The role of culture in agriculture
Corn is a staple crop with a wide range of uses.
The role of this grain plant in agriculture is important. It allows you to solve two complex problems at once - replenish grain supplies and produce nutritious feed for livestock. The fact that not only grains, but also cobs have a rich chemical composition makes the crop a valuable food product.
Grains are an important ingredient for animal feed. Because when animals eat only grains, they are not getting a balanced protein content.
Silage is also prepared from this crop, which is well digested by the stomach of animals and has milk-producing properties, which is so useful for both cattle (cattle) and small cattle (small cattle). This plant is also used as green fodder. Not only grains are used as feed, but also dried leaves, stems and cobs.
In addition to the fodder use of this cultivated plant, it is also used as a fertilizer - it also has a beneficial effect on the soil in which it grew. After harvesting, the soil remains free of weeds, pests and diseases. It is also called row crop.
But sowing this type of grain has both positive and negative effects. After the crop began to be grown in Russia, environmental problems arose. For example, the soil has become poorer in organic matter, the composition of the soil has deteriorated, and it has become too dense due to harvesting and transporting crops.
Interesting Facts
Corn has not only an interesting history of its origin, but also a lot of other amazing facts.
- In Russia this crop is called corn, and in the rest of the world it is called maize.
- Growth like a tree. This plant tends to grow up to almost 7 m in height (a standard two-story house).
- This is a heterosexual plant, but it has both female and male inflorescences. The male inflorescence is the upper panicle, and the female inflorescence is the cob. And yet, corn will not bear fruit if planted alone. She is a group plant.
- It won't grow without people. This species cannot be found in the wild. Culture will not grow without the participation of people. It grows from seeds, and if the cob itself falls into the ground, it will rot.
- This grain must be cooked without adding salt or sugar, otherwise the grains will be hard. Moreover, the young one is cooked for only 15 minutes, and the old one – more than 2 hours.
- A common stereotype is that corn is only yellow. However, this is not true; it has more than a thousand varieties. They grow white, red, purple, and even black corn. There are also multi-colored ones.
- Parity. An interesting fact is that the number of grains on the cob is always even, as are the rows (from 10 to 14). And there will also be an even number of seeds from such an ear.
- The stamens or hairs are valuable in the field of medicine. They are rich in vitamins and microelements, which have a beneficial effect on the gastrointestinal tract, help remove toxins from the body and strengthen the human immune system.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with Photos and descriptions of sage species
Planting corn on the site
The culture is unpretentious. However, only compliance with the rules of agricultural technology and the choice of a suitable variety will allow you to obtain voluminous harvests.
Which variety should I choose for growing?
When choosing a variety, not only the growing season is taken into account, but also the purpose of the grains. There are 10 botanical groups in culture, of which several are the most popular:
- Sweet corn is in great demand. It is used for boiled consumption and for preservation. The varieties Spirit, Dobrynya F1, Megaton F1 are in demand;
- tooth-shaped is represented mainly by late-ripening varieties Klarika and Anasta. Grains are processed into flour, cereals, alcohol;
- siliceous is one of the most common. Popular varieties are Elite, Orzhitsya. The grains are used to make cereals, animal feed, and cereals;
- Starchy, soft corn has a short shelf life. It is grown to produce starch and alcohol. Common varieties: White Arrow, Blue Jade;
- Popcorn is used to make popcorn. The grains can have a variety of shades - striped, blue, red, white. Common varieties Miracle silver cone, Miniature red cone, Early Beaded;
- waxy varieties are distinguished by the absence of monosaccharides in grains, therefore they are used in the diet of diabetics. Common varieties: White Miracle, Royal Silver.
Hybrid white corn produces small, sweet kernels. Popular varieties: Snow White, Snow Queen, Medunka. The cobs are suitable for canning, freezing, and eaten boiled.
Planting dates for different regions
Naturally, when choosing varieties, you need to take into account the climatic conditions of the regions. Late frosts can destroy sprouts
Therefore, it is important to plant the crop after the threat of frost has passed. Optimal periods by region:
- in the south - late April-early May;
- in the Moscow region, sowing begins in the second half of May. Cold-resistant hybrid varieties can be planted at the beginning of the month. But it is advisable to play it safe and cover the beds with covering material;
- in the Urals and in regions of Siberia, suitable agroclimatic conditions occur in mid-June. To ensure that the harvest does not disappoint, it is practiced to plant seedlings in open ground.
The best signal to start planting work will be stable warm weather, in which the soil warms up to 10-12°C.
Choosing a location and following crop rotation rules
Corn is a heat- and light-loving plant, so plants are planted in well-lit areas, protected from drafts. The beds are also not located in wetlands or in vegetable gardens where groundwater is located high.
In order not to violate the rules of crop rotation, you need to take into account the plants that grew in the beds last season and the crops that will grow in the neighborhood. Corn is not very capricious in relation to its predecessors, but it is advisable to plant it in areas where last year they grew: cucumber, watermelon, pumpkin, tomatoes, potatoes.
Corn is often planted along the perimeter of beds with other plants so that it serves as protection from the winds and provides a natural support for climbing plants. To prevent crops from harming each other, it is also necessary to take into account the rules of crop rotation. Corn makes good friends with cucumbers, pumpkin, tomatoes, beans, and beans.
Schemes and technology of planting:
According to the rules of agricultural technology, grains are planted using the wide-row method. It is preferable to place 2-4 rows on the bed. Planting scheme: the distance between plants in a row is 20-30 cm, and row spacing is 50-70 cm wide.
South Africa
In 2016, according to the latest report by analysts from the South African National Crop Estimation Committee, the country's maize production was at 7.78 million tons . This is 21% less than in the previous year, 2015. This decline in harvest is due to drought in the region.
UN PSO analysts predict that by the end of this year 2022, production volume will increase to 13 million tons. Which is 60% higher than in 2016. This is due to favorable conditions for the growth of corn. In 2016, 3.1 million hectares of grain maize were sown in South Africa. Of these, farmers allocated 1.9 million hectares for white corn and 1.2 million hectares for yellow corn.
Corn care rules
For the correct development of the plant during the growth process, it is necessary to establish proper care for the cultivation of the crop. Corn, a plant that germinates rather slowly, and the weed during this time, can clog the tender seedlings. To do this, it is necessary to weed the rows as necessary, but do it carefully so as not to damage the already weak root system of the plant.
Corn responds well to the application of organic and potassium-phosphorus fertilizers. Therefore, the first fertilizing with compost must be done when the plant begins to grow. And add mineral fertilizers to the soil before planting, about two weeks. Daily watering is also necessary when caring for seedlings; for better absorption of moisture by corn, water early in the morning or in the evening. Subsequent care of corn seedlings should include mandatory loosening of row spacing, at a safe distance from the plant, so that root damage does not occur.
During flowering, some gardeners artificially pollinate corn to increase yield and achieve high quality cobs. To do this, the pollen from the male panicle must be transferred to the female inflorescence. This procedure improves the quality of the grains on the cob. During active growth, corn may produce additional young shoots; they must be cut off, otherwise the corn will not produce cobs, but will grow in breadth.
Mexico
In Mexico, the main crops are corn, wheat, legumes, soybeans, and rice. According to UN USAR forecasts, by the end of the 2016/2017 season. the volume of corn production will be 27.4 million tons , which is 5.5% higher than in 2015 (25.9 million tons). This is due to sufficient rainfall this season. However, in Mexico, the area under corn planting is decreasing. In this regard, an increase in imported corn is expected. Imports typically come from the USA, Argentina and Brazil.
How to care for corn?
There is and cannot be anything difficult in caring for this cereal; the main thing is regular watering, fertilizing, weeding and periodic application of poison to control pests. Corn grows well in well-fertilized soil.
Watering and fertilizing
The plant needs to be watered while the ovaries are forming; the grain will not tolerate excess moisture. In order for corn to grow quickly, it needs natural rainwater.
The first fertilizing is done after at least 6 leaves appear on the seedlings. For this purpose, humus or compost made from chicken manure is used.
Ammonium nitrate, potassium, phosphate and nitrogen fertilizers will be a good help for growth. They should be applied before the heads of cabbage appear.
Corn diseases
During the period of intensive growth that occurs after the plant reaches 20-25 centimeters in height, a rather dangerous moment of possible disease damage occurs.
- smut is a fungus that attacks the above-ground part of the plant and the root;
- helminthosporium - a fungus that attacks the leaves of corn;
- dry rot affects cabbage heads;
- rust - the stem and leaves suffer;
- white rot affects grain quality;
- red bacteriosis is a fungus that affects the entire plant.
Smut
Rust
Rot
Stem rot
To combat these diseases, various insecticides are used, and only healthy, well-dried and soaked grains are selected for planting.
Pests and their control
The corn harvest will decrease if a farmer who does not know how the plant grows does not take measures to control pests:
- stem borer, sign of damage - curling of leaves, breaking of stems and heads of cabbage in the wind;
- meadow cutworm, winter cutworm - a butterfly whose caterpillars damage all parts of the plant;
- Swedish fly - its larva destroys young seedlings, corn does not grow;
- Wireworm is a beetle that destroys roots.
Stem borer
scoop
Swedish fly
Wireworm
The main method of pest control is deep plowing of the soil and treating plants with pesticides.
The country's leaders in growing and harvesting crops
The leading countries where corn is successfully cultivated, their ranking has not changed for decades. This includes not only those major states with a historical corn cultivation system, but also those that are introducing innovative growing methods. In the world, both countries with warm climates and temperate climates are cultivating cereals.
USA
American farmers grow cereals in the southern states. Production volumes are such that the harvest is enough to satisfy our needs and export grain to other countries. The USA provides the export market with commercial grain by 20-25%.
China
Since the 90s of the last century, the country has been a leader in the production of cereals in the world. Over the past 25 years, corn grain has overtaken the main Chinese crop, rice, in terms of harvest volume. Now corn is the main product for fattening livestock, especially pigs and poultry.
Brazil
Half of the agricultural area is occupied by corn, beans, and cassava. Brazil competes with the United States in sweet corn exports. Favorable climatic conditions contribute to the cultivation of cereal crops in the fields twice.
European Union countries
In Romania, Hungary, France, and Greece, the cultivation of fodder varieties is developed, which leads to high rates of meat and milk production. The countries of the union export corn grains, abandoning almost completely genetically modified products.
Argentina
Agriculture is developed in the country, where cereals are given a leading position. Maize is used to satisfy their needs and for export. Since food production is in first place in the state’s economy, large areas are allocated for the cultivation of fodder varieties of corn.
Ukraine
In the agricultural sector, cereal crops occupy one of the important places. Corn yields are stable from year to year due to comfortable climatic conditions.
Mexico
Farmers harvest up to 22 million tons of corn grain a year, importing another 10 million. The country buys maize for its needs from South African countries.
India
About 80% of the country's cultivated area is occupied by corn. After all, constantly high temperatures allow grain harvests to be harvested all year round. Only the period of monsoon rains does not allow plants to develop due to high humidity.
Canada
Industrial production of corn and soybeans is natural for the country. Over the past 50 years, the area under cultivation has increased in the prairies, where the temperate climate is ideal for the development of cereal crops. Canadian breeders also pay great attention to the development of maize hybrids.
Russia
Climatic conditions for growing crops are not favorable in all areas. On a global scale, plant yields are lower for Russian farmers. Therefore, we have to import grain and flour from other countries. Corn is grown everywhere for silage and feed.
South Africa
Drought is a common occurrence in southern Africa. Therefore, farmers grow maize hybrids that are drought-resistant. On the African continent, South Africa is the main producer of agricultural crops.
Features of cultivation
The plant loves sun, moderate watering and fertilizing. The technology for growing sweet corn is not particularly complicated, but requires compliance with a number of rules to obtain a rich harvest:
- Planting begins in the first ten days of May in the southern regions, and at the beginning of summer in central Russia.
- Choosing the right variety is one of the main conditions for obtaining the expected result.
- Sow in areas protected from drafts, with sufficient lighting.
- The soil must be fertile and allow moisture and air to pass through. Swampy soils are not suitable for growing corn.
- Heavy and clogged soil, poor in nutrients, is put in order: peat, sand, and organic fertilizers are added. Acidic soil is treated with lime, sandy soil is enriched with organic matter. The earth is dug up using a bayonet shovel and loosened.
- Sweet corn is planted in fields where potatoes, legumes, melons or tomatoes were previously grown.
- Before sowing, the grains are sorted and whole and large-caliber seeds are deposited. Testing for germination is carried out by soaking the material in a low concentration saline solution. The settled seeds are used for planting.
- Disinfection of grains is carried out using a concentrated solution of potassium permanganate.
- Seeds are sown in furrows 7-8 cm deep, with an interval of 10-15 cm. The beds in the neighborhood are formed at a distance of 40 cm. This ensures better cross-pollination.
- In practice, the square-cluster sowing method is often used. The plot of land is divided into squares and holes up to 10 cm are dug. Seeds are planted in them and covered with earth.
- Planting sweet corn is possible using seedlings. Seeds are sown in pots with a nutrient substrate in early spring. Seedlings are planted with the onset of warm weather.
- From the moment of rapid growth, the corn is hilled, weeded and fertilized. Watering is carried out twice a week.
- Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and compost are used as fertilizing.
- Stems are tied up if varieties are prone to lodging.
- From time to time, pinching is carried out, leaving 2-3 ears.
Composition and calorie content of corn
Corn grain is rich in starch and proteins, but the proteins lack two essential amino acids for humans: lysine and tryptophan. Lysine and tryptophan accumulate only in the germ of the grain.
Essential amino acids are not synthesized in our body from other substances. Therefore, corn grain is an inferior food, but if along with corn there are beans or other legumes, then this deficiency will be compensated.
| Nutrients | Content in % |
| Carbohydrates | 70 |
| Squirrels | from 7 to 20 |
| Fatty oil | from 4 to 8 |
| Mineral salts | 2 |
- One medium cob provides 83 kcal, a cup of corn kernels provides 13% of the recommended daily folate intake. Corn is also a good source of potassium, thiamine and dietary fiber.
- Corn is rich in the carotenoid lutein, a powerful antioxidant. This substance reduces the risk of retinal damage, the main cause of vision loss in old age.
- Corn grits are popular in Asia and North America. It is harmless for gluten intolerance as it does not contain gluten. It is used to prepare porridges and flatbreads.
- Corn flour is inferior in nutritional value to others, but in combination with legumes it provides all the necessary amino acids.
Corn is an incomplete food for humans, but it remains one of the main agricultural crops. It is used both for livestock feed and for the industrial production of more than 800 industrial products.
Why doesn't corn grow?
For some summer residents, attempts to grow corn end in failure. Why doesn’t everyone grow this culture? In order for corn to grow well, cultivation and care must meet certain requirements.
- Warm. Corn is a heat-loving crop; it does not grow if it does not have enough heat. The minimum temperature for grain germination is +10°C. At temperatures below 15°C, flowering of panicles and fertilization of ears does not occur, but warming above 25°C is also unfavorable for flowering. Corn develops best at 22-25°C during the day and about 18°C at night. With frosts of -2-3°C, young leaves are affected, and for flowering and fertilization, the danger is already -1°C.
- Moisture. Forage varieties of corn are not very demanding on moisture, but sweet varieties require abundant watering; with a lack of moisture, plants grow poorly, and drought can cause crop failure.
- Poor soil composition. Corn is a large plant with a large volume of green mass, so it does not grow well in poor soils. For normal growth and fruiting, the soil must be fertilized with organic and mineral fertilizers.
- One of the reasons why corn does not grow is the increased acidity of the soil. To eliminate this factor, it is necessary to do a soil analysis and, if necessary, add dolomite flour in the fall to remove excess acidity.
- Thickened plantings can also inhibit plants and reduce yields. Make sure that the gaps between the stems are at least 50-70 cm. It is better to orient the rows in the north-south direction so that the plants do not shade each other.
- Poor growth may be caused by dense, airtight soil. Corn needs soil rich in oxygen; clay soil can cause failure in cultivation. The looser the soil, the more oxygen it contains, and the better the plants develop. Hilling helps saturate the soil with oxygen, and the corn will thank you for it with rapid growth and a good harvest.
- A large number of stepchildren. If we are not talking about highly tillering varieties, then many stepsons can also impair the growth and yield of corn. When they break off, an infection can occur that can completely destroy the plant. Why do corn grow shoots? Corn usually fails due to stress factors - frost, hail, and the action of chemical plant protection products.
- Sometimes the cause of poor corn growth is poor quality seeds. When sowing seeds from your own collection, they may lose varietal qualities due to cross-pollination of plants. To maintain seed purity, there should be a distance of at least 40-50 m between planting different varieties of corn.
Sugar or grain?
On bags of many imported corn seeds and some domestic ones, you can see markings that are worth paying attention to. Let's see what it means
1. The most delicious corn is super sweet (“sh 2” type). It is also called wrinkled, because. its seeds are really wrinkled. The grains are high in sugar, which very slowly turns into starch. If this type of corn is grown near others, the quality of the cobs will deteriorate due to cross-pollination. The kernels on the cob will become tough rather than juicy and crispy. The best qualities of wrinkled corn are preserved only in purchased seeds, because... this is a hybrid (F1)
It is worth paying attention to the variety of grain colors. The cobs may contain not only yellow, light yellow or cream grains, but also inclusions of a different color
It is worth looking for the seeds of super-sweet early ripening hybrids “Honey Nectar”, “Creamy Nectar”, “Trophy”, “Madonna”, “Gamma” on sale.
2. Seeds of less tasty sweet corn, which have only 25% “sh 2” type grains and 75% “se” type grains, are often on sale. The cobs are harvested when fully ripe, because if harvested early, they will be unsweetened and watery.
3. Sweet corn “se” and “se+” - also quite tender and sweet only when fully ripe.
4. Old varieties of sweet corn (“su” - type) are inferior to modern ones, because have a lower sugar content, which quickly turns into starch.
Recently, many new hybrids and varieties have appeared. Among them there are black (medicinal) and bronze grains, with cobs in which multi-colored grains are collected. I even grew low ornamental corn. But I didn’t like corn for making popcorn. Everyone praises “Triple Sweetness”; I haven’t grown this corn yet.
The cobs of decorative corn turned out to be tasty and tender. They can be frozen
Preparing for landing
For better results, it is recommended to change the place for growing vegetables every five years. Different types of soil are suitable for planting cucumbers. Seeds grow best in soil containing humus.
In the southern regions, soil with a flat surface is used for planting. In regions with a cool climate, the beds are made elevated. This allows you to create a sufficient air-thermal regime.
Cucumbers grow well in soils that have adequate aeration and drainage.
Preparing the site in the fall
After harvesting in the fall, gardeners prepare the land for the new season. Choose a place for planting that is warm and well-lit. The area for vegetable crops is dug up and organic fertilizers (manure or humus) are added to the soil.
The beds are irrigated with a solution of copper sulfate. Mix 1 tbsp in 10 liters of water. l. substances. Next, according to the scheme, the weeds are removed and 2 tbsp are added to the ground. l. superphosphate and a glass of ash per 1 sq. m of land. Dig up the soil and leave it until spring.
Preparing the site for spring planting
1.5 weeks before planting, peat, a bucket of manure, sawdust and a glass of wood ash are added to the soil. Fertilizers are dug up and leveled. Irrigate the ground with hot water. To saturate the soil with nutrients, use a solution of potassium permanganate (1 g of substance per 10 liters of water).
The beds are covered with film and left until planting.
The best time to plant cucumbers
Planting dates depend on climatic conditions. The best time to sow vegetables is mid or late May. Provided that by this moment the soil temperature has established itself above +15°C, and the air temperature is not lower than +14°C. The soil temperature is checked using a thermometer. If there is a risk of night frosts, the plantings are covered with film.
In the southern regions, cucumbers are sown in open ground. In the middle zone, greenhouses are used.
Some gardeners check the lunar calendar. It changes every year. Seeds are sown for seedlings only during the waxing moon or closer to the new moon. During eclipses, it is not recommended to plant crops; this will reduce the amount of harvest.
Growing corn from seeds
Sowing corn seeds
Corn is grown by seed method - seedlings and non-seedlings. Sowing corn for seedlings is carried out in cassettes with cells with a volume of 45 cm² or in peat-humus pots with a diameter of 12 cm. Fill the cassettes and pots with a mixture of well-structured turf soil, mixed in equal proportions with rotted humus. To increase the moisture capacity of the substrate, you can add a hydrogel to it, but when filling cells and pots with soil mixture, keep in mind that the gel can absorb up to 500 volumes of water. The hydrogel will allow you to reduce the number of waterings by 3-5 times, since the crystals that have absorbed water will gradually release moisture and release it into the soil.
Corn seeds are sown in early May, after germinating them for 5-7 days in a damp cloth or filter paper at room temperature. Place 3-4 corn grains in pots, two in cells. The seeds are buried 3-4 cm, after which the soil is moistened with a warm solution of 4 g of Fundazol in 10 liters of water and the crops are transferred to a sunny windowsill with eastern or south-eastern exposure.
Growing corn seedlings
Corn seedlings develop very slowly, and it is advisable to provide additional lighting for them with a phytolamp or fluorescent lamp from the moment the seedlings emerge. During the growth period, seedlings are fed once or twice with Polyfide, Terraflex, Master or Kemira-hydro. When 3-4 leaves appear, leave one strong seedling in a cell, two in pots, and cut off weaker plants with scissors above the soil surface. The growth and development of seedlings accelerates from the moment they develop 4-5 leaves.
A week before planting seedlings in the ground, they begin to harden them with daily sessions of staying in the shade in the open air, gradually increasing the duration of the procedure until the seedlings get used to the new development conditions.
The role of culture in agriculture
Corn is a staple crop with a wide range of uses. The role of this grain plant in agriculture is important. It allows you to solve two complex problems at once - replenish grain supplies and produce nutritious feed for livestock.
Grains are an important ingredient for animal feed. Because when animals eat only grains, they are not getting a balanced protein content.
We recommend that you read St. John's wort and blood pressure
Silage is also prepared from this crop, which is well digested by the stomach of animals and has milk-producing properties, which is so useful for both cattle (cattle) and small cattle (small cattle). This plant is also used as green fodder. Not only grains are used as feed, but also dried leaves, stems and cobs.
But sowing this type of grain has both positive and negative effects. After the crop began to be grown in Russia, environmental problems arose. For example, the soil has become poorer in organic matter, the composition of the soil has deteriorated, and it has become too dense due to harvesting and transporting crops.
Useful and harmful properties
Benefits for the body Corn is rich in carotenoid antioxidants, which boost immunity and help protect the body from viral and colds.
Positively affects the functioning of the brain and nervous system. Improves concentration and memory. Helps fight nervous tension, stress, overwork and insomnia.
Has a choleretic effect. Helps painlessly dissolve deposits of kidney stones.
Has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system. Helps strengthen the walls of blood vessels and heart muscle. Normalizes high blood pressure. Helps remove “bad” cholesterol and increases the level of “good” cholesterol.
Improves skin condition. Strengthens nail plates, hair, as well as teeth and bones.
Has a positive effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Supports “good” bacteria in the intestines. Improves peristalsis, helps remove waste and toxins.
Corn does not contain gluten and is an excellent substitute for “gluten” grains.
Harm to the body Corn is contraindicated in the presence of allergies and individual intolerances.
It is also worth avoiding use for varicose veins, increased blood clotting, gastritis and acute peptic ulcers.
Features of cultivation depending on the region
Agricultural technology for cultivating corn differs depending on the climatic conditions of the region:
- In the Krasnodar region, early, mid-season, and late varieties of crops are grown everywhere. In this case, direct sowing of seeds in open ground is used.
- In the Leningrad region and Moscow region, preference is given to early and mid-season varieties. Here they use sowing in open ground and growing through seedlings.
- In the climatic conditions of the Urals and Siberia, it is preferable to plant heat-loving corn through seedlings. Then the cobs will have time to ripen before the end of the garden season.
Early corn
In regions where summers are hot and long, grain crops grow well and always ripen. Any type of cereal can be sown in the southern regions on an industrial scale. In a short period of time, the ears of early varieties of corn ripen. In mid-latitudes, hybrids bred through selection feel normal. They are sown by seeds and are suitable for growing in seedlings.
Trophy F1 is distinguished by its rapid ripening and high yield. The variety produces its first ripe cob weighing about 200 grams on the 76th day. The fruit reaches a diameter of 45 mm. The sweetish grains have a golden color and are eaten boiled and canned.
For cultivation in the Urals, in the Central Black Earth regions, breeders developed the hybrid Ladozhsky 191. Corn ripens in 113 days. On average, farmers harvest 120 centners of grain from 1 hectare, and about half a ton of green mass.
Tall bushes tolerate cold weather well, are resistant to drought, and are not affected by:
- bacterial rot;
- fusarium;
- stem borer;
- bubble smut.
In the North Caucasus, Lower Volga region, and central regions, the hybrid Ladoga 250 MV is cultivated. Corn of this variety grows to a height of almost 3 meters. The grains on the cob are arranged in rows, the number of which reaches 16. Farmers begin harvesting the crop on the 105th day after sowing in open ground. The hybrid is not afraid of drought, does not suffer from insect attacks, and rarely gets sick.
Early varieties of cereals are used in cooking, the food industry, and livestock breeding. Landmark F1 corn has a very short growing season, can be stored for a long time, and has sweet grains of bright yellow color.
The Jubilee F1 hybrid is not infected by bacteria and viruses. The plant, whose stems reach 2.5 m, pleases with a stable harvest. On the cobs, in rows, and their number is 18, round grains are formed, covered with a thin shell.
The best crop varieties for various regions of Russia
Although the climate in Russia is not entirely favorable for the development of corn, many farmers grow the plant for livestock feed . And the crop yield is at the world level: more than 5 tons per hectare. Areas where soil and weather conditions are favorable for grain cultivation receive higher yields per hectare.
Moscow region and Central Russia
In temperate climates with high air humidity and unstable weather, it is better to plant early ripening plant varieties. In 3 months, Trophy, Gamma, and Madonna varieties will have time to reach milky ripeness. In addition, hybrid grains have excellent taste and a high sugar content in the cobs.
Altai region
The short summer, but favorable for corn with its warmth, allows the cobs to ripen on time. Of course, it is better to choose varieties with early ripening:
- Triple sweetness. Harvest 100 days after germination. On bushes 2 meters high, cobs with yellow grains grow weighing 200 grams. Grains contain a lot of protein and sugar.
- Mid-season hybrid Gourmand. Small grains are of high quality, scoring 5 points in taste. The seeds are used for canning, freezing, and drying.
- Farmer of local selection. The plant produces harvests within 71 days. The length of the cobs is 13 centimeters, and the weight is 140-160 grams. The variety is valued for its compactness and medium height.
See also
The use of corn silk in official and folk medicine for the treatment of diseases, medicinal properties and contraindications
Read
It is better to choose zoned varieties of corn for regions with a temperate or cold climate.
Siberia and Urals
Here you also need to grow varieties with early or medium ripening periods. Hybrids Khutoryanka, Lakomka, Bylina are suitable.
In open ground, the frost-resistant Landmark and Jubilee successfully develop and bear fruit. Of the sweet varieties, it is recommended to cultivate Bonus F1. Milk ripe grains are used for canning.
How many ears are there on a stem?
Many summer residents are interested in how many ears corn can produce and how to grow a good harvest of this crop in the country. From one plant you can get from 1 to 4 ears. To grow the maximum number of cobs on a stem, you need to:
- Choose the right variety. In the conditions of central Russia, southern Siberia and the Urals, it is better to give preference to early and mid-early varieties.
- Do not thicken plantings. The optimal distance between plants in a row is 40 cm, between rows - 60 cm.
- Follow the rules of agricultural technology to ensure the necessary care and protection of plants.
An average of 2-3 heads of cabbage per stem is considered a good harvest. To increase the number of ears, some gardeners remove panicles from half the plants at the moment they appear. This encourages the corn to continue forming leaves and ears in its axils. And the left panicles are enough to pollinate all plants.
However, even a large harvest may not please you if the cobs are half empty. To avoid this, you need to take care of high-quality pollination. It is better not to trust the wind, and as soon as stigmas appear on the cobs, pollinate them manually, shaking pollen from the panicles onto them.
But it often happens that by the time the stigmas appear, the pollen from the panicles is washed off by rain or blown away by the wind. There is a way to insure yourself in this case. Several plants are planted (or sown) a week later. Thus, by the time the stigmas appear in the main area, a reserve supply of pollen will be ready, which will help solve the problem in case of its shortage.
Useful information from Bonduelle
At the moment, Bonduelle in Russia is very actively developing their website (bonduelle.ru) - there is really a lot of useful and interesting information there.
For example, there is an extensive and convenient section with recipes
, which currently contains 480 different options for breakfasts, snacks, salads, etc.
Page « Geo-gourmania
"talks about the gastronomic habits, culinary traditions and passions of residents of different parts of the globe.
In the section " Children"
“presents an interesting concept “We eat vegetables while playing!”, which provides recipes for children's dishes, and also describes how to prepare them together and why they are useful for the child.
The site also has a funny cartoon about the brave Pea, thanks to which you can see the entire production process in 6 minutes (you can watch it here)
This is probably all we wanted to tell you about our trip. If you have questions, ask them in the comments, we will be happy to answer!
Similar articles:
- Krasnodar - a city of bronze sculptures and fountains, our photo walk or how we got from autumn to summer
Preparing corn grains for sowing
Before planting grains, they must be prepared:
- First, a careful selection is made; preference should be given to the largest seeds; they should not be damaged.
- Next is the germination test. Selected specimens are placed in a 5% saline solution for approximately 5 minutes. Some grains will sink to the bottom; they are the most suitable.
- Next comes etching. It is necessary to protect against diseases. To do this, take a special solution - powdered pesticide, hydrogen peroxide or a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Afterwards, you need to disinfect the seeds by alternately immersing them first in hot water (no more than +50 °C), then in cold water. No more than 20 minutes.
This is interesting: Rich harvest of root celery - from seeds through seedlings
Can corn grow without human intervention?
The genus corn includes 6 plant species, but only 1 of them, sweet corn, is suitable for human consumption. There are no wild varieties of it that can grow without pre-cultivation in the open ground.
In abandoned areas you can find plants that grow on their own. In this case, seeds from unharvested or overripe and spilled cobs germinate without tillage, in open ground.
Medicinal properties and contraindications of corn silk, their useRead
Over time, with repeated self-sowing, the characteristic properties of the variety are lost, and the use of such corn becomes possible only for feeding farm animals. The conditions necessary for complete grain ripening rarely occur in this case.
Areas where corn grows and is best grown in Russia and the world
Corn or maize is one of the leading food, feed and industrial crops today. This is the oldest grain plant on our planet. Many countries in the world where corn grows are exporters of this grain.
Wild maize is native to Central and South America. Grain was brought to Europe by Columbus back in 1496. The crop came to Russia during the Russian-Turkish War in 1768-1774. Its spread throughout the country began from Bessarabia, where maize was cultivated everywhere.
In Turkey, maize is called “kokoroz” - a tall plant. Thanks to N. Khrushchev, active crop selection began in our country in the 60s of the last century. Due to the development of a large number of zoned varieties and hybrids, corn is now grown in Siberia, the Urals, and the Far East.
How does corn grow?
Corn in Russia is cultivated for grain and green fodder. The main advantage of the crop is its productivity: corn can produce 4.5 or more tons of grain and 17 tons of green mass per hectare. Corn grain is used to produce flour, starch, ethanol, dextrin, glucose, syrup, oil, and vitamin E. It is canned, processed into cereals and flakes, and used for the production of animal feed.
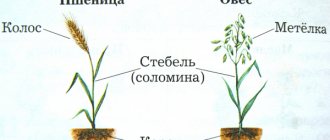
Corn is a tall annual herbaceous crop. The stem can reach a height of 3 m or more. Today, low-growing varieties are also widely cultivated. The stem can reach 7 cm in diameter. The leaves are large, about 1 m long and 10 cm wide, linear-lanceolate in shape. There can be from 8 to 42 leaves on 1 stem.
The plant has a powerful, well-developed root system that penetrates the soil to a depth of 1 m or more. Roots can also form on the lower nodes of the stem - to additionally provide the plant with moisture and nutrients, as well as support.
Maize is a monoecious, wind-pollinated plant, so its flowers are unisexual: male flowers form panicles at the top of the stems, and female flowers form cobs located in the axils of the leaves. The yield is determined depending on the variety. Corn on 1 shoot can form 1-2 cobs (or more) 4-50 cm long and 2-10 cm in diameter.
The mass of the cob can be 30-500 g. The cobs are sealed in leaf-shaped wrappers, and only long pistillate columns come out. The wind carries pollen from the male inflorescences to the pistils of the cobs, on which, after fertilization, fruits - caryopses - are formed. The plant cannot self-pollinate. In small areas, manual pollen collection and pollination may be necessary.
The grains have a cubic or round shape, they are planted tightly to each other and are located in rows on the core of the cob. One cob can contain up to 1 thousand grains. In most cases, the fruits are yellow, but there are also varieties with red, purple, blue and even black grains.
In order to learn to distinguish varieties, you can use the description and photo provided on the package of seeds; Growing corn, depending on the variety, lasts 90-150 days. Shoots appear 10-12 days after planting the seeds in the soil. Initially, this is a heat-loving crop that germinates at +8…10 ºС and develops at +20…24 ºС.
There are a large number of regionalized and adapted varieties and hybrids with a short growing season. They are able to grow and bear fruit in the cold climate of Siberia and other regions at lower temperatures and withstand frosts down to -3 ºС.
Corn is a light-loving crop. Lighting is especially important at the beginning of the growing season. Therefore, the optimal sowing method is square-cluster, in which the shadowing of each other by the shoots is minimal.
Maize is dependent on soil aeration. Loosening and other soil cultivation are necessary to obtain a good harvest. The culture is dependent on moisture supply. In hot weather, 1 plant can absorb more than 1 liter of water.
The large volume of green mass and its high content of monosaccharides involved in lactic fermentation during the silage process is the reason that corn is the main silage crop in our country.
Maize is classified as a row crop. In crop rotation, it takes the place of a predecessor of grain and leguminous crops or fallow planting when grown for green fodder.
Despite the fact that the plant greatly depletes the soil and deteriorates its structure, it frees it from weeds, many diseases and pests. In the south of the country, corn is sown in repeat crops.
What kind of soil does corn need?
The main areas for cultivating maize for grain for the production of compound feed and for the food industry are Central Asia, Transcaucasia, North Caucasus, Central Black Earth region and the Volga region. This is due to the fact that the best soils for growing crops are fertile: black soil, floodplain river soils and structural field soils. Corn can grow on sandy loams, dark gray loams and peat bogs. The plant develops and bears fruit poorly on heavy clay, marshy, salty and acidic soils.
Corn is less demanding for green fodder, and therefore is cultivated everywhere, including in the Non-Black Earth Region, on peat swamp and sod-podzolic soils.
The crop requires soil with a neutral reaction; slightly acidic soils are also acceptable. To grow maize on podzolic, acidic soils, dolomite, wood ash and organic fertilizers (humus, compost, peat) are added before planting. With sufficient application of organic and mineral fertilizers, corn can be grown on sandy soil.
Due to the characteristics of the root system, the plant requires loose soil with good aeration, enriched with oxygen.
On soils infested with weeds, especially rose bitter, creeping wheatgrass, sow thistle, and other rhizomatous and root shoot weeds, corn grows poorly. This is especially important at the seedling emergence stage.
When growing grain for the food industry, the soil must have enough phosphorus, potassium, calcium, sulfur, iron, magnesium, manganese, boron, chlorine, iodine, zinc, copper and other substances.
The mineral composition of the soil is of greatest importance at the beginning of the growing season, as well as at the stage of cob formation and milky ripeness of the grain. Timely application of organic and mineral fertilizers is an important condition for obtaining high yields and healthy corn grains for the food industry.
In the first half of the growing season, the plant especially needs nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, and after the start of flowering - phosphorus and potassium. Excess nitrogen retards grain formation.
How long does corn grow?
The length of the growing season for maize depends on the variety or hybrid of the plant. It can last from 90 to 150 days. Since Russia is 95% a risky farming area, early ripening varieties are the most popular. In this case, the grain has time to ripen before the onset of cold weather.
In the Urals, when sown in open ground, even the earliest ripening varieties do not have time to ripen, so here maize is cultivated for green fodder. To obtain grain, preliminary cultivation of seedlings is practiced, although this method is not used in large volumes. Seedlings are planted from the second half of May. Harvest occurs in August-September.
To grow corn in the North-West region and, in particular, in the Leningrad region, first-generation hybrids (F1 Candle, Spirit, Trophy and others) with a short growing season are used, the cobs of which ripen 70-75 days after emergence. For small areas, the seedling cultivation method is used. In the southern part of the region, varieties with a ripening period of 90-100 days can be cultivated. Corn grown in the Pskov region is sown in open ground in May and harvested in the first weeks of September.
Can corn grow without human intervention?
The genus corn includes 6 plant species, but only 1 of them, sweet corn, is suitable for human consumption. There are no wild varieties of it that can grow without pre-cultivation in the open ground.
What do predecessors depend on?
Crop rotation assumes the presence of plants after which the crop produces maximum yields. Maize can withstand monoculture for a long time. This is explained by the presence of a huge mass of organic matter in the soil after harvesting.
In the steppes, the highest yields are obtained after planting after winter wheat, barley, and melons. An acceptable predecessor is corn.
In the northern steppe regions, humidity is higher. It’s easy to grow a good harvest there using industrial technology. Its essence lies in the rational use of monoculture while observing the rules of agricultural technology. Good predecessors are winter wheat after black fallow.
In the forest-steppe zone, ideal predecessors are: legumes, corn for grain, potatoes. In areas with high humidity (north, northwest), the best beet yields are grown. But it should be removed early: it takes time to prepare the soil.
In the middle zone, a sufficient amount of grain is produced by plants planted after potatoes, winter crops, and corn for silage. They are placed in front of maize in this region. They do the same in areas with artificial irrigation of crops.
India
Agriculture is the most important sector of the economy in India, and is mainly focused on crop production.
India has quite a large potential for growing maize in large quantities. However, it is not used to its full capacity. This is due to ineffective financing of this sector of agriculture and the current socio-economic situation in the country. Today, India produces 26 million tons of corn (data for 2022). Next year, 2022, the harvest is predicted to decline to 25 million tons.