Benefits of joint plantings
Joint planting of herbs, flowers, vegetables and fruit and berry crops opens up great opportunities:
- allow you to reduce or reduce the use of high doses of mineral fertilizers
- give up pesticides
- get a larger yield from the same area compared to monoculture
- receive a harvest throughout the season, occupying the freed up area for early ripening vegetables
- improve the taste of fruits or berries (for example, bush beans improve the taste of radishes, mint improves the taste of cabbage) and their nutritional value (the content of sugars and vitamins increases)
- prevent unilateral soil depletion (for example, greatly reduce nitrogen or phosphorus content)
Restoration of the site
Potatoes are one of the few crops that can be planted, if necessary, in the same area for several years in a row. However, in order to ensure that the yield level does not fall below the permissible level, a number of special measures will need to be observed.
The most effective way to restore soil fertility is to use fertilizers. Organic and mineral fertilizers contribute to intensive replenishment of the balance of missing microelements in the soil. First of all, the addition of phosphorus and potassium is required. Fertilizers with a high content of these components can be added to the soil both after harvesting in the fall and at the beginning of the spring (a couple of weeks before planting).
It is customary to use rotted manure as organic fertilizers. Herbivore manure is best. Since there are always cattle on farms and villages, they have gained particular popularity. It is very effective in restoring the properties of the soil as it can enrich the soil with the missing elements and also enhance the properties of the soil.
The most appropriate time to treat the garden with manure after potatoes is before planting a new crop. An alternative can be bird droppings (chickens, geese, ducks), which will enrich the soil with nitrogen, potassium and other components.
Before planting potatoes next year, you can sow cereal crops in the garden after harvesting. Oats and rye are best. Legumes are also used - beans, peas. Sometimes mustard or rapeseed is planted.
Plants that should not be planted nearby
Among garden plants, relationships of mutual assistance are much more common than relationships of hostility. Poor compatibility of plants is most often explained by their root or leaf secretions, which can inhibit the growth of neighboring crops. The secretions of some plants have a specific inhibitory effect only on one or two other species. For example, sage does not get along with onions, turnips suffer from the proximity of the reedweed and knotweed, marigolds have a bad effect on beans, wormwood - on peas and beans, tansy - on kale, quinoa - on potatoes.
There are plant species that produce substances that are poorly tolerated by most other species. An example is black walnut, which releases a substance called juglone, which inhibits the growth of most vegetables, azaleas, rhododendrons, blackberries, peonies, and apple trees.
The close proximity of wormwood is also undesirable for most vegetables.
Among vegetable plants there is also an uncooperative, or, as they say, “asocial” species that has a bad effect on many cultivated plants. This is fennel. It damages tomatoes, bush beans, cumin, peas, beans and spinach.
Some weeds of field crops not only compete with them for water and nutrition, but also suppress them with their secretions. Wheat is oppressed by a large number of poppy and chamomile plants, rapeseed - and field mustard. Rye, on the contrary, itself inhibits the growth of weeds, and if it is sown for two years in a row in one place, then wheatgrass will disappear from this field. Other cultivated plants are also capable of inhibiting the growth of weeds. From them they are trying to isolate the substances responsible for this action in order to create environmentally friendly herbicides based on them.
A striking example of a negative interaction is the relationship between clover and all plants from the ranunculaceae family. The substance ranunculin is formed in their roots, which, even in extremely low concentrations, inhibits the growth of nodule bacteria and therefore makes the soil unsuitable for clover. If a buttercup appears in a field of perennial grasses, then the clover here will soon completely disappear.
The American biologist R.B. Gregg, in his book on herbs, gives such a devastating characteristic of the buttercup family. “Delphinium, peony, aconite and some other garden flowers belong to the ranunculaceae family, which is very strong and viable, but lives only for itself. They require large amounts of organic fertilizers, and leave behind lifeless humus. The plants next to them won’t grow well without plenty of compost.”
In the kingdom of trees, according to the same author, spruce is distinguished by its aggressive character. It is hostile to all other trees; the adverse effects of spruce appear in the soil within 15 years after its felling.
There are many examples of such relationships when in large quantities plants have a depressing effect on a crop, but in small quantities they are beneficial for its growth. It is recommended to plant such plants along the edges of vegetable beds, but only in small quantities. This applies to white nettle (dead nettle), sainfoin, valerian, and yarrow. Chamomile in large quantities is harmful to wheat, but in a ratio of 1:100 it promotes better grain quality.
What is mixed planting
Mixed plantings involve placing vegetable crops on a small plot of land that have a beneficial effect on each other, taking into account their characteristics
When planting, be sure to follow the rules for arranging plants with each other, taking into account their height, size and ripening period. They should not suppress each other’s growth, but create a certain microclimate or be protected from sunlight or wind
Advantages of mixed vegetable plantings
Growing several types of plants in one place reduces soil fatigue and makes it possible to abandon annual crop rotation. Planting in compliance with all compatibility rules will increase the yield several times by the end of the season.
The main advantages of mixed plantings:
- proper placement of vegetable crops allows harvesting from early spring until the first frost;
- The area of land allocated for a vegetable garden is used more rationally, from 1 sq.m. you can get up to 20 kg of vegetables with the right combination;
- vegetable crops feed on different elements contained in the soil, which helps to avoid unilateral depletion of the soil;
- substances secreted by the roots of one plant influence the taste and size of the neighboring vegetable, stimulating or suppressing;
- the mixture of odors emitted by leaves or fruits of different crops plays the role of chemicals that repel pests or prevent them from finding the desired plant.
Conditions for mixed plantings
Mixed plantings are part of biodynamic farming, which means growing vegetables and berries only using natural forces, without resorting to chemicals and artificial fertilizers. To get as much harvest as possible from each piece of land, follow these tips when planting in a mixed way:
- The width of the future bed should be 1 m. This is the optimal size for further convenient processing and sowing.
- The main, long-ripening crop is planted in the central part of the bed. It could be tomatoes or cabbage. By the end of the season, its growth will increase significantly, and it will occupy the area of the entire bed.
- Something that ripens quickly is planted on the sides of the bed. Such friendly crops can be greens - spinach, radishes, green salad. They are compatible with almost all vegetables and stimulate their growth. While the main crop grows, the side crops will already be collected and space will be freed up.
- Plants for lateral planting are chosen to be small and stunted, with a small root system.
- To protect against pests in an organic way, herbs with a strong aroma are planted in the garden bed - sage, basil, coriander, lemon balm or mint. There should be a lot of them so that the spicy fumes can repel pests and attract beneficial insects.
Undesirable neighborhood for vegetables
When different crops or varieties are grown in one area, an exchange of chemical compounds occurs between them and the plant next door has a direct impact on the quality and quantity of the crop. Before making a plan for planting vegetable and berry crops, figure out what placement should be avoided.
Cucumbers and tomatoes are not planted next to each other. Tomatoes require constant ventilation, and cucumbers require heat and high humidity.
Tomatoes are bad neighbors; they inhibit the growth of vegetables growing nearby. Such proximity does not have a negative effect only on garlic, beans, radishes and greens. Beans and vegetables such as carrots should not be placed next to cabbage; they inhibit the growth of each other. Place celery next to it and get a good harvest of both crops.
Sage and legumes should not be planted near the onion bed; they have an adverse effect on its growth and taste. For potatoes, cucumbers, celery and pumpkin are bad neighbors; close placement of tomatoes is also undesirable. You will not be able to get a good beet harvest if dill or potatoes are planted next to it.
Peas are good neighbors
If you want to harvest a good harvest of peas and other vegetables, you need to know which of them will not only not interfere with each other, but also help. Peas have many friends with whom they are willing to share nutrients and are even able to enrich the soil with nitrogen, which they produce with the help of a special type of bacteria. Many plants themselves are not averse to “lending a shoulder” to peas: some crops can form a mutually beneficial alliance with them
When deciding what to plant next to peas, first of all pay attention to the following crops:
- cucumbers - many gardeners alternate cucumber beds with pea beds, resulting in a rich harvest of both legumes and cucumbers;
- cabbage - its peas feed it with nitrogen, stimulating the formation of leaves, which are of the main value for the gardener, protects its roots from various types of rot, and does not suffer from this in any way;
- carrots - they also take advantage of the peas’ ability to enrich the soil with nitrogen and do not harm it in any way;
- radishes, radishes and spinach - their peas also generously feed them with nitrogen;
- mustard - peas have a mutually beneficial exchange with this crop: mustard roots secrete substances that improve pea fruiting, protect pea beds from weeds, and peas, in turn, feed it with nitrogen;
- corn - its tall, strong stems become a natural support for the peas, and it repays it with nitrogen, which is extremely necessary for this crop to develop;
- basil repels one of its main enemies from peas - the bean weevil;
- Lavender, rosemary, and yarrow also protect peas from insect pests.
Neutral relationships develop between peas and potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants, parsley, and lettuce.
The best predecessors for peas
Crop rotation, that is, alternately growing different annuals on the site, will help you get a good harvest and prevent the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms in the soil.
With a well-designed schedule, previously planted plants not only do not deplete or contaminate the soil, but also help increase the yield of vegetables and berries next year. Moreover, each subsequent crop must replenish the supply of nutrients in the soil that was consumed by its predecessors.
So, for example, to get a good harvest of legumes, you need to know how to plant peas in open ground.
Legumes will feel normal after many plants, except for their “relatives,” that is, representatives of this family.
The ideal predecessors of peas in crop rotation are: potatoes, cabbage, cucumbers, pumpkin, zucchini, dill, and corn. You can plant it after strawberries, wild strawberries and carrots.
But in an area previously sown with grains, it is better to place vegetables, provided that the beds are well cleared of straw and weeds.
Important! This vegetable loves light, fertile soil, so it will grow well after those vegetables and root crops that were covered with cow manure last year.
Next year, peas can be safely planted in the garden after the tomatoes.
Is it possible to sow peas after peas?
Soil oversaturated with nitrogen (and this is exactly what it becomes after legumes) is least suitable for growing vegetables. For this reason, you cannot plant peas after peas the next year. The next time legumes can be sown in this area no earlier than four years later.
There is no point in planting peas after beans - there will be no good harvest
Compatibility with fruit and berry crops
Considering the love of peas for bright light and warmth, it is not recommended to grow them near mature spreading fruit trees and berry bushes, the dense foliage of which will obscure the sun. However, peas do not object to the proximity of young seedlings. This proximity is especially beneficial for young apple trees: the legume crop grown under them actively loosens the soil and saturates it with easily digestible nitrogen. If you decide to sow peas under fruit trees, first add light fertile soil to the tree trunk circles in a layer 10-12 cm thick.
A berry crop such as strawberry (strawberry) cooperates very productively with peas. The roots of these plants lie at different depths, so they do not compete for nutrition and moisture. Nitrogen released by pea nodule bacteria promotes the development of berry bushes.
Planting peanuts
It is rare to see such a plant in the gardens of our compatriots, and in vain. Growing it is not at all difficult, but as a result it will be possible to harvest a nutritious product. It is worth saying that peanuts in the garden do not get along with all crops, but they will coexist well with cucumbers, corn and any legumes.
Recently, corn is not often planted in gardens. But one cannot help but notice that the boiled vegetable is endowed with good taste and is liked by adults and children. But that's not all its advantages. In addition to the fact that it is endowed with useful microelements, it can be used as a natural support for cucumbers. Considering that this crop is avoided by aphids, cucumbers will be protected from pests. Along the perimeter of the corn bed you can plant climbing legumes: peas, beans. Corn also goes well with potatoes, melon, sunflowers, and zucchini. You should not plant tomatoes next to it.
As they grow, tomato bushes try to take over all the space next to them, so they are not favorable to the proximity of other crops. They are planted in different ways. For example, a high mound is built in the center of the bed. On this hill they sow: basil, asparagus, lettuce, dill, parsley, onions, spinach, thyme. Tomatoes and legumes go well together. Therefore, it is worth planting beans between the rows. A good planting option would be melon and carrots, which can be grown in the nearest plot. There is no need to place corn and cabbage next to tomatoes.
Cabbage has many varieties. Everyone grows their favorite variety in their garden. Cauliflower and white cabbage are most often planted. An inexperienced gardener may think that it would be convenient to plant them side by side and that it would be possible to first remove the cauliflower, which ripens earlier, and then the white cabbage. However, it is better not to combine these two types of one crop, and when making a common garden bed, plant cucumbers, beans, and celery next to the cabbage. It will be nice to have aromatic herbs next to the cabbage: sage, thyme, spinach, onion, dill. They will protect her from harmful insects. Radishes and greens can be grown between the rows of cabbage heads. But in this case, cabbage should not be planted very thickly.
Cauliflower does not like being next to its relative, but gets along well with beets, beans, cucumbers, celery, sage, and thyme. You should also not plant strawberries and tomatoes next to it. It does not like to be in the same bed as broccoli cauliflower, but goes well with the above mentioned crops.
More friendly are Brussels sprouts, which can coexist next to other species. This variety only tolerates tomatoes and cruciferous vegetables. Often in a bed with Brussels sprouts you can see lettuce, dill, spinach, radishes, sage, and turnips.
When planting cucumbers, make sure that their location is away from melons, potatoes, and aromatic herbs. For cucumbers, you should create a warm, high bed, where beans, peas, lettuce, corn, radishes, and lettuce can be planted next to them. You can plant plants according to this scheme: corn is sown in the center, which will serve as a support for cucumbers, as well as peas and beans. By the way, they can be planted either mixed or in one hole. The edges of the bed can be occupied for radishes and lettuce, which will ripen quickly.
What to plant next to cucumbers
Cucumbers tend to cling to any object with their antennae. And so that they do not damage neighboring plants, they should be grown on a trellis in a greenhouse.
To cucumbers you can add dill, parsley, basil, fennel, leaf and head lettuce, white cabbage (of course, if there is enough space for it), radish, eggplant (varieties Siberian early ripening 148, Mushroom Picker's Dream), sweet pepper (Giganto Rossa F1 , Ural thick-walled F1, Yellow giant F1, Red giant F1, Orange giant F1, Dutch giant, Queen Elizabeth F1).
Eggplant
Crops have similar requirements for watering and care. When growing them together, you need to provide the cucumbers with supports for the vines in time, then they will not oppress each other. If you plant eggplants in a greenhouse together with cucumbers, then plant the eggplants in a sunny place first, since the wide leaves of cucumbers can shade them.
Will bell peppers grow along with cucumbers?
This is another advantageous neighborhood. Peppers like the same growing conditions as cucumbers. They do not tolerate drafts, dry soils and dry, hot air. Just tie up the vines so as not to shade the nightshade crop. Cabbage and peppers are also excellent predecessors for garden beds in front of cucumbers.
Here's what you can plant in a greenhouse with cucumbers
Zucchini
Both cultures do not oppress each other. Their proximity is not dangerous, since they do not inter-pollinate, although they are relatives. Both plants love water and light. But make sure that the large zucchini leaves do not shade the cucumber leaves.
Corn and cucumbers
For large garden plots this is one of the best combinations. Corn serves as a curtain for cucumbers, protecting them from the scorching sun and drafts. The root systems differ: in the first they go deep, in the greenfinch they are superficial. Plus, the vines of cucumbers curl perfectly along the stems of a strong neighbor.
Neighborhood of cucumber and onion
Both plants are friendly to each other. The meadow is also an excellent predecessor for cucumbers. But it is better not to plant onions immediately after cucumbers; first grow legumes in this place.
Is it possible to plant dill with cucumbers?
This aromatic herb is an exception among spicy plants; it is not advisable to plant others. It is useful to grow wormwood, thyme and thyme nearby; they repel pests such as slugs that eat young fruits.
Cucumbers also work well with radishes, different varieties of cabbage and broccoli, mustard and spinach.
Many gardeners are concerned about whether it is possible to plant different varieties of cucumbers side by side. There is no definite answer, since if the varieties are pollinated, then as a result of proximity they can be cross-pollinated. If the varieties are self-pollinating, then nothing bad should happen. But even in the first case this is not catastrophic. It all depends on whether you will use grown seeds or plant purchased ones every year. In case of cross-pollination, fruits can receive varietal characteristics of each other. For home use this is not important.
Is it possible to plant cucumbers next to cabbage?
Cruciferous crops make excellent neighbors with cucumbers, so you can plant them side by side not only in open ground, but also in a greenhouse. Both crops love abundant watering, so it will be easier to care for the plantings.
Is it possible to plant cucumbers next to potatoes?
Potatoes are an undesirable neighbor for cucumbers, despite their distant relationship. Both of these crops are susceptible to late blight, which can have a negative impact on the harvest. Also, during processing of potatoes, some of the chemicals may get on the cucumbers. Therefore, it is not worth taking risks and planting these plants nearby. True, the experience of some summer residents is more favorable, but only on the condition that cucumbers are grown under film.
Is it possible to plant cucumbers next to garlic?
Gardeners have different opinions about such planting. Some believe that there will be practically no benefit, and the cucumbers themselves can slow down their growth. Others, on the contrary, claim that garlic relieves lashes from angular leaf spot (bacteriosis), aphids, mole crickets, etc. In general, both sides are right. Just to achieve a positive effect, you don’t need to plant garlic too close to cucumbers, keep a distance of at least half a meter.
Is it possible to plant watermelons and melons next to cucumbers?
Watermelon and melon, like cucumbers, belong to the Pumpkin family, therefore, on the one hand, they are not bad next to each other, but on the other hand, some problems may arise. For example, lack of nutrition, damage by the same diseases and pests, cross-pollination, due to which the taste of the fruit will suffer. Such a proximity in a greenhouse is especially undesirable. In open ground, you can try planting these plants in neighboring beds. But in general it is better to come up with another placement.
The benefits of mixed beds
To summarize all that has been said, I would like to note that planning mixed beds greatly helps save space and significantly improves the quality of the harvest. Soil resources are used more evenly, and the plants themselves serve as natural protection for each other from diseases and pests.
It should be taken into account that the planting scheme can be changed to suit the needs of your garden; we have given only general templates. But be sure to observe the compatibility of vegetables. This simple rule always gives excellent results and does not require any additional costs or investments.
Experienced gardeners harvest 11-15 kg of a wide variety of vegetables from one bed. The correct arrangement of plants in the garden also helps to save resources, as less water and fertilizers are required.
That, perhaps, is all about what the compatibility of vegetables in the beds is. For a list of plants that are “friends” and “not friends” with each other, see the table. Use it - and you are guaranteed a good harvest!
published on udachnyesovety.ru according to the materials jenskiymir.com
Benefits of compacted fit
Even if you do not need to save space, joint plantings are desirable on the site. If you choose the right crops, symbiosis will arise when plants of different species help each other. Please note that some species cannot coexist, even if they have different diseases and pests. If you plant without taking into account compatibility, the crops will begin to oppress each other and there will not be a good harvest.
When growing vegetables in a greenhouse, you need to take into account their requirements for temperature and air humidity. They could get along with each other, but they have different requirements for temperature and humidity conditions. If there is only one insulated room, you can separate the crops with film or non-woven material. With good protection from pests and infections, it is better to grow peppers in this greenhouse; they love the same conditions as tomatoes. Plant an unpretentious onion next to the bushes; you don’t need to create special conditions for it. If you want, you can plant the ground with early kale; it will ripen quickly and will not interfere with other crops.
There are plant species that have a positive effect on their neighbors. Often such herbs have a good effect on human health; they are used in folk medicine. Everyone knows the healing properties of valerian, yarrow, chamomile - they will also support tomato seedlings. Just don’t let the ground become overgrown with weeds, leave a few bushes around the edges, that will be enough.
You can sow green manure near the tomatoes; they enrich the soil and improve its structure. Mustard will also protect young seedlings from strong winds or scorching sun. Just make sure that the helper plants do not grow too tall and drown out the main crop. The roots of lettuce and spinach add nutrients to the soil. The smell of marigolds will repel pests - make a decorative border of these flowers around the garden bed. Plant tomatoes next to strawberries in the greenhouse, and you will eat early berries in the spring, and enjoy juicy tomatoes in the summer. You can also plant peppers there, but be careful not to spread the infection.
Why some crops cannot be planted next to cucumbers
The space on the site for installing a greenhouse is limited, so you need to select neighbors very carefully. For many decades, people have been studying the interaction between neighboring plants. Proper placement of crops helps protect them from diseases and pests, as well as increase productivity. And all this without the constant application of mineral fertilizers, which saves money and makes the products more environmentally friendly.
Plants create favorable conditions for each other for growth, healing the soil, feeding it with useful substances, in particular nitrogen. Other plants loosen the soil with their roots, prevent harmful weeds from growing, and prevent soil depletion and weathering.
Some plants attract pollinating insects for various crops in the garden, as well as birds and pest-killing insects. Other plants drive away rodents and harmful insects that spoil the crop.
It is also necessary to think through a planting plan because different crops require special growing conditions. What is good for one may be bad for another. Cucumbers require moist air and constant maintenance of moist soil, infrequent but plentiful. These conditions are not suitable for many garden plants. For example, it is difficult for nightshades (potatoes) to grow next to cucumbers; they become depressed and weak. High temperature and humidity are not good for tomatoes. However, some gardeners successfully grow tomatoes with cucumbers. An example will be the heroine of the video posted at the end of the article.
Features of growing cucumbers
Cucumbers need to be planted on fertile, light and warm soil that does not become waterlogged and contains many nutrients. In the fall, when preparing the bed for the next year, rotted manure or compost is added at the rate of 5-6 kg per 1 sq.m. When decomposition processes begin, heat is released and the bed is saturated with nutrients. And cucumber leaves absorb carbon dioxide released during the decomposition of manure.
Every morning, the cucumbers are watered with warm, settled water. They have a superficial root system, which is also fragile and delicate. Lack of oxygen and damage lead to their death, or damage to spider mites and diseases. Therefore, the soil must be kept loose and moderately moist. This option is not suitable for most plants.
Cucumbers are picky about temperature.
When it drops to 10 degrees, the leaves turn yellow and growth stops. When it drops to 5 degrees and below, the leaves fall off and are affected by powdery mildew. And when the air temperature rises, the pollen in the flowers sticks together, they are not pollinated, and the flowers fall off.
It is best to grow cucumbers vertically; to do this, they are tied to a trellis. This makes them easier to care for and reduces the risk of disease and pest damage.
This growing principle is not suitable for all plants. Not all crops are suitable for growing together with cucumbers for the following reasons:
- Spreading mustaches of cucumbers can oppress neighbors in the garden.
- Also, on the contrary, neighboring plants may have too strong a root system, which will not allow the cucumber plant to develop.
- Other plants will draw all the moisture from the ground, which creates extremely unfavorable conditions for cucumbers.
- It is not recommended to grow plants belonging to the same family nearby, as they will “argue” with each other.
- Neighbors can consume a lot of nitrogen, which is necessary for the growth and development of cucumbers.
What vegetables grow well in one bed?
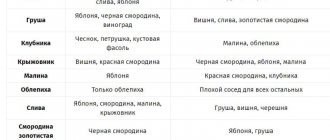
I offer you a short table of vegetable compatibility. More detailed information is provided later in the article.
| Vegetables | Good neighborhood | Bad neighborhood |
| Asparagus | Tomatoes | No |
| Beans | Corn, celery, garden savory, cucumbers, radishes, strawberries | Onion and garlic |
| Beet | Cabbage, broccoli, lettuce, onion, garlic | Beans |
| White cabbage, broccoli, Brussels sprouts | Beets, chard, potatoes, celery, dill, lettuce, onions, spinach | beans |
| Carrot | Legumes, tomatoes | No |
| Celery | Beans, tomatoes, cabbage | No |
| Corn | Cucumbers, watermelons, pumpkin, peas, beans, pumpkin | Tomatoes |
| cucumbers | Beans, corn, peas, cabbage | No |
| Eggplant | Beans, pepper | No |
| Melon | Corn, pumpkin, radish, zucchini | No |
| Onion | Beets, carrots, chard, lettuce, peppers | Legumes |
| Peas | Beans, cucumbers, turnips, carrots, corn, radishes. | Onion garlic |
| Potato | Beans, corn, peas | Tomatoes |
| Zucchini | Corn, melons, pumpkins | No |
| Tomatoes | Carrots, celery, cucumbers, onions, peppers | Corn, kohlrabi, potatoes |
Other useful neighbors for vegetables
In addition to the neighborhood of one vegetable crop with another, it is good to consider other possible neighborhoods - vegetables and flowers, vegetables and herbs. Such combinations in garden beds are not only beautiful, but also useful.
Flowers next to vegetables.
Good advice: plant a few marigolds in the tomato bed; they repel pests. You can even decorate the entire perimeter of the garden with marigolds - this will help keep pests at a distance.
Some flowers act as pest traps, luring insects to them. Nasturtiums, for example, are very popular with aphids.
These pests will prefer to feast on nasturtium and will not pay attention to nearby vegetables.
Vegetables and herbs.
Planting herbs nearby will give your vegetables a more refined taste. They also repel harmful insects. Rosemary repels beetles that attack beans. Thyme repels cabbage pests. Onions and garlic repel aphids. Oregano, like marigolds, is a good all-purpose barrier against most insect pests.
When deciding which vegetables to plant nearby in the garden, you need to be guided not only by scientific data, but also by common sense. Lettuce, radishes and other fast-growing plants can be planted between melons or pumpkins. Lettuce and radishes will ripen before the pumpkin grows. Shade-loving green leafy vegetables such as spinach and chard are grown in the shade of corn. Sunflowers also grow well next to corn because their roots occupy different levels in the soil and do not compete for water and nutrients.
Well, let's move from the particular to the whole, and consider the successful and unsuccessful neighbors for each vegetable.
This is interesting: Russian black beans (growing) (video)
Technology of growing vegetables in a greenhouse
In addition to the fact that you need to plant vegetable crops taking into account their compatibility, you need to know how to grow them correctly. Even if you have taken into account the neighborhood, you can ruin everything if you do not create the necessary greenhouse conditions. Why do you need a greenhouse anyway? And it is needed in order to create the necessary microclimate for the growth of vegetables.
In essence, a greenhouse is the tropics in miniature, but do not forget about one important nuance: the temperature should not be too high or too low. Therefore, in very hot weather it is necessary to ventilate
Watering greenhouse plants should be more abundant than those of crops growing in the garden, because strong evaporation occurs in the greenhouse.
With mixed planting, you don’t have to plant all the crops at the same time; gradual planting, taking into account the time of ripening of vegetables, would be more correct.
The importance of compatibility in the same bed
In nature, plants form communities. This allows them to better withstand the aggressive influence of the environment, protect themselves from diseases and pests, and share accumulated substances with each other.
If this happens in the wild, why not transfer the experience to our areas? Scientists have proven that combining plants in one bed will bring many benefits.
Why is neighborhood so important?
The book of the biologist, written on the basis of foreign research (“Good and bad neighbors in the garden bed.” Compiled by N. M. Zhirmunskaya, 1995), describes in detail the benefits of compatible plantings.
Cultures biologically influence each other; The roots and leaves of plants release phytoncides, antibiotics and other biologically active substances into the soil and air. The sown area is used rationally
This is especially important when there is a deficiency. The land is not depleted by monoculture sucking nutrients from it. Useful elements of the soil are redistributed in it during the simultaneous cultivation of different crops. Plants have a beneficial effect on each other through physical influence - tall plants shade low ones that need it, serve as support for them, etc. Possibility of obtaining a harvest from one bed throughout the season. Reducing the likelihood of disease or pest attacks, since in compatible plantings it is difficult for insects to find their prey; In addition, the lack of free soil prevents pests from laying eggs. Protection from weeds - there is no longer room for them on earth.
But in order for the garden to become a single organism, you need to know the rules of planting, which may consist of combining plants, including flowers and weeds. They too can play their role with dignity.
How to choose a neighbor?
In order not to make a mistake in choosing a worthy partner, you need to understand what a culture needs for proper development.
Onions love light, humus-rich, neutral soils and are responsive to nitrogen and potassium fertilizers. In acidic soil, the ability to absorb nutrients is reduced, and the plant is affected by downy mildew. In order to coexist harmoniously in the same bed, onion neighbors should also be comfortable on such land.
Onions are a natural antibiotic. The essential oils of this plant contain phytoncides that can kill germs and viruses. Any culture is good with him - is it bad to have a permanent healer with you?
But plants that will not block the sun from it and will not compete with it for food and water are suitable for onions.
What cannot be planted in a greenhouse with cucumbers
Basil is a bad neighbor
Fighting ants in a greenhouse with cucumbers
Improper selection of crops will lead to reduced yields, slow down development, and sometimes can even lead to death. Therefore, it is important to find out not only what can be planted with cucumbers in a greenhouse, but which crops are incompatible with each other. The ability to inhibit nearby growing organisms is called allelopathy.
Undesirable neighbors of greenies include:
- Spicy herbs: basil, hyssop, cilantro and oregano (dill is an exception). These herbs will not have the best effect on the taste of green fruits, so beds with such plants must be formed in another place.
- Tomatoes. There are different points of view about the proximity of cucumbers and tomatoes. Some believe that such a neighborhood is possible, others, on the contrary, exclude joint planting. Nearby, these crops dry out and the harvest turns out to be poor. The favorable environment for tomatoes must be completely different than for cucumbers. Greens love humidity, frequent watering, and high temperatures, unlike tomatoes, which get sick when exposed to excessive moisture.
- Unfavorable neighbors for this crop are potato tubers.
What crops are best to plant after garlic?
Garlic, which disinfects and heals the soil, belongs to the category of rare garden plants, after which flower, green, and vegetable crops grow well. And yet, many gardeners often cannot decide what to plant in the area where garlic previously grew.
They might want to try one of our tips:
- To heal the soil and enrich it with microelements and nutrients before winter, you can sow green manure plants. If you plan to grow cruciferous crops in this area in the spring, it is advisable to sow oats, rye or phacelia. If you plan to plant pumpkins or tomatoes, it is better to sow rapeseed, mustard or radish: these crops will effectively cleanse the soil of rot.
- After garlic, you can plant potatoes, legumes, and cucumbers.
- With great success, strawberries can be grown in place of garlic plantings. The bushes of this berry crop will be especially strong, healthy, and the harvest will be unusually generous.
- Planting and growing beets, tomatoes and cabbage is completely acceptable.
When purchasing a summer cottage or a house on land, the owners begin to think about how to organize a vegetable garden. I want to make it not only useful, but also beautiful, blooming, fragrant. Many novice gardeners get lost, don’t know where to start and make many mistakes in their “career as a plant grower.”
A bountiful harvest depends on proper planting planning. It is not enough to simply stick seeds into the ground and wait for the harvest. It is necessary to correctly compose the soil mixture, choose a suitable location, organize watering and caring for the plants. It is better to learn about all these features of setting up a vegetable garden in advance, rather than later being disappointed in the results of your hard work. Here the gardener will find all the useful advice from experienced plant growers on organizing a summer cottage, plant compatibility and a lot of other useful information.
Requirements for growth conditions
For growing peas, a sunny area protected from strong winds with deep groundwater is suitable. The soil is preferably light, fertile, but not oversaturated with readily available nitrogen. The optimal pH value is about 6-7 pH. On acidic soils, peas grow poorly, often get sick and produce meager yields. It is very good if last year the crops under which manure was applied grew in the chosen place. The best predecessors for peas are considered to be tomatoes, cucumbers, cabbage, potatoes, and pumpkins; the worst are all plants of the legume family.
In joint plantings, peas are usually grown as an accompanying (compacting) crop, which has a lot of positive qualities:
- On the roots of peas there are characteristic swellings in which nodule bacteria develop - microorganisms that fix nitrogen absorbed from the air and saturate the soil with it.
- The powerful roots of the plant loosen the soil.
- Peas are a good honey plant. Its purple or white bisexual flowers are eagerly visited by bees and bumblebees, at the same time pollinating neighboring plants.
- The dense foliage of the legume prevents moisture evaporation, protecting the soil from drying out.
- After the leaves close, peas suppress weeds, depriving them of light.
Thanks to these features, peas are an enviable neighbor for most cultivated plants.
Bush beans
This is a very friendly plant. It grows well next to radishes, all types of cabbage, corn, celery, cucumbers, potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants, beets, lettuce, strawberries and spinach. Plus, beans release nitrogen into the soil and thereby help these crops develop well.
But the proximity of onions, garlic, fennel and peas is undesirable for beans. It is better to plant it next to thyme: it will protect against black aphids.
Good neighbors for garlic are tomatoes, beets, carrots, cucumbers, strawberries, and radishes.
But beans, peas and cabbage have a negative effect on it.
To make it easier for you to remember this information, we have prepared a visual diagram that you can save and keep handy while drawing up your garden plan.
We hope this will help you correctly plan the location of the beds on your site. Have a rich harvest!
Shared boarding rules
If you suddenly don’t remember the various combinations of crops in the beds, or doubt the beneficial effects of some herbs and vegetables on others, there are always rules that have decisive weight when drawing up planting schemes:
- Do not place crops of the same family next to each other - they have common diseases and pests, with the exception of eggplant and pepper
- Combine early ripening greens and vegetables with plants that have a longer growing season:
- short ripening period for radishes, lettuce, Chinese cabbage, onions, kohlrabi, watercress, lettuce, white mustard, early potatoes and early cucumbers
- long ripening period for cucumbers (not counting early ones), zucchini, pumpkin, eggplant, peppers, tomatoes, cabbage, beets
- Orientation by light in such a way that tall plants do not shade short light-loving plants, but shade seedlings sensitive to excess light
- light-loving vegetables: watermelons and melons, cucumbers, tomatoes, eggplants, peppers, corn
- those who like to grow in shade: Chinese cabbage, lettuce, parsley, zucchini, rhubarb; young seedlings of any vegetables do not like the hot sun
- moderately light-loving: carrots, cabbage, garlic, onions, beans, radishes, turnips
- We take into account the rules of crop rotation - good and bad predecessors - What to plant next
Joint planting of cucumbers in a greenhouse or polycarbonate greenhouse
Everyone knows that cucumbers take up a lot of space in the beds; the length of the vine of some varieties reaches 2.5-3 m. When grown in a greenhouse, due to the stable humid environment, it becomes necessary to tie the stems to trellises, which frees up a lot of space.
The greenhouse method of growing vegetable crops requires considerable effort, so it makes sense to fill each empty area with seedlings of other plants.
They get along quite well with cucumber:
- tomatoes;
- pepper;
- watermelons;
- peas;
- leaf turnip;
- mustard;
- Chinese cabbage, etc.
When choosing a neighbor for a cucumber, you should study the moisture and fertilizing needs of the vegetable being added. The indicators must be identical.
What can't be combined with?
In addition to the favorable proximity, there are plants that are strictly prohibited from being planted next to onion beds.
For example, classic cabbage. Unfortunately, there is no general consensus regarding the combination of these vegetables. Some say that onions give cabbage vigor and ward off pests. Others argue that there is no point in their proximity; cabbage, with its size, blocks the onion from getting sunlight, thereby limiting its ability to grow.
Beans and peas in neighboring beds will not bring any benefit. The same goes for beans, to which onion inflorescences are aggressive. The proximity of these plant species can have a detrimental effect on the onion harvest.
Otherwise, the vegetable and fruit neighborhood for onions is not a problem. The vegetable is unpretentious, although it requires care during growth. You can even combine plantings with it not only in the neighborhood, but also in the same bed.
Why “good neighbors” are useful and why “bad” ones are undesirable
Video: What can be planted next to corn
For joint cultivation, plants are chosen that cover the area at different times or occupy different tiers in height. A positive effect from combined plantings can be achieved when these vegetables are adjacent to crops that:
- do not suppress, but promote their development,
- have similar requirements for the degree of humidity, soil composition, lighting and fertilizing,
- repel pests of neighboring plants.
Attention! Joint cultivation means competition between plants for water, light and nutrition, so their volume should be increased by 1.5 - 2 times.
However, not all neighbors of cucumbers in open ground have a positive effect on their growth. It is not recommended to plant other crops of the pumpkin family in close proximity. Having common pests and a predisposition to similar diseases, if one plant is infected, the entire crop of vegetables in that family will die.
Crops that emit substances that slow down or interfere with the development of cucumbers should not be placed as neighbors.
Savior flowers
It turns out that the crop can be saved from diseases and pests not only with chemicals, but also with flowers, which should be planted next to the vegetables. Both beautiful and practical.
Marigolds will provide good protection against pests
. It is good to plant them not only in flower beds next to the window, but also along the perimeter of the garden and between the rows. Marigolds, thanks to their properties, repel nematodes from tomatoes and potatoes, save strawberries from weevils, and also drive away onion flies, cutworms and cabbage whites.
Marigolds protect flax, clover and wheat from fusarium.
To improve the soil in the area and scare off mole crickets in the meantime, before plowing the ground, you can scatter finely chopped marigold stems.
Marigold infusion protects peas, cabbage, apple trees, cherries, plums, currants and gooseberries from aphids
To prepare the infusion, take the above-ground part of the plants, chop them with pruning shears and fill the bucket halfway. Fill with warm (about 40-60 degrees) water and leave for two days. Then filter, add 40 g of liquid soap (so that the infusion does not drain, but remains on the plants) and pour the mixture into the sprayer. Treatment rates: for the garden - 2 liters per 10 square meters; for one bush or tree under 6 years old - also 2 liters; for fruit trees and shrubs older than 6 years - 6-8 liters.
Nasturtium will help against whitefly and whitefly
. Flowers can be planted next to tomatoes and cabbage. Nasturtium is also useful for fruit trees. Plant two or three bushes under a cherry, peach or apple tree. In autumn, flowers can be crushed and buried in the tree trunk. This is an excellent green fertilizer.
Chamomile-pyrethrium
called a natural insecticide. If planted next to cabbage, the vegetables will not be afraid of cabbage cutworm and white moth caterpillars, as well as aphids. Try planting pyrethrum near the trunks of an apple tree in the spring. The apple tree will be reliably protected from the codling moth, aphids and other pests. Phlox's proximity to chamomile will save you from nematodes. Rodents also do not like pyrethrum.
There is another beautiful defender of vegetables. The Colorado potato beetle, for example, cannot tolerate the smell of calendula.
Experienced gardeners advise planting calendula next to potatoes. Some people do this - in the spring they plant a row of potatoes, a row of calendula seeds, and so on. If potatoes are already planted, plant calendula somewhere nearby. In the fall, plow it into the ground where you plan to plant potatoes next year. Calendula is a good green manure. The flower will also save asters from fusarium, and rose bushes from nematodes.
Lavender
will protect the area from ants and aphids, and the house from real moths.
You shouldn’t completely abandon chemical means of protection, but try to focus on natural protectors.
Cabbage (white cabbage and broccoli)
Crops such as bush beans and celery have a beneficial effect on cabbage. The latter, for example, protects cabbage from flea beetles.
Cabbage and celery make great neighbors
Also, white cabbage and broccoli get along well with peas, cucumbers, carrots, spinach, tomatoes, beets, and chicory. Dill has a positive effect: planted between rows, it improves the taste of cabbage and repels aphids and caterpillars. And aromatic herbs save this crop from cabbage butterflies: thyme, sage, rosemary, mint, chamomile.
Cabbage does not go well with crops such as parsley, garlic, grapes, turnips and tansy.
The best neighbors for this crop are spinach, beans, and bush beans. The latter, in particular, enriches the soil with nitrogen and repels the Colorado potato beetle.
If this striped pest does not allow the potatoes to develop well in your area, plant catnip, coriander, nasturtium, tansy or marigolds nearby.
Potatoes are not a picky crop when choosing neighbors. Therefore, it is easier to list which plants it is not recommended to plant with. These are quinoa, cucumbers, pumpkin, asparagus, sunflowers and celery.
Garden strawberries (strawberries) are recommended to be planted next to bush beans, spinach and parsley. It can also be combined with garlic, onions, radishes, radishes, beets, dill, and lettuce.
Related article: Thrips, aphids, leafhoppers and spider mites on potatoes
But you shouldn't place strawberries next to horseradish.
Onions go perfectly with carrots. These crops protect each other from pests: carrots repel the onion fly, and onions repel the carrot fly. Due to its compact shape, onions thrive in the inter-rows of main crops such as beets, cucumbers, strawberries, spinach, and radishes.
It is recommended to plant onions and carrots side by side not only because these crops have a beneficial effect on each other. And they are compactly located in the garden bed
Some herbs have a positive effect on onions: thyme, chamomile (no more than one plant per meter of bed).
But proximity to beans, asparagus, watercress, peas and beans is contraindicated for it.
This crop tolerates the proximity of many plants well, but develops best next to onions, peas and spinach. And herbs such as dill, anise, celery and parsley cannot be planted nearby. They act in a depressing way.
Cucumbers go well with bush and climbing beans, celery, beets, lettuce, cabbage, garlic, onions, spinach, fennel, dill, basil, and marjoram. But it is best to plant beans around a bed of cucumbers: they help the plants develop faster.
It is not recommended to plant cucumbers next to potatoes and pumpkins.
But there are conflicting opinions about tomatoes; some gardeners doubt the fruitfulness of such a neighborhood.
Pepper feels great next to eggplant, kohlrabi, tomatoes, basil and thyme.
And hostile plants are fennel, beans and beets.
Plant compatibility.
Neighbors for carrots.
What can I plant carrots next to? The optimal neighborhood for carrots will be:
And here is a negative neighborhood for carrots:
Optimal conditions for pepper.
What vegetables are recommended to plant peppers next to? Pepper grows well next to:
Do not plant peppers near beans.
Potatoes and their neighbors.
What can I plant potatoes next to? Potatoes will bring a good harvest if planted next to:
You can’t plant potatoes if they grow nearby:
Neighbors of tomatoes.
It is recommended to grow tomatoes next to:
- asparagus;
- basil;
- beans;
- cucumbers;
- carrots;
- celery;
- dill;
- salad;
- melons;
- onions;
- parsley;
- pepper;
- radishes;
- spinach;
- thyme;
Do not place tomato beds and any types of cabbage, potatoes and corn next to each other.
Neighbors for asparagus.
What can you plant asparagus next to? An excellent neighborhood for asparagus would be:
What should you not plant asparagus with?
Fortunately, there are no plants that negatively affect the growth of asparagus.
Neighbors for beans.
What can you plant beans next to? Optimal neighborhood for beans:
- broccoli;
- corn;
- cabbage;
- carrot;
- celery;
- cauliflower;
- cucumbers;
- eggplant;
- peas;
- potato;
- radish;
- zucchini;
- strawberry;
- tomatoes.
Undesirable neighborhood for beans:
Neighbors in the beet bed.
What can you plant beets next to? Beets will give a greater yield next to:
Undesirable neighbors in the beet bed:
Broccoli and neighbors in the garden.
What should I plant broccoli next to? Optimal neighborhood for broccoli:
Unwanted neighbors for broccoli:
- cabbage;
- cauliflower;
- salad;
- green beans;
- tomatoes.
Brussels sprouts bed neighbors.
What is the best place to plant Brussels sprouts next to? Best neighbors:
Brussels sprouts have one unwanted neighbor: tomatoes.
Neighbors for cabbage.
What can I plant cabbage next to?
Undesirable neighbors in the cabbage bed:
Cauliflower and its neighbors.
It is recommended to plant cauliflower next to the following plants:
Bad neighbors for cauliflower:
Companions of celery.
Celery has no unwanted neighbors. But it’s better to grow it next to:
- beans;
- broccoli;
- cabbage;
- cauliflower;
- leeks;
- spinach;
- tomatoes.
What beds to make next to cucumbers?
It is recommended to plant cucumbers next to:
- beans;
- broccoli;
- corn;
- cabbage;
- cauliflower;
- sunflowers;
- peas;
- salad;
- radish.
Cucumbers should not be planted next to herbs, melons and potatoes.
Corn and its neighborhood.
Where is it recommended to plant corn next? Optimal neighbors:
But you can’t plant corn next to tomato beds!
Recommendations for eggplants.
Eggplants do not have unwanted neighbors in the garden, but they feel great next to:
Lettuce.
Optimal bed companions for lettuce:
- asparagus;
- beet;
- cabbage;
- Brussels sprouts;
- carrot;
- corn;
- cucumbers;
- onion;
- peas;
- eggplant;
- potato;
- radish;
- spinach;
- strawberry;
- sunflowers;
- tomatoes.
But broccoli is the worst companion for lettuce.
What should I plant onions next to?
The best neighborhood for onions will be:
Peas and their neighbors in the garden.
What vegetables should I place next to the pea beds? Peas feel great next to:
- beans;
- carrots;
- corn;
- cucumbers;
- eggplants;
- salad;
- melons;
- parsnip;
- potatoes;
- radishes;
- spinach;
- turnip.
Do not plant peas near beds with onions and garlic.
Useful weeds in the garden.
Sometimes plants can only be beneficial to each other at a certain stage of growth. This is true for some weeds as well. How can weeds in the garden be useful? Some weeds pull nutrients from deeper layers of soil and bring them to the surface. As weeds die and decompose, nutrients become available at the soil surface for shallow-rooted vegetables. This is why some vegetables grow very well next to nettles.
How to solve the problem if there is only one greenhouse
If there is only one greenhouse, but many crops are planned to be planted, then sometimes cucumbers cannot avoid an unfavorable neighborhood. Therefore, you can plant cucumbers with different plants, but only by making special partitions so that they do not touch each other. By selecting zones and creating partitions, you will grow many different crops in one greenhouse that will not interfere with each other at all.
There is also this option: you can make multi-story beds, and also hang pots with a variety of seedlings at the top of the greenhouse. Thus, they will not touch the cucumbers at all.
This approach is very good if there is a lot of space in the greenhouse for your imagination to run wild. Various structures are being built to highlight zones, but such that they do not block light and air flow. They should be light, not bulky. You should also create a sufficient number of vents in the greenhouse so that all plants receive air during ventilation. It is better to plant the cucumbers further away from these windows, and be able to cover them during this procedure. After all, they are so afraid of drafts.
If you don’t know what to plant in the greenhouse along with cucumbers, then you need to study the literature about gardening, about care, about plants. Choosing the right neighbor will help you get an excellent harvest of all crops.
For beginning gardeners, one of the most exciting questions is: “What should I plant with in a greenhouse?” What's wrong with that? For those who have not yet encountered gardening, this question seems stupid. In fact, this is not so: like flowers in a bouquet, vegetables can be “friends” or “not friends” with each other, so if you want a rich harvest, you need to take into account their compatibility.
Conditions for growing peas
Peas are the most common vegetable crop of the legume family. Its peculiarity is its fairly high protein content, in terms of this indicator it is equivalent to meat products. True, the human body absorbs vegetable protein much faster and better. In addition, each pea contains a huge amount of useful minerals and vitamins.
To cultivate the crop, you need to choose a well-lit place in your garden away from drafts. Plots of land near a fence or wall of a building are perfect for growing the plant. Legumes tolerate partial shade well, but to obtain higher yields, their stems and leaves must be illuminated from all sides.
To achieve a good pea harvest, you must follow several rules for growing it:
- plant seed material in well-moistened soil;
- water promptly and abundantly;
- choose slightly alkaline soil for planting;
- take into account the compatibility of peas with other crops.
Pea cultivation
Peculiarities
Planting potatoes, like any other plant, is considered hard work. Especially when it is necessary to combine various vegetables in neighboring beds. The science of allelopathy shows that the interaction of neighboring plants can beneficially or negatively affect growth and yield. Above-ground and underground parts of vegetable crops fill the soil with minerals and trace elements that affect the composition and taste of the vegetable. The question arises what vegetables and plants can be sown nearby.
Several factors need to be taken into account:
- how well the beds are illuminated, whether they are located in the open sun or whether there is shade at the planting site;
- what is the composition of the soil (clayey soil, sandstone or black soil);
- what is the acidity of the soil (neutral or alkaline);
- Is it necessary to regularly fertilize plants?
- how much watering different crops require.
Related article: Causes and methods of preventing potato late blight
Based on these parameters, you can safely select “partners” for potatoes in the garden.
Neighborhood with vegetable crops
There is no better company for garden strawberries than root parsley. Planted between rows, it will repel slugs and snails. Similarly, proximity to carrots has a beneficial effect on the growth of strawberries. However, you should not mix carrots with parsley - it is better to plant one thing for the garden. Separately, it is worth noting the benefits of growing strawberries together with onions and garlic. These plants are natural protectors. This is how onions repel pests and help increase yield and propagate berry bushes. In addition, together with onions, you can forget about the problem of rotting bushes. Garlic prevents the manifestation of fungal diseases: late blight, white and gray rot and others.
Legumes will be good neighbors for garden strawberries. Plants help loosen the soil and saturate it with nitrogen
But when choosing such a companion in the garden, you need to pay attention to the fact that weeds grow well in close proximity to legumes, and the plants will also acidify the soil. If you decide to plant strawberries and legumes, prepare for more frequent weeding and fertilizing with alkaline fertilizers
What to plant nearby in open ground
In addition to the predecessors, the gardener must know the list of crops that can be planted near the cucumber bed. A well-chosen neighborhood not only does not prevent cultures from fully developing, but also helps each other grow. These can be root vegetables, greens and other various vegetables.
Corn
Surprisingly, corn helps increase the yield of cucumbers. Growing up, it becomes a protective wall for the vegetable. This is beneficial for cucumbers, since they are considered a heat-loving crop.
The proximity of cucumbers to corn will save space on the plot of land. The stems of the plantings serve as excellent support for the vegetable. Branches of greenery curl over them, cluttering up the space on the ground.
Beans
Planting this vegetable near cucumbers occurs in a different way. Several bushes are planted around the perimeter of the cucumber bed. A representative of legumes saturates the soil with nitrogen. Thanks to this, the yield of green vegetables increases.
Green beans
Has the same properties as regular beans. It is planted around a cucumber bed, making a hedge. Other types of beans are also used for this purpose, but it has been proven that asparagus beans are the best of all members of the family.
Cabbage
Among a large number of vegetables, cucumbers do not mind the cabbage neighborhood. Moreover, it can be any type. Greens do not need anything if white cabbage, broccoli or kohlrabi grows nearby.
Salad
Lettuce bushes are often planted near cucumbers. Greens go well with cucumbers. They grow simultaneously without harming each other. Lettuce stimulates the growth of the cucumber root system.
Spinach
In addition to lettuce, gardeners also recommend planting spinach. Greens can protect the earth from overheating, which greens do not like so much. With such protection, the vegetable develops calmly in hot climates.
Parsley
In this case, it is more likely to plant cucumbers near parsley, especially if the plant is perennial. The crops easily share the garden bed without harming each other. Parsley can also be root parsley.
Garlic or onion
A person who does not know what is best to plant cucumbers in a nearby garden makes a choice between onions and garlic. They disembark together. Onions and garlic prevent the development of bacterial diseases.
Garlic and onion plantings practically do not help cucumbers in development and vice versa. Their main task is to drive away pests. Gardeners allow these crops to be located nearby in one place.
Dill
The proximity of cucumber and dill ends in great luck for the gardener. The greens continue the fruiting period, and people enjoy the greens much longer. Dill attracts ladybugs, which kill the pesky pests.
Radish
Used as a spider mite repeller. The essential oils that radish exudes are so fragrant that the insect cannot tolerate them. If a root crop is planted near the cucumbers, over time the tick will have to leave the area.
Calendula
Few people know that unpretentious and at the same time bright flowers are good neighbors of cucumbers. Their color and scent attract many pollinators. Thus, more ovaries appear on the branches, and the yield increases.
Peas
The cucumber feeds on nitrogen, as it makes the vines strong and healthy. It is peas and other legumes that saturate the soil with this vital element. The close proximity of peas and cucumbers will save space on the site.
Watermelon
Cucumbers and watermelons love warmth, so they easily become neighbors during growth. To make it convenient for both crops, cucumber branches are placed along the supports, and watermelon lashes are placed along the ground. But plants can compete for nutrition, so it is recommended to saturate the soil with additional substances.
melon
The principle of planting is the same as with watermelons. Such a distribution of the lashes will prevent them from getting tangled. From such a neighborhood, space on the site will be saved without damage to both crops.