the stem is pinched so that the lash does not grow anymore, and secured to the upper support.
Pinching is shortening the length of the shoot.
Bee pollinated
Bee-pollinated varieties form ovaries only after pollination, so they are planted in open greenhouses. Experts recommend forming a bush into one stem, as is the case with parthenocarpics.
The ovaries of bee-pollinated varieties are formed on the side shoots - pruning is carried out in a gentle way.
- The main stem is not cut until it reaches the top crossbar of the support.
- Only the first two shoots are removed.
- The shoots are cut off when 4-5 leaves appear on them, leaving 3-4 inflorescences.
- In the area of the crossbar, the side shoots grow up to 50 cm - they wrap around the crossbar with the main stem, pinching off the side shoots.
Pruning of brown, yellow, damaged and dried leaves is carried out at any time, regardless of the growth of the cucumber vine.
How to properly trim cucumbers
When pruning vines, they try not to change the position of the shoots and leaves, so as not to break off the desired shoots.
Is it possible to pick off the first leaves?
For a young plant, cutting off the first leaves can negatively affect the yield - in the phase of formation of 3-4 true leaves, the entire mass of flowers of the future harvest is laid.
Do I need to remove cotyledon buds?
One elongated leaf of the cotyledon is formed at the very beginning of seedling growth and grows for about a week. As the plant grows, it no longer needs the cotyledon leaf; it dries out and falls off.
It is not recommended to remove cotyledons; the leaf is important for the growth of the seedling - sometimes the plant dies due to the breakage of the cotyledon leaf.
Trimming the lower leaves
The lower leaves are removed only from healthy and lush plants - if there is little greenery on the bush, trimming the lower leaves can destroy the plant.
The lower leaves are cut at a distance of 20-25 cm from the ground - excessive soil moisture and the likelihood of fungus or root rot are reduced.
Is it necessary to pick off the first flowers?
Experienced gardeners recommend removing some of the male empty flowers so that the plant does not waste energy on their growth - leaving 1-2 male flowers per vine.
Female flowers are never picked off - they form ovaries.
Should I remove the first ovaries?
The first ovaries in the lower part of the bush develop very slowly. Experts advise removing them and leaving only those ovaries that have formed at a height of 80-90 cm - after removing the first ovaries, the plant will direct the released forces to the development of the stem and root system.
CUCUMBERS - DO YOU CUT THE LEAVES? HOW?WHEN?
Which shoots are recommended to be pruned for a good harvest?
Removing excess shoots promotes plant growth - pruning on a cucumber bush:
- lower shoots in contact with the ground;
- lateral shoots on which fruits are not formed;
- old, yellowed lashes;
- stems with deformed fruits.
Aftercare for cucumbers
The fruits get their nutrition from a leaf that is located next to the cucumber itself; if you cut it off, the vegetable will immediately die. To ensure that the yield does not decrease, you need to provide maximum nutrition for the remaining greens.
To properly feed a plant, you need to carefully monitor its changes and pay attention to the needs of the bush during all phases of growth. It is important to moderate nitrogen fertilization and increase the supply of potassium and phosphorus.
If there is an abundance of barren flowers on the plant, it is better to stop watering and allow the soil to dry out. If no deviations are observed in the formation of ovaries, then watering should be carried out according to the schedule. You only need to take warm water.