In greenhouses and open ground, tomato bushes are often affected by diseases. Some of them carry pests, while others attack plants due to non-compliance with agricultural practices or the consequences of unfavorable weather.
Any of these reasons can have dire consequences for your crop. Therefore, it is so important to identify the disease in time and begin treatment. Of course, this is not so easy to do in the field, because many pathogens are perfectly camouflaged. But we hope that detailed descriptions and photographs will help you navigate.
Below we will look at the most common signs of fungal, viral, bacterial and some other diseases that can attack your beds. We will also present measures to combat them.
When using chemicals, remember that tomatoes can be eaten only 3-4 weeks after the last treatment.
Brown spots on leaves, stems and fruits of tomatoes
Brown necrosis with a light edge forms on the leaves and stems. A whitish coating is noticeable on the reverse side of the leaf blades in humid weather. The plant dries out. The inside of the fruits becomes covered with brown spots and rots.
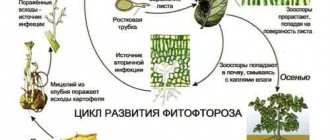
Diagnosis: late blight of tomatoes is a fungal disease caused by microscopic fungi Phytophthora infestans.
The disease becomes more active in damp weather, and is especially dangerous in the second half of summer, when night temperatures become much lower than daytime readings. Fogs and dew also influence the development of the disease. At risk are tomatoes in open ground and film greenhouses without heating. After the leaves and stems are damaged, late blight spreads to the fruits and makes them unfit for consumption. If signs appear at the beginning of the growing season, complete loss of the crop is possible. The disease spreads very quickly, especially in humid weather.
Phytophthora also affects potatoes, eggplants, sweet peppers and other nightshades.
Control measures. To prevent the appearance of late blight, spray the plantings with Abiga-Peak, Consento, Revus or other fungicidal preparations. Repeat the treatment every 10 days. If the bushes are severely damaged, use Kuprolux or Famox fungicides. Just before ripening - biological products Fitosporin-M and Gamair. If the fruits begin to turn black, remove the remaining unripe tomatoes and place them in hot water (50°C) for a minute. Then dry and put in a box for ripening.
- Effective folk remedies for late blight on tomatoes and potatoes
The fight against late blight is not an easy task. How to protect tomatoes and potatoes from this disease?
Tomato diseases of fungal origin
Fungal infection is carried out with the help of microscopic, phytopathogenic fungi. And, these fungi, in turn, infect not only tomatoes, but also other vegetable crops. It all depends on the specialization, which can be narrow or broad. Let me explain that with a narrow specialization, only certain crops can get sick. And when spread widely, many crops become infected.
Excess humidity helps these pathogens spread in the first place. And yet, this can only be dealt with in the initial stages of the disease. Usually, if the matter has taken on an avalanche-like character, it will no longer be possible to do anything.
Various preventive measures when growing tomatoes (and not only) can help you first. For example, compliance with crop rotation, temperature and humidity conditions. Also, the pre-sowing preparation of seeds and soil is very important.
Alternaria or macrosporiosis (brown or dry spotting)
Typically, excess humidity primarily affects the development of the disease. Consequently, greenhouses and various film shelters are the first to fall into the risk zone. The main thing here is to maintain the required level of humidity. And this is easily done with the help of ventilation.
The first signs of tomato disease due to Alternaria blight:
- Brown spots on the lower leaves (initial stage).
How the infection process occurs:
- Excessive humidity and high temperature in the greenhouse contribute to the development of the disease.
- Infected seeds
How to prevent trouble in advance (prevention):
- We buy healthy seedlings or grow them ourselves.
- Pre-sowing preparation of soil and seeds is mandatory . Disinfection of seeds and disinfection of soil using a solution of potassium permanganate. We soak the seeds and spill the solution on the soil. Also, the seeds can be treated with fungicides such as “Albit”, “Baktofit”, “Maxim”, “Planriz”, “Fitosporin - M”.
- Cultural turnover. After tomatoes, you can plant tomatoes only after 3 - 4 years.
- Grow varieties and hybrids resistant to Alternaria. For example: Sanka, Nadezhda F1, Lyana, Golden Bullet, Alex F1, Aurora F1.
- We maintain humidity at the proper level (don’t forget to ventilate). Moderate watering.
- The garden beds are clean. We remove (burn) plant residues.
If, nevertheless, infection occurs:
- At the initial stages, we use biological drugs. For example: Trichodermin, Fitolavin, Fitosporin-M, Alirin B.
On a note!
All working solutions are usually prepared immediately before use and always according to the instructions. By the way, tomato diseases, if they are neglected, cannot be cured for sure. Remove the sickest ones and treat others.
- If everything is serious, then you cannot do without chemicals. For example: Skor, Quadris, Ditan, Acrobat, Title, Phital, Metaxil.
We work with chemicals strictly according to the instructions.
Late blight (late blight)
This is probably the most common disease for tomatoes (and not only). The infection is transmitted through fungal spores. Fungal mycelium can be present in the soil, on plant debris, and on garden tools. It winters well, and in the spring, under favorable conditions, it wakes up. Typically, this scourge appears in the second half of summer, when temperature differences between day and night are greatest.
Symptoms of late blight:
- Brown spots on the bottom of the plant.
- In damp weather, the leaves seem to be covered with a light film.
- The inflorescences dry out and fall off.
- Subsequently, gray-brown spots form on the fruits.
On a note!
Any tomato diseases, including late blight, usually develop very quickly. Therefore, it is advisable to notice the enemy in time.
How to get hooked:
- Large temperature changes.
- Dense plantings, poor ventilation.
- Abuse of nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
- Lack of microelements. For example: potassium, iodine, copper, manganese.
How to prevent disease (prevention)
- Maintain the required temperature and humidity conditions.
- Avoid the proximity of other nightshades.
- Prophylaxis with the use of biological drugs according to schedule.
How to fight if necessary:
- By chemical means
. For example: Hom, Furacilin, Fitosporin, Trichopolum or metronidazole, Ordan
Fighting with folk remedies:
- Lactic acid products
. Whey and kefir. The whey is mixed 1 to 1 in water. For kefir, take 1 liter of kefir per 10 liters of water. By the way, instead of kefir, you can use milk, to which we add 20 drops of iodine. - Soda
. For half a bucket of water, add a tablespoon of soda and add soap for adhesion. - Salt
. Here, 250 grams of salt are placed in 10 liters of water. - Vinegar
. We dilute half a glass of vinegar (9%) in a bucket of water (10 l). - Toothpaste
. Tube for a bucket of water. - Garlic infusion
. 1.5 cups of crushed arrows and heads per 10 liters of water (1 bucket). We insist for a day. - Hot water
. Water with hot water. By the way, at +30 degrees the spores die. - Ash
. 5 kilograms of ash are diluted in 10 liters of water. Insist for 3 days. Strain and spray. - Yeast
. 100 grams of yeast per 1 bucket of water. - Rotten hay
. 1 kilogram of hay per 10 liters of water and 100 grams of urea. We insist for 3 days. - Iodine
. 20 drops per bucket of water. Can be used in combination with other recipes (kefir, milk, ash). - Hydrogen peroxide
. 2 tablespoons per 1 liter of water.
Cladosporiosis or brown spot of tomatoes, treatment
A fungal infection that easily lives in the soil and beyond. Vitality is the worst quality of almost all fungi. And therefore, they winter well almost anywhere and survive.
Also, I would like to note that it is almost impossible to cure tomato diseases, and cladosporiosis is no exception. Premature prevention is the best thing you can do. These are constant inspections and preventive spraying.
Symptoms of cladosporiosis:
- Yellow-green spots on the lower leaves, which then turn brown.
- Terry coating on spots.
Main causes of the disease:
- Greenhouse climate
. Failure to comply with temperature and humidity conditions, dense planting patterns, poor ventilation. - Seeds
. Infected untreated seeds. - The soil
. Undefeated soil in a greenhouse.
Prevention of cladospora:
- Cultural turnover
. Tomatoes, after tomatoes, can only be planted after 3 - 4 years. - Seed and soil treatment
. Pre-sowing preparation of tomato seeds in a greenhouse. Disinfecting the soil in the greenhouse and generally fumigating the entire greenhouse. Phytosporin will come in handy for this purpose. We spill the solution on the ground. - Humidity level
. Here, we completely control the humidity. At the same time, water moderately, ventilate and make sure that there are no thickened plantings. - Cleanliness in the greenhouse
. At the end of the season, we remove all plant debris. - Variety selection
. We select varieties and hybrids resistant to cladosporiosis. For example: Our Masha F1, Titanic, Centaur, Victoria, Red Comet.
The best folk recipes for cladosporiosis:
- Iodine chloride
. 45 drops of iodine and 30 grams of potassium chloride per 10 liters of water. Spray and water the tomatoes well. - Potassium permanganate
. We spill a weak solution. We alternate with the ash solution. This is useful. - Garlic
. 0.5 kilograms per 10 liters of water. In this case, you can add 20 - 30 drops of iodine. - Serum
. We aim 1 to 10, and it is also useful to add 20 drops of iodine.
Chemical control:
- Chemistry with a wide spectrum of action
. Copper oxychloride, Bravo, Ditan NeoTek 75, Azofos, Abika-pik. Such drugs are used only in the initial stage. - Directional fungicides
. Khom, Polykhom, Polyram, Tsineb, Kaptan. We work strictly according to the instructions. - Fitolavin
. Here, with large foci of infection. We also read the instructions. - Bio Means
. Pseudobacterin-2, Strobi, Fitosporin. By the way, they are safe for humans.
Septoria, white leaf spot
A fungus that reproduces only in high humidity conditions. Where, the optimal temperature for this is 20 - 25 degrees with a humidity of 80 - 100%.
Note that tomatoes in open ground are mostly affected by this disease. And the disease spreads very quickly, just like other tomato diseases. If other nightshades grow nearby, then there is a possibility of infecting each other.
What does septoria look like:
- Whitish spots on lower leaves. Which are subsequently covered with a gray coating.
Causes of septoria:
- High humidity.
- Lack of prevention.
Preventive measures against septoria:
- Processing of seed material
. Mandatory pre-sowing preparation of seeds. - Crop rotation
. We choose the right predecessors. - Varieties and hybrids resistant to septoria. For example: Horeb, Golden Fleece, Beryl F1.
- Air humidity
. Here, moderate watering, planting density, ventilation. - Plant inspections and weeding
. We inspect the field and remove plant residues in a timely manner.
Chemical agents for the treatment of septoria:
- Fundazol, Revus, Ordan, Thanos, Bordeaux, Hom, Kuproxat.
Biological remedies for septoria:
- Planriz, Fitosporin M, Alirin B,
On a note!
Soap can be added to all solutions for better adhesion to plants.
Gray rot
Fungal infection, where the working temperature for pathogen development is +3 - 42 degrees. In addition, it forms sclerotia, which remain viable for 2 - 3 years. But this only happens under unfavorable circumstances.
The spores overwinter on plant debris, just in the ground, or on garden tools. Transmitted by air and by water (during watering). Under favorable circumstances, they reproduce very quickly. Therefore, the disease must be detected in time. Otherwise, you can lose a healthy harvest.
Symptoms for gray mold:
- Grayish spots similar to ash dust. Then, the spots become terry, and then soften and die.
Causes of infection:
- High humidity. Incorrect watering. Thickened plantings.
- Crop rotation was not observed.
- Infected seeds and soil.
- Excess nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
Preventive measures against gray rot:
- Maintaining crop rotation
. We choose the right predecessors. And I would also like to note that tomatoes after tomatoes can only be planted after 3 - 4 years. The earth stores fungal spores for a long time. - Resistant varieties and hybrids to gray rot
. No completely resistant varieties or hybrids have yet been developed. But still, there are some hybrids that can more or less resist gray rot. For example: Pilgrim F1 and Vasilyevna F1. - Humidity regime in the greenhouse
. Here I would like to note several important points. For example, timely ventilation, moderate watering, correct planting scheme. - Treatment of seeds and soil before planting
. Here, before planting, we spill the soil with a solution of potassium permanganate. And we subject the seeds to pre-sowing preparation, if they are not store-bought. Seeds from the store are usually ready to eat. - Keeping the greenhouse clean
. This means cleaning up plant residues and timely weeding. - Helpful neighborhood
. Nearby you can plant marigolds, marigolds or mustard. These plants secrete substances that kill fungal spores. - Water carefully
. We carefully ensure that moisture does not get on the leaves. Otherwise, there may be burns. - Clean Plant Shaping Tools
. Indeterminate tomatoes need to be shaped and this requires clean, sanitized tools.
Prevention of gray rot with chemicals:
- Can be used
. Ditan M-45, Bordeaux mixture, Profit, Integral, Skor, Fundazol. - Special paste
. Proportions: 300 grams of CMC glue and 30 grams of any fungicide per 10 liters of water. And to make a paste, you need to add chalk to the mixture. Then, coat the affected areas.
Control by biological means:
- Drugs are used
. Trichodermin (suspension, lubricate sore spots), Glyocladin.
On a note!
Typically, biological drugs are used for prevention or for tomato diseases in the early stages.
Using folk remedies for gray rot:
- Soap solution
. Spray with a solution of green garden soap. - Boric acid
. Spray the 1% solution. - Baking soda
. 80 grams of soda per 10 liters of water.
Brown rot (fomoz)
Fungal infection on tomato plants. At the same time, brown spots appear on the fruits in the area of the stalk.
Signs of Phomasis:
- Small spots on leaves
. The spots can vary in color from brown to black. - The fruits have dark spots in the stalk area.
Causes of Phomasis:
- Temperature difference.
- Infected seeds.
- High humidity and poor ventilation. And thickened plantings.
Worth remembering!
What, fungal spores can be everywhere: in the ground, on plant debris, on garden tools, on seed material.
How to avoid Phomasis (prevention):
- Cultural turnover
. Here, we select good predecessors. And also, don’t forget about the neighbors. For example, other nightshades nearby are bad. - Disinfection of seeds and soil in a greenhouse
. In our case, there should always be pre-sowing seed disinfection. And also, every spring we water the soil in the greenhouse with a solution of potassium permanganate or fungicide. - We choose varieties and hybrids resistant to brown rot
. For example: La Boheme, Blitz, Opera F1, Spartak F1 and Virtuoso F1. - Optimal humidity
. This includes moderate watering, ventilation, and planting density. Here, make sure that water does not get on the leaves.
Chemical means of protection:
- For example: Fundazol, fungicide Previkur, Fitosporin, Thiovit Jet, Ridomil, pharmaceutical Trichopolum, copper sulfate, Switch, Bordeaux mixture, copper oxychloride.
Folk remedies:
- Garlic infusion. 1.5 cups of garlic per bucket.
- Dairy products. Kefir, milk, whey. You can add 20 drops of iodine everywhere.
- Ash solution.
Blackleg
A fungal infection that affects the root system. In this case, subsequently the lower part of the stem dies and the plant lies down.
Signs of blackleg:
- The bottom of the stem dies and the plant lies down.
Root causes of blackleg disease:
- Failure to comply with temperature and humidity conditions.
Here, excess humidity, lack of ventilation and temperature changes usually lead to disastrous consequences. - The soil was not disinfected in the spring.
Preventative work to prevent illness:
- Soil disinfection
. In the spring, we spill the soil in the greenhouse with a solution of potassium permanganate or fungicide. For example, Benomyl 500, Fundazol. - Optimal humidity
. In our case, the main thing is moderate watering and the correct planting pattern (not thickened). Also, do not forget about the ventilation of the greenhouse. - Disinfection of seed material
. Pre-sowing preparation of seeds in the spring should be mandatory.
Fighting with chemicals:
- Previkur
. 15 ml per 10 liters of water. - Fundazol
. 10 grams per 10 liters of water.
Biological products:
Baktofit
. 3 ml per 1 liter of water.
Planriz (0.1%)
. 100 ml per 10 liters of water.
Fitosporin
. Powder 1.5 grams per 1 liter of water.
Fitolavin
. 2 ml per 1 liter of water.
Trichodermin, Trichophyte
. 200 grams per 10 liters of water.
Small spots on leaves, dark sunken spots on tomato fruits
Spots up to 1.5 cm in length are noticeable on the leaves and stems, sometimes with a black coating. Lesions most often form along the edges of the leaf. Then the spots increase in size and merge. The stems crack and the fruits become pitted with dark, dry spots.
Diagnosis : Alternaria blight, or dry spot, of tomatoes - a fungal disease.
Alternaria blight attacks plants immediately after planting tomato seedlings in open ground or a greenhouse. The fungus loves dry and hot weather, so it is especially dangerous for plants in glass greenhouses and film greenhouses. All parts of the bush are affected, and in the absence of treatment, yield losses amount to up to 85%. Fruits from infected bushes cannot be stored. The disease is easily transmitted to potatoes, and vice versa, so it is better not to plant them next to tomatoes.
Control measures . Spray the affected bushes with a 0.4-0.5% solution of Ordan. The following fungicides have also proven themselves in the fight against Alternaria: Profit Gold, Skor, OxyHOM, Proton. Carry out the treatment according to the instructions every 7-10 days until the signs of the disease disappear.
Other causes of fruit spotting
In addition to white, dry and brown spots, as well as blossom end rot, tomatoes are susceptible to other ailments, the main symptom of which is various dents or specks. You should be wary if you see:
- silvery spots on leaf blades;
- a yellow or green mark near the stalks.
Such symptoms do not indicate a tomato disease. The reasons lie elsewhere. For example, silver spots occur due to sharp temperature fluctuations, when it is very hot during the day and cold at night. Another reason is genetic changes. They occur in tomato hybrids that were poorly processed during the selection process.
A yellow or green spot in the area of the stalk may be a varietal feature of a particular type of tomato. It is believed that uneven coloring is characteristic of fruits with a high sugar content. Another reason is exposure to high temperature. Due to intense heat, the pigment of tomatoes literally burns out in the sun. Therefore, during the growing process, shade your plantation if you want to get evenly colored fruits.
Attention! Another version of the appearance of yellow-green spots on tomatoes is a lack of phosphorus and potassium.
Round brown spots with dark edging on tomato leaves
Small watery spots appear on old and then young leaves. At first they are not very noticeable, but then they turn white and become covered with a brown edging. The rest of the leaf turns yellow and dries out. The fruits are small and flaccid. Young leaves at the top of the bush are rarely affected.
agroflora.ru
Diagnosis : septoria, or white spot, of tomatoes - a fungal disease.
Most often, the disease affects plants in open ground. Foci of septoria can also occur in a greenhouse with high humidity. The fungus spreads from the lower leaves and base of the stem higher and higher, damaging young leaves, shoots and flowers. As a result, the bush is forced to spend energy on restoring green mass, and not on setting fruits and their ripening. Fungal spores quickly spread throughout the garden bed. High humidity, heat, and windy weather contribute to the reproduction and dispersion of the pathogen.
Control measures . At the initial stage of infection, it is important to remove the affected leaves so that the spores are not scattered with the wind to other plants. If the bush is completely affected by septoria, it is better to dig up the plant and burn it. Fungicides Abiga-Pik, Ordan, Profi, etc. are suitable for treating tomatoes. Spraying with copper sulfate (50-100 g per 10 liters of water) is also effective.
Gray rot
Gray rot
Gray rot affects the above-ground organs of plants. Brown weeping spots appear on the leaves, buds, and flowers, covering the entire plant in 8-10 hours (usually overnight) with an abundant ash-gray powdery coating - fungal spores. The spots on the stems are brown or gray, at first dry, then slightly slimy. They are most often located around wound sites, for example, when stepsons break off or at the branches of stems. The viability of the spores lasts 1-2 years.
Gray rot - affects tomatoes at the end of summer, when it becomes cool and cold rains occur. This is one of the most common fungal diseases of tomatoes. It occurs when there is poor ventilation, when the greenhouse is poorly ventilated, with high humidity, or a violation of the temperature regime, if we are talking about growing in a greenhouse.
The first signs of gray rot on tomato leaves
The first signs of gray rot on a green tomato
The first signs of gray rot on a ripe tomato
As long as the fruits have such faint whitish concentric spots, they are suitable for eating. There will be no particular problems with fruits that have time to turn red on the bush. But problems will begin (if measures are not taken in time) at the end of summer, that is, when you have to collect green fruits for ripening. Then such fruits will be the first to begin to deteriorate and can infect healthy fruits in the boxes. Therefore, if you notice fruits with such whitish concentric circles, it is better to tear off the tops of the bushes so that the fruits have time to ripen on the plant. One way to combat this disease is to remove the affected leaves before the disease goes further and penetrates inside the trunk. It is advisable to remove leaves in sunny weather, so that by evening the places where the leaves are cut have time to dry out and fungal spores do not fall on the trunks. Try not to irrigate by sprinkling immediately after removing shoots or leaves.
To prevent gray rot, spraying plants with garlic infusion is useful - leave 30 g of chopped garlic (arrows can be used) for 2 days in 10 liters of water.
Yellowish spots on tomato leaves
First, the lower leaves become stained, then the disease spreads to the entire plant. The leaves dry out, curl and fall off, and hard olive-colored spots are visible on the fruits.
sazhaemvsadu.ru
Diagnosis : cladosporiosis, or brown spot, of tomatoes - a fungal disease.
The development of the disease is facilitated by growing in unheated and rarely ventilated greenhouses. Leaves are most often affected. Fruits, stems and ovaries are less likely to suffer. But since the plants lose their leaves, the harvest is very poor. And if the disease spreads to the fruits, they shrink and dry out.
Control measures . Treat the first lesions with Abiga-Peak, Sporobacterin or Pseudobacterin-2. During the summer, spray the bushes with a 0.05% solution of Fitosporin-M. For prevention, regularly remove old leaves and maintain the humidity in the greenhouse no higher than 80%.
White coating on tomato leaves
The leaves on both sides are covered with a white coating. Round spots are located throughout the leaf blade, then merge and darken.
mislife.ru
Diagnosis : tomato powdery mildew is a fungal disease.
The development of the disease is facilitated by excess nitrogen fertilizers and errors in irrigation. Powdery mildew does not cause much damage to open ground tomatoes, but greenhouse tomatoes have a hard time. Photosynthesis processes are disrupted and leaves gradually die. With severe damage, the stems and peduncles turn white. The fungus weakens plant immunity and significantly reduces yield. If measures are not taken, the bush may die entirely. Many summer residents mistake the white coating for dust, but in fact it is the mycelium of the fungus, which grows very quickly and is transferred to other plants. It can also coat fruits, impairing their taste.
Control measures . When the first signs appear, treat the tomatoes with fungicides: Pseudobacterin-2, Sporobacterin, Topaz, Provisor, etc. For prevention, spray the beds with a 0.5% Baktofit solution. After two weeks, repeat the procedure. Carry out the third treatment 7-10 after the second.
Signs of malnutrition
Timely, competent feeding increases the immunity of tomatoes, helps them develop normally and produce a plentiful, tasty harvest. All this is relevant if the owner of the personal plot does not apply fertilizer randomly, whatever and whenever he pleases, but strictly adheres to the scheme, alternates different types of fertilizing and carefully monitors the tomato bushes.
The appearance of plants will tell you what they are missing at a particular stage of development. Or, conversely, some symptoms indicate an overly high dose of one or another component. Adjust the “diet” of tomatoes according to how the bushes look.
Element | Signs of deficiency | Signs of excess content |
| Nitrogen | The bush lags behind in growth and acquires a light green color. The lower leaves turn yellow and fall off. The green vein disappears. | Leaf blades and stems become dark green, powerful, thick, juicy, and increase in size. Flowering and fruit formation occurs late, tomatoes crack. |
| Potassium | The greenery takes on a bluish tint, the leaf blades become variegated, yellowish, and dry out at the edges. The top and bottom leaves curl. There is a delay in the growth of tomatoes. | Partially due to nitrogen deficiency. The growth of the bushes slows down, the foliage darkens, and new blades grow smaller. The absorption of calcium, boron, magnesium, zinc, etc. is difficult. |
| Phosphorus | The foliage becomes rich green, dull, sometimes with a purple tint, and becomes smaller. Pathologically thin, short shoots grow poorly. Drying leaves have a dark color. | It is rare, but leads to a deterioration in the digestibility of iron and zinc, the appearance of chlorosis on tomato leaves, yellowing, and falling off. |
| Calcium | Deficiency provokes blossom end rot, the leaves on the tops of the bushes curl and become twisted, as if torn. The roots are highly branched. | Pale, shapeless spots appear on the leaf blades, resembling necrosis. The absorption of other nutrients deteriorates. |
| Magnesium | The foliage in some places becomes almost white; purple, yellow, and red shades predominate between the veins of the plates. Tomato leaves bend like a dome, their edges wrinkle and gradually die. | Due to excess magnesium, calcium is poorly absorbed, which leads to a deficiency of this element. |
| Zinc | Rapid tissue death is observed over the entire surface of the leaf blade. Young leaves turn yellow, while mature leaves show spotty corrosion. | Watery spots form along the central vein on the lower leaves, and the plates themselves fall off over time. |
| Iron | The leaves seem to be burning out. The whitened areas show signs of dying. | Happens rarely. Slows down the growth of roots and the entire tomato bush, impairs the digestibility of other elements. |
| Copper | The upper leaves constantly wither and bend down. The green veins clearly stand out against the grayish-white background of the leaves. | Tomato bushes are stunted in growth, the leaves turn brown (primarily more mature specimens). |
| Molybdenum | Specks appear on the leaves, the edges may turn yellow and curl inward, like paper (typical of the first two pairs at the base of the leaf). Sometimes the plates swell and signs of necrosis become noticeable. | It provokes copper deficiency with all the consequences characteristic of this process. |
| Bor | The upper leaves acquire a light green color, curl, and yellow or orange spots appear on the lower ones. The stems and foliage become brittle and feel like cork in tactile sensations. Flowers fall off or do not set, the tops of tomato fruits rot. | Small brown spots are visible on the lower leaves, which, as they grow, lead to the death of the plates. |
| Manganese | Young leaves resemble a chessboard: green veins contrast with faded areas. Over time, a metallic sheen appears on the leaf plates, and purple marks are possible. Dark spots and dying areas become visible along the veins. | The leaf blades become covered with brown spots and fall off. |
| Sulfur | The leaves turn pale and acquire a reddish color (pinkish on the underside), but signs of drying out do not appear on them. In advanced cases, necrosis can affect the petioles. Stems stop gaining thickness | Along the edges, the foliage acquires a yellow or lilac-brown tint, the plates turn inward, then die. |
Dark sunken spots on tomato fruits
The fruits are covered with softened spots up to 1 cm in diameter. At first they are hardly noticeable and do not differ from the color of the skin. Then they darken and turn black. The fruits are completely mummified. Brown flaky spots are visible on the roots.
seminis.ru
Diagnosis : tomato anthracnose is a fungal disease.
Anthracnose is widely found both in open ground and in greenhouses. More often, mature bushes suffer from it. The peak of the disease occurs in late summer and early autumn. Mainly fruits, roots and root collars are affected. Ripe tomatoes cannot be eaten; they are watery and tasteless. The spots darken over time, and fungal spores become visible on them. Anthracnose often appears on bushes together with Alternaria, causing a mixed infection.
Control measures . Remove the affected fruits and spray the bushes with copper oxychloride (40 g per bucket of water) or 1% Bordeaux mixture. The latter can also be used to prevent disease. To do this, spray the plantings 3-4 times every 10-12 days. When the greenhouse is empty, completely disinfect it with bleach (200 g per 10 liters of water).
What do tomatoes need?
It’s worth saying a few words about what is required for tomato crops cultivated in greenhouse conditions.
Photo of yellowing foliage of tomatoes
Requirements:
- systematic watering;
- maintaining the required humidity level (60 – 70%);
- monitoring the temperature inside the greenhouse (from +23 to 30 degrees);
- ensuring sufficient access to light, excluding direct rays of the sun.
These conditions need to be created already at the initial stage of seedlings. From time to time it is necessary to carefully inspect the tomato bushes in order to take timely action if a problem is detected, for example, yellowing of the leaves.
Caring for tomatoes in a greenhouse - video
Important!
Drying and yellowing on tomato leaves is a serious problem that you need to immediately pay attention to and start looking for the cause of its appearance.
Necrotic spots on leaves and stems, white spots on tomato fruits
The stalks and petioles become covered with ulcers, the stems crack, and mucus is released from them. The leaves dry out and curl on one side, but do not fall off. The fruits are speckled with small hard spots. The plant is withering.
Diagnosis : bacterial canker of tomatoes is a disease caused by non-spore-bearing aerobic bacteria.
Cancer most often affects greenhouse tomatoes growing in conditions of high humidity and insufficient lighting. High temperature and waterlogged soil also influence the development of the disease. Crop losses can reach 30%.
Control measures . Affected plants cannot be treated. Dig them up and burn them. Treat the remaining tomatoes with 1% Bordeaux mixture to prevent infection. For prevention, use Fitosporin-M, Gamair, Fitolavin.
Damage to tomatoes by insect pests and yellowing of foliage
The yellowing of tomato leaves is caused by mole crickets and wireworms, which feed on the root part of tomatoes.
Photo of the mole cricket
The mole cricket loves soil that has been supplemented with organic fertilizers.
To find it, you need to dig up the ground a little, since it makes a nest at a depth of no more than 15 cm and feeds on roots from there.
This leads to yellowing of the leaves and eventual loss of yield. Insecticides are used to eliminate mole crickets.
The wireworm harms tomatoes by laying larvae near the plants, which, eating the tomatoes, gradually penetrate inside the stems. To eliminate the larvae, use a mixture of sawdust, sand and Bazudin.
Photo of wireworm
Tomato leaves can dry out or turn yellow for various reasons. When you notice the first signs of yellowing and wilting of tomato leaves, you should carefully examine the plants, diagnose the cause, and then take appropriate treatment measures. It is important to carry out timely prevention and systematically care for tomatoes so that the foliage is juicy and green, and the tomatoes themselves are healthy and tasty.
Recently searched:
Tomato leaves are curled, yellowish in color, and have a white coating on the roots.
The lower leaves quickly die and the petioles become deformed. The tops of the bushes become limp. The vessels in the stems turn brown, metabolism is disrupted and the plant withers.
koppertus.com
Diagnosis : fusarium wilt of tomatoes - a fungal disease.
The disease is very dangerous because The fungus that causes fusarium is resistant to many chemicals. This makes diagnosis difficult. Many people confuse the disease with non-infectious chlorosis, which occurs from improper watering and fertilizing, or verticillium, which is also characterized by wilting. Meanwhile, it is the pronounced chlorosis in this case that excludes the disease with verticillium and, together with the signs described above, indicates the infectious origin of the disease.
Control measures . Treat the affected plants with working solutions of drugs: Bacterra, Fitosporin-M, Alirin-B or others. By the way, they can also be used to treat seeds before sowing. For prevention, after planting in the ground, water the tomatoes with Pseudobacterin-2.
Disease Prevention
It has long been known that prevention in any matter is the solution to 80-90% of problems that could appear in the future. Tomatoes are no exception and there are some recommendations for growing them:
- Maintaining a balance of nutrients in the soil will prevent up to 50% of all diseases.
- When interacting with plants, you need to do everything as carefully as possible to prevent damage.
- Humidity levels can be maintained with mulch.
- It is important to correctly determine the time of planting tomatoes to prevent their hypothermia.
- You should not plant only one variety, it is better to use several. This will help you determine which one is more suitable for you in the future.
- Before sowing, seeds must be disinfected and treated with various solutions to protect against various diseases and increase yield.
- We must not forget about proper landing. The distance between bushes should be at least 50 cm.
The lower leaves of tomatoes dry out and fall off, the upper leaves curl
The leaves partially turn yellow, then necrotic spots appear on them, and the roots gradually die.
kccc.ru
Diagnosis : verticillium wilt, or verticillium wilt, of tomatoes - a fungal disease.
Until recently, verticillium was one of the most dangerous and widespread diseases of tomatoes. But today, many varieties and hybrids that are resistant to it have been bred, so infection occurs less and less often. Meanwhile, the fungus that causes wilting still lives in the soil and, under favorable conditions (low temperature and high humidity), infects plants. Young tomato bushes that have just begun to grow are especially affected.
Control measures . For treatment, use the drugs Previkur Energy, Trichocin, Trichoderma Veride. After picking, when the plants take root, feed them with the following mixture: 2 g of copper and zinc sulfate, 3 g of boric acid and 10 g of potassium permanganate per bucket of water. After 10 days, repeat the procedure. Carry out the third feeding after 20 days, and after another 30 days - the fourth. This will strengthen the immunity of tomatoes.
Tomato diseases of bacterial origin
Infection with bacteria occurs in much the same way as with viral infection. The only difference is in the pathogens.
Bacterial wilt of tomatoes (bacteriosis)
When this disease occurs, a slimy mass consisting of bacteria forms in the plant stem. Here, hot and humid weather negatively affects the development and progression of the disease.
Signs for bacterial wilt:
- Aerial roots.
- Brown stripes on the leaves.
- The lower leaves turn yellow.
- In the section of the stem you can see mucilage.
How can you become infected:
- Mechanical impact through wounds.
- Insect carriers, such as aphids.
- The disease can be transmitted through irrigation (contaminated water) or through contaminated garden tools.
- Abuse of nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
- Temperature changes (day and night).
How to prevent bacteriosis (prevention):
- Pre-sowing preparation of tomato seeds . Disinfection of seed material in a solution of potassium permanganate. Also suitable are the drugs “Albit”, “Baktofit”, “Maxim”, “Planriz”, “Fitosporin - M”.
- Selection of bacteriosis-resistant varieties.
- Cleanliness in the garden beds . We periodically weed and remove weeds. It is especially important to tidy up at the end of each season in the fall.
- We disinfect garden tools . Garden tools sometimes need to be disinfected. For this, you can use Ecocid-S. Here are the proportions: 50 grams of the drug per 5 liters of water.
- Cultural turnover . You cannot grow tomatoes in one place for 2 years in a row. You can return only after 3 - 4 years.
- Soil disinfection . Every spring we disinfect the soil in the greenhouse with fungicides (Benomil 500, Fundazol). Or you can simply pour a warm solution of potassium permanganate. The choice is yours.
Tomato stem necrosis
Typically, such a misfortune appears in tall tomatoes in protected ground (in a greenhouse). Here, mucilage is formed in the plant stem. Where, first of all, the lower part of the bush is affected. Subsequently, the fruits are also affected.
Symptoms of tomato necrosis:
- Aerial roots at the bottom of the plant.
- Dark stripes on the stem. A slimy mass inside the stem.
- The leaves lose their attractiveness and then dry out.
- The fruits are the last to be damaged.
Causes contributing to the disease:
- Abuse of nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
- Sudden temperature changes. And constant, high humidity of air and soil.
- Infected tools, water for irrigation, untreated seeds.
- Incorrect agricultural technology: weeding, prevention of pests (aphids).
Prevention of tomato necrosis:
- Pre-sowing preparation of seed material, soil (we disinfect), crop rotation (we return after 3 - 4 years).
- Necrosis-resistant varieties and hybrids, for example Red Arrow F1, Maeva F1, Resento F1.
- Maintaining temperature and humidity conditions . Here, moderate watering (as it dries) and ventilation are considered vital procedures. It is also worth paying attention to the density of the plantings.
- There is no need to overuse nitrogen fertilizers . This is especially important at the end of the season and during fruit ripening. Note that nitrogen is needed mainly at the initial stage of cultivation.
Watery spots on leaves, stems and fruits of tomatoes
The affected areas increase in size, then sporulation of the fungus in the form of brown dots becomes noticeable on them. The leaves turn yellow due to metabolic disorders. The plant withers and dies.
Diagnosis : gray rot of tomatoes is a fungal disease.
The fungus becomes active during the fruiting period in humid weather. The first signs of damage can be seen on the leaves. Small gray dots quickly become large, merge and become covered with plaque. The disease is especially dangerous for greenhouse tomatoes that grow in conditions of high humidity.
Control measures . If there are few lesions, immediately treat the plantings with this composition: add 1 cup of ash and 1 tsp to 10 liters of water. copper sulfate. The mixture is enough for 2-3 sq.m. If the disease is severe, spray the leaves and stems of tomatoes with Fitosporin-M, Sporobacterin, Bacterra, Trichocin or a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture.
Why is root rot (blackleg) dangerous?
This disease also occurs due to fungus. Root rot is also popularly known as blackleg. It often occurs at the stage of seedling germination. Characteristic of greenhouse tomatoes that are grown in violation of technology. The basal part of the stem turns black, becomes thinner, and brown spots sometimes appear on the leaves. Plants wilt and can die in less than a week.
Blackleg
Like other fungal diseases of tomatoes, blackleg progresses in thickened plantings. It is usually transmitted through contaminated soil and poorly disinfected garden tools. Additional risk factors include changes in air temperature, lack of ventilation, and excess fertilizer. Water the tomatoes rarely but generously, thoroughly disinfect the tools you use in the garden beds, and loosen the soil. Treat seeds with fungicides before planting. Among the drugs that will help are Bordeaux mixture, potassium permanganate, Pseudobacterin-2, etc.
Advice. Add sand to the planted tomato seedlings (layer thickness - 2 cm). It will absorb excess moisture and stimulate the formation of additional roots.
Light speckled spots and wrinkled areas on tomato leaves
The leaves are mottled in color, then become deformed and take on a thread-like shape. Leaf-like outgrowths appear on the lower part. The plant slows down in growth, cannot set fruit and soon dies.
gardenaddict.ru
Diagnosis : tomato mosaic is a viral disease.
Mosaic causes enormous damage to tomatoes in open ground and greenhouses. Plants pick up the virus during an invasion of aphids, nematodes and thrips, which carry this disease, as well as when tissues are damaged by dirty garden tools. If a bush is infected at the beginning of development, its fruits will grow defective and unsuitable for food. Possible loss of half the harvest.
Control measures . Infected plants cannot be treated. To stop the spread of infection, dig them up and burn them. Treat the soil with Indigo, Bordeaux mixture or other fungicides. You can spray lightly affected bushes with a whey solution (100 ml per 1 liter of water) with the addition of Farmayod. For prevention, before sowing, treat the seeds in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate.
Bacterial diseases
All kinds of bacteria perfectly adapt to environmental conditions, causing various diseases of tomatoes. For example, bacteriosis (bacterial wilt) . Gardeners should be wary of the situation when a tomato bush begins to wilt sharply. This is one of the signs of an illness that spreads with lightning speed, in some cases literally overnight. Other symptoms: the stems become hollow, brown when cut, and liquid accumulates in them. All these are signs of internal rotting of the tomato bush.
Bacterial wilt can destroy several plants at once. The disease has no cure. Infected tomatoes should be immediately removed and burned, and the soil should be disinfected. Treat the remaining plants with Fitolavin-300, which will help protect the crop from bacteriosis.
Attention! Try to ensure that when watering the water gets under the bushes and not on them. This will reduce the risk of developing bacteriosis.
Another tomato disease that affects the stems is necrosis . You can notice its main signs in good lighting. Inspect the tomato trunks. If they have stripes or cracks in the lower part, where aerial roots form over time, it means that the bush has developed stem necrosis. Infected specimens fall and disappear, their leaves wither. Fruits that have already begun to form do not have time to ripen.
Bacteria that provoke necrosis of stems penetrate through infected soil or seeds. Diseased tomato bushes should be removed and burned. The soil around them should also be removed. All other soil is treated with Fitolavin-300. Prevention of the disease - dressing the seed, destroying all plant residues after harvesting the tomato crop.
Attention! Hybrids Maeva, Red Arrow, etc. are capable of resisting necrosis.
Watery dark spots on the bottom of tomato fruits
First, barely noticeable watery spots appear at the base of the fruit (usually green or just beginning to ripen), which soon increase in size and acquire a brown tint. The fruits become dark by a third, wrinkle and turn black.
youtube.com
Diagnosis : tomato blossom end rot is a physiological disease associated with violations of agricultural practices and genetic characteristics of plants.
The disease usually occurs due to improper watering or excessive foliage of plants. Rot is also caused by unbalanced feeding and the development of fruits, when nutrients (in particular calcium) do not have time to get to the top. This is especially true for large-fruited tomato varieties. Temperature changes can also affect the appearance of watery spots. Tomatoes are affected in greenhouses and open ground. Bushes weakened by disease bear fruit poorly. Rotting fruits harm plant immunity. As a result, up to 50-60% of the expected harvest may be lost.
Control measures . When the first signs appear, remove rotten fruits from the bushes and spray the leaves with a 0.2% solution of calcium chloride. Repeat the treatment two more times during the week. For prevention, treat the leaves and soil with a solution of calcium nitrate (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water). Among the drugs you can use Fitosporin-M, Gamair, Alirin-B. Do not apply too much nitrogen fertilizer, and avoid applying fresh manure. During autumn digging, enrich the soil with calcium.
Tomato diseases of non-infectious origin
Such diseases usually appear due to lack of nutrients. For example, such as phosphorus, nitrogen, potassium, calcium.
I would like to note that lack of nutrition for plants occurs not only from soil depletion. Here, the process may be affected by heavy rains. Which can simply wash away microelements from the soil.
Apical rot
Tomato diseases can occur due to disturbances in the water-salt balance of the plant. So, blossom end rot is considered a physiological disease, and it is here that we observe a violation of the water-salt balance. Here, calcium starvation occurs. At the same time, the fruits are damaged.
Signs of blossom end rot on tomatoes:
- Dark spots on unripe green fruits that form at the tip of the fruit (floral scar).
Causes of the disease:
- Dry air and high temperatures. Here, the root system cannot take enough moisture from the soil. And therefore, moisture is taken from the fruit.
- Irregularity of watering.
- There was no loosening of the soil.
- Poor sandy soil.
- Calcium deficiency or excess.
- Too much nitrogen.
- Soil salinity.
Preventive measures:
- Feeding according to the rules
. We feed strictly according to the instructions. We remember that both excess and lack of nutrients are harmful. - Moderate watering
. 1 - 2 times a week in the evening. - Loosening after watering
. After each watering, we loosen the soil. - Mulch
. For this purpose, mown grass, peat, and straw will be used. Prevents moisture evaporation. Less need to weed and loosen. - Varieties and hybrids resistant to blossom end rot
. Liya, Alpatieva, Dubok, Astrakhan, Volgograd, Pharaoh, Lunar, Marfa, Rotor, Grand Canyon. - Soil preparation
. Digging in the fall and laying fertilizers. Disinfection in spring. - We follow the rules of crop rotation
. - Seed disinfection
. We disinfect seed material according to the rules. - Ventilation
. Don’t forget to ventilate and choose the right planting scheme.
Fighting crown rot:
- With a lack of calcium
.
Here we use the following preparations: Limestone nitrate
. For 10 liters of water there are 5 - 10 grams of saltpeter. - Calcium chloride
. 3 - 4 grams per 10 liters of water. - Universal fertilizers for tomatoes
. We work according to the instructions. - Nutrivant PLUS and Fertivant
. 25 - 30 grams per 10 liters of water. - Calcium nitrate and boric acid
. 10 by 10 grams in a bucket of water.
Folk remedies:
- Soda solution.
- Ash.
Tomato diseases such as fruit cracking
Cracking of tomato fruits is a fairly common phenomenon in gardening circles. Typically, this happens with tomatoes of yellow and pink varieties with thin skin.
Bursting skin is a non-infectious disease, and everything depends on the agricultural technology used by the gardener. Where, unfavorable conditions lead to such sad phenomena.
Why do tomatoes crack?
- Incorrect watering
. Here, improper watering is irregular watering. Abrupt transitions between moisture and dryness contribute to cracking. The fruits, having received a lot of moisture, quickly fill and burst. Therefore, moderation is needed here. By the way, in hot weather you also need to water correctly. Here, we take into account that the earth dries faster. - Temperature regime
. In a greenhouse in hot weather, the temperature can rise above 40 degrees. And then, plant growth stops. In addition, in this situation, the ovaries fall off and the skin hardens. Then, the plants receive a lot of moisture and begin to grow rapidly. As a result, the skin cannot stand it and bursts. By the way, differences between day and night temperatures also lead to cracking. - Pinching during fruit ripening
. Here, by pinching the top, we seem to redirect the growth to the fruit. And they begin to grow rapidly, and eventually burst. Usually this happens at night. - Incorrect formation of bushes
. Having stripped the plant of stepsons and leaves, the fruits begin to grow quickly. And in the end, the fruit bursts. - Mineral fertilizers
. When growing tomatoes, it is imperative to follow the dosage of mineral fertilizers. Here, both shortage and overdose negatively affect the development of the plant. As a result, they may crack. - Sometimes illness contributes to this.
Preventive measures:
- Moderate watering
. Let's see. so that the ground is always moist. We don't let it dry out. In a greenhouse, once every 5 days will be enough. We act according to the weather. - Using mulch
. Here, the moisture does not evaporate, and watering lasts for a longer time. - Temperature control
. We monitor the temperature and ventilate. - We choose varieties that do not crack
. For example: Bohemia A1. - Grushovka.
- Raspberry Viscount.
- Pink honey.
- Asteroid.
- Lady fingers.
Yellow or green spot near the stalk
Here, a yellow or green spot appears in the stalk area. Also, the taste of the entire fruit changes. He becomes unpleasant.
Why green spots appear:
- Bad light.
- Potassium deficiency.
- There is not enough magnesium.
- Little phosphorus.
- Excess nitrogen.
Preventive measures:
- Correct planting pattern
. In dense plantings there is not enough food and light for everyone. Therefore, there is a deficiency of nutrients and a lack of light. - Regular stepsoning
. Tall varieties of tomatoes must be constantly planted, otherwise there will be a jungle. - Selection of varieties for southern or northern regions
. We choose varieties specifically for your region. Because varieties are bred taking into account climatic conditions. - Ventilation
. We ventilate the greenhouse 2 - 3 times a day in hot weather. This is especially important during flowering and fruit formation. - At the stage of fruit formation and ripening
. Here, we feed with potassium and phosphorus. Nitrogen is not needed, and even at this time it is harmful.
Silver spots on tomato leaves
If silvery spots appear, there is no need to panic. This is not dangerous, and occurs for several reasons:
- With a sharp change in temperature.
- Infected seeds.
Prevention:
- Ventilation.
- Zircon, Sprout. Anti-stress drugs.
- Quality seeds.
White and yellow stripes on tomato fruits, purple leaves and stems
The fruits are woody and tasteless, covered inside with a white network of vessels. The leaves are curled, have an unnatural color, and become smaller over time. Stamens and pistils in flowers are underdeveloped. The roots are covered with cracks. The plant is stunted in growth.
Diagnosis : mycoplasmosis, or stolbur, of tomatoes is an infectious disease caused by mycoplasmas, tiny bacteria that live in the vessels of plants.
Stolbur most often affects plants in open ground. The peak of the disease usually occurs at the end of August. The disease is carried by sucking insects, in particular the leafhopper (slobbering frog), a dangerous garden pest. The risk of infection with stolbur increases in hot and dry weather, when insects actively reproduce. The infection can also enter the soil through infected seeds and seedlings.
Control measures . Infected bushes need to be dug up, because... they cannot be treated. To prevent re-infestation, weeds must be controlled. You can also spray plantings against leafhoppers with Kinmiks or Aktara. Dusting plants with wood ash (30 g per bush) will also help.
Prevention of tomato diseases
Timely preventive measures will help you protect plants from pathogens:
- plant disease-resistant tomato varieties;
- before sowing seeds for seedlings, treat them in a solution of Fitolavin or Maxim Dachnik;
- disinfect garden tools;
- disinfect the soil using Trichoderma Veride, Trichocin, Fitosporin-M and other biological products; a solution of potassium permanganate is also suitable;
- discard weak and diseased plants;
- observe crop rotation;
- increase plant immunity with a double dose of potassium fertilizers;
- follow the watering and fertilizing regime;
- regulate the temperature and humidity in the greenhouse (the norm is no higher than 32°C and 80%);
- destroy pests and weed;
- Clean the greenhouse at the end of the season, remove plant debris and dig up the soil.
To ensure that the tomato harvest increases every year, monitor the health of the plants and take timely measures to combat major diseases. Also read about how to identify and treat diseases of cucumbers, peppers and zucchini.
Tomato diseases of viral origin
In this case, the infection is transmitted by viruses. Diseases can also be transmitted by insect vectors (aphids). Also, infection can also occur through plant debris that we thoughtlessly buried after the end of the season. Further, there is an option when this infection can enter the plant through the seeds. Basically, the infection process occurs through mechanical contacts (through wounds on the plant).
I would like to note that inactivation of viruses occurs at a temperature of 90 - 92 degrees. This means that they are very tenacious, and therefore it is not easy to cope with such diseases. One might even say that it is impossible. The main thing is prevention.
Mosaic
Typically, the source of infection is contaminated seeds and insect vectors, such as aphids. Sick plants cannot be cured. They just need to be destroyed, for example, burned.
Another very effective method is prevention. Where, before each planting, we carry out pre-sowing preparation of seeds and soil. This point cannot be neglected.
Signs!
Here, yellowish or brown spots form on the leaves. Then, the leaves curl and then dry out.
Preventive actions:
- Preparation of seed material . Disinfection of seeds in a solution of potassium permanganate. Or, in any other way, for example, with fungicides “Albit”, “Baktofit”, “Maxim”, “Planriz”, “Fitosporin - M”, etc.
- Soil disinfection . Spill with a solution of potassium permanganate. Or the drugs Benomil 500, Fundazol. We work strictly according to the instructions.
Chloratic leaf curl of tomatoes
With this enemy, tomato plants become light green, and even, as it were, yellowish. They are infected with tobacco mosaic virus and tobacco necrosis virus. Infection occurs through the soil or through seeds. The disease has no cure, but preventive measures, in our case, will be simply vital.
Symptoms of chloratic curl:
- Plant growth stops.
- Light green color of the bush.
- Curly leaves.
- The green mass is thinning.
Causes of infection:
- Contaminated irrigation water, garden tools, seeds, insect vectors (for example: greenhouse whitefly).
Preventive measures:
- Seed disinfection . Treatment of seed material with a solution of potassium permanganate. Can be treated with “Albit”, “Baktofit”, “Maxim”, “Planriz”, “Fitosporin - M”.
- Moderate watering . Water correctly as the soil dries out. We remember that with both a lack of moisture and an excess, problems are inevitable.
- Maintaining crop rotation . We choose our predecessors correctly. At the same time, we constantly change the landing site. We will return to this place, no earlier than in 3-4 years.
- Disinfection of garden tools and soil . We treat garden tools with disinfectants. For example, such as Ecocid-S. For soil you can use Benomil 500, Fundazol.