You can not only buy a variety of fertilizers for feeding cucumbers in the store, but also prepare them yourself. Such fertilizers have a certain advantage: you select their components at your discretion and prepare them immediately before use.
Summer residents feed their cucumber plantings with whatever they can. The ingredients used are yeast, ash, bread, chicken droppings, onion peels, and various infusions. And, what’s most interesting, such fertilizers work great. Here are some proven recipes.
What types of fertilizers are there for greenhouse cucumbers?
During the entire growth period, cucumbers growing in the greenhouse are provided with fertilizing. In this case, they use not only mineral fertilizers, but also organic matter, as well as folk and store remedies.
Mineral fertilizers
Such fertilizers consist mainly of potassium, nitrogen or phosphorus, and can also be complex. Conventionally, there are 5 groups of mineral fertilizers for cucumbers:
- Nitrogen. Nitrogen is considered the main element necessary for the full growth and development of cucumbers at all stages. Apply:
- ammonium nitrate;
- urea (carbamide).
- Phosphorus. Phosphorus is responsible for the normal development of the root system, so feeding is simply necessary for them. Use:
- phosphate rock;
- superphosphate;
- calcium monohydrogen phosphate (precipitate).
- Potassium. Allows you to increase the plant's immunity. Used for cucumbers:
- potassium chloride;
- potassium salt;
- potassium sulfate.
- Phosphorus-potassium. Combined fertilizers for cucumbers use potassium phosphate.
- Complex fertilizers. Contain two or more useful components. Apply:
- nitroammophoska;
- ammophoska;
- nitrophoska.
Mineral fertilizers for cucumbers are used during the first feeding after planting in the greenhouse, when the seedlings produce 3-4 leaves. One of the most popular mineral compositions is the following:
- 20 g double superphosphate;
- 15-20 g of potassium sulfate;
- 10-15 g of ammonium nitrate.
This amount is enough for 10-15 sprouts.
Other useful mineral compounds for cucumbers include:
- 1 tbsp. l. urea and 60 g of superphosphate per 10 liters of water;
- 10 g of ammonium nitrate, 10 g of potassium salt and 10 g of superphosphate per 10 liters of water;
- 15-20 g of potassium nitrate per 10 liters of water;
- 50 g of urea per 10 liters of water.
Organic
The main types of organic matter used to fertilize cucumbers include:
- Compost. The product is formed as a result of the overheating of organic residues, it is enriched with various nutrients. Mandatory for use when preparing the soil substrate during the formation of beds for cucumbers.
- Manure. Enriched with nitrogen, iron, copper and potassium. In its fresh form, it is used to form warm ridges for cucumbers, and when rotted, it is used for digging.
- Bird droppings. Contains potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen. Makes the soil loose and fertile.
They are used in different ways, the main ways are:
- compost is diluted in water (1:5), 4-5 liters of solution are added per 1 cubic meter. m beds;
- a barrel with a solution of fresh cow manure is kept in a greenhouse to accelerate the growth of ovaries and increase the yield;
- For irrigation, chicken droppings (1:15), manure (1:6), and slurry (1:8) diluted in water are used.
Folk remedies
Proven folk remedies are also used to feed cucumbers in a greenhouse. They activate the development of cucumber vines and stimulate fruiting. Apply:
- Yeast infusion. 100 g of fresh yeast are stirred in 10 liters of warm water, left for 24 hours, after which the starter is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:5 and a liter of fertilizer is applied to each bush. Fertilizing stimulates plant growth, enriches it with amino acids, iron and proteins.
- Ash solution. 100 g of ash are diluted in 10 liters of water, pour 250 ml of the mixture under each bush. Fertilizer enriches the soil with calcium and potassium.
- Infusion of onion peels. For 10 liters of water take 1 glass of onion peels. Bring to a boil, remove from heat, cover with a lid and wrap in a towel. Leave it like this for several hours. Strain and use a watering can to water the above-ground part of the bushes. This procedure will help get rid of yellowing of the leaves and enrich the plants and soil with essential nutrients.
- Infusion of black bread crusts. Pour crusts of black bread into a 10-liter container, filling it 2/3 full. Fill it to the top with water, put a weight on top that will prevent the bread from floating. They insist for a week. After this, dilute another 2 liters of water. Fertilizer is applied once a week during the period of flowering, pouring under the root.
- Nettle infusion. Use fresh nettle tops. It is placed in a large container, filled with water and left for a week. Before watering, dilute the infusion with water in a ratio of 1:7. Water 0.5 liters only under weakened bushes.
Store products
The most popular and effective store-bought products for feeding cucumbers in a greenhouse are:
- "Fontanelle." Mineral fertilizer in granules. Does not contain chlorine, increases the number of ovaries. Can also be used for zucchini, squash and pumpkins. Dilute 50 g per 50 liters of water.
- "Agricola". Available in powder form. Enriched with microelements. Used at the rate of 25 g per 10 liters of water.
- "Vegetable." Mineral powder fertilizer. Contains trace elements and humic acids. Used for feeding cucumbers, pumpkins, squash and zucchini, at the rate of 20 g per 10 liters of water for irrigation.
- "Good Power" Used as protection against diseases. Available in liquid form, use 20 ml per 1.5 liters of water. Do not use on newly planted plants!
Fertilizer recipes for cucumbers
It is necessary to control the temperature regime, soil fertility, acidity level and nutrient supply in open plantings, and in tunnels (greenhouses), and greenhouses. We will tell you in more detail about some of the nuances of growing cucumbers.
Feeding cucumbers in open ground
In cold regions, cucumbers are not planted in open areas. The crop does not like temperature swings, and the productivity of the plant decreases. It is difficult to control nighttime temperature changes in open ridges; additional shelter is required.
Bee-pollinated traditional varieties are most often planted in open ground :
- Elegant;
- fontanel;
- Chinese kite;
- Competitor, etc.
The fruits of these varieties are considered more tasty and juicy, and yields are on average higher.
Types of feeding
Based on the method of administration, there are root and foliar fertilizers for cucumbers.
Root
This type of feeding is practiced when unfavorable conditions occur, for example, low temperatures. There are primary and secondary:
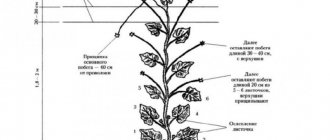
- Primary. Produced after the appearance of the 3rd leaf. For 1 sq. m in 10 liters of water, dissolve 3-8 g of potassium chloride and 10-15 g of superphosphate and add them to the grooves 3-5 cm deep. The grooves are made at a distance of 7 cm from the plant.
- Secondary. It is carried out with the same composition after a month, but the grooves are already made 10-12 cm deep, and retreat from the plant by 10-15 cm.
Foliar
Foliar feeding consists of spraying the leaves with useful compounds. For this use:
- 10 g superphosphate, 1 g boric acid, 30 g potassium nitric, 0.4 g manganese sulphate, 0.1 g zinc sulfate;
- 1 tsp. boric acid, 10-12 crystals of potassium permanganate per 1 liter of water.
Although foliar feeding has a quick effect, it cannot fully provide the plant with everything it needs.
When and how to feed cucumbers?
For abundant fruiting, cucumbers are fed at different stages of development, and the feeding differs from each other.
Feeding seedlings and fertilizing the soil before planting
The stage of growing seedlings is very important; during this period, plants need nitrogen, phosphorus and calcium. To enrich these elements, according to the instructions, use complex preparations designed specifically for seedlings.
Before planting, seedlings are fertilized and the soil is done about a week before the intended planting. The soil in the greenhouse is dug up and added:
- 20-30 g of ammonium nitrate;
- 20-30 g of superphosphate;
- 20 g of potassium sulfate.
After planting the seedlings
After 2 weeks, after transplanting the seedlings to a permanent place of growth, fertilize with the following composition:
- 15 g potassium chloride;
- 15 g urea;
- 20-25 g double superphosphate;
- 15-20 g of potassium sulphide.
Dilute all the ingredients in a bucket of water and inject the solution under the root; this amount is enough for 10-15 seedling bushes.
Watch a video about how to feed cucumbers after planting in the ground, during flowering and fruiting:
Feeding bushes during flowering
About 2 weeks after transplanting the seedlings, the plants begin to bloom. At this time, the next feeding is carried out. Fertilizers of this period are based on organic matter. Apply:
- 500 ml mullein;
- 1 tbsp. l. nitrophoska;
- 100 g wood ash;
- 0.5 g boric acid;
- 0.3 g manganese sulfate;
- 50 g of potassium sulfate.
The components are diluted in a bucket of water.
Mineral substances are also used, for example, ammophoska or azofoska (at the rate of 1 tbsp per 10 liters of water).
Fertilizers during fruiting
During fruiting, cucumbers are fed with one of the following compounds:
- for 10 liters of water 25-30 g of potassium nitrate;
- for 10 liters of water 50 g of urea;
- mullein or ash, diluted in water in a ratio of 1:5.
For 1 sq. m. takes 7-8 liters of composition.
Do I need to fertilize after harvesting?
In the fall, after harvesting, it is also necessary to disinfect and fertilize the soil. To begin with, all plant debris is removed from the greenhouse. Then dilute 300 g of bleach in 10 liters of water and leave for 4 hours. The solution is sprayed on all internal surfaces of the greenhouse and the soil.
After this, rotted manure is scattered over the soil surface. Loose compost or humus soil is also used. Per sq. m area use a bucket of organic matter.
How to feed cucumbers
Cucumbers are easy to grow. The plant is tall, grows quickly, and abundantly increases its vegetative mass. you should not plant seedlings in open ground or greenhouses too early . In the southern regions, the crop is sown directly in open ground (seedless cultivation method).
The tropical vegetable loves moisture, fertile soil, light and warmth . It is grown all over the world, with the leading producing countries being China, Russia and Turkey.
Features of seasonal feeding
The nutritional preferences of cucumbers differ significantly from the needs of other vegetables and root vegetables.
Important: cucumber, unlike tomatoes, is especially sensitive to the presence of organic matter in the soil; the crop grows poorly in poor soils .
Despite the fact that the vegetable produces a voluminous, powerful vegetative mass, it is less demanding of nitrogen nutrition than tomatoes.
Most nitrogen fertilizers are applied at the very beginning of growth. Potassium is a key nutritional element and is added throughout the growing season.
In addition, the crop loves calcium and magnesium ; fertilizing is applied in the same amount as nitrogen fertilizers. In autumn or early spring, during the main filling of the soil for cucumbers, the soil is limed and dolomite flour or ash is added.
Organic matter (rotted manure, compost, bird droppings) is added to the planting holes immediately before planting or sowing. When planting late, green manure, nettles, and weeds are placed in the holes.
How to understand what cucumbers are missing?
Cucumbers react quite quickly to a lack of one or another nutritional element, which affects their appearance. If the plant lags behind in development, the fruits set and develop poorly, the leaves turn yellow, then the cucumbers are missing something.
Everyone who grows cucumbers has encountered yellowing of cucumber leaves. Watch a video about why cucumber leaves turn yellow:
Next, we will consider deficiency conditions, their manifestations and methods of correction.
Potassium deficiency
Potassium starvation often occurs due to excessive application of potassium fertilizers. Potassium deficiency is manifested by some characteristic features:
- excessive growth and development of vines and leaves;
- darkening of the leaves, they become bright green;
- fruits are disproportionately narrowed towards the stalk;
- burns of old leaves - yellow edges appear, over time they curl;
- the taste of the fruit becomes neutral, the sweetness and characteristic aroma disappear.
To compensate for the lack of potassium, use an aqueous solution of potassium sulfate or wood ash.
Nitrogen deficiency
Cucumbers have a special need for this element in the spring, during the period when the green part is formed. An unreplenished deficiency can also affect the fruits.
Signs of nitrogen deficiency:
- the lower leaves become pale green, turn yellow and dry out over time;
- the lashes become thinner and woody;
- the flowers fade and the ovaries fall off;
- the fruits become hook-shaped and acquire a light color.
Even if nitrogen-containing fertilizers were applied in sufficient quantities, there may have been insufficient watering, so the plants may also become nitrogen deficient. To normalize the situation, greenhouse cucumbers are fed with a solution of ammonium sulfate or urea (10-15 g per 10 l), using a foliar method.
Magnesium required
Magnesium deficiency is judged by the following signs:
- light green spots on leaves;
- chlorosis appears;
- flowers fall;
- The fruits ripen prematurely and are very small.
The problem can be solved by constant foliar feeding with magnesium nitrate (100 g per 10 liters of water).
Not enough boron
A lack of boron is characterized by the death of roots and growing points in cucumber crops. Other signs are:
- fruit deformation;
- leaf fragility;
- flowers fall off;
- dwarfism of bushes due to slow development.
The plants are fed with boron solution (0.3 mg per 1 liter of water) or foliar fertilizing with Kelkat boron (50 g per 100 liters of water).
Calcium deficiency
Calcium in the right amount ensures proper growth of cucumber crops. If it is missing, the following is observed:
- the appearance of narrow light stripes on the leaves, which leads to brittleness, weakness, wilting and, ultimately, death;
- rot on inflorescences;
- bending the edges down;
- the leaves become dome-shaped and even claw-shaped.
The problem is solved by foliar feeding with chelated calcium (3%).
Phosphorus deficiency
A lack of phosphorus is indicated by:
- small size of young leaves compared to old ones;
- leaf veins turn purple;
- slowing down the growth of lashes;
- the leaves darken, acquiring a bluish tint;
- the edges of the leaves become sharp and curve upward.
They solve the problem with a solution of ammophos and diammophos (1 tbsp per 10 l of water) or superphosphate (1 tbsp per 10 l of water), spray the bushes with them.
Molybdenum deficiency
Cucumbers growing in acidic soils are deficient in this element. An excess of heavy metals and ammonia nitrogen contributes to a lack of molybdenum.
Molybdenum starvation is indicated primarily by a change in color - the color of the leaves becomes less intense. Also, the edges of the leaves curl into tubes and chlorosis appears.
A lack of molybdenum is “treated” by applying phosphorus fertilizers.
Iron deficiency
The lack of this element is characterized by:
- the appearance of chlorosis on all young foliage;
- slow growth of bushes;
- light green, lemon and even white color of the leaves, this is due to the fact that it is the lack of iron that inhibits the formation of chlorophyll;
- growth points do not develop;
- lightening of fruit tips.
To eliminate this, apply root feeding with a 5% solution of iron sulfate.
Deficiency of copper, zinc and manganese
The lack of these elements retards plant development and reduces fruiting. Thus, with a lack of copper, the leaves turn pale, the shoots become weak, the flowers quickly fall off, and the edges of the leaves curl into a tube.
In order to avoid the problem, in the spring the place where the cucumbers will grow is treated with a 1% aqueous solution of copper sulfate.
A lack of zinc is fraught with asymmetrical leaf shape, darkening and death. To compensate for the deficiency, zinc sulfate is used. Apply 1 g per 10 square meters to the soil. m.
Manganese starvation is manifested by the appearance of light dotted spots on the upper leaves and a marbled coating. To eliminate the problem, root fertilize with a manganese solution (0.3 mg per 1 liter of water).
How to understand and what to do if too much fertilizer has been applied?
Plants suffer not only from a lack of nutrients, but also from their excess. Sometimes gardeners get so carried away with applying fertilizers that they destroy plants while they are still standing. Large amounts of chemical fertilizers are especially dangerous.
If too much fertilizer is applied, the plant is watered with plenty of water. If the bush is still small, then transplant it to another place.
When growing cucumbers in a greenhouse, the feeding procedure is especially necessary, since it is not possible to completely replace the soil every year. Timely application of the necessary fertilizing can save you from many troubles and not only significantly increase productivity, but also improve the taste and appearance of the fruit.
0
0
Copy link
Benefits of folk remedies
Folk remedies for feeding cucumbers (and other garden crops) are the favorite type of fertilizer for many summer residents and gardeners. a number of significant advantages to this
- Benefit. Many formula ingredients are cheap or at least not very expensive, and you probably already have some of them at home. There is no need to spend money on purchasing mineral or specialized preparations.
- Quality. At the preparation stage, you choose the ingredients yourself, and you can be sure that they are of high quality. The main thing is to make them according to the recipe, observing the dosage.
- Environmental friendliness. It is difficult to cause significant harm to plants and pollute the soil using folk remedies (unlike mineral fertilizers). However, if abused or used incorrectly, it can cause harm, so you need to proceed carefully.
- Efficiency. Many drugs, made correctly according to the prescription, are highly effective, and although, most likely, you will have to perform not one, but several feedings, the effect will soon come.
Note! If you properly feed cucumbers with folk remedies, you can stimulate growth, improve budding and flowering, accelerate fruit growth, prolong and improve fruiting, and make them more tasty.