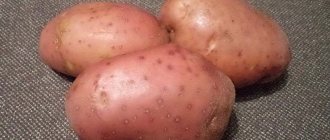
After grain crops, potatoes are perhaps the most common food product. There are thousands of varieties that can be grown in different climates and on different types of land. In many countries around the world, entire institutes are working to create potatoes with improved performance. In the first years of Soviet power, the famous Korenev experimental station was created, which became the homeland for many domestic varieties. One of them is the Lorch potato, which is still in demand after more than half a century.
Description of the variety
Lorch has an attractive appearance and excellent taste , for which it has gained its popularity among gardeners of several generations.
Origin and development
This potato variety was bred in the Kursk region in 1922 at the breeding station in Korenevo by the Soviet specialist breeder Alexander Georgievich Lorkh.
Reference. All-Russian Research Institute of Potato Farming named after. A.G. Lorja bears his name.
Since 1931, this variety has been included in the State Register and for almost 90 years it has been one of the most popular.
Distinctive features
Main features of potatoes:
- the color of the tuber is light beige, with natural dark inclusions;
- starch content - 15-20%;
- the pulp is creamy white, with excellent taste;
- eyes small, in small numbers;
- the weight of a mature tuber ranges from 90 to 120 g;
- high keeping quality of the variety - up to 92%;
- high yield - from 10 to 12 kg/m2.
Growing and care
Water the bushes during hot periods, as well as shortly after germination and during budding.
During the flowering period, the number of tubers is laid, it depends on humidity.
Fertilizers are applied to wet soil three times per season. Before flowering, nitrogen fertilizers are used, during flowering - phosphorus-potassium fertilizers, and when the bush fades - a mixture of nitrogen and phosphorus.
Plants are hilled twice during the growth period - at a height of 10 cm and 20 cm. Hilling is also carried out in moist soil. Regularly loosen the soil.
Description and characteristics of the plant and crop
Lorch bushes are tall, with erect or semi-erect stems . Stems and leaves are pale green. Leaves are produced in large numbers. The flowers are purple-pink in color.
The tubers are light beige in color, with a thin, strong skin , smooth, oblong in shape, with slight peeling near the top of the tuber. Each bush produces up to 16 potatoes, approximately 120 g each. The eyes are practically absent and are located shallowly and evenly. The pulp is not watery, soft.
Productivity
Many vegetable growers speak of this variety as high-yielding . Since their appearance, potatoes have not lost their leading positions in taste and yield. The crop is unpretentious and can be grown on any soil; it tolerates frost and drought well. From one bush of the Lorch variety you can collect up to 2 kg of tubers.
Characteristics of the potato variety Lorch
This variety is suitable for cultivation in various climatic conditions. Among the regions where it is cultivated:
- Central Chernozem;
- Middle Volga;
- North Caucasian;
- Central;
- Northwestern;
- Ural.
It can also be cultivated in Ukraine and Moldova.
Lorch potatoes are a mid-late variety, ripening 110–120 days after planting. One bush produces an average of 15–25 potatoes. About 90% of the entire harvest remains until spring, which is considered a high figure. The variety has good yield - from 10 sq. m you can collect about 25–35 kg. Lorch exhibits resistance to many diseases of root crops, in particular rust, viral infections, late blight, etc. Scab and potato cancer are dangerous for the variety.
This variety is characterized by high starch content (15–20%), which makes it an excellent raw material for starch production. This property is also determined by the fact that Lorch quickly softens during the cooking process. Therefore, these potatoes are great for making mashed potatoes, pureed soups and baking.
One of the diseases to which the Lorch variety is susceptible is cancer, which, although harmless to humans, makes the tubers unsuitable for food.
How to grow this variety
To plant and grow Lorch, it is necessary to follow agricultural techniques , prepare equipment and nutrients.
Dates, scheme and rules of planting
Favorable soil temperature for planting is +9-10˚С , air temperature is +13-15˚С, therefore the right time for planting in different regions:
- for the middle zone - the first half of May;
- in the Urals and Western Siberia - the last week of May - the first week of June;
- in the North Caucasus region - early April.
The planting scheme is maintained based on the growth characteristics of the tubers . Since Lorch is a spreading plant, it is necessary to maintain 35 cm between future bushes and 50-70 cm between rows. This scheme leaves the crop space for greenery to grow, allows it to be well ventilated, and the bushes do not shade each other.
With this planting, the plants are easy to hill up and weed: there is still room to get to the plantings without injuring the stems.
Interesting. Our ancestors determined the favorable time for planting potatoes according to the birch tree. If the young leaves have already begun to open, then it’s time to plant potatoes.
Depending on the depth of groundwater, Lorch potatoes can be planted in three ways :
- Lunochny - with deep underground waters. The depth of the holes is laid depending on the type of soil - from 8 cm on heavy loamy soils to 10 cm on loose soils.
- Trench - in soils that quickly lose moisture.
- Grebnevy - in heavy soils when groundwater occurs close to the surface of the earth.
Two tubers are placed in one nest, sprouts down, at a distance of 8 cm from each other. The top is covered with fertilizer 5 cm thick and covered with a layer of soil. After planting, the potatoes are watered.
Important! It is not recommended to plant Lorch in separate pieces with eyes, as the yield is significantly reduced.
Care
To get a good harvest , you need to properly care for the plantings. How exactly? We'll tell you further.
Hilling
This is one of the most important agrotechnical procedures , since it allows potatoes to gain access to oxygen and moisture, increasing yield by 20-30%.
The procedure is carried out in three stages. The first time - when the height of the tops reached 15 cm, the second - after 15-20 days. The third time the potatoes are earthed up after 10 days, only the mound is trimmed and the top layer of soil is loosened.
Watering
The first mandatory irrigation occurs at the moment the first shoots appear . The second - before setting the buds, the third - during the flowering period, the fourth - immediately after flowering. The water requirement for each bush is approximately 3-4 liters.
Watering is done in the evening or in the morning in the absence of extreme heat. During abnormal drought, it is recommended to water potatoes at least once a week, and this should be done between the rows and under the bush.
Loosening
It is recommended to perform this after the boundaries of the rows have been visually determined . Typically, the first loosening occurs when weeds form, and then is carried out regularly as they appear.
It is advisable to loosen after each watering or rain - this breaks up the earthen crust, which inhibits the flow of oxygen to the tubers.
Weeding
It is carried out constantly, as weeds appear. It is recommended to remove the grass during the loosening process, this makes the procedure easier. The last weeding should be done when the potatoes have finished flowering.
Top dressing
Carried out in several stages:
- Fertilizer is applied during planting directly into the ground along with the planted potatoes. For these purposes, use a handful of ash or 700 g of humus. Instead, you can use a mixture of “Nitrophoska” and bone meal - 1 tbsp. l. by 0.5 cups.
- The second feeding is carried out before the first hilling. After watering, it is necessary to add a solution of chicken manure in a ratio of 1:15.
- The last feeding is carried out during the flowering period of the plant with a solution of potassium sulfate - 30 g of fertilizer per 10 liters of water.
Nuances of cultivation and possible difficulties
Potatoes need constant sunlight , so it is not recommended to plant them in a shady area - the stems will trail along the ground and die as a result. The variety loves moist soils, but you should not overdo it either - the roots may rot.
Lorch grows well in soil where legumes and cucumbers previously grew - they saturate the soil with essential nutrients.
Interesting. The soil after planting oats is also perfect for Lorch, since the oats disinfect the soil and destroy fungus.
Although the Lorch potato has increased immunity to diseases, it is susceptible to some diseases and pests, due to which the crop can die - let's look at them in more detail.
Rhizoctoniosis
A fungal disease that can occur at any stage of plant development . It appears as black spots on tubers and dry areas on the tops. Can be destroyed with Agat-25K or Baktofit. Infected plants are removed from the site and burned. If rhizoctonia blight is detected for three years, nightshades cannot be grown in such an area.
Common scab
It appears on tubers as dark tubercles . The vegetable becomes spotted and rough. Productivity is reduced several times. The appearance of the disease can be avoided only by taking preventive measures: spraying with a solution of potassium permanganate and copper-containing substances.
Wireworm
The larvae of the click beetle, which create “wirey” passages in tubers , are found in the soil, so it is almost impossible to find them. The pest feeds on tubers, eating holes in them. If the damage is severe, the plant dies. Diseased tubers are not recommended to be eaten even after the passages have been completely removed.
To combat the pest, digging up the soil and removing weeds in which the larvae live helps. A decrease in soil acidity will also have a positive effect, since the pest loves an acidic environment.
Potato cancer
A fungal disease that enters the soil from planting material . Quickly destroys large volumes of seedlings. It appears on tubers as large uneven growths from light yellow to dark brown in color, leading to putrefactive processes. The disease has no cure.
The infected bush is destroyed or buried 1 m deep away from the plantings. Lime is poured on top or burned. For prevention, it is recommended to monitor the seed and treat it with boric acid before planting.
The soil in which cancer-infected potatoes grew can only be reused after several years.
Landing Features
Obtaining a good harvest depends on whether a number of rules are followed, in particular, whether the planting dates are met, whether the soil is prepared and whether the planting material is selected of high quality.
Landing dates
Previously, before planting potatoes, people paid attention to the birch tree. If the leaves on this tree began to open, this indicated that weather conditions were favorable for planting the crop. In general, potatoes begin to be planted from the beginning of May. The required soil temperature for planting is +9-10 C, the air temperature is about +13-15 C.
Site preparation
Lorch potatoes need to be grown in well-ventilated and illuminated areas. Any shadow will reduce the productivity of the bush.
Lorch is not picky about the type of soil. But still, potatoes grow ideally on loamy and sandy loam soils. Also, special attention should be paid to the density of the soil. The denser the soil, the worse the tubers will develop; the looser it is, the better.
The soil is prepared long before planting, in the fall. For this:
- The area is cleaned, removing weeds and crop residues.
- Fertilizers are applied. It is advisable to use humus at a rate of 4 kg per 1 m2.
- The fertilized soil is dug up to a depth of at least 15 cm. We do not break up the piles. They help retain snow, which will allow the soil to be saturated with moisture in the spring.
Planting scheme
Lorch is a spreading plant. When planting this variety, maintain 35 cm between holes and 70 cm between rows. This distance will allow the crop to be well ventilated and illuminated. Also, the hilling process will be significantly simplified.
The tuber planting depth is 10 cm. This is if the soil is good. In heavy soils, root crops are placed closer to the surface, at a depth of no more than 8 cm.
Collection, storage and use of crops
The most favorable time for digging Lorch is the end of August-beginning of September . Drying and falling tops are a sign that the tubers have already matured in the soil. About 10 days before the planned digging of potatoes, the tops are cut off, leaving 10 cm of the length of the stems above the surface.
Digging is done using a fork - a tool that is least traumatic for potatoes. After digging, leave the potatoes for some time to dry. After this, they clear the soil and sort out diseased and damaged tubers and put them in boxes.
Attention! It is necessary to dry potatoes in a shaded place, since exposure to direct sunlight provokes the production of poisonous solanine, which appears on the surface of the potato as a green color change.
Optimal storage conditions for the Lorch variety are temperature 2-4˚C , good ventilation of the room, humidity up to 85%. It is advisable to periodically sort through the potatoes, removing rotten tubers - this way the harvest will last until spring.
How to store
In proper conditions, Lorch potatoes can remain in storage not only all winter, but also until the next harvest, because The variety has good shelf life.
But for this you need to create certain conditions:
- Prepare the basement for storage: whitewash the walls, pour a fresh layer of sand or sawdust on the floor. Dry the boxes where the potatoes will be stored. The basement must be dark, otherwise the surface of the tubers will begin to turn green; such potatoes are not suitable for food.
- The storage temperature in the cellar or basement should not be lower than +1-2°C, otherwise the tubers will lose their taste and become sweetish. At temperatures above +5°C, the potatoes will begin to sprout and the tubers will become flabby.
- The optimal humidity for storing potatoes is 80-90%. If the air in the basement is too humid, there is a high probability of fungal diseases spreading. Dryness is also harmful to potatoes - moisture and elasticity of the tubers are lost.
- Potatoes should be placed in the basement for winter storage only after they have dried thoroughly. First, the tubers are carefully sorted, removing all potatoes damaged during digging, spoiled by pests or diseased. Seed material is immediately separated for planting next year; it should be stored separately from edible potatoes.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
It’s not for nothing that the Lorch potato has retained its leadership for more than 80 years - all thanks to a number of advantages:
- high yield - fruiting does not depend on weather conditions;
- frost resistance - if one sprout freezes, the plant replaces it with another;
- tubers are approximately the same size, which facilitates mechanized harvesting;
- excellent taste with optimal starch content;
- good adaptability to soil;
- keeping quality and transportability.
Minuses:
- poor tolerance to too wet soil;
- average resistance to infections.
Which regions is best suited for?
At the moment, Lorch is officially approved for cultivation in the following regions :
- Northwestern;
- Central;
- Central Black Earth;
- North Caucasian;
- Middle Volga;
- Ural;
- Nizhnevolzhsky.
Diseases and parasites
As noted above, the variety is not protected from potato cancer and common scab. Of the parasites, wireworms very often attack Lorch.
Potato cancer
With this disease, growths appear on the surface of the tubers, which are somewhat similar to cauliflower. At the initial stage, the growths have a light yellow color, which over time becomes dark brown.
Prevention of the disease consists of selecting high-quality seed material, treating it with a solution of boric acid (before planting), and maintaining crop rotation.
Common scab
This is the most common fungus (after late blight) that affects crop tubers. An infected root crop becomes covered with brown sores that resemble warts. Scab leads to a significant reduction in yield (up to 50%) and deterioration in taste, in particular due to a decrease in starch content.
We recommend reading: “Description of the Skazka potato variety”
Preventive measures include maintaining crop rotation and high-quality watering (scab multiplies in dry soils).
Wireworm
The wireworm is the larva of the click beetle. Finding this pest is almost impossible. The larva lives in the soil. Having noticed the tuber, the insect gnaws a hole in it and begins to gnaw on it from the inside. Ultimately, this leads to the death of the tuber due to the presence of numerous passages.
Preventive measures include digging up the area, removing grass (nutcrackers live in it) and normalizing the acidity of the soil (the insect prefers acidic soils).
Reviews from gardeners
The Lorch variety is grown in different regions of Russia, and everywhere there are only positive reviews from gardeners.
Alexey, Pskov : “This is not the first year I have been planting Lorch potatoes on the plot. I am glad that the tubers are formed uniform and large, as in the photo on the Internet. It’s upsetting that you have to constantly treat plants against late blight. And so I always tell my acquaintances and friends that Lorch is the best of everything I have tried. Delicious, aromatic. The harvest is always successful."
Milavitsa Petrova, Torzhok : “I have been growing this particular variety for several years now. I've tried others, but they don't compare. The tubers are always large, there are few small potatoes. When cooked they give a wonderful aroma. I’ve been harvesting a large harvest for five years now and I’m very pleased.”
Diseases and pests
Hybrids are obtained in laboratory conditions; at the genetic level, they have high immunity to infections and pests. The Lorch potato is a varietal representative of the crop, created by cross-pollination of varieties in the natural environment. Therefore, the plant’s resistance is average.
During the rainy season and low temperatures, Lorch potatoes are affected by late blight. The fungal infection appears in the second half of summer as brown spots on the tops. The disease can destroy the plant, including tubers. For preventive purposes, planting material is treated with manganese and boric acid. At the first signs of the disease, antifungal agents are used: “Exiol”, “Oxihumate”.
Rhizoctonia is a threat to potatoes, a fungal disease that develops at any stage of the growing season. Initially localized on the leaves, the lesion spreads to the tops and root crops. The disease develops quickly, the infection quickly spreads to neighboring plants, and within two weeks it can completely destroy a potato plantation. Signs of rhizoctonia: black spots on tubers, dry areas on the tops. Infected plants are removed from the site and burned. For the next three years, the site is not used for planting nightshade crops. Potatoes are treated with Agat-25 or Baktofit.
The Colorado potato beetle parasitizes crops. If there are few larvae, they are collected by hand and burned. When insects spread massively, the bushes are treated with Actellik or Decis. The root-knot nematode causes great damage to the crop, the parasite attacks the root system, the plant lags behind in development, the leaves dry out, the tops are exposed, the tubers turn out to be small and underdeveloped. It will not be possible to completely destroy the worm and save the plant. There are no remedies against nematodes. The plant is completely removed from the ground, removed from the site, and the planting site is poured with boiling water. Neighboring plants are sprayed with Aldicarb and Heterophos.
Hilling and weeding
Hilling
Hilling and weeding are mandatory procedures for caring for potatoes. During the entire period of Lorch's maturation, hilling is carried out no more than 2 times. The potatoes are hilled for the first time when the tops reach 15 cm.
Important! You should not carry out hilling in hot weather.
The second hilling is carried out 3 weeks after the first.
Potatoes need regular weeding, as it rids the soil of weeds and, accordingly, reduces the risk of many diseases.
Necessary care for potatoes
Hybrid plant varieties always have features in their characteristics and care. Potatoes of the Lorch variety are no exception; in order for a healthy and fruitful plant to grow, you will have to follow some rules.
Irrigation
In the absence of a sufficient amount of moisture during the ripening period of tubers, their deformation occurs.
Irrigation measures are especially important in arid, southern regions. The first sign of soil dehydration is wilting of the bush.
- The first abundant watering occurs after seedlings appear.
- The following irrigation works are carried out at the beginning of the growing season.
- Plants need abundant irrigation during the period of active flowering.
- The final stage of irrigation work occurs after the end of the flowering period, when the main forces and nutrients are spent on the growth and development of root crops.
During watering, the soil should be moistened to a depth of 45-50 cm, water consumption per 1 m. sq. is 50 liters.
Loosening and mulching the soil
In order to retain moisture in the soil for a long time, it is loosened. Such activities are carried out after watering or precipitation. The top layer of soil is covered with a dense crust, which prevents air and moisture from penetrating to the root crops. During loosening, this crust is removed, and weeds are also removed, which take nutrients from the plant.
Potatoes are hilled. Such methods of care saturate the soil with oxygen and retain moisture in it, and during unexpected frosts, they protect the root system from freezing.
Fertilizer application
The crop has a long period of growth and flowering, so it needs additional feeding.
The main activities for fertilizing potatoes are carried out:
- During planting, the crop is fed with humus and bone meal.
- After 2 weeks, organic fertilizers are added to the soil.
- Potash fertilizers are applied during the growing season.
Important! The breeder and professor Lorch, who created this variety of crop, believed that the new potato variety requires exclusively organic fertilizers and fertilizing
Protection from diseases and insects
The hybrid potato variety has natural immunity to many diseases and pests. But root canker, or scab, is a common cause of plant death.
To prevent this disease, it is necessary to follow the rules of care, and timely feeding saturates the plant with useful substances that will prevent the disease from developing. The greatest risk zone for cancer development is in arid regions with dry soil. Proper watering will protect the plant from infection and death.
And so that the root crops are not spoiled by the mole cricket, they are treated with special preparations before planting.
Characteristics of tubers
Characteristics of
Lorch tubers are distinguished by high tops, which have many branches. The leaves are light green in color and have medium dissection. The bushes bloom profusely, the color of the corollas is light purple.
The characteristics of the Lorch potato variety say that the tubers have an oval, slightly elongated shape. The peel color is light. The pulp has a light yellow tint. The average weight of one tuber is 115 g. The surface of the potatoes is smooth, the eyes are small, and their depth is about 4 mm.
Due to the increased starch content, potatoes turn out crumbly during cooking, which allows you to prepare a variety of first courses and first-class purees from them.
For your information! When subjected to heat treatment, the pulp retains its color by 98%.
How to properly care for the crop?
Summer residents cannot imagine their table without this root vegetable. Therefore, they boldly take on the cultivation of varietal potatoes to obtain maximum yield.
Caring for the crop is as follows:
- Watering. The Lorch variety loves water. Water at least 4 times: after germination, before flowering, during and after it. During dry periods, at least once every 10 days.
- Weeding. Weeds in the garden pull out all the useful substances from the ground, which is why the cultivated plants starve. They must be removed promptly.
- Hilling. Providing oxygen access to the roots. The first time they do this is after the potato bushes reach 15-20 cm in height.
- Treatment against insect pests and crop diseases is carried out in a timely manner. In order to identify them, it is necessary to inspect the bushes.
- Fertilizer. Potassium and phosphorus are substances that plants need to actively fight pathogens. Wood ash 20 g per 1 bush will help in the fight against pests and some diseases. Plants need nitrogen both when preparing a site for planting and during growth.
Following the rules of care helps to get healthy plants and a rich potato harvest.
Preparing tubers for planting
Preparing tubers for planting
Few people know that tubers need careful preparation before planting. This process will not only allow you to launch biological processes in the planting material and obtain strong bushes, but also protect the crop from many diseases.
To quickly obtain healthy sprouts, it is recommended to germinate the tubers. You can use the dry or wet method. Drying involves placing the planting material in a dry, well-lit place. Despite the fact that abundant light promotes the production of solanine, tubers should be sprouted in this way.
Note! Solanine is harmful to products that are consumed directly, but the appearance of this toxin in planting material forms its strong immunity and resistance to many diseases.
In the first 2 weeks, you should maintain a room temperature of about 20 ⁰C. After the first shoots appear, it is recommended to reduce it to 14 ⁰C.
The wet germination method involves placing planting material in moist peat. The content temperature should not exceed 15 ⁰C. The sun's rays should not fall on the container in which the tubers are stored.
Important! The substrate in which the potatoes are placed must be regularly moistened.
On average, the potato germination process takes about 30-35 days.