Observant gardeners have probably noticed that not all plants in the beds get along well with each other. Such an influence actually exists, and this fact has already been proven. Professional farmers have well studied the problem of cultural proximity; they have developed recommendations for placing plants in garden beds in such a way that they help each other develop and protect neighbors from pests. In specialized literature you can find the answer to the question of what to plant next to peas, and this information will surprise some plant growers.
Features of joint planting with peas
By planting other crops next to peas, the gardener, first of all, saves territory. In addition, joint plantings bring the following benefits:
- The productivity of vegetable crops increases.
- The taste of fruits improves.
- Due to compacted plantings, the number of weeds is reduced. The gardener does not have to spend a lot of time weeding the beds.
- The soil retains moisture longer. Water is saved, and when using a pump, electricity is saved.
- The washing away of the top layer of soil, which is the most fertile and contains a large amount of organic matter, is prevented.
- Favorable neighbors have a healing effect on each other. There is no need to use chemicals.
You need to select neighbors for peas so that they do not shield it from the sun's rays with their foliage. In addition, there should be no competition between cultures underground for water and food.
The most productive pea varieties are late-ripening. But they have a drawback: they are often affected by powdery mildew.
Planting calendar: white cabbage, cauliflower, kohlrabi, broccoli
Many types of vegetables are planted in the soil early enough that they can ripen 4 weeks before hard frost. Almost all plants have many varieties with different ripening periods and different yields.
In order to obtain high and stable yields, you must adhere to the requirements of agricultural technology and wait until the soil warms up enough to plant seedlings.
Like most vegetables, cabbage requires at least 6 hours of sunlight, moist soil rich in organic matter, and a pH of 6.5 to 6.8 for normal growth and ripening. Depending on the weather conditions of the year, you should try to plant plants in the soil at the optimal time for them.
Good neighborhood
Peas will interact well with the following plants.
Carrot
Carrot leaves thin out phytoncides that repel harmful insects. Peas, in turn, saturate the soil with nitrogen, which is necessary for the good development of the root crop. Therefore, joint planting is beneficial for both crops.
Carrot seeds must be sown in loose soil, otherwise the root crop will form small, with a large number of lateral roots.
Radish
With a lack of nitrogen, radishes do not set root crops well. A sign of a lack of substance is the pink color of the leaves. Nitrogen fertilizing can be provided by peas growing in the neighborhood. The presence of the element in the soil increases the quantity and quality of the harvest.
Radishes can be sown throughout the season at 10-day intervals. But there is a limitation: if sowing is done from the end of May to the end of June, it will go to seed. This happens because radishes are a short-day plant.
Beet
This culture has a long period of development. In spring, the shoots and root system of beets are small, so they will not interfere with the development of peas. The crop can be destroyed by a pest - the beet fly. To get rid of its larvae, the plantings are sprayed with an infusion of wood ash.
Cabbage
Cabbage needs well-fertilized soil, otherwise it will form a small head. Pea roots will loosen the soil and make it more nutritious. In addition, this proximity will improve the taste of cabbage.
Potato
Legumes are often planted between potato rows. Peas contribute to the yield of root crops by enriching the soil with nitrogen. After collecting the pods, the potatoes have room to develop.
Pea shoots will repel the Colorado potato beetle. This pest can destroy potato bushes in a short time. Without the above-ground part, the tubers of the nightshade crop will not be able to fully form.
Tomatoes
It is better to plant late varieties of tomatoes next to peas. Their development of the ground part occurs slowly. Due to this, there is no competition among vegetable shoots for sun and air.
Full-fledged tomato seedlings are obtained by planting seeds in a high-quality substrate. Then the tomatoes will need a minimal amount of fertilizing. Bushes in fertile soil will grow strong and the root system will be powerful.
Corn
The neighborhood will be favorable if the peas are planted on the sunny side of the corn. The legume crop will provide the neighbor with nitrogen. Its lashes will comfortably weave along the corn stalk.
To ensure that peas set fruit well, they are planted in the ground as early as possible. It can even tolerate frosts down to -6°C, so planting begins in early April. At air temperatures above +30°C, crop development stops.
cucumbers
The root system of cucumbers is weak. It reaches a depth of 25-30 centimeters. There will be no competition between the roots of cucumbers and peas; they get along well in neighboring beds.
Cucumber shoots reach 1.5-2 meters and can interfere with the development of legumes. But if you tie them to a trellis, or direct them to grow in the other direction, they will not interfere with peas.
Salad
These are early ripening greens that can be planted in the inter-rows of legumes. Lettuce can also be sown around the perimeter of the pea bed. First, lettuce is removed from the garden, and soon they begin to collect the pods.
Spices
Parsley, celery, mint, rosemary contain essential oils. They help repel harmful insects from the garden. The proximity benefits both herbs and peas.
Peas are a honey plant. During the flowering period, it attracts beneficial insects to the site, collecting pollen from the bushes.
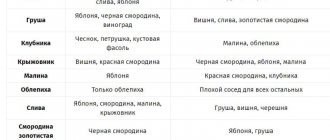
Plant compatibility.
Neighbors for carrots.
What can I plant carrots next to? The optimal neighborhood for carrots will be:
And here is a negative neighborhood for carrots:
Optimal conditions for pepper.
What vegetables are recommended to plant peppers next to? Pepper grows well next to:
Do not plant peppers near beans.
Potatoes and their neighbors.
What can I plant potatoes next to? Potatoes will bring a good harvest if planted next to:
You can’t plant potatoes if they grow nearby:
Neighbors of tomatoes.
It is recommended to grow tomatoes next to:
- asparagus;
- basil;
- beans;
- cucumbers;
- carrots;
- celery;
- dill;
- salad;
- melons;
- onions;
- parsley;
- pepper;
- radishes;
- spinach;
- thyme;
Do not place tomato beds and any types of cabbage, potatoes and corn next to each other.
Neighbors for asparagus.
What can you plant asparagus next to? An excellent neighborhood for asparagus would be:
What should you not plant asparagus with?
Fortunately, there are no plants that negatively affect the growth of asparagus.
Neighbors for beans.
What can you plant beans next to? Optimal neighborhood for beans:
- broccoli;
- corn;
- cabbage;
- carrot;
- celery;
- cauliflower;
- cucumbers;
- eggplant;
- peas;
- potato;
- radish;
- zucchini;
- strawberry;
- tomatoes.
Undesirable neighborhood for beans:
Neighbors in the beet bed.
What can you plant beets next to? Beets will give a greater yield next to:
Undesirable neighbors in the beet bed:
Broccoli and neighbors in the garden.
What should I plant broccoli next to? Optimal neighborhood for broccoli:
Unwanted neighbors for broccoli:
- cabbage;
- cauliflower;
- salad;
- green beans;
- tomatoes.
Unwanted neighbors
The following plants should not be planted next to legumes.
Sunflower
A tall sunflower can suppress many plants, including peas. Its large stems will cast a shadow over the area. In such conditions, the pea fruits will not be able to gain the necessary sweetness.
Fennel
This is a difficult plant. Fennel grows best when grown alone. If you add neighbors to it, it will invade someone else’s territory with its powerful root system, taking away moisture and nutrients.
Onion
All varieties of onions have an adverse effect on peas. The root system of amaryllis crops secretes substances that inhibit the development of beans. In addition, onions can transmit fungal diseases to peas.
The use of chemicals in the fight against pests and pathogens in early-ripening crops is undesirable.
Garlic
This is another plant of the amaryllis family. Garlic also releases substances that adversely affect peas. It is better to plant them at a sufficiently large distance from each other.
Alfalfa
Cultures belong to the same family. It is not advisable to plant related crops nearby. They are affected by similar diseases and pests. In addition, they extract the same useful substances from the soil.
Beans
This is another relative of the pea. Crops have the same need for nutrients, which is why competition occurs, as a result of which the development of both plants will deteriorate.
Pumpkin
The garden crop has powerful shoots, leaves and a root system that goes 1.5 meters deep. As the pumpkin grows, it will begin to oppress the tender pea bushes. The shoots will grow thin and weak, and the fruits will become tasteless.
Horseradish
This plant occupies a large area. Horseradish has a powerful root, extending 2.5-5 meters deep. With it, it draws moisture and nutrients around itself.
Horseradish leaves are wide, oblong, slightly spreading, and compete with peas for air and light. The leaf blades create a shadow on the ground that has an adverse effect on delicate legume bushes.
Sagebrush
Wormwood shoots have a specific aroma, which helps reduce the viability of the legume. In addition, the taste of the fruits decreases: they acquire a bitter taste.
When planting peas, you need to take into account not only the plants growing safely next to it, but also its predecessors. The best of them: potatoes, pumpkin, cucumbers, tomatoes.
Conditions for growing cabbage
Before sowing seed material, it is worth getting to know a little more about the conditions that need to be created on your site for the favorable growth of cabbage.
Temperature
As mentioned above, white cabbage is a cold-resistant crop, and therefore a short-term drop in temperature to -5 ° C will not cause severe damage to the heads of cabbage. In autumn, mature plants can survive even more unfavorable conditions.
White cabbage
The optimal temperature ranges from +15 to +18 °C. If the weather is very hot outside, it will have a negative impact on the formation of heads of cabbage. At elevated temperatures, nitrates accumulate in the crop.
Humidity indicator
The size and taste of the crop depend on how regularly the farmer waters the plant. Excessive soil moisture leads to the development of various diseases. If cabbage is constantly in damp soil, its root system will begin to die, the foliage will turn purple, and then bacteriosis will develop.
Watering cabbage
What should the lighting be like?
Shaded areas are not a suitable place for this crop. The formation of dense and juicy heads of cabbage occurs under the influence of a sufficient amount of sunlight. The longer the daylight hours, the faster the cabbage will develop.
Lack of lighting leads to the following negative consequences:
- the plant stops developing normally;
- nitrates accumulate in the heads of cabbage;
- the growth of the lower foliage stops, it turns yellow and begins to die;
- The development of the apical bud and the formation of leaves continues, but without the ovary of heads of cabbage.
What crops can be placed in the same bed with peas?
Legumes require the following maintenance conditions:
- Well-lit area.
- Moisture-absorbing, permeable, non-acidic soils. Air will flow well into loose soil. It is necessary for the activity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria found in pea roots.
- The land must be well fertilized for the previous crop.
- Low groundwater level. The plant has a tap root, which can be affected by fungus with constant humidity.
- The soil must be dug to a depth of at least 25 centimeters. This is necessary for good penetration of the root system into the deep layers of the earth.
- After seed germination, watering is required 1-2 times a week. The next day the soil needs to be loosened.
- During the period of active growth, the bushes are fed with organic matter, for example, mullein infusion.
- In case of aphid infestation, plants are sprayed with folk remedies: garlic infusion, soapy water. Due to the short growing season of early-ripening vegetables, chemicals are not used.
In the same bed with peas, crops with the same conditions will be able to develop. The following plantings will grow safely:
- strawberry;
- radish;
- carrot;
- beet;
- salad.
In order for new fruits to form on peas, ripe pods must be promptly removed from the bushes.
Cabbage and grapes
Another theory that has not been scientifically explained is that cabbage beds should be kept as far away from grapes as possible. They say that the taste of the latter's berries noticeably worsens. Considering that this gardening “belief” is more than 2000 years old, it is still worth listening to.
Among the crops that benefit grapes are hyssop, basil, geranium, and oregano, which repel pests with their strong smell. You can also plant peas, beans, clover, and blackberries next to the vineyard.
Cabbage, in turn, loves the “company” of dill, mint, chamomile, rosemary, sage, and thyme.