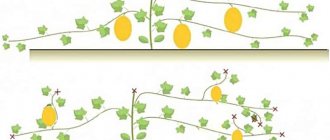
Reasons for yellowing of melon leaves
Knowing the main reasons why the leaves of the grown melon turn yellow, you can determine the method of its treatment. This will help you choose how to treat, as well as select the necessary fertilizers or growth stimulants.
Water scarcity
Lack of moisture is one of the consequences of the onset of problems for a planted melon. It has a powerful root system that penetrates deeply (up to 1 m) into the soil and can independently extract water. But it still needs watering, although not too much.
Weekly irrigation is sufficient. Water should only be used warm, infused in a container under the sun's rays. It is preferable to equip a drip irrigation system to avoid water drops falling on its above-ground part and not cause yellowing of the melon stems.
Why do melons rot in areas that are too wet? Because waterlogging can initially cause rotting of the root system, and then the above-ground part begins to turn yellow.
Damage to the root system
How to understand that a melon is suffering due to a damaged root system? This can happen if plants are planted too close to each other. Eventually they will begin to turn yellow and then disappear.
Lack of mineral salts
You can clearly see the consequences of an insufficient amount of mineral salts in the soil by looking at the leaves. At first glance, one might assume that greenhouse pests are to blame. Dark spots appear on the leaves, they wither and turn yellow.
What can you do in this case? Carry out complex feeding of melons and melons with nitrogen and mineral fertilizers.
Excess sunlight
Too intense sunlight is also an important factor why melon vines dry out. Especially during dry times, this becomes the main reason why the leaves on melons grown outdoors dry out and then dry up completely. What needs to be done to get rid of this problem? For example, beds with planted plants should be covered with dry grass.
How to treat onychauxis?
To correct the condition of the nails and return them to normal thickness, careful care and elimination of the factor that caused the changes are necessary.
If the cause is diabetes, you need to be more careful in keeping your glucose levels within normal limits. This is done by following the recommendations of the endocrinologist, taking glucose-lowering drugs or insulin injections, depending on the type of disease.
To treat edema and hypoxia in the tissues of the lower extremities caused by impaired venous and lymphatic outflow, medications are prescribed to strengthen the walls of blood vessels, thin the blood, and compression stockings.
For atherosclerosis, medications and diet are prescribed to reduce blood cholesterol levels.
If the cause is a vitamin deficiency, nutritional correction or taking vitamin-mineral complexes is necessary.
If there is inflammation or infection, antiseptic treatment is carried out and medicinal ointments are prescribed.
To improve blood circulation in the extremities, special gymnastics for the feet helps.
To treat onychauxis with folk remedies, you can find many tips on the Internet for softening nails. These are warm baths with apple cider vinegar, hydrogen peroxide, soda, and herbal infusions. Before using this treatment, consult your doctor, as some diseases, including circulatory problems, these procedures are contraindicated.
The main thing is to eliminate the cause of the violations, then in the future the nail will grow correctly. In case of injury, it will take time for the nail plate to recover. A medical manicure or pedicure will help keep your nails healthy and control their growth during this period.
Causes of yellowing and falling off of melon ovaries
Sometimes, for some reason, in a seemingly healthy melon, the ovaries that appear turn yellow and fall off, and the leaves curl. To understand why this happened, it is necessary to find out what negative circumstances preceded it.
Mineral deficiency
An insufficient amount of microelements and minerals in the soil is one of the reasons why melon ovaries wither and subsequently fall off. In greenhouses, this resembles pest damage to the crop. This problem can be dealt with by adding complex mineral fertilizers to the soil.
See also
Description of the Altai melon variety, features of cultivation and careRead
Not pollinated
In the absence of pollination, there is a high probability that the fruit will not set, and this will lead to the falling of flowers. To prevent this phenomenon, it is recommended to spray the flowering vines with sweetened water to attract more insects. Or you can pollinate artificially.
No pinching
To promote normal development, melons require pinching of the main stem. It is enough to leave 3 stems on the bush (one main and two lateral). If you do not follow the requirement, then this becomes the reason why the melon lashes dry out.
Temperature jump
If the temperature during the day is much higher than the night level, the development of all pumpkin crops deteriorates. Under such climatic conditions, the negative process of drying out the vines during the fruiting period intensifies.
Preventive measures
As already mentioned, if the leaves of a pumpkin turn yellow, it means that the care rules were violated or the vegetable became ill.
Eliminating the problem is always difficult, and there is a risk of crop loss, so it is best to carry out prevention.
Preventive measures are aimed at creating conditions under which the risk of diseases and pests is minimized.
Agricultural techniques
- removal from the garden of plant residues in which pathogenic pathogens, fungi and insect larvae can survive over the winter and subsequently become active;
- changing the place where the pumpkin is planted, returning it to its original place only after 3-4 years;
- sowing seeds and seedlings in dry sunny weather in moist soil;
- regular loosening of row spacing, which reduces moisture evaporation and reduces the amount of watering, increases the penetration of air flows to the roots;
- pinching the stems, leaving up to 4 ovaries, forming a bush of 2 stems, which supports adequate nutrition of the entire plant.
Pumpkin diseases and their control / Bacteriosis
Why do leaves on seedlings turn yellow and how to fix it. Causes and remedies for yellowing leaves!
Why do leaves on plants turn yellow?
Chemical and folk remedies
- carry out pre-sowing treatment of seeds; this can be done by soaking them in a weak solution of potassium permanganate before planting;
- twice during the growing season, the plantings are sprayed with Bordeaux mixture to prevent the occurrence of fungal infections;
- choose pest-resistant varieties;
- increase plant immunity by adding fertilizer complexes and organic matter;
- spray the plantings with infusions to repel pests (with garlic, onions, wood ash, tobacco);
- When primary signs of damage appear, they are treated with fungicidal and insecticidal agents.
Causes of melon rotting
This can happen if agricultural technology during cultivation was not followed. One of the reasons provoking this phenomenon is damage to root rot. Often, rotting begins when crop rotation rules are not followed and seeds are planted in contaminated soil.
Weakened plants are more susceptible to rotting. Initially, the root system dries out, and then the foliage withers and turns yellow. As a result of this process, the bush disappears. If rotting occurs during the period of fruit ripening, then the harvest cannot be harvested, since the fruit rots from the inside.
Answers to frequently asked questions on growing melons
Question No. 1. What fertilizers are best to choose?
Melons love phosphorus and nitrogen fertilizers. It is better to apply them before planting and after the first four full leaves appear.
Question No. 2. Why do you need feeding?
Fertilizers help the crop grow healthy, increase productivity and improve the taste of the fruit.
Question No. 3. How to apply fertilizer?
Fertilizer is spread manually into the holes made before planting seeds or seedlings. Liquid fertilizers are applied at the root of each crop. Foliar fertilizers are sprayed using a spray bottle.
Question No. 4. Is it possible to apply fertilizers during the growth stage of the crop, and not before planting? What will happen in this case?
Melons respond quickly to feeding. If the soil contains a sufficient amount of humus (in the case of chernozem), then fertilizing can, as an exception, be done at the flowering stage. But in this case, the yield is reduced by 40%.
Question No. 5. How to determine that a crop needs additional feeding?
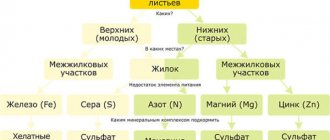
Mineral deficiency is determined by the condition of the plant. When manganese is deficient, the leaves turn yellow or pale green. The formation of pale green chlorosis on young leaves indicates iron deficiency. If the crop wilts with sufficient watering, the cause may be potassium deficiency. With a lack of calcium, young leaves curl and the ovary does not appear, even during flowering.
Nutrient deficiencies can be seen by the color of the leaves.
Diseases characteristic of melons and melons
Some types of diseases and pests prevent a decent harvest of fruits. One should know the signs of diseases to know how to protect them from such problems. Melon crops can be affected by various types of infections (viral, bacterial or fungal).
The most common diseases of pumpkin crops are the following:
- ashtray (powdery mildew);
- fusarium wilt;
- anthracose (dry copperhead);
- flower parasite broomrape;
- mosaic virus;
- ascochyta blight
Planted melons and melons are often damaged by insects:
- spider mite;
- melon fly;
- melon (cotton) aphid.
They usually damage the skin of ripe fruits and lay larvae in them.
The spread of diseases can begin from infected seeds, as well as weeds or soil. It should also be noted that some types of diseases can be carried by insects. Therefore, timely pest control must be carried out.
melon aphid
Damage by this pest occurs through the reproduction of small insects on the underside of leaves. They suck the juice from the plant, which causes it to wither and the ovaries to fall off. This is why the leaves curl and the stems dry out.
Fusarium wilt
This infection is caused by a special type of fungus. It penetrates through the root system from the soil. Initially, the roots rot, which leads to complete drying of the above-ground part. From the first signs of the disease to the death of the plant, it takes from 1 to 1.5 weeks.
The danger of this disease is that it can spread throughout the area. Fusarium can occur at almost any stage during periods of high soil and air humidity. As a preventative measure, it is not recommended to plant melons for several years in a row in the same area.
Anthracose lesions of melon
This type of fungal disease affects plants grown in greenhouse conditions. First, spots of a brownish-pinkish hue form on them, then the stems become brittle and the fruits rot.
See also
Description of the Torpedo melon variety, benefits and harm to humans, how to choose a ripe oneRead
Spider mite
Colonies of this parasite appear on young shoots, ovaries or buds. Adults spin webs and lay eggs. The larvae feed on cell sap. Scars appear at the site of the bite, and the melon crop dries out during the fruiting period. After this, the parasites can migrate to healthy plants. The eggs of this pest can remain viable for 5 years.
Broomrape
This is a parasitic plant species. It does not have a root system, but instead there are fleshy suckers that dig into the stem and feed on foreign juice.
Since one broomrape produces more than a million spores, it is difficult to cope with this problem. You can use herbicides during pre-sowing tillage.
Powdery mildew
The peak of powdery mildew disease occurs in the second half of summer if dry weather sets in with minimal precipitation. Whitish spots appear, the foliage gradually turns yellow and disappears.
Melon fly
This pest most often spoils the melon harvest. This fly lays its larvae in ripe fruits. As they grow, they make holes for themselves, resulting in complete rotting of the melon. The presence of larvae can be recognized by small holes in the peel. Affected fruits become vulnerable to fungal or viral diseases.
How to deal with the problem?
If pests are found on the leaves of the fruit, it is recommended to spray with a soap solution. To remove spider mites, sulfur or phosphorus compounds are used, to combat aphids - Karbofos and Actellika have shown themselves to work well.
To prevent infection, it is recommended to spray the plant with Bordeaux mixture, frequently loosen the soil, destroy infected plants and remove all remnants of plantings from the site for the winter. Remember that it is worth keeping an eye on other crops as they may also suffer from parasites or diseases. So, for example, zucchini leaves often turn yellow and so on.
Control measures and prevention
Melon crops are treated with the same methods and identical preventive measures are used. For this purpose, timely removal of weeds is carried out, as well as cleaning of the beds from plant debris.
To strengthen the bush, shoots affected by the disease are cut off. It is important to moderately water the soil to prevent stagnation of water or severe drying out.
Deep digging and autumn tillage are provided for pre-sowing soil preparation. In addition, seeds are disinfected before sowing. You can use an aqueous solution of formaldehyde (40%).
Crop rotation is considered a prerequisite for the normal development of planted plants. To prevent waterlogging of the soil, melons are planted in high beds.
When throwing out the buds, the beds are treated with water with the addition of potassium chloride. To prevent infection by pathogenic microorganisms, it is necessary to loosen the soil and remove weeds.
For the purpose of prevention and treatment of plants, acaricide preparations containing phosphorus or sulfur are used. Today, a biological control method is also used by propagating the small phytomysa fly. Its larvae eat parasitic organisms during growth.
The following chemicals are used for spraying melon plantings:
- Karbofos (add 70 g of product to 1 bucket of water).
- Actellik (solution of 3 ml of the drug per 1 bucket of water).
If you want to treat the beds with chemicals, use laundry soap dissolved in water. It is enough to grate 1/3 of the bar and dissolve it in 10 liters of water.
What to do, how to save a tree
If the reason for the yellowing of leaves on a cherry tree is drying out of the soil, begin to water the tree regularly. Nutrient deficiencies are compensated by feeding the trees with phosphorus, ash or potassium.
When yellowing and falling occurs due to fungal diseases, the following measures are taken:
- after harvesting, the tree is sprayed with 1% Bordeaux mixture (100 g of copper sulfate, 150 g of quicklime per 10 liters of water);
- affected branches are cut off and burned;
- the sections are treated with a special composition, which is made from lime mortar with the addition of iron (3%) or copper sulfate (1%).
Also, for diseases and pests, chemicals are used, for example, “Horus”, “Kaptan”, “Strobi”, “Gamair”. They are used for treatment and prevention. The products are used in accordance with the instructions on the packaging. If entire shoots are affected due to disease or pests, they are removed and burned. After which the plant is treated with mustard solution (100 g of powder per 10 liters of water). Spraying is carried out in the morning. This remedy strengthens the cherry’s immunity and helps it recover.
If the main problem of yellowing is insect pests, then first they try to remove them by hand, after which the tree is treated. Special tape traps are used, insects are washed off with water from a hose, then the soil is watered with boiling water.
Ant holes are filled with a decoction of wormwood or wild mint, or the tree trunk is smeared with tar. The Anteater remedy is also used. May beetle larvae are dug out from the ground and destroyed. Lupine, which is planted next to cherries, helps to get rid of them. Its roots are poisonous to insects.
- water the cherries with soft water from natural reservoirs or rain;
- do not use fresh manure for fertilizing;
- humus with bird droppings is used as nitrogen fertilizers, which is diluted with water 10-12 times;
- for quick help, the tree is sprayed with a solution of iron sulfate (50-70 g per 10 liters of water), the procedure is repeated 3 times after 2 weeks;
- in the autumn, add 150 g of iron sulfate and 10 kg of humus or compost to a depth of 60 cm;
- To improve the oxygen regime in the root system zone, use a solution of potassium permanganate (30-40 g per 10 liters of water), consumption per tree - 10 liters.
To prevent the appearance of chlorosis before the leaves bloom, it is recommended to treat the crown with a solution of iron sulfate (300 g per 10 liters of water).
What to do if the leaves fall
When the leaves from the cherry tree begin to fall, experienced gardeners recommend pruning. To do this, remove dry, diseased and bare branches. Such measures prevent the death of the entire tree. After that, fallen leaves and weeds are collected under the cherry tree. Branches and debris are burned.
To protect the plant from leaf fall next year, it is recommended to apply ammophoska before winter. The product is used to fill the grooves under the plant at the rate of 30 g per 1 square meter. m. The base of the cherry tree is sprinkled with dry ash, which strengthens the plant’s immunity.
After pruning, the soil under the tree is loosened and watered with warm water. Then the weakened plant is fed with complex fertilizers containing iron, nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus, zinc, calcium, copper, boron. For this purpose, products for fruit and berry trees are used: “Gumi-Omi”, “Kemira”, “Magic Leika”.
Downy mildew on watermelons
A whitish or gray-pink coating on the leaves of melons may mean that the plant is infected with powdery mildew. This is the first phase of the watermelon disease. Then the heavily inseminated leaves become deformed, weaken and dry out, and at the site of the lesion by autumn you can see black dots - the fruiting bodies of the fungus, ready to take over healthy plants in the spring.
Powdery mildew rarely affects engorged fruits, but the damage caused by this disease of watermelons is very great. Plants inseminated by the fungus develop poorly, form ovaries less well, and the fruits do not gain juiciness and proper sweetness.
The optimal infection temperature is 20–25 °C, but even outside this range, the causative agent of this watermelon disease is capable of infecting plantings, and powdery mildew is observed even in dry times, but in the presence of abundant morning dew.
Downy mildew is found on the leaves in the form of angular or rounded spots, and on the back of the leaf blade there are traces of a gray or lilac coating consisting of fungal spores.
The infected parts of the plant become brown, withered and die, and the watermelon pathogens remaining on them, as in the photo, survive for 2 to 3 years in a favorable soil environment, persisting even after frosts and thaws.
Application of mineral fertilizers
It is more convenient and effective to use complex minerals. Agritek Drip is used for fertigation of melons. The timing and dosage of this drug are as follows:
- 3-4 leaves 3 kg per hectare;
- growing season-budding period 5 kg per hectare;
- during flowering and fruit setting 4-5 kg per hectare.
The composition of the root dressing must include superphosphate-50g, saltpeter -10g, potassium chloride -20g. This is the dosage for 10 liters of water.
Feeding schedule
Feeding for melon is introduced according to the following schedule:
1️⃣ After April 15, the treated seeds are planted in a container or greenhouse. The soil should consist of earth and humus (proportion 1:3), with the addition of 3 tbsp. spoons of phosphorus mineral fertilizer and 1 tbsp. l. potassium and nitrogen fertilizers.
2️⃣ A month after planting the seeds, the seedlings are given 2 fertilizers: the first - after the plant has 3 leaves; the second - a week later.
3️⃣ Organic fertilizers (humus or biohumus) are added when planting seedlings in open ground. This is done in mid-May, when the crop has 4 leaves.
4️⃣ On the 10th day after planting, nitrogen fertilizers are introduced into the soil: 20 g of ammonium nitrate per bucket of water.
5️⃣ A week later, they are fed with fertilizer made from humus and chicken droppings, diluted with water, and ash.
6️⃣ Repeat the manipulation after 7 days.
Foliar fertilization is introduced by spraying. Once every 7 days, foliar fertilizers continue to be fed.
Watermelon mosaic disease
Common cucumber mosaic, which affects all pumpkin plants, usually develops on adult plants and is expressed in the appearance of green and yellowish areas on the leaves and tissues. In this case, the surface of the sheet plates is often deformed, acquiring a swollen appearance in places.
However, the watermelon disease shown in the photo is not only manifested in this. Infected plants develop worse, the leaves become smaller, and the internodes become shorter. The initial phase of the disease affects the tops of the shoots, the mosaic is especially pronounced during the period of fruiting, when the leaves on the lower parts of the vines completely die, and then the lashes themselves weaken, the flowers fall off, the fruits acquire a mosaic color, are deformed and do not develop.
This type of mosaic disease of watermelons is more common in warm regions of the country, for example, in the Crimea, Kuban and the Caucasus region. During the growing season, the mosaic virus can be spread by colonies of aphids; in cold weather, the pathogen persists on the seeds of melons, as well as on the roots of perennial plants, including weeds.
If plants are infected with the green mosaic virus, convex swellings become noticeable on the leaf blades, but light green areas of mosaic color are not always formed. The disease in most cases settles in greenhouses. Green mosaic can spread when damaged parts of the plant come into contact with healthy ones.
You can reduce the risk of developing a dangerous watermelon disease:
- using tested, disinfected seeds for sowing;
- using disinfected soil mixtures for sowing and observing the rules of crop rotation;
- planting only healthy seedlings;
- observing agricultural practices, including the rules of watering and protecting plants from low temperatures;
- destroying weeds, especially field thistle;
- promptly removing diseased watermelon plants;
- destroying aphid colonies on the site.