The area in summer cottages allocated for vegetable gardens is usually limited. Therefore, amateur vegetable growers use every opportunity to obtain the maximum yield from a small number of beds. Growing different crops together is one of them. It’s worth figuring out what can be planted next to cucumbers and how to care for joint plantings.
Cucumbers are planted in open ground beds, in film shelters, polycarbonate greenhouses, in containers (barrels, buckets, bags) and even in apartments on the windowsill. Depending on the place where the crop is grown, the most suitable varieties are selected. Each variety has its own agrotechnical characteristics, but to obtain a bountiful harvest, the basic requirements for cucumber care must be met.
What is plant compatibility?
Plant compatibility is the harmony between crops planted next to each other, and it is achieved at the chemical level. The fact is that certain plants release various organic substances into the environment (air, soil): colins, phytoncides, etc. These substances can influence the growth and development of other plants, both negatively and positively. A broader and more scientific name for this phenomenon is allelopathy.
Each plant has its own strength of allelopathic activity. For example, corn and potatoes emit few volatile substances, so these crops do not poison the soil. At the same time, this makes them almost defenseless against weeds.
Let's look at the main groups of substances responsible for allelopathy:
Colin
Colins are released by plants and affect other plants, suppressing their vital functions. For example, such a colorless gas as ethylene (emitted, for example, by apple fruits) inhibits the germination of seeds, the growth and development of sprouts, and also leads to yellowing and premature falling of leaves, and even the death of neighboring plants.
This is only relevant when colins are released in high concentrations. Microdoses, on the contrary, stimulate the growth of neighboring plants. But too high a concentration of colins is dangerous even for the plants that secrete them.
It has been noticed that when located close to specimens that excessively produce colin, neighboring plants are affected: they turn out to be lethargic, stunted, with a thickened stem, short roots, and prematurely yellowed or fallen leaves. But with distance from the source of negative influence, the opposite effect is observed - growth stimulation.
In addition, the released substances accumulate in the soil and gradually create an allelopathic environment, which favorably affects some plants and inhibits others. That’s why it’s so important to observe crop rotation.
Phytoncides
Phytoncides have a detrimental effect on bacteria, protozoa and fungi. Thus, substances secreted by linden and birch trees suppress the development of harmful microorganisms and improve the growth of neighboring plants. Therefore, it is recommended to plant these types of trees along the borders of the garden plot. This will help protect the orchard from fungal diseases carried by the wind from diseased trees of neighbors in the dacha area.
As for garden plants, phytoncides of garlic, onion and horseradish kill many types of pathogenic microorganisms and fungi, and also repel insects. For example, the proximity of onions is beneficial for lettuce, because its phytoncides repel aphids.
Adviсe
Growing vegetables together is sometimes necessary to designate places to plant seeds that take a long time to germinate. For example, in a bed of carrots, rows of carrots can be distinguished by using lettuce seeds planted along the edges of each row.
The best neighbor for all garden crops is cilantro or coriander. They only prevent fennel from growing and forming.
On a note! Cilantro is the only plant that can control fennel.
Carrots simply need to be planted next to onions. It turns out that carrots can repel pests that destroy onions. Conversely, onions repel carrot pests. In order for carrots to develop well, they need to be sown between rows of radishes. After all, radishes ripen before they begin to form carrot roots. This condition is excellent for growing root parsley.
Black currants planted on a personal plot will get rid of the invasion of mice and other rodents.
Under no circumstances should you use seeds collected from mixed beds for sowing.
Cucumbers will not produce a good harvest if they are planted in the same bed as basil.
You can plant quite a lot of different cultivated plants next to peas. But which one contributes to better plant growth is up to the gardener himself to decide. It is clear from the article that peas are well compatible with other crops.
5 3 votes
Article rating
Why is it important to follow the rules of planting compatibility?
Some crops release beneficial substances for neighbors growing nearby, while others release harmful compounds and deplete the soil, preventing another crop that grows nearby from fully developing. Therefore, it is so important to follow the rules of planting compatibility.
The correct selection of companion plants allows you to:
- increase the amount of harvest;
Growing tomatoes and basil about 25cm apart can increase tomato yield by about 20%. And cumin, planted next to strawberries, helps to grow faster and more sweet berries.
- avoid soil fatigue;
- protect against diseases and increase the immunity of neighboring plants;
For example, horseradish increases potato disease resistance, and garlic is more effective than fungicides against potato late blight.
- prevent the growth of unwanted weeds;
- improve the taste and appearance of fruits;
Radishes grown with lettuce taste better. And peas and beans give spinach a natural color.
- increase the resistance of perennial plants to frost;
- control pests without the use of chemicals;
Personal experience has shown that peas planted next to potatoes reduce the number of Colorado potato beetles.
- Use the garden area economically.
However, even with the right surroundings, it will not be possible to grow a strong and healthy plant without following agricultural techniques. When planting, you should take everything into account:
- plant compatibility and crop rotation;
- need for moisture and sun (some plants are shade-tolerant, others are light-loving);
- the composition of the soil and the effect of applied fertilizers on it (some of them acidify the soil, others alkalize).
It is advisable to select crops with the same requirements for growing conditions. But when planting a crop that prefers acidic soil next to a crop that needs neutral soil, a borderline pH value should be created.
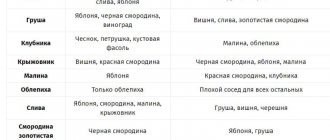
What vegetables grow well in one bed?
I offer you a short table of vegetable compatibility. More detailed information is provided later in the article.
Other useful neighbors for vegetables
In addition to the neighborhood of one vegetable crop with another, it is good to consider other possible neighborhoods - vegetables and flowers, vegetables and herbs. Such combinations in garden beds are not only beautiful, but also useful.
Flowers next to vegetables.
Good advice: plant a few marigolds in the tomato bed; they repel pests. You can even decorate the entire perimeter of the garden with marigolds - this will help keep pests at a distance.
Some flowers act as pest traps, luring insects to them. Nasturtiums, for example, are very popular with aphids. These pests will prefer to feast on nasturtium and will not pay attention to nearby vegetables.
Vegetables and herbs.
Planting herbs nearby will give your vegetables a more refined taste. They also repel harmful insects. Rosemary repels beetles that attack beans. Thyme repels cabbage pests. Onions and garlic repel aphids. Oregano, like marigolds, is a good all-purpose barrier against most insect pests.
When deciding which vegetables to plant nearby in the garden, you need to be guided not only by scientific data, but also by common sense. Lettuce, radishes and other fast-growing plants can be planted between melons or pumpkins. Lettuce and radishes will ripen before the pumpkin grows. Shade-loving green leafy vegetables such as spinach and chard are grown in the shade of corn. Sunflowers also grow well next to corn because their roots occupy different levels in the soil and do not compete for water and nutrients.
Well, let's move from the particular to the whole, and consider the successful and unsuccessful neighbors for each vegetable.
Vegetable compatibility table
Below is a table of popular garden plants with exact compatibility between crops:
| Plant name | What crops are compatible with? | Incompatible plants |
| Watermelon | Potato | Horseradish, cabbage, tomatoes |
| Eggplant | Beans, tomatoes, lettuce, peppers, watermelon | Cucumbers, garlic, onions |
| Peas | Parsley, kohlrabi, spinach, lettuce, radish, radish, cucumbers, carrots, corn, watercress, eggplant, potatoes | Garlic, beans, celery, zucchini, onion, fennel, tomatoes |
| Melon | Radish, tomatoes, beans, corn | Cabbage, cucumbers, potatoes |
| White cabbage | Spinach, corn, beets, dill, celery, onions, potatoes | Grapes, sweet peppers, beans |
| Potato | Coriander, cauliflower, broccoli, kohlrabi, red cabbage, dill, horseradish, onion, garlic, spinach, watermelon, corn, radish, beans, beans and peas | Apple tree, raspberries, cucumbers, pumpkin, tomatoes, fennel, sorrel, sunflowers, cherries, beets |
| Corn | Beans, melons and watermelons, peas, zucchini, pumpkins, cucumbers, potatoes, cabbage, lettuce, beans | Onions, celery, fennel, beets |
| Bulb onions | Garlic, Brussels sprouts, broccoli, kohlrabi, beets, carrots, celery, spinach, strawberries, eggplant, cucumbers, tomatoes | Beans, beans, peas |
| Carrot | Onions, garlic, onions, lettuce, parsley, spinach, marjoram, tomatoes, peas, beans | Fennel, horseradish, celery, chard, parsley, dill, beets |
| Cucumber | Peas, beans, beans, lettuce, celery, dill, carrots, beets, radishes, cabbage, kohlrabi, onions, garlic, sunflowers, corn | Potatoes and tomatoes, radishes |
| Sweet pepper | Garlic, basil, onion, coriander, lettuce, eggplant | Hot pepper, cabbage, beans |
| Tomatoes | Garlic, radishes, carrots, onions, basil, spinach, parsley, cabbage | Fennel, dill, kohlrabi, peas, beets, potatoes |
| Parsley | Zucchini, basil, asparagus, watercress, dill, garlic, onion, peas and pumpkin, tomatoes | Sorrel and lettuce |
| Radish | Lettuce, watercress, spinach, dill, basil, carrots, beets, tomatoes, pumpkin, parsley, onions and garlic, beans | Chard, cucumbers, grapes |
| Leaf lettuce | Kohlrabi, cabbage, beets, rhubarb, cucumbers, radishes, peas, onions, corn | Beans, parsley, pumpkin and tomatoes |
| Beet | Onions, cabbage, lettuce, zucchini, lettuce, radishes and radishes, garlic, cucumbers | Fennel, potatoes, tomatoes, mustard, corn |
| Pumpkin | Corn, onion, lettuce, radish, beans | Potatoes and cabbage |
| Dill | Radishes, turnips, beets, cabbage, zucchini, garlic, cucumbers, beans, peas, fennel | Basil and carrots, tomatoes |
| Beans | Celery, melon, cabbage, radishes, strawberries and wild strawberries, carrots, beets, corn | Fennel, all types of onions, pumpkin, garlic, pepper |
| Garlic | Currants, cucumbers, beets, strawberries and wild strawberries, lettuce, parsley, carrots, tomatoes, onions | Beans, eggplants, potatoes, peas, cabbage, beans, grapes |
| Spinach | Cucumbers, strawberries, lettuce, cabbage, radishes, turnips, radishes, carrots | Fennel, tomatoes, beans and pumpkin |
| Sorrel | Melissa, strawberries, mint, asparagus, cabbage, radish, carrots and potatoes | Beans, peas, beans, basil, parsley and tomatoes |
Plant compatibility table in the garden
What to plant with in a greenhouse
Greenhouse conditions differ significantly from site to site. Planting homemade cucumbers and tomatoes together in the same greenhouse is a bad idea. Such neighbors get along together, but for tomatoes you should choose less humid places. Frequent ventilation and dry air lead to a decrease in the quality of plants.
If it is not possible to organize 2 greenhouses, the lashes should be placed in the corner farthest from the exit. Tomatoes can tolerate high humidity if they are located in places with good air circulation.
The size of the greenhouse usually does not allow for planting corn or sunflowers, so most often the following vegetables are planted along with cucumbers:
- turnip;
- Chinese cabbage;
- greenery;
- mustard;
- beans.
The best neighbors in greenhouses for cucumber bushes are bell peppers or eggplants. However, it is not recommended to plant all 3 plants together: peppers and eggplants do not get along well with each other.
Bell peppers love stuffy and warm places and do not tolerate drafts well, however, unlike cucumbers, peppers need more light.
You can also plant melons and watermelons, but these crops are more heat-loving than cucumbers, so they should be planted in the farthest corner from the entrance.
Compatibility table for fruit trees and shrubs
Compatibility in the garden is also important. If trees and shrubs are planted in a chaotic manner, without respecting the proximity, then some plants may get sick and even die. For example, a walnut planted in a garden negatively affects all other plants. It inhibits their growth and has a bad effect on the taste of the fruit.
To avoid incompatibility, check out what you can and cannot plant seedlings with:
- Cherry. Grows well next to cherries, plums and grapes. Bad neighbors are pear trees, some apple trees and currants. Also, the tree does not grow well with garden representatives: strawberries, tomatoes and peppers. Nightshades can infect cherries with wilt.
- Pear. Other varieties of pears suit her well as neighbors. Comfortable with rowan. An apple tree is not suitable (although the proximity of a pear tree itself is favorable).
- Currant. Its two types, red and black, are not suitable for planting together next to each other. The latter loves well-moistened soil and shady areas. Red prefers drier soil and warm sunny areas. Currants and gooseberries get along well, but it is not recommended to plant them next to each other due to the same type of diseases.
- Blackberry. Grows well with raspberries (you can carry out the same treatment and fertilize the soil). Plants do not cross-pollinate each other. Blackberries and gooseberries go together. And currants and fruit trees are incompatible neighbors.
These were the most popular combinations in which gardeners often make mistakes. We have provided more examples in the table below.
| Fruit trees and shrubs | Favorable landing compatibility | Not suitable for the neighborhood |
| Apricot | Any varieties of apricot, cherry plum, pear, peach, plum, cherry, dogwood, blueberry, hazelnut | Apple and cherry |
| Quince | Apple, pear, hawthorn | Viburnum, bird cherry |
| Cherry plum | All varieties of cherry plum, mulberry, blueberry, apple, cherry plum, cherry, peach, sweet cherry, hazelnut, dogwood | Only pear |
| Hawthorn | Cherries and cherries | Apple tree |
| Grape | Pear, cherry and sweet cherry | Apple and pear tree creates shadow |
| Blueberry | Cranberries, currants, raspberries | Apple tree, sea buckthorn, apricots, pear |
| Pear | Cherry, sweet cherry, cherry plum, blueberry, hazelnut, dogwood, rowan | Peach, plum, apple, apricot |
| Honeysuckle | Gooseberry, plum, currant, grape, sweet cherry, quince, hawthorn, rose hip, juniper | Raspberry, apple tree, blueberry, pear, apricot, blackberry, bird cherry, rowan, walnut |
| Irga | Raspberries, black currants, gooseberries | Apple tree, walnut |
| Kalina | Lilac, rowan | Apple tree, chokeberry, chokeberry, spruce |
| Dogwood | Cherry, apple tree, sweet cherry, plum, peach, blueberry, hazelnut | Pear, sea buckthorn |
| Raspberries | Apple, pear, plum, blackberry, red elderberry, rowan | Strawberries, grapes, currants, sea buckthorn, elderberry |
| Sea buckthorn | All varieties of sea buckthorn of the opposite sex (for pollination) | Currants, raspberries and more, since sea buckthorn greatly oppresses all trees and shrubs |
| Peach | Does not like proximity to other cultures | Cherry, cherry, apricot, pear, apple, walnut |
| Rowan | Viburnum, pear | Apple tree, cherry |
| Plum | Sweet cherry, sour cherry, black currant | Pear and apple tree, apricot, walnut trees |
| Red currants | Apple, peach, cherry, rosehip | Black currant, honeysuckle, raspberry, walnut |
| Black currant | Golden currant, plum | Hazel |
| White currant | Cherry, red currant | Raspberries, black currants |
| Golden currant | Black currant, plum, honeysuckle | Hazel |
| Mulberry (mulberry) | Only other mulberry varieties are favorable | Oppresses all trees and shrubs |
| Hazelnut | Raspberry, old apple tree, hazelnut | Affects almost all trees and shrubs |
| Cherries | All varieties of cherries, cherry, blueberry, dogwood, sea buckthorn | Plum, pear, cherry plum, apple, peach and apricot |
| Apple tree | Raspberries, grapes, other apple varieties, plums, honeysuckle | Cherry, peach, cherry plum, elderberry, rowan, walnut |
What should you not plant cucumbers with?
Among the unfavorable neighbors is zucchini. Planting this vegetable near a cucumber will result in cross-pollination, since these plants belong to the same species. This will not deteriorate the taste of the greens, but the seed material will become unsuitable for subsequent cultivation of the variety.
Also, the low compatibility of domestic cucumbers and zucchini is explained by the strong weaving of the zucchini, with which it clogs the cucumber bushes. As a result, the plants do not receive enough light and die.
Fragrant herbs are incompatible with cucumbers. Basil, cilantro and oregano do not grow well near bushes. Also, the greens themselves acquire a specific taste and smell.
It is especially not recommended to plant fragrant herbs in the same greenhouse with other crops. In a confined space, such a neighborhood can ruin the harvest.
Cucumbers also have poor compatibility with potatoes. This vegetable consumes a lot of nitrogen, which is why cucumber bushes grow slowly and produce a small harvest.
How to properly organize joint plantings?
Joint planting is when a garden bed is taken and many different crops are planted on it, which complement each other. To do this, they first draw up a plan indicating the selected companion plants.
When planning such a multi-planting, you can not only successfully arrange the plants, but also create a beautiful composition.
What recommendations should be followed when assembling a joint bed:
- Make the width of the bed generous. It must be at least one meter. Length – 3-4 m.
- Take crop rotation into account. Plant plants that previously (last season) did not grow on a specific piece of land.
- Alternate plants with different root systems in the garden bed (underdeveloped root - large root).
- Place earlier ripening crops along the edges of the bed (most often these include greens, herbs, strawberries).
- Pay attention to plant care requirements. All specimens planted nearby should be equally moistened, have similar lighting requirements and be suitable for the specific acidic environment of the soil.
Choosing the right predecessors
It is very important to understand not only what to plant cucumbers next to, but also what crops are best to plant them in the garden after.
- All legumes . They saturate the soil with nitrogen, which has a positive effect on the growth of cucumbers. The exception is beans, as they are susceptible to white rot, the spores of which remain in the soil and can affect cucumbers the following year.
- Plants of the nightshade family . Most often, cucumbers are planted after potatoes, tomatoes or peppers and this is a good option. All these plants contribute to the accumulation of potassium in the soil, which is very important during the formation and ripening of cucumbers.
- Onion and garlic . They are good predecessors due to the fact that they release phytoncides into the soil and heal it, killing many pathogenic microorganisms.
- Root vegetables . Another option that makes cucumbers feel great. Such crops usually take moisture and nutrition from deeper layers of soil. The only exception is carrots; they are undesirable as a predecessor for the same reason as beans - the plant is often affected by white rot.
- All types of cabbage . It doesn't matter which variety was grown the previous year, they all work well.
Examples of successful joint plantings
To correctly create mixed plantings, familiarize yourself with the compatibility of certain crops and pay attention to illustrative examples and sowing patterns.
There are 4 ways to plant plants together:
- Simple. Several crops that are similar in agricultural technology are being planted. Equal in terms of ripening and care.
- Alternate. Plants are not planted together; the order of timing is simply taken into account. Two different crops are grown in one place at different times.
- Leading. Even before the first crop is harvested, a new crop is planted in place, gradually replacing the first.
- Intensive. Together they grow crops that have a positive effect on each other: protect against pests, improve taste and volume, and strengthen the immune system.
What options are successfully used by gardeners:
- Eggplants next to peppers. Good neighbors in the garden. The crops have similar agricultural techniques. But it’s better to plant sweet peppers, otherwise they can impart bitterness to the eggplants.
- Pepper next to cucumbers . Favorable combination. Cucumbers are planted in the center of the bed, and peppers along the edges. Most often in a greenhouse.
- Watermelon and melon. Acceptable proximity. Similar agricultural technology. But, due to growth, it is advisable to plant them further away.
- Carrots next to garlic. Such a successful planting will protect carrots from pests and garlic from scab.
- Carrots next to onions. You can plant them side by side and even together. Protect each other from pests.
- Onions next to strawberries. It is permissible to plant together, since the meadow protects the berries from rotting.
- Dill and cucumber. Both cultures feel comfortable.
- Radish and garlic. Protects the “first one” from the cruciferous flea beetle and slightly shades the radishes so that they do not start growing ahead of time.
What crops should not be combined in one garden bed:
- Onion next to garlic. Similar plants can compete with each other. More often than not, garlic is dominant.
- Tomatoes and cucumbers nearby. They are characterized by different agrotechnical conditions. Cucumbers love frequent watering and a lot of sun, they do not tolerate drafts, and tomatoes love fresh air and lack of sun.
- Tomatoes and peppers nearby. The crops are considered nightshades and can easily infect each other if one of them gets sick.
- Zucchini next to pumpkin. They will oppress each other. As a result, both crops will not receive the required amount of nutrients. It is recommended to plant at a distance of at least 4 meters from each other.
Mixed planting schemes:
Features of growing cucumbers
To get a good harvest, you need to know the conditions for keeping vegetables:
- Light, fertile soil with a high content of nutrients. To do this, in the autumn, when preparing the site, it is recommended to add rotted manure at the rate of 6 kg per 1 sq. m. m.
- The optimal temperature for growing in open ground is +22-28°C during the day and +18°C at night. Even minor frosts can cause the death of the plant. Also, sudden temperature changes are contraindicated for the culture. In such conditions, it is at risk of disease, the bushes lag behind in growth, and some of the roots die off.
- When caring for the crop, it is important to organize proper watering, since cucumber is a moisture-loving plant and does not respond well to dry soil. Moisturize in the morning using warm and settled water. Each bush should receive at least 2 liters of liquid.
- The need for regular loosening, since the crop is demanding on soil aeration. Oxygen deficiency causes the death of roots, the development of diseases and the appearance of parasites. Therefore, the soil must be kept loose.
- Mulching is useful. This procedure will retain moisture in the soil and provide the plant with nutrition.
- Tying bushes to a trellis for vertical plant growth. This will contribute to better lighting, protection from infections and parasites, and easier care.
- Choosing good neighbors. To achieve a positive effect from joint plantings, you need to plant crops next to cucumbers that promote their development, have similar requirements for the degree of humidity, soil composition, fertilizing, lighting, and also repel pests.
Joint cultivation is the competition of crops for light, food, water, which is why it is necessary to increase their volume by 2 times.
Is it possible to plant different varieties next to each other?
Most often, it is allowed to plant different varieties of the same crop next to each other. Let's look at a few plants:
- Strawberry. Despite the myth about the prohibition of growing different varieties of this berry in one place, different varieties are allowed in the same bed. There will be no crossings or pollinations between each other.
- Grape. Different varieties on one plantation are very welcome. They cross-pollinate among themselves, improving productivity. Does not affect the taste of the variety. It is only important to plant varieties with the same height, so that one variety does not shade another.
- Raspberries. It can also grow mixed up. The berry will not hatch and will not lose varietal characteristics.
Compatibility of vegetable crops in garden beds: secrets of a rich harvest
One of the secrets of successful gardening is allelopathy - the compatibility of vegetable crops. In other words, this is knowledge about how plants are “friends with each other.” This approach will help not only achieve high yields and healthy crops, but also preserve the natural fertility of the soil, which is an essential condition for any type of farming.
When a summer resident draws up a planting plan for his plot, he needs to know what grew on it in previous seasons
This is very important, since when growing monocultures, one-sided depletion of the soil occurs, which means that not all plants will be able to survive and produce a good harvest.
Crops differ in the time of fruit ripening. This allows you to rationally distribute plantings and make sure that the land does not stand idle. The size of the plants, their need for light and soil moisture, resistance to pests, and requirements for fertility must be taken into account. In the latter case, there are strong consumers of nutrients, and there are weaker ones, which is one of the factors influencing the compatibility of vegetables in the garden.
All of the above criteria lay the foundation for natural farming called “mixed plantings”.
This is a method of organic farming, based on many years of experience of famous gardeners who carefully observe natural processes in the plant world and implement them in their plots. It was this approach - observation and application - that made it possible to accurately determine the compatibility of plants in the garden.
The essence of this method is to plant different vegetable crops on one plot of land in such a way that they have a beneficial effect on each other, creating a good microclimate that provides a rich harvest and natural protection from pests.
People who have been planting vegetable crops using a mixed principle for several years now note the following positive aspects of this approach:
- The yield has increased significantly - 15-20 kilograms per 1 m 2;
- there is no need to thoroughly weed out;
- the time spent on gardening work has been reduced;
- vegetables in the garden practically stopped getting sick, their appearance became healthier;
- it became possible to obtain fresh vegetables before the first frost;
- the taste and aroma qualities of products have improved;
- mixed plantings attract more pollinating bees;
- the plants' need for watering has been reduced;
- the available land area began to be used more rationally;
- soil depletion has stopped with further prospects for its improvement;
- the need for crop rotation disappeared.
When creating the right mixed plantings in the garden, a separate “kingdom” is formed, which has its own laws that do not require unnecessary human intervention. Vegetables and other plants, above- and below-ground insects and other fauna coexist in harmony, maintaining a natural balance, just as in the wild. Of course, a person is not completely removed from work, but his physical labor in the garden is reduced to a minimum.
https://tobehome.ru/ogorod/priyatnoe-sosedstvo-ili-kakie-kultury-mozhno-sazhat-ryadom.htmlhttps://fermoved.ru/tyikva/chto-mozhno-posadit-ryadom.htmlhttps://naogorode. net/sosedstvo-ovoshhej-na-gryadkax-tablica/
What plants should not be planted nearby?
There are some pairs of plants that are not recommended to be planted not only together, but also next to the beds. These include:
- Peas and onions. The second inhibits the development of peas.
- Potatoes and tomatoes. Both are nightshades. They have the same diseases and are susceptible to pests.
- Carrots and dill. There are more rumors than facts, but gardeners claim that grass prevents carrots from growing.
- Cabbage and grapes. The taste of the berries spoils.
What to plant next to zucchini
When choosing a place to plant zucchini, you should take into account not only the proximity of groundwater, soil structure and lighting. Neighbors play a significant role in the development of vegetables. Cultural compatibility is a factor that is not always taken into account. How do plants interfere with each other? The main problem is common diseases and pests. Some vegetables are resistant to infections and insects, while others get sick often. When planting together, problems cannot be avoided with both crops.
It is desirable that the vegetables have similar agricultural technology. It is very convenient to care for crops with the same watering and fertilizing regime. Zucchini loves moisture and needs abundant watering at the root. Vegetables growing nearby should also need water. Who are the friends of zucchini in the garden? Lucky companions:
- beans;
- radish;
- peas;
- nasturtium;
- corn.
Beans are an excellent neighbor to zucchini.
Tomatoes will be good neighbors; the smell of their tops repels many pests. When growing late varieties, the green mass will develop slowly; radishes can be planted between the zucchini, which ripen much earlier. Corn growing on one side of the bed will not affect the light. This area is useful for zucchini; strong stems protect it from the wind. Onions and garlic coexist in the same bed with zucchini. Plants with antibacterial phytoncides prevent the spread of diseases.
Crops in open ground have less influence on each other than in a closed greenhouse. But in the vastness of the garden, phytoncides and alkaloids from leaves and roots can negatively affect companions. Tall plants shade small ones, climbing species are limited by compact bushes. What should you not plant zucchini next to? Potatoes are considered a bad companion. The vegetable requires a large amount of minerals, which it takes away from other crops. Neighborhood with related crops - squash and pumpkins - negatively affects the quality of fruits. It is better not to place the beds close to the cucumbers.
Between the rows of vegetables in vegetable gardens you can see flowers, most often orange marigolds, marigolds and nasturtiums. Plants don't just decorate the landscape, they act as protection against pests. Flowers release special substances into the soil and air that repel insects. Natural repellents without chemicals save the crop from the invasion of aphids, Colorado potato beetles, whiteflies, and caterpillars.
Flowers protect vegetables from pests
Each flower distributes phytoncides that act on a specific pest. Marigolds repel weevils and cabbage whitefly with their bitter aroma. Low bushes of bright colors are often found in joint plantings. In the fall, plants are cut and buried in the soil for disinfection. Nasturtiums protect pumpkin crops from aphids. The Colorado potato beetle is afraid of calendula, so it often appears next to potatoes. Plant phytoncides drive away spider mites and nematodes from cabbage and peppers. Calendula is one of the best green manures; its substances are an effective prevention of fungal diseases.
Garden neighbors that can repel insects
There are plants that effectively fight pests, improving the quality of the crop.
List of pests in the garden and their “repellent”:
- Carrot fly. Onions, sage, garlic and radishes are suitable for destruction.
- Slugs with snails. Wormwood, parsley, mint and sage will help.
- Aphid. It will be brought out by coriander, mint, marigold flowers, mustard, nasturtium and onion.
- Colorado beetle. It helps with sage, thyme, tansy, coriander, capuchin, flax, beans and myta with thyme.
- Nematode. Prevention with chicory, marigolds and marigolds.
- Cabbage caterpillars. Mint, basil, wormwood, nasturtium and tansy.
What can you plant after peas next year?
The beneficial properties of legumes make it possible to use representatives of this family as green manure.
Incorporation of plant tops into the soil:
- helps saturate it with useful substances;
- improves soil structure;
- provides a favorable environment for the development of beneficial microorganisms.
Therefore, the next year after peas, you can plant almost all cultivated plants, except for the legumes themselves.
Advice! If you harvest in the first half of summer, you can sow radishes in an empty place.
Do all plants love proximity to green manure?
Green manures are helper plants that help improve soil quality. They are grown so that in the next cycle, subsequent plantings of crops will be strong and tasty. They protect the soil from weeds and control some diseases and pests.
Green manure can be planted next to plants, but there are nuances in which they are considered bad neighbors. These include:
- Potato. It is not planted next to rye, as green manure attracts wireworms, which are destructive to potatoes.
- Strawberries and tomatoes. Rapeseed is not suitable for their neighborhood, as it breeds nematodes.
- Radishes and cabbage. They do not grow well with mustard. It attracts the cruciferous flea beetle.
Plant compatibility is a delicate process that requires careful study of the topic in order to competently plan your area for planting. This significantly saves space and the environment in terms of reducing (or even eliminating) chemical processing of crops due to their “mutual offset” with each other.
Select suitable crops for planting nearby
Excellent neighbors who get along well with cucumbers . They do not interfere with each other at all, so they can land next to each other without restrictions.
It is important to place the beds so that the peppers or eggplants are in the sun . Both cultures love warmth and do not tolerate shading.
Another good option is that plants release phytoncides into the soil and help reduce disease incidence . At the same time, their root system goes deep, so it does not take moisture from the upper layers of the soil.
If there are moles on the site , you need to plant onions and garlic around the perimeter of the bed . Then they will not be able to penetrate and damage the roots of the cucumbers
An excellent option that grows well with cucumbers . It has deep roots, so it does not take away nutrition and moisture, which is very important.
Serves as a natural trellis for cucumbers, which is also important . And protects plants from the sun during hot periods. At the same time, the sunflower itself tolerates any heat normally.
Many consider this culture to be an ideal neighbor . A very deep root system allows the plant to feed without harming neighboring plantings. It creates shading if necessary during hot periods.
Cucumber vines grow well on corn stalks . Due to this, they are better ventilated, get sick less, and harvesting is much more convenient.
It is categorically not recommended to plant this crop nearby in greenhouses . But in open ground the plant does not have any negative effect and can be located nearby without any problems.
When planting, you need to think about a proper location in advance so that the crops do not shade each other . You should not plant tomatoes in a bed with cucumbers; they are located next to each other, this provides better conditions for the development of both crops
Good neighbors because they consume other nutrients . But most importantly, they saturate the soil with nitrogen and serve as a natural fertilizer after they bear fruit.
You can plant as you like - even between rows . It is important that plants do not block sunlight from each other. This is especially important when growing plants on trellises, when they rise to a considerable height
This is an early crop that has a short growing season. Therefore, most often it is removed even before the seedlings are planted in open ground.
Of course, you shouldn’t plant radishes in the same hole with cucumbers. But you can place it between rows at a close distance, so the soil in the place where the main crop is planted will not be depleted
Another good neighborhood option . This crop has a deep root, which allows it to take moisture from the depths. And during growth, the wrong microelements are used that are especially important for cucumbers.
You can plant both in adjacent beds and interspersing crops . The main thing is to choose the optimal distance so that both crops have enough space for growth and normal development
You can plant marigolds nearby . They attract insects that destroy aphids. Therefore, planting them nearby is very useful.
Calendula attracts pollinating insects . This is especially useful for bee-pollinated varieties.
Nasturtium repels whiteflies. Therefore she is also good as a neighbor
The best neighbors for zucchini
Before describing what to plant zucchini next to, it is worth considering zucchini as a similar crop. For starters, this is a melon plant. Zucchini are vine-like plants, some species of which can literally cover an entire area if their growth is not controlled. Based on this, you need to understand that not every garden plant can grow next to them.
The best neighbors for zucchini
Important!
The best predecessors for zucchini are root vegetables, eggplants, herbs, legumes and nightshades.
The maturation period of the crop also plays an important role in the choice of cohabitants for zucchini. So, in the spaces between the rows you can plant early plants, such as winter garlic or onions, radishes. By the time the zucchini begins to grow as much as possible, they will need to be removed. The following are considered reliable and good neighbors for zucchini:
- clover;
- nasturtium;
- black radish;
- mustard;
- radish;
- garlic;
- onion;
- sunflower;
- corn.
Interesting!
Black radish has long roots, due to which it can obtain nutrients for itself even next to such a “voracious” companion. At the same time, the smell of black radish will repel pests from zucchini. So this is a good option for those who don’t know what to plant zucchini next to.
In addition, many gardeners practice planting near peas. It grows quickly, upwards, enriches the soil and does not interfere with the zucchini. Carrots, like beets, can also be good partners. Of course, zucchini leaves can shade them from the sun, but if you keep the distance, this will not happen
In addition, not only the sun is important for the growth of root crops, but also nutritious soil - these are good neighbors
Difficulties in growing
Even if all the rules for growing are observed, not all gardeners are able to obtain a high-quality and abundant harvest. This happens for several reasons:
- Using low-quality seeds when planting. Low-quality seeds often produce weak bushes with a small number of inflorescences. As a result, the harvest is meager and not so tasty.
- Frequent overwatering causes the root system of plants to rot, as a result the bushes begin to turn yellow, then dry out and die. Yellowing and drying of the aboveground part often occurs due to insufficient moisture, so when growing it is important to adjust watering and make it regular but moderate.
- Poor flowering and fruiting are observed in plants that have not received the required amount of nutrients. With an excess of nitrogen, zucchini intensively grows the root system and above-ground parts and practically does not form inflorescences and ovaries. When applying this fertilizer, the dosage should be strictly observed. A lack of potassium and phosphorus causes fruits to become less juicy and tasty.
- Zucchini, like other vegetables, suffers from gray rot, anthracnose, and powdery mildew. To avoid infection, the bushes should be regularly inspected for damage; if a disease is detected, they are sprayed with copper-containing preparations: Bordeaux mixture or copper sulfate. In case of severe damage, the plants are removed from the site and burned to prevent infection of healthy bushes.
- Spider mites, aphids, and whiteflies love to feast on the succulent foliage and inflorescences of this crop. In the fight against harmful insects, folk remedies are used: garlic, onion, pepper infusions, a solution of soap and ash. In case of severe damage, plants are treated with insecticides: Actellik, Aktara or Fundazol. All treatments are carried out a month before the planned harvest.
- Planting zucchini in the same place for several years in a row is another reason why zucchini does not grow or bear fruit. If you follow the rules of crop rotation, a person can get a good harvest.
Why plants may not be compatible
In the plant world, cooperation and mutual assistance can be found more often than hostility. But leaf and root secretions of some plants can still inhibit the growth of others. Garden crops can also compete for sun, moisture, nutrients in the soil and suppress each other. All this must be taken into account when planting plants together or in adjacent beds.
When planting two crops in the same bed, remember that one of them should be the main one, and the second should be a compactor or accompanying crop. It is planted to thicken and fill gaps. In this photo from the album of FORUMHOUSE user with the nickname Sadovnik, the main crop is carrots, and the accompanying crop is garlic.
The principle of combining crops on a narrow ridge. Garlic (onion) will protect carrots from carrot flies.
How else do plants influence each other?
Tall plants can be planted together with shorter ones - they will create the necessary shade and protect from the wind.
All legumes are capable of accumulating nitrogen in their nodules, which they absorb from the air. Not only do they not take nitrogen from the soil, but they also share their own accumulations with their neighbors, releasing it from the nodules in a form that is easily digestible by other plants.
Substances released from the roots and leaves of some plants can repel pests from others, or throw them off the scent with their strong odor.
The main thing is to confuse the pest, because it follows the smell.
4. The onion fly will be scared away from the onion by the smell of carrots, and the spider mite will think three times before attacking the carrots; onions are planted next to the bark. Cruciferous flea beetles cannot tolerate the smell of garlic, etc.
5. The most delicious, large, non-bitter, pure radish grows in the same bed with bush beans. In such plantings, beans are sown two weeks later than radishes.
What types of zucchini and squash are there?
These vegetables have a variety of species, which makes it possible to choose a plant for your site:
- Albin. Single-stem plants with bush habit. They are famous for their productivity. The fruits are soft and cream-colored.
- Pineapple. Single-stem vegetable crops with large leaves. Vegetables are bright orange in color, the flesh is dense.
- Adaya F1. Zucchini. Early ripening zucchini. They have large leaves and white fruits.
- Aeronaut. Vegetables of bush habit are cylindrical in shape. The harvest is rich green in color, the flesh is dense and juicy.
- Gribovsky. Bush garden crops with pentagonal green leaves. The fruits are light green in color and mid-ripening.
- Yellow-fruited zucchini is a plant with a bush habit. The leaves are large and green. The fruits are cylindrical and yellow in color.
- Zebra. Vegetables with dark leaves, the offspring are light green and dark zebra-shaped. The pulp is juicy and ripe.
- Video clip. A bushy plant with a shortened stem. The leaves are pentagonal, green with white spots. Vegetables are light green, medium soft. This variety is resistant to cold.
- Pharaoh. A variety of zucchini with medium-sized leaves, slight spotting, dark green color.
- Tsukesha. A bush-shaped garden crop with large leaves. The pulp is white, medium thickness. Cylindrical zucchini.
- Anchor. A bush-shaped plant from the pumpkin family, with yellow-green leaves. The variety is distinguished by its high resistance to low temperatures.
Zucchini and cucumbers
Zucchini and cucumbers
Zucchini and cucumbers are melons, and these are completely incompatible crops
They can cross-pollinate if they grow next to each other (which is important for those who collect seeds). In addition, they have similar pests and diseases, so if the cucumbers get sick, the zucchini will also become infected.
But the main problem is that zucchini takes too many nutrients from the ground, leaving nothing for the cucumbers.
Experienced gardeners note that it is possible to plant both of these crops at one dacha, but away from each other. In addition, cucumbers cannot be planted in the same area after zucchini, and zucchini cannot be planted after cucumbers.
Reviews from gardeners
Sofia, Moscow
To increase the yield of cucumbers, you can plant calendula next to them. Flowers attract insects, which also pollinate cucumbers. In addition, calendula is very useful, so it will definitely come in handy.
Source: forum.kozovod.com
Olga, St. Petersburg
The most favorable neighbors for beans are cucumbers. Therefore, it is recommended to plant beans around cucumber beds.
Source: farmerforum.ru
Growing hot peppers
In the northern regions, peppers are usually grown from seeds, and then the seedlings are planted in loosened soil. They are planted in open ground mainly only in warm regions. Pepper loves well-dug soil, fertilizers and high-quality watering. In order for it to grow well and quickly bear fruit, it is pruned, the tops are cut off, and it is fed with organic minerals. In open ground, ripening occurs more slowly and care will be more thorough. Chile prefers warmth.
Hot peppers can reproduce by seeds and shoots. Small shoots are cut off, placed in water, and then after some time they grow roots. Many people grow this crop on their windowsill at home. The seeds can be dried and germinated for next year.
Hot peppers are harvested in mid-summer or autumn. There is no need to wait until it is overripe, but pick the fruits while they are still green. It is perfectly stored in winter, seasonings are made from it, and added to snacks and pickles. Its benefits are to increase immunity and improve metabolism. It contains a lot of vitamin C, A, B, and iron. They say about it that it contains hormones of joy.