The gardener should plan vegetable plantings and lay out the beds early, on the first visit to the plot, in early spring. It would seem that each vegetable crop has its own place. But sometimes it can be strange to find sprouted tomato bushes in the beds originally intended for growing potatoes or beans. They are quite strong, and in early June they do not look like weak seedlings, but already formed bushes.
Such seedlings grow independently from seeds that fell into the ground in the fall, during harvest. A tomato forgotten in the garden, having overwintered in the soil, produced seeds, which, when warm March days arrive, begin to germinate. And so, the first leaves of tomatoes appear, in a place completely undesignated for them. If the seedlings are not removed, then a small, independently sprouted sprout will turn into a large plant, quite capable of flowering and setting fruit. This feature of vegetable crops, namely sowing seeds directly into the ground, bypassing the method of growing seedlings in a greenhouse, is quite successfully used by many gardeners.
Features of growing tomatoes by seeds
Some people welcome sowing tomato seeds in a garden bed in a greenhouse, bypassing the method of growing seedlings, and get an early harvest with minimal physical effort, because the seedling method is a rather labor-intensive process. For this purpose, seeds of early varieties are sown in garden greenhouses.
Others sow tomato seeds directly on the future garden bed, build mini-greenhouses over them, and grow vegetables in this way. It is believed that tomato bushes are not subjected to a kind of “violence” when transplanted from garden cups to a permanent place of growth. Tomatoes take root well in the place where they sprouted and develop qualitatively, growing the root system, stems and leaves. Such bushes are stronger and more resilient, will hurt less and produce abundant flowering and ovary.
Pursuing the goal of growing and obtaining fruits at a later period, at the end of the summer season, it is recommended to sow seeds directly into open ground in the garden bed. They are sown in the same way as under a mini-greenhouse, but there is no need to build a shelter. Such crops are carried out in June, and in September ripe fruits are obtained, with minimal expenditure of physical strength.
Thus, tasty tomato fruits grown from seeds can be obtained both at the beginning of summer and at the end, without using the labor-intensive seedling method at all. This method is simple and easy to implement.
How to plant tomatoes
Typically, tomatoes in a greenhouse are formed into 2 or 3 stems. To form 2 stems, you need to leave only one of the strongest stepson, located under the first flowering brush. All leaves and side shoots below must be removed and further monitored for their appearance, also removing them.
Photo: Stepsoning in a greenhouse
When forming 3 stems, 2 stepsons are left, usually the first is located above the first flowering cluster, and the second above the first stepson.
How to sow seeds correctly?
The rules for sowing and growing tomatoes using the seedless method, that is, by conventionally sowing seeds in a greenhouse bed or in open ground, are exactly the same, the peculiarity is that the chosen location is at the discretion of the owner.
- Crops in greenhouses. The production of tomato seeds in greenhouse beds is carried out at the same time as for obtaining seedlings. This period falls at the end of March. If the greenhouse is heated all winter, then sowing can be done earlier than the specified period - the resulting harvest will be earlier. If the greenhouse structure “rests” in winter, and heating of the room begins at the end of February, then by the beginning of March, the greenhouse soil will be completely warmed up and ready for growing vegetable crops.
- Sowing in open ground in a garden bed. Sowing seeds in open ground is carried out immediately after the onset of warm and stable weather. The end of April and the beginning of May is quite a suitable period for sowing tomato seeds in open ground in the garden. There will be no more frosts, the ground is slightly warmed up, and the constructed mini-greenhouse will help the seeds acclimate and germinate in the soil.
- Sowing in the summer in the garden, with a later harvest. There is probably no specific time for sowing seeds to obtain late tomato fruits. In this matter, you need to focus on weather conditions and the location of your site. Just buy seeds whose packaging indicates that they offer tomatoes with a late ripening period, and there must be a clause indicating the month of sowing in open ground. You can safely navigate by these indicators. Typically, sowing seeds to obtain autumn fruits occurs at the end of June.
Basic preparatory work for sowing tomatoes
Whether in a greenhouse or in an open garden bed, the soil needs to undergo a series of preparatory work that will become indispensable in practice.
- Selecting a location according to crop rotation. When growing tomatoes in a greenhouse, the choice of location is practically unimportant; anywhere in the structure should be warm, light, moderately humidified and ventilated. But it is best to lay out the beds in sunny places, where there is no shade, the sun warms up well, and the rain moistens the soil. Particular attention is paid to crops that were previously grown in the selected area. Remember, tomatoes don’t grow after corn and nightshades. Potatoes, peppers, eggplants, and tomatoes are affected by the same insect pests - larvae hide in the soil for the winter, and diseases whose spores also overwinter in the ground. We expect a good harvest in the garden beds after harvesting root vegetables, white cabbage, pumpkins, cucumbers and zucchini, and onions. Consider and observe crop rotation.
- Soil preparation is an important point. It would be good to remove the top layer of soil 20 centimeters deep, lay dry hay instead, cover it with a mixture of humus and wood ash, and lay garden soil on top again. But practice shows that gardeners rarely remove soil from their garden beds, especially in open areas. Usually garden soil is simply dug up and fertilized. In greenhouses, if necessary, they still replace the existing soil with a more fertile one. When deep digging, last year's rotted compost, potassium and phosphorus fertilizers are added to the soil, based on the manufacturer's recommendations indicated on the packaging of chemicals. Remember, under no circumstances should you add fresh manure during spring digging - this will destroy the young plant.
- Correct choice of planting material. Gardeners are especially sensitive and attentive to the choice of seeds for future plantings. Many people collect and prepare seeds themselves, selecting seed material from beautiful and large plants and fruits that are not affected by disease. This method does not require financial costs and is quite accessible, but is not always successful. Collected seeds from a hybrid plant, and most often it is tomato hybrids that produce large, tasty fruits and delight the owner, will not produce a seedling similar to the mother bush, and, moreover, there will not be identical fruits. Seeds collected from hybrid plants are not suitable for re-sowing, which gardeners rarely take into account and fail. Conclusion, it is safer in this matter to purchase seed material in a specialized store, where you will be offered the necessary hybrids with guaranteed germination and production of large fruits.
- Preparatory stage for the seeds themselves. A day before sowing, seed grains are discarded, giving preference to dense, large and beautiful grains. Selected seeds are soaked for 10 minutes in saline solution. During this time, the incomplete, remaining grains will float to the surface of the solution, and those suitable for sowing will sink to the bottom of the glass. Next, the tested seed material is disinfected in a weak solution of potassium manganese for 30 minutes and washed with warm water. Next, the tomato seeds are laid out on a wet cloth, covered and left for the grains to swell for about a day. This process is also called germination of seed material. Such manipulations are recommended for sowing seeds in a greenhouse. The swollen seeds, with sprouts already pecked, are sown in the prepared holes. And when sowing in open ground soil, the seeds do not need to be germinated; they can be sown immediately after disinfection.
- Recommended temperature for tomato seed germination. In greenhouse structures, the recommended temperature is 20-25 degrees, in open ground at least 15 degrees Celsius. Lower air temperatures in greenhouses will stop the development of the root system and affect the early development and productivity of the future tomato bush. Higher temperatures will speed up the development of the plant, and flowering will occur earlier than expected. To maintain the required temperature in cool weather, covering material is used for growing tomatoes in open ground; in greenhouses, temperature indicators are simply adjusted.
Fertilizing tomatoes in open ground
Foliar fertilizers involve saturating vegetables with minerals in the leaves and branches of bushes. The advantages of this type of fertilizing are: fertilizer savings and rapid efficiency. In addition, this type of nutrition is used to help a plant suffering from a deficiency of a certain microelement. Foliar feeding is less intense compared to root feeding. In addition, the raw material for fertilizing through the green parts of the plant does not contain chlorine.
Feeding tomatoes in the soil involves alternating two feeding methods at the beginning of the growing season. In the second half of culture development, it is better to use the root method. It is recommended to start fertilizing tomatoes after 7 days of their growth in the ground. The following can be used as foliar fertilizers:
- Milk or whey, iodine and water (in a ratio of 1:10 drops:9);
- Preparations "Zdraven" and "Fitosporin" (dosage according to instructions);
- 2 liters of whey, half a glass of sugar, 8 liters of water, 15 drops of iodine;
- Birch mushroom, diluted in water until dark in color;
- Boric acid, copper sulfate, magnesia, manganese, grated laundry soap, dissolved in a bucket of water;
- 10 Trichopolum tablets, a bottle of brilliant green, a bucket of water;
- Unconcentrated manganese solution;
- Whey and half a glass of sugar.
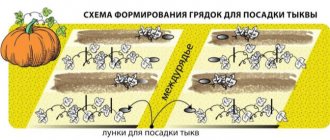
Principle of planting seeds
Each gardener has his own proven methods of sowing seeds. Some sow in a staggered pattern - saving land area. Others sow the seeds in a row.
On the designated bed, make two furrows for future rows, maintaining a row spacing of 50 centimeters. In a row, in a checkerboard pattern, at a distance of 30 centimeters, shallow holes are made, spilled with a weak solution of potassium manganese for disinfection, and 3-4 seeds are placed on a damp surface around the circumference of the hole. This is how they are sown to safely remove excess seedlings from the soil. The laid out seeds are covered with loose soil and the entire hole is moistened with a spray bottle. Next, cut plastic bottles or glass jars are placed on each well, and covering non-woven material or polyethylene film is stretched along the row, over previously installed small arcs. Using garden soil, fill the edges of the polyethylene to prevent the formation of drafts.
Thinning tomato seedlings without seedlings
As soon as 2-3 true leaves appear, the seedlings should be thinned out. I try to leave those plants with a distance of 5-10 cm between them.
Of course, I leave the strongest plants. I do the second thinning when the small tomato plants already have at least 4-5 true leaves. Again, I leave only strong plants in the hole, the distance between which increases to 12-15 cm. Before the last thinning, I water the soil in the hole well, trying to keep the soil very wet.
Those tomato plants that I decided to remove from the hole, I do not pull out of the ground, but carefully dig them up with a lump of earth. They can be transplanted into new holes or planted where there are weak seedlings.
Thus, during the final thinning, I leave 3-4 plants with a distance between them of up to 40 cm. I try to have the plants grow along the perimeter of the hole.
Secrets of balanced seedling care
The film cover is not removed until the first leaves appear on the sprouts. Everything else is based on weather conditions. When growing in a greenhouse, you can remove both the film and the bottles. When growing in a garden bed, the film is removed only when you are sure that the seedlings are already strong and the air temperature will not drop below 20 degrees Celsius. Only two strong sprouts are left in the hole, through natural selection based on external data.
- Organization of watering. The soil in such beds is moistened less often than in a usual tomato plot. This is explained by the fact that the sprouts are not subject to mechanical violence during the growing process, they are not transplanted to a new place, the root system grows to the sides and the seedling itself can find the necessary moisture in the soil. But, if there is no rain for a long time, then the rows of tomatoes are still moistened using a garden watering can, irrigating in the evening. Usually water the sown seeds once a week. Avoiding stagnation of water, irrigate the soil in the hole with a spray bottle.
- Pinching and pruning. Tomato bushes need thinning, regardless of their growing methods. Grown bushes must be pruned, removing lateral and excess shoots that lead to thickening, and cutting off the lower leaves. Using sharp garden scissors, cut off all the lower leaves located up to the first almost blooming cluster. Remember, it is also advisable to pinch the tops of the stems, which will lead to an increase in plant productivity.
- Fertilizer application. If the soil preparation before sowing the seeds was carried out efficiently, the land was fertilized and cultivated, then additional nutrients are not required. If the grown seedlings look unwell, the leaves are faded and weak, then it is necessary to inspect the seedlings for damage by disease or insect pests. There are no signs of damage - feed the seedlings with nitrogen-containing fertilizer, which will help the development of the root system and foliage mass. Fertilizing is done with a solution on moist soil.
- Loosening and hilling is an important stage in caring for tomatoes. Throughout its growth, from seedlings to fruit-bearing bush, the soil around the plant is loosened and fluffed, filling the roots with oxygen. During the loosening process, sprouted weeds are removed, and the bushes are necessarily covered with earth - hilled up. Irrigation is still carried out in ditches between the rows.
- Garter of tomato vines. Plants that have reached a height of 50 centimeters need a garter. Less tall stems grow independently, while longer ones are tied to installed supports. A well-fruiting bush with many ovaries may break under the weight of future fruits, and the harvest will be irretrievably lost. Wooden stakes, metal rods or trellises attached to the roof of the greenhouse on which tomato stems are suspended are suitable for installing supports.
How to prepare seeds for sowing in a greenhouse
After you have prepared the soil in the greenhouse, you can begin preparing the tomato seeds for sowing. In order to speed up their germination, tomato seeds must first be heated. To do this, just wrap them in a cloth and place them near the heating radiator in a place where the temperature is around 40 degrees. It is recommended to keep the seeds there for a couple of days.
______________________________
After heating, it is advisable to disinfect the tomato seed material. Tomato seeds collected by hand or purchased at a seed store are usually disinfected; as a rule, they are not disinfected.
______________________________
Soaking seeds before sowing
The simplest disinfection option is soaking tomato seeds before sowing in the greenhouse soil. They need to be soaked for a quarter of an hour in a light crimson solution of potassium permanganate, then rinsed under running water and dried on a cloth until free-flowing.
If the seeds have been stored for a long period, and you do not know whether they are viable, then you can first warm them up for a day, as we described above, and then place them in the refrigerator door for another day. The temperature in the refrigerator compartment should be from 1 to 5 degrees Celsius.
Photo: Warming up and soaking
How to sow tomato seeds in a greenhouse
- Seeds should be sown in holes arranged in rows at the optimal distance for further growth and development of plants. Leave the distance between the holes approximately 40 cm, sow a couple of seeds in each hole, and if you are not sure of their germination, you can sow 3 seeds per hole. The seeding depth should be about 2 cm. The seeds in the hole must be covered with nutritious soil, humus or compost can be used.
- After sowing, be sure to water the soil well. It is necessary that the soil is wetted by 4-5 cm with water. After watering, cover the beds with sown tomato seeds with a transparent film, which will create a greenhouse effect and speed up the emergence of seedlings.
- As soon as the shoots appear, the film must be removed. If at that time the temperature in the greenhouse is below 14 degrees Celsius, then the seedlings can be additionally insulated by building a greenhouse over the beds - simply insert wire arcs and cover them with plastic film. You get a greenhouse in a greenhouse.
- Keep track of the number of seedlings emerging. If all 3 or 4 seeds have sprouted, then you need to wait until the first pair of true leaves appear and remove one or two extra plants. You shouldn’t throw them away; if suddenly no seedlings appear in some holes, then the seedlings can be carefully replanted.
- Let us remind you once again that if you are confident in the quality of the seeds and know for sure that they will sprout, then sow no more than a couple of seeds in each hole.
Photo: Watering after sowing