Planting peppers and eggplants: about the compatibility of vegetables
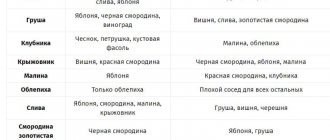
If you want to plant two different crops next door, you definitely need to find out their compatibility, which is based on these principles:
1) To what height can the plant grow? This is important because cultures should not overshadow each other and interfere with growth and development;
2) Suitable percentage of air humidity;
3) Suitable ambient temperature;
4) Sufficient soil moisture;
5) Time of fruit ripening.
If we compare the requirements of pepper and eggplant, we can conclude that they are ideal for each other as neighbors. They both love warmth, light and moist soil. Both do not like drought, frost and cold drafts. And the ideal temperature for both is around twenty-five to twenty-eight degrees.
What crops can be grown nearby?
It is better not to mix planting eggplants in a greenhouse with planting other crops, but this, of course, is unrealistic for any of our summer residents. Therefore, you should figure out what eggplants can coexist with next to them, and which neighbors are contraindicated for them. Eggplants get along well with plants that need similar conditions and the same soil composition; tomatoes are acceptable neighbors for them. But in the case of tall tomato bushes, eggplants should be placed on a sunnier side so that the tomatoes do not shade them. Planting together with peppers is also possible: they have identical growing regimes. But eggplants need more space.
When planting together with nightshade crops, it is necessary to take into account certain risks associated with the fact that they will attract the same pests. Their diseases are also the same.
Many gardeners plant eggplants along with cucumbers in greenhouses. And, although in numerous discussions various arguments are given in defense of such a neighborhood, it should be recognized that it is far from the best. First of all, cucumbers and eggplants have different requirements for air and soil humidity: cucumbers need more frequent watering than eggplants. But this is not scary: they can be planted in neighboring beds, and watering can be controlled. But cucumbers like to stretch upward, shading neighboring plantings, and eggplants need light. Therefore, if you plant cucumbers in a greenhouse with eggplants, you should separate them as much as possible in space.
To save space in the greenhouse, you can’t plant all the vegetables in one pile.
Legumes (beans, beans, peas) are considered excellent neighbors for eggplants. True, it is better to choose bush varieties among them, which is again due to the possibility of shading eggplant plantings with climbing peas or beans. You can plant any green crops along the edges of the beds. And if, for example, parsley does not require greenhouse conditions at all, then basil will say a huge “thank you” for the warmth and moisture provided to it by its owner. You can even plant onions next to the eggplants, especially if you add greens. Flowers and herbs with a strong aroma, for example, marigolds, nasturtium, thyme, oregano, will have a beneficial effect.
How to stratify the soil
These crops love fertile soil rich in microelements, macroelements and nutrients. But even if the soil is suitable, it still needs to be fertilized in order for the crops to actively grow and develop. For one square meter of the selected location, you need to add:
1) Two or three full glasses of wood ash (it is important that the ash is clean, not from painted, varnished or glued wood);
2) One tablespoon - potassium sulfate;
3) One tablespoon - superphosphate;
4) One teaspoon - urea.
After adding such a layer, you need to dig up and level the ground. Such feeding will give impetus to the seedlings for rooting and growing green mass, because it contains all the necessary macroelements, microelements and nutrients.
Preparing both seeds and site for planting seedlings
From the moment the eggplant seeds are sown in the ground, 60-70 days should pass before it is planted in a permanent place. In central Russia and the Moscow region, sowing seedlings is carried out from late February to mid-March.
Before sowing, the seeds are prepared in the same way as the seeds of other crops grown by seedlings: they are disinfected in a solution of potassium permanganate or fungicide, soaked in Epin or Zircon, and germinated in a dark place.
Finally, the moment has come when the seedlings, grown with special trepidation and care, must move to a permanent place of residence: in open or closed ground. Before you begin this process, it is important to prepare the bed and soil. If the soil is well structured, aerated and initially meets all the requirements of the crop, then the manipulations regarding its preparation will be the simplest: the application of rotted manure in the fall, ash (1-2 cups / m2), basic fertilizers containing phosphorus (Superphosphate 50-60 g ./m2) and potassium (Potassium salt 60-80 g/m2). If the soil is heavy, then this scheme must be supplemented with the appropriate fractions: sand, perlite, sawdust, straw cutting (bucket/10m2), other raising agents, peat, humus, compost (up to 5 kg/m2), dolomite flour or lime (if acidity soil below 6.5-7.0 units).
About care
Loosening the soil around crops is not recommended. But if such a need arises, you need to do it very carefully. After all, their root system has a superficial type of location, that is, it is very close to ground level and is quite easily damaged when loosening.
To maintain the required level of air exchange, as well as protect the plantings from weeds, you can resort to mulching. You can mulch with these materials:
1) Sawdust;
2) Dry straw;
3) Dried cut grass;
4) Peat.
The better the quality of the mulching material, the more beneficial properties it will bring. Mulching will also help retain moisture in the soil.
Ideal soil
Eggplants and peppers prefer a light substrate with low acidity .
Ready-made soil mixtures consisting mainly of peat are not suitable for seedlings. Every gardener has his own signature recipe for ideal soil.
Among the most successful:
- a mixture of old garden soil and rotted humus with a small portion of washed river sand;
- peat and humus in equal parts with half a portion of sawdust;
- turf soil and old manure humus in equal proportions;
- garden soil with peat in a ratio of 2 to 1 with a small amount of vermicult.
Loam is not suitable for seedlings ; it is too heavy and acidic. Any mixture must be calcined to destroy insect larvae.
It is recommended to add superphosphate and wood ash to the prepared substrate (1 tablespoon of superphosphate and 2 tablespoons of ash per bucket of soil).
Some gardeners add crushed charcoal. A correctly composed mixture turns out crumbly and airy.
Caring for adult specimens
The point of caring for adult plants is to maintain the necessary conditions for their life. Namely: 1) The required percentage of air humidity;
2) Required air temperature;
3) The required landing pattern;
4) watering mode;
5) Application of fertilizing and fertilizers.
If you carry out care procedures correctly and in a timely manner, the plants will give you an abundant and tasty harvest.
During hot summer days, it is important not to let the plants overheat. Because at temperatures of thirty degrees or more, the pollen of crops becomes sterile and because of this, even self-pollinating varieties will not be able to form ovaries. If you want to increase the yield level, then you need to shake the plant bushes a little every two to three days to ensure that they pollinate naturally.
Scheme of planting eggplants in a greenhouse, including polycarbonate
To make the beds look beautiful and the rows of eggplants to be even, you can stretch a rope along the planned rows to accurately mark the location of the holes. The planting scheme depends not only on the size of the greenhouse and the preferences of the owner, but also on the type of eggplant: among the greenhouse varieties there are varieties of varying degrees of bush growth. But in any case, the distance between the bushes in the rows should be at least 35 cm: the bushes of most varieties grow very spreading and take up a lot of space. The distance between the rows is at least 60 cm, and it turns out that there are no more than 5-6 bushes per 1 m2 of greenhouse. Denser planting increases the risk of disease due to poor ventilation of plants. Seedlings can be planted either in a regular pattern or in a checkerboard pattern: the second option is more suitable for tall varieties.
One of the eggplant planting schemes involves arranging two beds, in each of which two rows are organized
Depending on the geometry of the greenhouse, it may be convenient to plant eggplants in one or two lines. In wide greenhouses (from three meters), they most often equip a wide bed in the center, planting two rows of eggplants in it. Narrow beds are arranged along the walls for planting other vegetables. In smaller greenhouses, it is more convenient to make two wide beds along the walls with one passage between them. Three narrow beds are also possible, each of which will have only one row of eggplants. The distance from the rows to the walls of the greenhouse depends on their slope. In greenhouses with vertical walls, 25–30 cm is enough; in the case of inclined walls for tall bushes, you need to retreat up to half a meter from the wall.
Planting peppers and eggplants: help and necessary procedures for growth
Pinching
Peppers and eggplants grow very quickly. Therefore, when they reach the required growth, it is necessary to pinch them and remove excess shoots. This way the plant will spend less energy on growing green mass, and will devote all its attention to the formation of the future harvest.
When the pepper reaches a height of twenty-five centimeters, its growth should be stopped. Eggplant can be allowed to grow up to thirty centimeters. You also need to cut off excess side shoots that grow above the middle of the bush, which has reached the maximum permitted height.
Watering rules
Young seedlings just planted in open ground can be watered only once every seven days. However, adult specimens will need more moisture. An adult plant will need three liters of water. You need to water every other day. If the space around the bush is mulched, then you can use a smaller volume of liquid, at a level of two to two and a half liters for each bush. Since these are heat-loving crops, the water for watering them must be warm and settled.
You can even place a container of water directly in the greenhouse; throughout the day it will warm up to the required level, and also provide the required percentage of air humidity. Watering should be carried out strictly at the root of the plant; you should not touch the foliage and flowers. This can wash away the pollen, which in turn will have a detrimental effect on the yield of the bush.
Caring for mature plants
Since eggplants love warmth, they are planted in a place without drafts. Water according to schedule. Otherwise, the plants will be susceptible to disease. Vegetables are fed 14 days after transplanting into the greenhouse. The fertilizer mixture is prepared as follows:
- 10 g ammonium nitrate;
- 50 g superphosphate;
- 30 g urea;
- a bucket of water.
Potassium fertilizers are applied at the rate of 20 g per 10 liters of water. After 20 days, a second feeding is carried out, and the third occurs when the fruits ripen. After applying fertilizers, watering with clean water is required.
Sweet peppers also love fertilizing and loosening the soil. Only it is fertilized on wet soil: first by watering, then fertilizing. Peppers require organic matter. Take 300 g of chicken manure in a bucket of water. Apply at the root with alternation of 14 days.
First feeding
It should be carried out when the first inflorescences begin to form, that is, approximately ten days after planting. In this case, fertilizing with a high content of nitrogenous elements will be needed. For example, you can use an herbal infusion; it must be diluted with water in a ratio of one to ten. For each bush you need to allocate a liter. You can also use a solution containing mullein, bird droppings, or a universal complex mineral fertilizer with a predominance of nitrogenous elements.
Second feeding
The second feeding is carried out at the time when the crop begins to bear fruit. It must be of the root application type. During this period, plants really need potassium substances. After all, potassium plays a very important role in the formation and further development of vegetable fruits. You can purchase universal complex fertilizers in which the potassium element will predominate. Or you can make the mixture yourself, for this you will need:
1) Ten grams of potassium chloride;
2) Thirty grams of superphosphate;
3) Ten liters of water.
All this needs to be thoroughly mixed and allocated a liter of solution for each bush.