Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse allows you to get a harvest much earlier than in open ground. But this process is fraught with certain difficulties. After all, greenhouse conditions are an ideal environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. And if certain preventive measures are not followed, gray rot appears on cucumbers. If the fight against this fungal disease is not started in a timely manner, the harvest will be very modest.
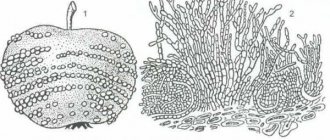
Gray mold can lead to the death of all plants in a greenhouse
Causes of gray rot
Certain conditions are necessary for gray rot to develop. The disease begins to progress at a temperature of +16-18 ° C and high humidity of about 90%. First of all, pathogens attack weakened cucumbers.
Factors contributing to the further spread of gray mold in the greenhouse:
- dense plantings;
- sharp changes between day and night temperatures;
- non-compliance with crop rotation rules;
- watering with cold water;
- excessive moisture;
- high levels of nitrogen in the soil;
- insufficient ventilation of the greenhouse;
- untimely removal of plant residues.
Important! When the temperature rises to +25-27 °C and the humidity sharply decreases, the pathogenic microflora stops its development, but does not die, but waits for favorable conditions.
Treatment and control measures
At the first signs of disease, stop watering and fertilizing until the cucumbers are processed. The greenhouse is ventilated. All plants are inspected.
Plants with minor stem damage can still be saved. The main control measures include cutting off the infected areas to healthy tissue, and smearing the stem with paste.
To do this, mix the drug “Rovral” or “Sumilex” with powdered chalk 1:1 and add warm water to form a thick paste. An alternative is wood ash and copper sulfate (200 g/5 g). To fix the solution on the stems, add a little CMC wallpaper glue.
Cut off all affected leaves and fruits, sprinkling the wounds with wood ash, chalk powder, crushed coal or lime powder. If the plant is severely affected, it is removed along with the earthen clod. Before planting another plant in this place, the hole is spilled with a 0.1% solution of the drug "Rovral" with a consumption of 0.5 liters.
The soil under the plants is cleared of fallen leaves and stems, the surface layer (2-3 cm) is replaced with a new one, and generously sprinkled with wood ash. All plant residues are burned off-site.
Next, the plants are treated with fungicides. Minor lesions in the first stages of infection can be treated with biological drugs and folk remedies. They are also indispensable during the fruiting phase of cucumbers, when chemicals cannot be used.
If the damage is widespread and there is a threat of epiphytotics throughout the entire garden plot, chemicals are used. They can only be used during the growing season 20 days before fruiting.
Causative agent of gray mold
The causative agent of gray rot is the fungus Botryotinia fuckeliana. It feeds not only on living cucumber cells, but also on dead organic matter. The causative agent of gray rot overwinters on plant debris in the soil and greenhouse structures. And with the arrival of spring warmth, its life cycle resumes.
The pathogen enters through microwounds on the shoots and leaves of cucumbers. It is also capable of penetrating flowers through the pistils and causing the ovary to rot. Having settled in the tissues of cucumbers, the fungus begins its destructive activity. It releases toxins that cause cell death and disrupts metabolic processes. Subsequently, the affected areas become a breeding ground for the development and reproduction of the fungus. At the end of the growing season of the crop, the pathogen, along with plant debris, enters the soil, where its mycelia and sclerotia overwinter.
How to fight
When the first signs of the disease are detected, it is necessary to stop watering and fertilizing, ventilate the greenhouse and carefully inspect all cucumbers.
Diseased leaves should be removed, and severely affected plants should be torn out and burned. This is necessary to prevent the fungus from spreading to other crops.
Then you can use various methods at your discretion.
Agrotechnical techniques
Seedlings with signs of gray rot are usually immediately destroyed. Of course, I want to save adult plants. To do this, make healthy pruning: the lower leaves are cut off and laid on the ground, sprinkled with soil with Trichodermin on top.
It is also very useful to add peat, ash, chalk or sawdust to the top layer of soil around infected cucumbers. They need to be brought in to a depth of 4-5 centimeters. You just need to do this carefully so as not to damage the root collar.
Ready-made drugs
Modern means of combating diseases are very effective and can destroy the fungus quite quickly. But chemicals can also cause some harm: disrupt the soil microflora, burn the plant, etc. Therefore, you must strictly follow the instructions on the packaging.
Proven chemicals:
- "Hom" is copper oxychloride.
- "Rovral" - contains 50% iprodione.
- "Euparen multi" is a moderately toxic fungicide.
- Tetramethylthiuram disulfide.
Biological drugs:
- "Koniotirine."
- "Trichocin."
- "Trichodermin."
- "Glyocladin."
Note : Biological drugs should be stored in a cool place, otherwise they may lose their medicinal properties. They contain beneficial fungi that penetrate the mycelium of harmful formations and destroy it.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies are less effective, but safer. They are suitable for the initial stage of the disease. To treat severely affected cucumbers, it is better to choose store-bought preparations. Before using any of the products, you must add 40 g of laundry soap to it for better preservation on the surface of the plant.
Here is a list of the most effective compounds:
- 10 ml of greenery, 10 liters of water.
- 1.5 g of potassium permanganate, 10 liters of water.
- 10 g of boric acid, 30 drops of iodine, 1.5 g of potassium permanganate, 10 liters of water.
- 1 liter of milk, 30 drops of iodine, 10 liters of water.
- 50 g of soda ash, 80 g of copper sulfate, 10 liters of water.
- 5 liters of whey, 5 liters of water.
- Pour 300 g of wood ash into 3.5 liters of water and boil for 15 minutes. Add water to a volume of 10 liters, let it brew for 4 hours, filter.
Folk remedies should be used 4-5 times every 5-7 days.
Signs of gray rot on cucumbers with photos
The first signs of gray rot damage to cucumbers begin to appear seven days after the pathogen penetrates the plant tissue. It is at this stage of the development of the disease that it is important to promptly identify the lesion and carry out treatment. In this case, the chances of saving the future harvest are quite high.
Since the pathogen overwinters in the soil, the first signs appear in the lower part of the plant
First, you can detect a gray coating on the leaves and at the base of the shoot of cucumbers. As the disease progresses, spots with jagged edges of a yellowish-brown hue appear on the affected areas. Subsequently, they increase in size and merge. As a result, the disease rises up the stem, affecting not only the leaves, but also the flowers and the ovary of cucumbers.
Fungal spores appear on the affected areas, which spread to all crops in the greenhouse. At this stage, it is much more difficult to resist gray rot.
How dangerous is the disease?
After infection, the fungus begins to germinate, increasing its mycelium more and more. At the same time, toxic enzymes are produced that spread throughout the plant. Neighboring healthy tissues also begin to become stained and rot.
If the stem is affected, the flow of water through the vessels is disrupted, and the cucumber experiences an acute lack of nutrients and moisture.
Gray rot causes cucumbers to significantly reduce their yield. With severe damage, the plant dies completely.
Preventive measures
To avoid having to deal with gray mold later, you must adhere to certain rules of prevention. This cannot completely eliminate the possibility of damage, but it can reduce it to a minimum.
Preventive measures:
- timely removal and burning of plant residues after harvesting;
- compliance with crop rotation;
- planting cucumbers in a greenhouse at a distance of 20-25 cm;
- mandatory tying of shoots to a support;
- pre-sowing treatment of seeds and soil with fungicides;
- regular ventilation of the greenhouse;
- watering with settled water, the temperature of which is not lower than +18 ° C.
Processing rules
It is very convenient to use a pump sprayer for processing cucumbers. It allows you to spray the solution evenly and control its quantity. It is advisable to use protective gloves and a respiratory mask. Clothes must be closed.
It is better to carry out treatment early in the morning or in the evening (before dew falls and after it subsides). It is important that the solution remains on the surface of the plant for at least 2 hours. For this purpose, choose a dry and windless day.
Spray the cucumbers from bottom to top at a distance of 15 cm. The soil should also be sprayed.
Prevention
The disease cannot always be cured, so everything possible must be done to prevent the causes. To do this, you need to regularly change the place where cucumbers are planted, observing crop rotation, removing the remains of the previous harvest, digging up the soil, cultivating it, and caring for the greenhouse. Following simple rules will help you not to remember the disease throughout the season.
Seed treatment
The first cause of root rot is infected seeds. Pathogens may be dormant and when they enter the soil they will begin to actively attack the roots. Disinfect the seeds with a solution of potassium permanganate or Fitosporin before planting as seedlings or in a greenhouse. Additionally, you can dip them in a growth-stimulating drug: this will make the first shoots appear faster, and the entire cycle will be shortened by several days.
The soil
Harmful microorganisms are often found in the soil, from where they move to plants. Therefore, soil preparation is a mandatory stage in growing cucumbers. Maintain crop rotation so that the soil does not lose its properties: cucumbers cannot be grown in one place for a long time. For disinfection, use a solution of copper sulfate in a ratio of 0.3:10. Treatment is carried out 7 days before planting. The soil needs to be renewed every season. You can leave the old one, but then it needs to be disinfected and saturated with minerals.
Important!
Loosen the soil regularly to improve soil aeration. When it stagnates, the risk of root rot increases.
Greenhouse care
Root rot affects crops in greenhouses due to the fact that a special microclimate is formed there. Harmful bacteria can remain not only in the soil, but also on the walls of the room, quickly spreading to plants at the first opportunity. The greenhouse must be cleaned after each season:
- treat all indoor structures with copper sulfate solution;
- treat metal parts with disinfectants or laundry soap;
- clear the soil of previous plants;
- Rinse walls and windows with a disinfectant solution.
The causative agents of viruses and diseases that affected plants last season may be in the soil. Treat the soil with a disinfectant, and before planting the plants, fill the beds with fertilizers: otherwise the cucumbers will have nothing to eat.
Plant treatment
The occurrence of the disease can be prevented by preventive measures. Treat plants in advance to avoid the problem. For this, a solution with an antifungal biological product or a composition of several components, which you can prepare at home, is suitable:
- copper sulfate;
- zinc sulfate;
- superphosphate.
You will need 2 teaspoons of superphosphate, one teaspoon of the remaining ingredients. Dissolve all components in a bucket of warm water and water the bushes at the roots once every two weeks, without mixing with other drugs or fertilizers. Each square of plantings should require 5 liters of the resulting solution.
Planting scheme and care
In addition to crop rotation, planting density must also be observed. If the plants are too close, their root systems will touch each other. The causative agents of the disease can migrate from bush to bush. The optimal number of bushes per square is 3-4 pieces. Place them in a crowd, but so that there is space between the rows. If you notice that the plants do not have enough nutrients, the planting may be too crowded. If you follow the basic rules for caring for cucumbers, you don’t have to worry about root rot.
- Water the plants only with warm water.
- Maintain an optimal humidity of 70-80% for cucumbers in the greenhouse.
- Inspect the plants to identify signs of rot in time.
- Promptly remove bushes that are too severely affected to treat.
- Control the moisture level so the cucumbers are hydrated, but not too hydrated.
- Protect crops from temperature changes.
You may be interested in:
How to feed cucumbers - in open ground, after planting and when? In any garden plot, gardeners cannot do without cucumbers, which have gained their popularity thanks to their special...Read more...
Mulching the soil will help maintain an optimal environment during cold weather. This will reduce the number of waterings, saturate the soil with useful substances and retain heat so that the cucumbers can grow even in cool weather.
Root rot in cucumbers develops in cold, damp conditions due to the causative fungus. To prevent the occurrence of the disease, you must follow all care recommendations. Regularly change the planting site and renew the soil. Maintain the desired climate in the greenhouse. You can fight root rot with chemicals, biofungicides or folk remedies, but all methods are effective only in the initial stages. You need to take action as soon as you notice that the plants’ leaves are turning yellow or rotting areas have appeared.
Which varieties are most susceptible to disease?
The varieties that are most resistant to white rot are Zozulya, Improved Telegraph, Claudia, Konny, and Sportresisting. Such varieties as Graceful, Makhaon, Izumrud, Regia, Farmer, etc. are more actively affected by sclerotinia than others.
As you can see, in order to get a good harvest of cucumbers you need to protect the bushes of the crop from diseases, in particular from sclerotinia. Neglecting the symptoms of white rot can lead to the death of cucumber plants, so if you notice that the tops of the bushes have begun to fade, immediately begin measures to combat sclerotinia.