Melon is considered a heat-loving melon crop, so gardeners in the Moscow region rarely try to grow it in the beds of their plots.
The climate of the Moscow region differs significantly from the hot and dry climate of Central Asia - the homeland of Asian melons. However, if you take into account all the features, create suitable conditions and choose the right variety, growing melon in the Moscow region in open ground will turn out to be a completely feasible undertaking.
What varieties of melon are best to grow in the Moscow region?
Summer near Moscow is short and capricious; late varieties of southern melons do not have time to ripen: they do not have enough time, little sun and heat. But it is not necessary to categorically refuse to grow melons in this region; the main thing is to choose the variety wisely.
Basic requirements for the variety:
- short ripening period (early and mid-early);
- cold-resistant;
- zoned to this climate zone.
Popular varieties for the Moscow region - new and time-tested crops and many years of experience of gardeners:
- Kolkhoznitsa is the most popular variety in the Moscow region, cultivated since 1939. Bright yellow, small, round fruits ripen in all weather conditions. Weight up to 1 kg.
- Aikido is an early-ripening, zoned variety with a compact spherical shape and excellent taste. It ripens quickly, it is important to remove it on time. Weight up to 2 kg.
- Altaiskaya is a cold-resistant variety that ripens a little later than Kolkhoznitsa. The oblong fruits are covered with a fine mesh, weighing up to 2.5 kg.
- Zlato Scythians F1 is a mid-early productive hybrid. The peel of the fruit is bright yellow, dense, thin, with a pronounced mesh, the flesh is yellow-cream. Each plant ripens up to 3 round melons weighing 1 kg.
- Tamanskaya is an early ripening variety. The fruit is medium-sized, oval in shape, with a bright yellow smooth rind. Weight up to 1 kg.
This is an incomplete list of varieties and hybrids that breeders offer for cultivation in the Moscow region - in fact, there are much more of them.
The best seed material is produced by companies whose fields are located in the Moscow region. Such seeds are zoned and are ideal for planting and successful cultivation. For example, it offers the following varieties and hybrids: Alina, Pineapple, Canary, Princess Catherine F1, Princess Diana F1.
When is the best time to plant
Seedlings are grown in soluble peat pots . This way, the delicate roots of the seedlings are not damaged when transplanted into the ground, and they do not get sick.
Seeds are sown no earlier than April 15, and seedlings are transplanted into the ground in late May - early June.
Important! You cannot delay the transplantation period - seedlings older than 25-30 days will not produce high-quality fruit-bearing plants.
In the Moscow region in May, the likelihood of cold snaps and return frosts remains; when planting at this time, the bed must be covered at night.
Top dressing
It doesn’t matter whether you grow juicy melons in open ground or in a greenhouse, in the Moscow region or harsh Siberia - every plant needs fertilizing. During the growing season, fertilizer should be applied to the soil no more than 3 times.
The first feeding occurs a few days after planting the seedlings in the greenhouse, when they have slightly adapted to the new conditions. Use organic fertilizers, for example, mullein solution or bird droppings mixed with superphosphate.
The second feeding occurs during the period of vine formation, when the plant needs nutritional support to gain green mass - an ash solution is used. And finally, the third feeding should help in the formation of ovaries.
For any variety growing in a greenhouse, the drug “Kemira-universal” is suitable.
Preparing for landing
The success of growing melons depends on proper preparation.
Seeds
Seeds are prepared sequentially:
- Disinfect by soaking for half an hour in a warm solution of “Fitosporin” or potassium permanganate.
- Sprout in damp gauze.
- Stratify by alternating cold and heat.
For sowing, seeds that are 3-4 years old are used. When sowing fresh seeds, there is a risk of getting a plant that will have only male flowers and not a single fruitful female one.
Sprouted seeds are sown in peat cassettes or cups, deepened by 2 cm. After 5 days, shoots will appear.
Seedling
To develop, seedlings need temperatures above +20°C, good lighting and regular moderate watering.
At two weeks of age, it is fed with mineral fertilizers, and 10 days before the intended transplant, it is taken out into the air for hardening.
Soil preparation
It is customary to plant a melon in the place where previously they grew: onions, garlic, tomatoes, herbs, legumes, cabbage and eggplants. You cannot grow melon for several years in one place, or after any pumpkins or carrots.
Only well-lit and protected from the wind areas with light, fertilized soil with neutral acidity are suitable for melon beds.
Fertilize the soil with potassium sulfate, superphosphate, sifted wood ash, add organic fertilizers - compost and rotted manure.
Advice. Planting melons under mulching agrofilm makes them easier to care for and retains the warmth necessary for growth.
Choosing a site for planting melons
In the southern regions, gardeners often grow melons in semi-shaded places, because it is very hot there - more than enough heat to ripen a sweet, not watery melon. But in most of Ukraine, as well as in the central and more northern regions of Russia, growing melon in open ground is possible only in sunny areas, where there will not even be partial shade. Over time, when the melons grow and fruits form, it is better to build a shelter yourself.
Important!
The choice of location must be approached responsibly. Melon is very demanding in this regard. Only unshaded areas, protected from cold winds, are suitable for her!
Only unshaded areas are suitable for melon
If we talk about soil, then melon needs light, fertilized soil with a low groundwater level (so that the roots do not rot). The acidity should be neutral. Melon can be grown by direct sowing of seeds or through seedlings. In the middle and northern regions of Russia and Ukraine, it is recommended to choose the seedling method. But before you make seedlings, you need to choose the right variety!
Planting scheme and technology
For plants to take root, the soil must be +15...+18°C. And for them to develop properly – above +20°C.
Melons require space for growth and development; at least 1 m² is allocated for each bush.
Add 10-15 g of nitrophoska and rotted compost into the holes and moisten the soil.
Planting pattern:
- distance between holes – 1.5 m;
- the distance between rows is 1 m.
A bush is placed in the center of the hole and covered with soil. In this case, the root collar should remain at soil level.
Further care
To prevent the planted melons from freezing, a temporary greenhouse is made for them or covered with a film, which is dismantled with the arrival of stable heat (most often in early July).
Further care of the crop consists of watering, fertilizing, pinching, as well as loosening the soil between the rows, which is carried out only until the leaves in the rows close.
Watering
Melon does not tolerate high air humidity and an abundance of water in the soil. Moderate watering is needed at the beginning of the growing season; watering is not necessary afterwards. Do not use cold water - this can cause illness.
Top dressing
Requires 3-4 feedings per season:
- nitrogen fertilizers 2 weeks after transplanting into the ground - this promotes active growth;
- After another 2 weeks, fertilizing is repeated;
- in the second half of July, pour in herbal infusion or mullein infusion;
- During fruit ripening, phosphorus fertilizers are applied.
In order for the melons to be juicy and sweet, it is important to properly apply nitrogen fertilizers. Part is applied at sowing, the other - in the phase of appearance of 4-5 true leaves.
Protection from diseases and pests
Root rot affects young shoots and sprouted seeds; prevention begins even before sowing. The seeds are treated with a light pink solution of potassium permanganate at a temperature of up to +25°C for half an hour, after which they are washed and dried.
Fusarium wilt affects melons at the beginning and middle of the season in open ground. Prevention against this dangerous disease is also carried out with a weakly concentrated solution of the drug “Trichodermin”. The first treatment is 2 weeks after planting in the ground, when the plants have taken root. If the plant is sick, treatment is carried out at the root according to the instructions for the drug.
Melons are often attacked by pests: aphids, spider mites, wireworms, cutworms. You can fight them with the help of bioinsecticides, which are sold in specialized stores and garden centers. The most effective drugs are “Actofit”, “Bikol”, “Bitoxibacillin”.
Compliance with cultivation technology
Typical mistakes of melon growers in the Moscow region:
- wrong choice of variety;
- method of planting directly into the ground, without seedlings;
- non-compliance with agricultural technology.
The technology for growing melon consists of timely sowing, proper care, proper formation of the bush, and disease prevention.
Bush formation
To get a good harvest, bushes are pinched.
The first time is at the seedling stage, removing all excess above the 4-5th leaf.
The melon forms the central trunk of the bush after planting in the ground. In order for the melon to bush, it is cut off after the fifth leaf, since it forms ovaries only on the side shoots.
It is recommended to leave one ovary on each lash, only 2-3 per bush. Then the plant will have enough strength to grow full-fledged large fruits.
During the formation of ovaries, non-fruiting canes are removed, and canes with ovaries are cut off above the 3rd leaf after the fruit. The cut areas are treated with a mixture of sulfur, coal and lime.
The formation of lashes continues until the melons begin to ripen, while the growth of lateral stems, flowering and fruit set occurs. The fewer fruits left to ripen, the larger they will grow.
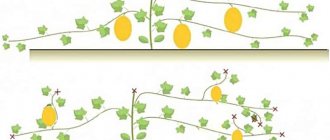
83.Melon. Forming a melon.
How to trim a melon
To grow a sweet and tasty melon, it is important to prune the shoots correctly.
1 - Melons form fruits exclusively on lateral branches. Therefore, it is imperative that the main shoot is cut off after the fifth leaf. This technique activates the formation of lateral branches.
2 - Then, when the side shoots come out, leave two on each side of the main stem. Flowers will begin to develop in the axils of their leaves. Pollination will occur thanks to bumblebees and bees.
3 - After the fruits set, I advise you to leave one on each shoot. If you leave everything, then the fruits will be small and tasteless. Once the melons have grown to the size of a medium apple, cut off all the tops of the side branches three leaves above the melon. Subsequently, regularly trim all new shoots - they are no longer needed. They will only take away the strength of the plant.
4 - During the formation and development of fruits, feed the plant with nutritional compounds every two weeks. An herbal infusion is best. When young melons are formed, place straw under them, this will prevent them from getting wet and rotting.
Try growing your own honey melons in your garden this season. Now you know everything! I wish you success!
Harvesting
The yield of melon depends on the variety; in open ground, 1-1.5 kg of crop per 1 m² is usually harvested. The fruits grow small, about 1 kg, but are sweet, juicy, and aromatic.
How to tell if a melon is ripe
The maturity of a melon in the garden is determined by the following characteristics:
- change in color of the rind to a typical varietal color;
- the appearance of a fragrant aroma;
- drying of the stalk, easy separation of the fruit;
- the peel is not hard, slightly springy under your fingers;
- When struck lightly, a melon produces a dull sound.
The ripening period of a particular melon variety is written on the bag of seeds. You can also calculate the approximate time by visually observing the development of fruits in the garden.
Storage Features
Early varieties are harvested at the stage of full ripeness and immediately used for food.
Important! Melons that have not yet fully formed will not be able to ripen during storage; they will remain tasteless and spoil.
The shelf life of melons that are harvested at the stage of technical ripeness is on average two weeks after harvest. It is better to store them in a cool place with low humidity.
Planting melon seedlings in open ground
Grown seedlings are planted in soil heated to +15°C, approximately in the second half of May. At this time, the bush already has up to 4 strong leaves and the direction of growth of the lashes.
Predecessors for melon are root vegetables, leafy vegetables, legumes and all types of cabbage
Selecting a location
The place on the site should be as illuminated as possible, protected from the winds, preferably the south side. It is not advisable to locate tall shrubs or trees nearby; the shade negatively affects the development of melons. The plant does not like accumulation of water, so the place should be flat or sloped, but not in a low place. The distance from the groundwater surface is at least 2.5 m.
Soil preparation
In the fall, the area is cleared of plant residues from the previous harvest. Dig into the bayonet of a shovel, adding 4 kg of humus, 30 g of superphosphate and potassium salt per m². If the soil is acidic, which is bad for melons, add wood ash 300–600 g/m². Dense and heavy soil is “diluted” with sand, approximately 1.5 kg per m².
In the spring, 2 weeks before planting, dig a trench and insulate its bottom with dry plant residues, sprinkle a little soil on top and fertilize it with ammonium nitrate 30 g/m². Vegetation will rot, releasing heat and nutrients. To warm the soil well, the trench is covered with film.
Important! In spring, it is strictly forbidden to add fresh manure to the planting hole: it will burn the root system.
Landing technology
Since melons grow long vines, you need to take care of support in advance. The most convenient way to garter a trellis. On the 4th day after planting, the seedlings are placed on a trellis and tied up as they grow. This method allows all the lashes to be evenly illuminated and warmed by the sun.
In a prepared trench, plants are planted at a distance of 50–70 cm from each other. A little water is poured into the formed holes, waiting for it to settle. The bush is placed in a hole without deepening the growth point; it remains above the surface. Water for irrigation should be used warm, not lower than +18°C.