When is it better to graft an apple tree: in spring or autumn?
Formally, apple tree grafting can be done all year round, even in winter. During the cold season, it is allowed to carry out the procedure only on seedlings growing in pots placed indoors. As a rule, trees are grafted either in the fall or in the spring, when it is not too hot outside or the trees enter the dormant phase.
On a note!
Astrologers advise planting all trees strictly on the growing Moon. During these periods the survival rate is the highest.
The question of when is the best time to graft an apple tree can be called controversial. If there is a ready-made rootstock (which is grafted onto) and a scion (the branch that is grafted), you should not postpone the grafting procedure until spring. In this case, the cuttings will need to be preserved somehow, and this is unnecessary labor costs.
Grafting tools
To plant a scion on a wild or cultivated tree, you need to prepare the following tools:
- Knife (you will need three types of it - budding, gardening and grafting);
- Sharp pruning shears;
- Gauze or cotton pieces of fabric, always clean;
- Cling film;
- Var;
- Water.
Tools
Interesting: Garden plot design: options
When can you plant apple trees in the fall?
The time for vaccination must be chosen correctly. The air temperature should drop to +17°C. A decrease to +13°C or less during the day is no longer desirable. In such conditions, the scion may not take root. But a temperature above +20°C does not guarantee a successful vaccination result.
Vaccination time in September
Experienced gardeners recommend grafting apple trees from mid-September. But you need to look at the condition of the rootstock. The seedling must finish bearing fruit. If the apple tree is early, it is worth postponing the grafting to the beginning of October. In the southern regions of Russia, as a rule, trees are not grafted in September.
Vaccination time in October
October is considered the most favorable month for vaccination. The air temperature has already dropped a little, but frost is still far away. In the southern regions, you can graft an apple tree throughout October, but in the northern regions it is better to do this before the middle of the month. At least 3 weeks must pass from the moment of vaccination until the onset of frost. If frost hits earlier, there is a high risk that the scion will not take root.
Apple tree grafting in autumn
After autumn grafting, the scion adapts more easily after spring transplantation. The technique depends on weather conditions:
- eye (budding) and bark grafting is performed before September 15;
- clefting is carried out in the second or third ten days of September and early October.
It is not advisable to practice grafting later, since after the leaves are shed, the sap flow slows down.
It is recommended to cut off lignified or semi-lignified annual cuttings immediately before the procedure. If necessary, you can store them for several days in a damp cloth on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator.
An apple tree takes root best if another variety or a wild one grown from seeds is chosen as a rootstock.
Can be grafted onto other plant varieties:
- hawthorn;
- chokeberry or red rowan;
- quince;
- viburnum.
Plant grafting. (Photo used under standard license ©ogorodnye-shpargalki.ru)
Goals and objectives of vaccination
The tree grafting procedure is very popular. With its help you can solve several problems at once:
- Extending the fruiting period of a tree. When the apple tree is old, you can carry out anti-aging pruning and subsequently plant another variety. If over time the tree bears fruit very poorly, grafting can change the situation.
- Improving fruit quality, increasing yield.
- Change in varietal properties. If the apple tree on the site is not satisfied with the taste characteristics of the fruit, you can re-graft using a twig cut from a tree of the selected variety as a scion.
- Saving space on the site. In small home areas it is difficult to place many trees at once. If you want variety, you can graft several varieties onto one apple tree at the same time (optimally 2 or 3 varieties).
- Increasing winter hardiness and endurance of apple trees. You can use a rootstock with a more branched root system and good resistance.
- Emergency rescue of an apple tree damaged by rodents or broken by the wind. Even if only a stump remains from the tree, you can graft it.
Gardeners who decide to grow an apple tree from a seed also face the need for vaccination. Especially when they are trying to get a hybrid. Fruit trees grown from seeds do not retain varietal properties. Such seedlings are wild. They may not bear fruit at all or produce tasteless, sour, small fruits. Grafting makes it possible to transfer all the varietal characteristics of the scion to the wild apple tree.
Why is vaccination needed?
Grafting is often used in gardening as a vegetative method of propagating trees by combining several plants and giving them the desired properties.
Graft 2 to 4 cuttings per branch. In the future, keep the best one (in 2-3 years)
There are several reasons and purposes for vaccinations:
- not satisfied with the apple tree variety in the garden;
- there is no room for new trees;
- the apple tree is old, damaged by bad weather or rodents;
- fruit tree productivity has decreased;
- grafting can be used to shape the crown of an apple tree and its growth;
- on the same tree you can harvest different grafted varieties, the main thing is that they coincide in ripening time;
- By grafting a cultivated variety onto wild animals, you will get noble fruits;
- It is possible to cultivate new varieties with increased winter hardiness, productivity and resistance to harmful lesions.
You can change the situation and achieve the goal by using the grafting method, but you should remember that the grafted variety is dominant and ensures the grade and appearance of the tree.
We advise you to read how to choose the right quality apple tree seedling.
Pros and cons of autumn vaccination
Autumn and spring vaccinations have their advantages and disadvantages. The main advantages of engrafting the scion before winter are that:
- Many gardeners prefer to graft apple trees in the fall, since it is much easier to obtain rootstock and scion. There are a lot of varietal plants in specialized stores, and wildflowers planted last year or the year before have already had time to grow.
- Another advantage is that the soil is well moistened in the fall, so there is no need to constantly water the tree after the procedure.
The disadvantage of autumn grafting of the scion onto the rootstock is considered to be the increased risk of freezing. If you vaccinate less than 3 weeks before the onset of frost, the shoot may not take root. Moreover, the tree’s protective powers are reduced; it may freeze if it is not covered.
Apple trees can be grafted in early spring. In this case, the risk of death is lower and the survival rate is higher. But there are also disadvantages. In the spring, as a rule, gardeners have a lot of other work to do. In addition, you need to constantly monitor the grafting and water the tree. If something goes wrong and the graft does not take root, you can always repeat the procedure. But it is advisable to do this no earlier than after 2 months. If you make your first attempt in early spring, you can repeat it, if necessary, in May. But at this time it is already quite warm outside, in some regions it is hot. Therefore, it is better to leave the vaccination until next autumn, and this is already a waste of time.
Watch the lessons of the course Grafting and re-grafting of fruit trees:
Video tutorial Nr.1
Introduction to the video course
Duration: 6:42
In the introduction, we will talk about different methods of grafting, especially tabletop grafting or, as it is often called winter grafting - why in winter?
Video tutorial Nr.2
Tool - sharpening. Banding material for vaccinations.
Duration: 07:37
In this lesson we will show you what tool we use and how to sharpen it.
For successful grafting, maintaining moisture in the grafted cutting is extremely important.
You will learn what is the best and most reliable way to seal and press the grafts.
Video tutorial Nr.3
Winter vaccination. Copulation
Duration: 08:58
If you have free time in winter, if you plan to graft several seedlings at once for your garden and shorten the growing period for a whole year, then this grafting method is for you.
It will also definitely be useful to those who will plant hundreds and thousands of seedlings.
In this lesson we will show you copulation in detail - we will show and tell you all the possible nuances so that all your vaccinations are guaranteed to take root!
Video lesson Nr.4
Improved copulation and self-destructive ribbon operation
Duration: 05:30
A simple copulation is done a little faster, but the improved one holds stronger and more reliably - neither birds nor the wind will break it. It’s not for nothing that they called it improved! I have seen more than once on YouTube how inexperienced gardeners show how they make improved copulation. You heard, you may have read, but the tongue is done incorrectly, and such a graft may simply not take root. But thousands of novice gardeners watch them and then make thousands of mistakes! Thanks to our Video Tutorial, you will do improved copulation like a real professional. And in this lesson I will show you how to use Japanese self-destructive film and tell you about all its advantages.
Video lesson Nr.5
We graft a family (multi-varietal) plum seedling
Duration: 22:30
Multi-varietal (family) seedlings are a very interesting and promising direction in nursery farming. Roman and I were convinced of this from our own experience: zero competition and a very high price. If you want to grow multi-varietal seedlings for your garden, we will answer all your questions: What rootstocks should you use? At what distance from the handler should I vaccinate? How to care for implanted vaccinations? How many varieties can be grafted onto one seedling?
See everything about grafting multi-varietal (family) plums in this Video tutorial.
Video tutorial Nr.6
About cuttings and rootstocks for winter and spring grafting
Duration: 14:00
This lesson will be especially relevant for those who will be involved in winter or tabletop grafting. I will show you how to determine whether cuttings are freezing. I’ll show you which cuttings will work and which ones won’t if we take them for grafting directly from the tree in the spring. You will see what freezing of the cambium looks like. I will show you which rootstocks I plant for summer budding, and which I graft in winter or spring. You will see how I sterilize the roots of rootstocks purchased from someone else's nursery so that pathogens do not enter my farm with them.
Video tutorial Nr.7
Storage of rootstocks and grafts
Duration: 5:52
The rootstock dug up in the fall, cuttings prepared in the fall for grafting, seedlings grafted in winter - all this must be preserved from frost and drying out. The novel will show where and how he stores the rootstock and scion for winter grafting.
Video tutorial Nr.8
What to do with excess seedlings?
Duration: 2:44
Sometimes we have extra seedlings left over. For some gardeners this sounds strange, but nevertheless it happens. I myself didn’t know what to do with them before. Now everything is going well for us.
See a very simple, and at the same time very effective idea on how you can very easily expand the variety of options in your garden or nursery assortment. And without any additional costs - just vaccination.
Video tutorial Nr.9
We graft plums (grafting pruners, bugs)
Duration: 13:30
I always consider mistakes to be the most valuable thing in learning. When I grafted these plums, I, as always, was confident that everything would take root perfectly. However, that was not the case: nothing took root! What is the reason? All the details are in the video. Here I will show how I work with a grafting pruner for winter (tabletop) grafting.
Video lesson Nr.10
Grafting into cleft and wedge. Protecting grafts from drying out with bags
Duration: 26:08
In this lesson we will graft a paradise apple tree blooming with red flowers onto a clonal rootstock and a large-fruited hawthorn onto a rowan tree. We will show three different grafting methods, and our main goal will be to produce seedlings that will bloom immediately after grafting and bear fruit in the first season. Such vaccinations must be sealed. Roman will show his method of protecting grafts from drying out.
Video lesson Nr.11
Grafting in the butt and in the butt with a tongue.
Duration: 16:54
Grafting into a cleft is quite simple, but we cause quite a large wound to the rootstock. The method in the butt allows you to graft parts that do not match in thickness without causing too large wounds, and the butt with a tongue will also be very durable.
Video lesson Nr.12
Grafting with insert
Duration: 15:14
Seedlings grown with the insertion of a clonal rootstock are the highest aerobatics in gardening. After all, in this way we can grow dwarf trees with a root system that grow vigorously! Such trees will not need supports and will not require watering, but they will be truly short-growing.
We will show how, with the help of grafting, you can make such a tree faster by a whole season.
Video lesson Nr.13
Re-grafting for the bark
Duration: 14:10
This method, as well as the splitting method, is used for grafting mature trees with thick branches.
Compared to “split” it has some advantages and disadvantages. Which method you choose will depend on your situation. However, I believe that you need to master both ways.
Video lesson Nr.14
Grafting an apple tree into a cleft
Duration: 43:03
When we need to re-graft an already mature tree, copulation will no longer help us, since we have to graft thick branches, the thickness of which is even 10 times greater than the thickness of the scion. This is where we have to use the cleft grafting method. This is a serious job for which you will need additional tools, certain skills and some tricks.
Which branches to graft, which ones to leave, and which ones to simply remove? At what distance from the trunk to vaccinate?
Where should the split be made? How many cuttings should I insert?
You will see all the answers in the detailed Video Tutorial.
Video lesson Nr.15
Result of re-vaccination
Duration: 05:04
We love to show not only the work, but also its results!
In this Video tutorial you will see how the grafting we did in the split and behind the bark on an adult tree took root and you will receive our recommendations for further care of the overgrafted tree.
Video lesson Nr.16
Preparation of cuttings for winter and spring grafting
Duration: 20:10
In areas with a mild, southern climate, cuttings can be taken directly from the tree even in winter or spring. And where there is a risk of cuttings freezing, it is better to prepare them in advance and save them until grafting begins. For all the details about preparing and preserving cuttings for winter and spring grafting, watch the video tutorial.
Video tutorial Nr.17
Is it possible to “cut off the head” of a pear?
Duration: 6:06
Here you will see how Roman did an experiment - he cut down a 10-year-old pear tree at a height of 1.5 meters and grafted the bark into this stump. It would seem that such a tree has no prospects. However, the cuttings took root and began to grow. See the video for all the details.
Video tutorial Nr.18
Results of re-grafting a pear into cleft
Duration: 4:54
Here we will show one of the results of regrafting a pear.
Video tutorial Nr.19
How to sharpen a grafting knife and pruning shears?
Duration: 21:37
Vaccination should only be done with a very sharp instrument. The grafting knife must shave! Only then will your vaccinations take root perfectly, and the work will go quickly and easily. The blades of the pruning shears do not need to be sharpened before shaving, but the pruning shears should also be sharp so that the cuts heal as quickly as possible. I will show you my method of sharpening grafting knives and pruning shears.
Video lesson Nr.20
Results of grafting by improved copulation
Duration: 7:41
In this video I will show several successful graftings and show the difference between two grafted trees: one was grafted on the root, and the second was transplanted immediately after grafting.
Video lesson Nr.21
How to graft coniferous plants?
Duration: 28:41
Our course is devoted to grafting fruit trees, but I decided that it would be extremely useful for you to master the skill of grafting coniferous crops. However, everything there is completely different from fruit...
My colleague Voldemar Bartoshevich is a great master in this matter - he annually grafts thousands of pines, fir trees and larches.
Now you can grow a variety of decorative forms of conifers yourself: weeping, dwarf, with interesting colors. Or maybe you want to graft Siberian cedar pine? After all, when grafted, it begins to bear fruit already in 4-5 years, but a seedling can bear fruit only after 30 years!
Video lesson Nr.22
How to regraft an old pear tree?
Duration: 24:03
But what should you do with a rather old and very tall pear tree that has been bearing fruit for a long time, but with very small fruits, can it be re-grafted, or maybe just cut down? Don't saw! See how you can re-graft even a 40-50 year old pear tree.
Video lesson Nr.23
We create family seedlings from annual plants
Duration: 14:49
This is my author’s method of grafting and you will not find its description in any book. I have developed and successfully used it on my seedlings since 2012. My students also successfully use this method in their nurseries.
Thanks to it, you can make a multi-varietal (family) seedling from an annual seedling. In this case, you will form the skeleton of the future tree the way you want. You yourself will determine the location of the skeletal branches, their direction of growth and the angle of departure.
This grafting method allows you to create multi-varietal seedlings faster by a whole year!
Video tutorial Nr.24
How to form the crown of an overgrafted pear?
Duration: 6:01
After regrafting, the growth of established cuttings goes up.
The novel will show how he shapes the crown of an overgrafted pear so that the branches still grow horizontally, so that the tree does not “run away” too high, so that all the fruits are within reach of an outstretched arm.
Video tutorial Nr.25
Spring budding of a cherry with an awakening bud
Duration: 11:32
Another non-standard method of grafting is spring budding with an awakening bud. It works great for stone fruits. It is especially relevant for nursery growers who do summer budding. With the help of spring budding, you can increase the yield of stone fruit seedlings to 95% and even higher. And it also guarantees that you are grafting a living kidney - after all, at this moment it is already waking up!
Video lesson Nr.26
What is better to seal vaccinations: bags or ribbons?
Duration: 8:20
In this lesson I will analyze the advantages and disadvantages of sealing vaccinations with bags and tapes, and I will show everything with specific practical examples.
Video tutorial Nr.27
Cherry grafting
Duration: 16:21
Cherries do not take root as easily as apple and pear trees. Here only certain methods of vaccination are suitable and certain rules must be followed. You will see all the nuances in the Video Tutorial.
Video tutorial Nr.28
What to do with constrictions on vaccinations?
Duration: 4:38
The graft took root and began to grow - hurray! However, you forgot to remove the straps - the ribbons that held the graft and protected it from drying out.
What is the result? – the constriction and, as a result, the graft breaks off even under the pressure of its own weight.
What to do if you are still late, and the constriction is already suffocating your vaccine? See the video tutorial for the solution.
Video tutorial Nr.29
Vaccinations have taken root - what next?
Duration: 10:12
Hurray - your grafts have taken root and produced very good shoots! Then the question arises: “What to do next?” .
We will come to a specific young apple tree, which I regrafted into skeletal branches and grafted onto very large shoots. We will take up the formation and further planning of its growth and development.
Video tutorial Nr.30
How and when to vaccinate with cuttings in the summer?
Duration: 12:06
There is a stereotype that in the spring we graft with a cutting, and in the summer we bud with a bud. However, I maintain that cuttings can be successfully grafted in the summer.
You will see how I made such a vaccination and how it took root perfectly - you will learn how to vaccinate at any time !
Video tutorial Nr.31
What grafting methods are used for which crops?
Duration: 22:25
There are many methods of vaccination. However, this seemingly most universal method of grafting, such as copulation, for example, on dogwood, does not take root at all. We have verified this with hundreds of our seedlings. And precisely so that you do not repeat our mistakes, we recorded this video lesson in which we will tell you for which cultures, which methods are suitable and which are not.
Video tutorial Nr.32
How to do ablactation?
Duration: 9:09
You can use ablactation in many cases. I will show ablactation using the example of creating an apple tree on three legs. Such a tree does not need any support for any crop load. I also use ablactation to create interesting decorative forms of trees, for example, to create living arched structures. If you are interested in the topic of living architecture, this Video Lesson is for you.
How to properly plant an apple tree in the fall
Grafting an apple tree is a rather complicated process. It is important to choose the right scion and rootstock, treat the surfaces, and attach them tightly to each other. If the most important recommendations are violated, the vaccine may not take root.
How to choose a rootstock
Gardeners who purchase trees from nurseries, as a rule, are not interested in the origin of the trunks on which varietal apple trees are grown. Often sellers do not have this information either. They only have information about the variety. This state of affairs can lead to the apple tree being weak and not suitable for growing in certain conditions.
To avoid mistakes, you need to choose the right rootstock. It can be a wild apple tree, a dwarf tree (if you need to grow a small tree), rowan, or pear. It is best to use wild apple trees or certain varieties of apple trees, suitable for:
- Antonovka;
- Grushovka Moscow;
- Cinnamon Striped;
- Borovinka.
On a note!
All these varieties grow well in central Russia and are distinguished by excellent hardiness and resistance to adverse conditions.
When choosing a rootstock, you should pay attention to the following points:
- Compatibility of scion and rootstock. It is desirable that the ripening periods of apples approximately coincide. If the scion bears fruit early and the rootstock is taken late, the survival rate decreases.
- No damage or pest damage. The rootstock must be healthy.
- Good development of the root system.
- Adaptation to the conditions of the growing region.
If the tree retains varietal characteristics from the scion, then early fruiting is transmitted from the rootstock. Some apple trees begin to bear fruit only at the age of 8-10 years. This needs to be taken into account. If you want to get the harvest much earlier, you should use a faster-growing rootstock.
How to choose a scion
As a scion, you need to take cuttings from a healthy tree of the desired variety. They are cut from the southern side of a young but already fruit-bearing tree, preferably from the middle part of the crown. These should be well-ripened annual shoots with a small piece (1-2 cm) of two-year-old wood.
The diameter of the shoots must be at least 7 mm, and they must reach 30-40 cm in length. Each scion must have 4-5 developed growth buds and short internodes. Good shoots have smooth and even bark.
On a note!
The cuts must be even. When harvesting, you need to use sharp pruning shears.
How to prepare cuttings
In autumn, shoots can be used immediately after cutting. No preparation is required if the tree can be grafted within the next few hours. When the scion is cut and the shoot is grafted in a few days later, the branches need to be properly preserved.
If grafting is planned for spring, cuttings need to be prepared for future use. To do this, they need to be cut and treated with garden varnish. Then the shoots should be tied into bunches and provided with labels indicating the variety of apple tree. Each branch needs to be labeled this way.
The storage location for the grafting material must be arranged so that the cuttings do not freeze, dry out, are not spoiled by mold and rodents, and do not “wake up” ahead of time. Such conditions will occur if you keep the scion in a cellar or refrigerator.
Tools and materials for grafting apple trees
For breeding processes, it is necessary to have a special set of tools, since not all kitchen knives and household utensils are suitable for grafting work. For example, kitchen knives have a wide blade, and ordinary scissors pinch the wood when cutting.
Recommended kit for grafting work:
- budding knife for the “eye” method with a rounded blade and a plastic part for peeling off the bark on the opposite side;
- copulating knife with a straight long blade;
- hatchet , mallet or mallet for working with rough branches and trunk;
- grafting pruner (garden shears) - its blades do not pinch the wood and make cuts on the grafting components, which fit completely together (like puzzles);
- saw , hacksaw or lopper;
- strapping material - tapes made of polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride (2x25 cm), electrical tape, twine, self-destructive budding legs with paper clips, washcloth or raffia;
- wood products for putty (garden pitch, mastic, plasticine);
- whetstone for sharpening tools;
- labels on threads or wires with information about the variety and date of vaccination, which you will use to mark the grafted areas.
To successfully carry out grafting, the instruments must be fine-tuned and sharpened - this way the sections grow together and heal faster.
Important! Before work and after each cut, the tool must be wiped with alcohol or calcined: fresh wounds on the plant can become centers of infection
.
Do-it-yourself methods for grafting a garden apple tree
There are several methods of vaccination. Some are suitable for beginners, while others are more advanced and are practiced mainly by experienced gardeners. But when choosing a method, you need to focus not only on the labor intensity of the process, but also on the type of rootstock, the thickness of the shoot that serves as the scion.
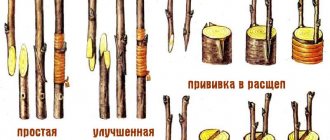
Into the cleft
This is one of the most popular grafting methods. A piece of cutting with 4-6 buds is used as a scion. Its upper cut should be vertical. The lower part needs to be sharpened into a wedge shape. In this case, the length of the cut surface should be 3 times greater than the thickness of the branch.
Graft into the cleft like this:
- The trunk or branch of the rootstock must be cut perpendicular to the surface of the bark and split vertically to a depth of 3-4 diameters of the horizontal cut of the scion.
- The cutting should be inserted into the split so that the scion and rootstock fit tightly to each other.
- The site of future fusion should be wrapped with electrical tape.
On a note!
Several cuttings can be inserted into one split.
Budding
This is a very interesting method of grafting, but it requires certain skills. In this case, they are grafted not with a cutting, but with just one bud.
To carry out the procedure, you need:
- Cut a bud from a branch. The “eye” is removed from the cutting along with a thin layer of bark and underlying wood.
- It is necessary to make a cut in the rootstock in the shape of the letter “T” and bend back the top layer of bark.
- A scion no more than 2-3 cm long should be inserted under the bark of the rootstock, making sure that they fit snugly against each other.
- Secure the scion with film or tape.
On a note!
Budding can be a real salvation when you need to do several vaccinations, but there is only one scion (cutting).
Copulation
When using this method, the thickness of the scion and rootstock should be approximately the same. The vaccination is done as follows:
- When performing copulation, you need to cut off the surfaces with a sharp knife. In this case, the sections must be mirrored so that they can be combined. The larger the contact area, the higher the survival rate. For this reason, you need to cut the branches at a good angle.
- The scion and rootstock should be combined so that the cambium layers are pressed against each other as tightly as possible.
- The vaccination site must be bandaged with electrical tape.
There is also a method of improved copulation. In this case, you need to make additional cuts almost parallel to the main ones so that you can hook the scion and rootstock. All other actions are exactly the same.
For the bark
Bark grafting is considered simple. But the rootstock in this case should be quite wide in diameter. It could be a thick branch or a stump.
The bark grafting is carried out as follows:
- A longitudinal cut should be made on the bark and carefully separated from the wood.
- The shoots that will be used as scion need to be cut. Their length should be 10-12 cm.
- On each cutting you need to make an oblique cut up to 4 cm long.
- It is necessary to insert the scion behind the bark of the rootstock so that 1-2 mm of its cut protrudes above the cut of the branch (trunk).
- The vaccination site must be secured with electrical tape or a tight tourniquet.
- All cut areas and edges of the bark should be coated with garden varnish.
During the process of grafting an apple tree, a bandage of gauze, bandage or breathable fabric can be applied to the junction. You cannot tighten the wound too much, but you must ensure that the scion and rootstock are properly fixed and fastened together. When grafting in autumn, you need to wrap and secure a plastic bag on top of the fabric or wrap this area with adhesive tape.
Budding method
The budding method also has another name – “eye” grafting. An eye is a bud that is grafted onto the rootstock. A rootstock is a plant to which a bud from another tree is attached. This method can be carried out without the use of cuttings, which is very convenient if grafting material is not available. The budding procedure should be carried out quickly and as carefully as possible. Only a healthy bud is grafted, which is cut off along with a piece of wood. This piece of wood is called a shield.
Attention!
When carrying out budding, it is important not to confuse the direction in which the bud is growing. She must look up.
Preparing the rootstock and scion
It may be interesting How to properly plant an apple tree in the spring: tips for beginners Peculiarities of treating an apple tree in the spring against pests and diseases Is it necessary to cover an apple tree for the winter and how to do it correctly
The first step is to select a suitable place with smooth bark on the tree to be grafted onto - the rootstock. There should be no swelling, swelling or knots. It is necessary to graft in a place located from the surface of the earth at a distance of 8 cm for seed rootstock and 15 cm for clonal rootstock. It is undesirable to choose sharp bends; grafting is carried out below the bend of the branch or trunk. Then the rootstock is prepared, cleaned of dirt and dust, and a T-shaped cut is made. To do this, cut the bark 1.5 cm in length in the transverse direction. 3 cm are retreated from the middle of the cut and cut from the bottom up, reaching the center of the transverse cut, turn the knife and carefully separate the bark from the tree along the longitudinal cut.
For the procedure to be successful, the harvested cuttings must be of high quality. To graft apple trees in the fall, it is necessary to take the eyes (buds) that appeared in the summer, but which will begin to grow only next spring. That's why they are called sleepers. They are mainly found on semi-lignified shoots of one year of life. To carry out autumn budding, it is from them that a piece of bark is cut off along with the eye. Holding a part of an annual shoot 15-20 cm long in your hand, make a transverse cut under the bud. You need to retreat 1.5 cm from and above it and cut off the shield along with a thin layer of wood. Do it quickly, carefully, without sudden movements. The manipulation can only be performed with one deft movement using a sharp instrument.
Connection of scion to rootstock
To connect the scion and rootstock, the first is inserted into a T-shaped cut. You need to make sure that the eye is looking up, then press down its edges with bark. Leave the kidney clearly in the center. The place where the budding was done is wrapped with plastic tape. The shield cannot be moved. The kidney itself is not wrapped. After 14-18 days, you need to check how the procedure went. The fact that the budding was unsuccessful can be judged by the dried out or rotten scion. Then it is removed, the place where it was located is cleaned and treated with garden putty. Next time you can try to graft an apple tree by budding only in the spring.
What can you graft an apple tree on in the fall?
Experienced gardeners advise not to limit yourself to using only wild apple trees as a rootstock. There are also alternative options. Sometimes the grafting needs to be done urgently (the scion is available), but there is no rootstock in the form of a wild apple tree. There is a solution to this problem, since you can graft a crop even onto an old stump or other fruit tree.
On an old tree
Grafting onto an old tree raises many questions. Some gardeners believe that this does not make sense, since such an apple tree may die in a few years. This is a common misconception. Such a rootstock can be used, but after radical anti-aging pruning.
You can graft another variety onto an old tree. This method allows you to develop new varieties in a limited area (when it is not possible to plant another tree), as well as solve the problem of lack of rootstock.
On a young tree
Grafting on a young tree is considered one of the most popular. In this case, a varietal apple tree can act as a rootstock. The point of grafting is that not all varieties are characterized by high winter hardiness or a developed root system. To increase the resistance of apple trees to adverse factors, it is recommended to graft onto a more hardy rootstock. These can be fruit trees of the following varieties:
- Antonovka;
- Anise;
- Chinese.
If grafting is successful, the tree will receive the varietal characteristics of the scion. But at the same time it will remain as hardy and strong as the rootstock.
Necessity of vaccination
Thanks to grafting, it is possible to acquire new varieties of apples, improve varietal characteristics, and renew an old tree. It becomes possible to propagate varieties already available in the garden. There is no need to rush to dig up a tree that is beginning to dry out. If you graft apple tree branches onto a cut stump, then after a few years a new harvest will appear on them. In a garden where there is no room for several varieties, from 3 to 5 types of apples are grown on one tree. The apple tree is a tree that bears fruit abundantly, so it is very convenient if the fruits on it ripen at different times. If there are no fruit trees in the garden, it is grafted onto:
- hawthorn and viburnum;
- pear and quince;
- chokeberry and common rowan.
However, if any of these seedlings is chosen as a rootstock, the scion takes root difficultly, the fruits are gradually crushed, their number will decrease, and the fruiting period will become shorter. In order to be able to collect many fruits that taste great and have a magnificent appearance in the future, it is necessary to graft apple seedlings and mature apple trees onto 2- and 3-year-old trees. Wild ones and seedlings of cultivated varieties are well suited.
Caring for grafted apple trees
Grafting is always stressful for an apple tree. The tree needs time for the graft to take root. The procedure is not always successful. To increase the chances, you need to provide proper care for the grafted tree. Experienced gardeners advise:
- 2 weeks after vaccination you need to see how the engraftment process is going. If the scion and rootstock begin to grow together, everything is fine. You should wrap the vaccination site back and completely remove the bandage only after a month. If the process does not proceed, the scion has begun to dry out, it is worth removing it and covering the junction with garden varnish. It will be possible to try again only in the spring.
- Before starting the procedure (or at least immediately after), the tree needs to be watered abundantly. It is not necessary to fertilize the rootstock. This can be done in the spring.
- Before winter, the tree needs to be well watered and covered. It is advisable to mulch the tree trunk circle with spruce branches or sawdust, and cover the central conductor with burlap.
- All shoots and shoots that may appear below the grafting site must be removed. They draw out the nutrition that is needed for the scion to take root well.
On a note!
Grafted apple trees must be tied up. The first time this is done immediately after the procedure at a distance of 25-30 cm from the ground. And later (after 1 year) they are tied again at a distance of 50 cm from the soil. It will be possible to remove the pegs and ropes only after 2-3 years, when the graft has taken root completely and there is no threat of breaking off.
Autumn grafting of fruit trees requires careful attention. You can choose not only an apple tree, but also other crops as a rootstock. There are several methods of vaccination. Therefore, everyone can choose the option of grafting a scion onto a rootstock that is suitable in a certain situation and is more consistent with the gardener’s skills.
How to care for a tree after grafting?
All grafted apple trees require proper care.
After vaccination:
- Loosen the windings after 2-3 weeks.
- In spring, remove the winding completely.
- Water and fertilize in a timely manner.
- Provide protection from pests.
- Install branches, pins, arches to protect against birds.
- Store grafted seedlings in appropriate conditions.
Further:
- Insulate your vaccinations for the winter.
- Of several grafted cuttings, leave only one.
- On the rest, pinch off the tops.
- Remove them either in the summer or next spring (depending on their condition).
Protecting seedlings from the wind.
Grafting fruit trees: all the secrets of the procedure
In the original, this surgical intervention is performed on wild trees. It is also common practice to use old or broken cultivated plants as a rootstock. These specimens are constant sources of nutrition, as well as the growth of young scions.
The following are grafted onto them using special devices:
- kidneys;
- branches;
- cuttings.
Each of these parts is cut from collection varieties, so they carry all the varietal characteristics of the mother plant. This is just one of the reasons why fruit trees are grafted. Also, using this procedure, you can obtain a cultivated plant with all its varietal qualities without unnecessary costs of money and time. In addition, you can increase the frost resistance of apricots or graft several different varieties at once. Some gardeners use this procedure to save damaged specimens. Nevertheless, you should always take into account the listed features of when it is best to graft fruit trees.
Reproduction of cultivated plants by seed does not allow preserving all their varietal advantages. For this reason, the scion method is popular among gardeners.
Step by step procedure
There are many ways to graft fruit trees, the best methods are given below. Having become familiar with them, even a novice gardener can carry out this work.
Into the cleft, half-split
It is easy to graft into a cleft. Especially if the rootstock has a larger diameter than the scion. In this case, you can plant 2-3 cuttings. To do this, make an even cut on the rootstock and carefully and smoothly trim it.
Next, a through slot is made into which the prepared scion is inserted. Oblique cuts are first made on it on both sides so as to smoothly cut off the bark. The cuttings are inserted into the gap, and the “joint” is covered with garden varnish. You don’t have to tie it tightly, as this method creates natural pressure on the scion. It is important to carry out vaccinations using this method before sap flow begins.
Cuttings
The second name of the method is copulation. The scion is shortened by 2-3 buds, a cut is made at the bottom at an angle of 45 degrees, and a similar cut is made on the rootstock. Then the cuttings are applied one to the other and the joint is wrapped with electrical tape. This method should be applied before sap flow begins.
By budding (by eye)
A very popular grafting method among gardeners. They use a kidney that is grafted onto a wild animal. One branch is enough to obtain a large number of eyes for subsequent grafting. It is important to cut the bud carefully without damaging the wood.
A T-shaped cut is made on the rootstock, into which the harvested varietal buds are inserted. After this, wrap it with electrical tape, it is important to do it tightly to avoid drying out. If such a vaccination was carried out in the summer, then its growth will be noticeable only in the spring of next year.
For the bark
This method is often used to rejuvenate old trees. The old trunk is cut off, the cut area should be clean, without traces of fungus. Using a knife on the side, vertical cuts are made in the bark, into which the cut and protected scion cuttings are inserted. Then they wrap the trunk tightly along the outer diameter and coat it with garden varnish.
It is recommended to plant several cuttings in order to subsequently leave only the healthiest and strongest ones. To understand what can be grafted onto what, experienced gardeners have compiled a table showing how to get the expected result.
Having examined the table, you can determine what can be grafted onto the shadberry and what cannot. You can also get one hundred by grafting an apple tree.
| Rootstock | Scion |
| Irga | Pear |
| Apple tree | Apple tree |
| Quince | Pear and apple tree |
| Plum | Felt cherries and peaches |
| Sloe or cherry plum | Apricot |