Garlic is one of the popular vegetables used in cooking. That’s why every gardener wants to grow a good harvest of garlic in his garden. But for this, the spicy plant needs to be provided with timely watering, good care and protect the plant from all kinds of diseases and pests. One of the diseases that we will talk about today, which does not allow us to grow large garlic plants, is garlic rust.
Rust on garlic is a serious and insidious disease. If measures are not taken in time to combat the pathogen, the disease will spread to nearby healthy plants. In addition to garlic, the pathogen can infect shallots, leeks and regular onions. That’s why it’s important to know why rust appears, what it looks like, and what control measures will be most effective.
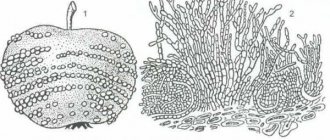
Signs of rust on garlic, photo
The time between damage to a plant by spores and the appearance of visible signs lasts from a week to a month, depending on the temperature and humidity. The plant may already be infected, but the signs may not be immediately noticed. Because in the early stages, subtle white dots appear on the leaves. And only over time, as the fungus matures, the dots acquire a characteristic brown-red color and become noticeable. New spores ripen in them, which are carried by the wind and infect new plants.
The garlic leaves themselves turn yellow and dry out prematurely. When growing bolting varieties of garlic, similar symptoms develop on the stem. But at the same time, when a rust disease occurs, neither the stems nor the garlic itself rots.
At the end of the growing season, black pads with overwintering spores appear on the affected leaves. Look at the photo to see what rust looks like on garlic.
Externally, diseased garlic looks like this:
- in a diseased plant, the tips of the feathers turn yellow and at the same time wither;
- Although the root system on a diseased plant does not rot, it still noticeably lags behind in its development.
The main causes of diseases in garlic
Factors provoking the development of garlic crop diseases:
- increased/lowered air and soil humidity combined with increased/lowered temperature;
- non-compliance with crop rotation rules;
- poor quality processing after harvesting;
- neglect of preventive treatments of soil and seed;
- improper storage of crops;
- watering with contaminated water;
- thickening of plantings.
Did you know? In ancient India, garlic was used as an external medicine. It was not used for food because of its spicy smell and taste.
Many diseases can be carried on the legs of insect pests and by wind from neighboring areas.
What harm does rust cause to garlic?
When the infection is widespread and not detected in time, the size of the bulb and its quality are noticeably reduced. The harm lies in the fact that photosynthesis is significantly reduced in leaves covered with fungal spores. In other words, the exchange of nutrients between the root and the green part of the plant decreases. As a result, due to lack of nutrition, the growth of the garlic head itself slows down.
However, cloves of garlic that have been damaged by rust remain edible. Remember that mushrooms live and develop only on living plants, so spores are not preserved in garlic left for winter storage, which is very important. This means that the seed remains uninfected with fungi.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of this disease are quite vivid and specific; it is difficult to confuse it with any other disease in principle. But the symptoms may still vary slightly. This is due to the fact that garlic rust can be caused by several types of microscopic fungi within the same genus.
These are Pucinia porri, Pucinia allii and Melamsora allii-populina Kleb.
Thus, the first two types are among the most widespread. They are more common. They manifest themselves in the form of oval, light yellow pustules protruding above the surface of the affected plant tissue, which darken as they mature, acquiring a bright brown color (“rusty beads”). Upon inspection, the rust is clearly visible. The size of the pustules is not significant, but is clearly visible to the human eye. They can be located either in separate groups or along the veins of plant leaves in the form of a chain. They contain the maturation of fungal teliospores, which are released over time by air currents and spread to other plants. Rust affects only the above-ground part of the crop, namely the stems and leaves.
The last type differs only in that rust manifests itself in the form of bright orange pustules, which are located on the primary light yellow pads on top, forming a layering, which is what differs from the first two types. This kind of rust is much less common.
Over time, damage to garlic by rust leads to loss or reduction in yield. The harmfulness of the disease lies in the premature death of leaves, which leads to a decrease in the accumulation and outflow of plastic substances from them to the head of garlic. As a result, it turns out to be small and underdeveloped. Such plants are greatly weakened and are more susceptible to secondary infections, both in the garden and during storage. They are affected, for example, by rot, mold fungi and other diseases. In this case, the question also arises of what to process. During storage, in storage areas, it is better not to do this. The best option is preliminary (before storing all vegetables and fruits) fumigation of such a room using smoke bombs. Dry the garlic itself in a sunny place for a few more days after that.
Ways to combat rust on garlic
To notice the disease in the early stages, garlic plantings are checked regularly once a week. Carefully inspect the feathers of plants to spot early signs of rust.
If you see small white dots on the leaves during inspection, immediately begin treating the garlic. But provided that there are 3-4 weeks left before harvest. If the harvest is 1-2 weeks away, it makes no sense to treat with fungicides.
- First of all, remove diseased leaves from the plant, remove them from the site, or better yet, burn them;
- Treat the plants with sulfur-containing fungicides - Strobi, Topaz, or use the modern, most effective fungicide Quadris. The drug shows the most consistent results in the treatment of rust on garlic.
- The preparations Alirin-B and Gamair will not only help cure plants from rust, but will be effective in treating such a dangerous disease of garlic - downy mildew.
When using fungicides, they should be diluted strictly according to the instructions. Plants are treated with the prepared solution on the same day, without delaying treatment until later. Treatment will stop the formation of spores and reduce the risk of infection of new plants. Repeated treatment is carried out after a week.
General protective measures (prevention)
Garlic diseases, like any other diseases of other plants, are a key problem for gardeners. Because in this case, you can lose a significant share of the harvest. And in some cases, almost the entire harvest. You can read more about garlic here in the article.
And to prevent this from happening, you need to see the problem in time and take action. It’s even better if these problems are prevented in advance. This is done through proper agronomic practices. For example, observing crop rotation, choosing a good place for garlic, preparing cloves for planting, preventing diseases, and proper care.
Later in the article, we will consider all these techniques in more detail and in order. And we will try to understand what to prevent the disease
much easier than curing it later. And this is the key point. Let's go?
Place for garlic and crop rotation
Garlic diseases will bother you much less if you choose the right place
. This means that the site should be on the sunny side. Also, make sure that our bed is not in a low place, otherwise there will be stagnation of moisture, and as a result the garlic may simply wither away. Also, the acidity of the soil is important, which should be between 6 and 7 pH.
Next, we pay attention to the fertility of the soil and its structure. Here, we make sure to fertilize with organic matter in the fall (and spring too). And make sure the soil is loose.
Crop rotation
, plays one of the main roles here. And here, it is necessary to find good and bad predecessors for garlic. For example, good predecessors include crops such as cauliflower, any legumes, cucumbers, zucchini and melons. Any green manure, proximity to berry crops (any) have a beneficial effect on the plant. All onions are bad predecessors. You can return to this bed no earlier than after 3 - 4 years.
On a note!
When fertilizing the soil with organic matter, we do not forget about mineral fertilizers. Here in the fall, 30 g - 40 g of superphosphate and 15 g - 25 g of potassium chloride are enough. By the way, nitrogen is not applied in the fall, because it is washed away in the spring by meltwater.
Fertilizers for garlic
Garlic diseases can avoid us if the plants are strong and healthy. It's no secret that strong plants usually get sick much less often, or don't get sick at all. Only weak and injured plants become infected.
First feeding
done immediately after germination. Here we dissolve 2 cups of ash in 10 liters of water. We water it.
Second feeding
done 2 weeks after the first. Here, for 10 liters of water take 20 g of urea or ammonium nitrate. Here, we are building up green mass, so we need nitrogen.
Third feeding
needed for the formation of bulbs. Therefore, there is an emphasis on potash and phosphate fertilizers. And here, in 10 liters of water we add 10 g of superphosphate and 15 g - 20 g of potassium chloride.
We read about fertilizing after planting in the ground in this article.
On a note!
3 - 4 weeks before harvesting, it is advisable to stop fertilizing completely. Vegetables must be peeled.
Preparing the Garlic Cloves
Before planting garlic, you need to prepare it. This is necessary in order to disinfect
cloves It's no secret that there may be some kind of infection in the cloves.
Ways
there is a lot of processing of the cloves. For example, they can be treated with solutions of biofungicides Fitolavin, Fitosporin - M, Maxim, Planriz, Gamair. Also, growth stimulants such as Zircon, Cytovit, Biostin are in fashion.
There are a lot of them in the store, so it’s up to you to choose. The main thing is to work with them strictly according to the instructions.
And yet, you can soak the cloves in a solution of potassium permanganate (weak) for 10 - 12 hours. Simple and angry.
In a saline solution, where 3 tbsp. spoons of salt goes to 5 liters of water. Soak for 3 minutes before planting.
Drying the harvest
carefully, otherwise the garlic will quickly begin to deteriorate.
Drying is key and is required after harvest. Also, make sure that the garlic is ripe
, otherwise problems are guaranteed. Most often, sick, injured and undried fruits get sick.
Maintaining optimal conditions
- this is the main thing when storing winter garlic. And here, temperature + 2 °C - 4 °C is considered optimal, while humidity should be within 70%. With other parameters, storage will be much worse.
Spring garlic
It is well stored at a temperature of + 16 ° C - 20 ° C and at a humidity of 70%. And for him, these are the optimal conditions.
Prevention from diseases
You can avoid garlic diseases if you carry out preventive work
s. Agronomic techniques (correct) play a major role.
If there are no particular problems with planting garlic, then it is advisable to use folk remedies for prevention. For example, a solution of shag and hot pepper is used to combat onion flies.
Fungicides can be used when everything is running rough, and simple means will not cope. Here you can use Ridomil, Oksikhom, etc.
About fungicides, read in more detail here in the article.
Storage Processing
should be done before adding any vegetables, and not just garlic. To store garlic, you need dry, well-ventilated rooms. We disinfect them with a sulfur bomb, disinfectin or a mixture of lime and copper sulfate.
Diseased plants
We remove it from the garden bed with a lump of earth (burn it). We spill the places where the diseased plants were sitting with solutions of potassium permanganate or copper sulfate.
Garlic care (correct)
Watering garlic plays a major role because high humidity usually promotes the spread of various infections. But lack of moisture gives garlic a sharper taste. Water the garlic only 3-4 times a month, no more. And before harvesting, 3 - 4 weeks before harvesting, you need to stop watering completely.
After each watering or fertilizing, it is advisable to loosen the soil. Also, don’t forget about weeding. It is important.
Folk remedies for fighting rust on garlic
To prevent the disease or at its early stages of development, gardeners use folk remedies.
- Ammonia . 1 tbsp. l. Ammonia is diluted in 10 liters of water, and the resulting solution is watered at the root of the plant. In addition, in this way you will also carry out nitrogen fertilizing.
- Table salt . Dilute 1 glass of salt per bucket of water, stir well and also water the garlic at the root.
- Tar soap . Grate a pack of soap and dissolve it in 10 liters of water; pour the resulting soap solution over the garden bed with garlic. Instead of bar soap, use liquid tar soap.
When the disease has already developed, in addition to the above fungicides, Bordeaux mixture, copper sulfate, and HOM are used. The products are dissolved and used strictly according to the instructions. The use of products is justified by the fact that they stop the further development of spores and spread to other plants.
Differences in diseases of winter and spring garlic
Spring crops are planted in early spring. They are susceptible to damage to the entire plant by bacteria and viruses. In addition, there is a high risk that spring garlic will be attacked by insects.
Winter crops are planted in open ground in the fall. Therefore, these species have problems when storing seeds. Diseases are mainly caused by fungi.
White rot
- Sclerotinia is most often found among winter crops. This is the so-called white rot. The white mycelium of the fungus is visible on the bulb. When planted, the plant lags behind in growth and quickly turns yellow.
- No less common among winter garlic crops is a disease called fusarium. This is also a fungus. A pinkish coating is visible on the stems. It spreads to the bulb and root. To combat these diseases of garlic (winter), certified fungicides are used.
Fusarium is characterized by a pink coating
Preventive control measures
In order to minimize infection of plantings next year, the following rules must be followed.
- Since spores overwinter only on living plant debris, after harvesting the area should be completely cleared of self-sown seedlings. Then they dig the soil deeply without breaking up the earthen clods. In addition, deep digging will allow onion fly pupae prepared for winter to be thrown to the surface.
- Strictly observe crop rotation. Do not plant garlic in its old place for at least 3 years. Especially where rust was found on the garlic.
- Before planting garlic, treat the soil with Fitosporin, an excellent biofungicide, but do not make the mistake of using it. But keep in mind that the soil is cultivated in the evening or in cloudy weather, since the sun's rays reduce the activity of the product. Before planting, garlic cloves can be soaked for 1-2 hours in a Fitosporin solution.
- Since rust spores are easily carried by wind over significant distances (up to 10 km), there is still a risk of re-infection. Therefore, for preventive purposes, plants are inspected once a week. If you see affected leaves, remove them immediately.
- In cool and humid weather, do not water the garlic in the evening. The leaves will not have time to dry out and will become an ideal breeding ground for fungi.
- Treat young plants in the spring with Quadris, when the air temperature is already above +10ºС. And, of course, such treatment will be required when the first signs of disease are detected on garlic.
- After harvesting, immediately remove all leaves from the garlic, take them out of the area or burn them.
I wish you good harvests!
Garlic turns yellow: what to do?
If the garlic begins to turn yellow, then most often it is fusarium
. The tips of the plant, stem and leaves change color, become deformed and gradually fade. You can see a pink coating on them. Moreover, the bulb loses its roots. Fusarium especially affects garlic, which grows in the southern regions. Crop losses in some cases amount to up to 70%.
What to do if garlic turns yellow due to fusarium? First of all, experienced farmers recommend doing the following:
- use high-quality planting material;
- treat garlic with preparations “Hom”, “Maxim”;
- disinfect the soil with fungicides;
- remove crop residues from the garden bed.
To prevent fusarium from affecting garlic, it is important to carry out a full range of actions: process, promptly get rid of plant residues, store dried tubers in proper conditions.
In the photo there is bacteriosis of garlic
Bacteriosis
garlic causes enormous damage to the crop and degrades its presentation. It affects plants during the growing season, when storing stocks. Cloves infected with bacteria begin to rot and therefore do not sprout. How does bacteriosis manifest itself? Yellow-brown wounds, transparency of the teeth, mucus with an unpleasant odor are some of the manifestations of the disease.
Measures to combat and prevent garlic bacteriosis:
- Maintaining crop rotation.
- Soil treatment with Hom.
- Fertilizing the soil with phosphorus fertilizers.
- Timely removal of plant residues.
- Application of insecticides.
- Compliance with tuber storage conditions.
Mosaic
Garlic is also often affected. You can determine the disease if you take a good look at the photo, and also know the symptoms of the disease:
Mosaic is a virus transmitted by ticks. The infection most often persists in perennial fruit plants and planting material. Initially, the disease manifests itself as a mosaic of the above-ground parts of the plant.
Ways to combat and prevent garlic mosaic:
- Removing affected plants.
- Selection of mother bulbs directly from uninfected plants.
- Vector and weed control.
- Spraying with karbofos.
Video about garlic diseases and the fight against them:
Garlic diseases and the fight against them, photos - those are the issues that interest farm owners. Compliance with the rules of crop rotation, removal of plant residues, weeds, following the recommendations from the article - this is what will help summer residents reap a generous harvest of garlic in their own garden.
Despite the many varieties of diseases and pests in garlic, these vegetables are still resistant to them. But, garlic is occasionally affected by certain diseases and overcome by various insects - pests.
In this case, weakened plants are often attacked simultaneously by several pathogenic microorganisms or pests. To prevent certain diseases of vegetables and attacks by various pests, before planting in a summer cottage, we disinfect the cloves in warm water (45 - 50 degrees) for 15 minutes.
After this, sprinkle them with chalk at the rate of 20 g per 1 kg of garlic. To prevent the spread of diseases, we immediately destroy all diseased plant specimens. To prevent the appearance of certain diseases and pests, we plant garlic in the same place no earlier than 3 years from the previous planting.
Signs and measures to combat garlic diseases
Downy mildew (downy mildew)
Signs: yellowing, brittle leaves of vegetables, with light green spots appearing on them. The causative agent of this disease spreads most actively in damp weather. Control measures: spray garden garlic beds with the microbiological preparation Fitosporin-M (15 ml/10 l of water), 1% solutions of copper oxychloride, Bordeaux mixture or copper sulfate (these measures also help zucchini well) . Warm up the cloves in warm water (50 degrees) before planting for 15 minutes, with further cooling in cold water and drying.
Rust
Signs: yellowish streaks appear on the leaves of garlic, which grow as the disease progresses. After a few days, they become dark and the leaves dry out. Control measures: to obtain a good harvest of vegetables, we use high-quality planting material. We treat the beds with Fitosporin-M (15 ml/10 l of water) and 1% copper-containing solutions of copper oxychloride or Bordeaux mixture.
Cervical rot
Signs: when storing the harvested crop, the neck of the bulb rots. Over time, the vegetable becomes soft and acquires a fetid odor. Control measures: leave only fully ripened and healthy garlic for the winter.
Bottom rot (fusarium)
Signs: Garlic becomes soft and rots during storage. A light coating of fungus is visible on the bottom of the diseased bulb. It is also visible between the scales. Control measures: we use only high-quality planting material.
Before drying the garlic before storage, treat it with Fitosporin-M (1 teaspoon/1 liter of water).
Bacteriosis
Signs: deepened stripes and ulcers form on the cloves of vegetables, running from the bottom to the top of the clove. The fabrics acquire a pearlescent yellow color. Penicillin fungi actively multiply in the affected areas of the plant.
When storing crops, bacteriosis often affects poorly ripened and under-dried garlic. Control measures: before planting, pickle the cloves for 5 - 10 minutes in a salt solution (3 tbsp/5 l of water), and then in a solution of copper sulfate (1 tsp. l./10 l of water). We remove garlic only when it is fully ripe. During storage, we regularly sort through the crop, removing diseased heads.
Penicillosis (green mold)
Signs: This fungal disease affects the heads during storage. At the same time, watery spots appear on the bottom and outer scales of the bulb. The cloves wither and turn yellow.
Over time, the affected tissues become soft and become covered with a white-green coating. Control measures: we remove the bulbs affected by the disease in a timely manner, since the fungi released from them will infect the rest. We observe normal storage conditions for garlic. Dry the vegetables thoroughly before storing them.
White rot
Signs: with this disease, caused by fungi, the leaves turn yellow, starting from the tip, and then the plant dies completely. Control measures: we plant only high-quality planting material at the dacha. Leave only fully ripened garlic for storage.
Aspergillosis (black mold)
Signs: in rooms with a temperature of 18 - 25 degrees, black mold appears on garlic. Diseased vegetable heads rot and a black spore mass is released from them. Control measures: we harvest only after the crop has fully ripened. Before storing, dry the plants well in the sun.
Mosaic
Signs: This dangerous disease, caused by a virus, is manifested by the formation of elongated spots on the leaves of garlic. Often the leaves become corrugated. Control measures: for planting we use only high-quality planting material. We regularly control pests.
We burn plant specimens affected by the mosaic. We follow the rules of crop rotation.
Signs and measures to control garlic pests
Stem nematode
Signs: This small pest is very dangerous. Plant specimens damaged by it turn yellow and dry out over time. The head becomes loose and wet. It has a very unpleasant smell.