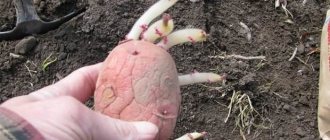
Potato variety Naiad: characteristics and description
According to the description, the variety is an erect plant of medium height of intermediate type. Potatoes are mid-season. Ripening period is 80-85 days.
The leaves have a green tint. Leaf size is medium to large. The flowers are colored red-violet. Edge waviness may or may not be present.
The tubers are oval in shape and have small eyes. The weight of one tuber varies between 72-126 g. One bush can have 6-10 fruits. The variety performs well in many regions of the country.
Naiad is suitable for growing in the following regions:
The yellow skin is smooth, and the potatoes have snow-white flesh. The starch content in potato tubers is 12.4-16.4%. The taste is excellent. The marketability rate is 82-90%.
Potatoes are resistant to the cancer pathogen, golden potato cyst nematode. The variety has moderate susceptibility to diseases such as late blight. The tops show particular resistance.
Important! The variety is used in making crispy potatoes. Tubers can also be stewed and added to clear soups.
Characteristics of Naiad potatoes
Due to its high taste, the variety is used in cooking for preparing various dishes. Potatoes do not fall apart or darken during heat treatment. The moderately crumbly pulp allows you to bake, fry, and stew naiad root vegetables.
Erect bushes of medium size. The height of the tops reaches 65 cm. Strong shoots with large or medium green leaves are formed. The waviness of the edge of the leaf blade may be absent. The corolla of the flower is red-violet.
Characteristics of tubers of the Nayada variety:
- oblong shape;
- smooth skin surface;
- a few small eyes;
- light yellow peel;
- white, dense pulp;
- starch content does not exceed 16.5%;
- average tuber weight – 73-126 g;
- marketability rate – 85-90%;
- keeping quality – 93%.
Planting and growing Naiad potatoes
Before you start planting potatoes, you need to prepare the soil and tubers.
Black soil, loamy and sandy loam soil are most suitable for the plant. Soils should be medium to light.
Heavy clay soil prevents oxygen from reaching the roots. This will provoke the development of dangerous diseases in the vegetable crop. Also, because of this, the tubers may grow irregularly shaped and small in size, and the taste will become much worse. The soil should not be too wet, as this will lead to the plant becoming infected with rot.
Important! Ideally, the soil should be slightly acidic and fertile. Potatoes cannot grow well in acidic and alkaline soil.
The following recommendations will help determine acidity:
You can get the harvest early by choosing a well-lit area with warm soil. Typically, soil fertility increases in the fall. To do this, you need to dig up the soil to a depth of 25-30 cm, mix the layers, and remove weeds. For 1 sq. m. of land it is recommended to contribute:
Important! Before planting, you should dig up the ground again, add ash and mineral fertilizers, if necessary.
It is equally important to prepare the tubers. They need to be germinated 1-1.5 months before planting. For germination, medium-sized tubers weighing up to 100 g are selected from good bushes.
The tubers are transferred to a lit, heated room and placed in boxes or in narrow film bags with a capacity of 7-8 kg. It is recommended to make holes in the bags to allow air to pass through.
You can also germinate tubers in greenhouses with a temperature of 15 degrees or more. Higher temperatures will speed up the germination process. On average, the length of the sprouts should be 9-10 mm. Successfully germinated tubers are laid out in boxes 7 days before planting and sprinkled with sawdust.
Important! It is recommended to treat the planting material with a solution of mineral fertilizers and a growth stimulator. This will contribute to the emergence of seedlings 11-12 days earlier than usual.
Planting occurs in April or early May. At this time, the earth is quite wet and warmed up to 10 degrees. Holes or furrows are made on the site. The depth of the hole is determined depending on the quality of the substrate. The lighter it is, the more it is necessary to bury the seed potatoes. As a rule, the recess is 8-10 cm.
The distance between root crops should be 35 cm, the row spacing is approximately 65-70 cm. To plant potatoes correctly, you should follow the step-by-step scheme:
You can plant root crops in furrows. To do this, dig a furrow 19 cm wide and 14 cm deep. The tubers are laid out at a distance of 30 cm from each other and sprinkled with earth. As the bush grows, more soil is added, which leads to the formation of a mound.
Landing Features
A month before the expected planting date, the stage of vernalization of seed material begins. Tubers weighing no more than 100 grams are selected. from healthy bushes. Naiad potato seeds are placed in a bright, warm room. If there is not enough space, the tubers of the variety are germinated in bags with holes or wooden boxes.
Treatment with mineral fertilizers or growth stimulants helps activate germination. Tubers are sprayed with Epin, Silk. This procedure must be carried out 2-3 weeks before planting potatoes. Spraying is combined with treatment with insecticidal and fungicidal preparations.
Landing dates
The Naiad variety is planted from early April to May. They are guided by the characteristics of the soil and temperature of a particular growing region.
If there is a high probability of return frosts, sowing is postponed until stable indicators are not lower than +10°C. It is important not to miss the time until the soil contains a sufficient amount of moisture after the winter period.
Site preparation
Naiad potatoes show high yield characteristics on loamy, sandy loam soils or black soil. Heavy soil contains insufficient oxygen. The development of the plant's root system is disrupted. Tubers are formed incorrectly, the taste of the variety and size are reduced. Waterlogged soils lead to the development of root rot.
An open area with warm soil will increase the yield of Naiad potatoes. In the fall, the soil is dug up to a depth of 30 cm. Mixing the layers of soil destroys pests and weed seeds.
The fertility characteristics of the site are increased by applying fertilizers. For 1 m² add:
- vegetable or food waste;
- up to 3 kg of humus;
- fresh manure;
- up to 30 gr. mineral fertilizer.
Planting scheme
With the classic method of planting the Nayada variety, rows are marked at a distance of 60-70 cm. The depth of the planting hole is determined by the substrate. On light, loose soils, the placement depth is 5-7 cm. On heavy, clayey soils – 10 cm.
Root crops are laid at a distance of 30-35 cm from each other. Sprouted seeds are placed in the holes with the sprouts facing up. Cover with a mixture of compost and wood ash. To protect against pests, add onion peels.
On heavy, wetlands, plantings are done in ridges 25-30 cm high. The depth of planting potatoes in holes is 10-12 cm.
How to properly care for the variety
To achieve positive results, it is recommended to adhere to the rules of potato care.
Moisten potato bushes during dry periods. Watering is not required until sprouts appear 5-10 cm high.
Water the plant for the first time a month after planting. For this, warm water is taken. For each bush, 3-4 liters of water are poured into the central part.
Before bud formation, the plant is watered once every 7-10 days. During the flowering period, the amount of water per bush increases to 20 liters.
It is necessary to regularly moisten the plant before the tops begin to turn yellow. Afterwards, watering is reduced to 3 liters of water every 3 days. The procedure is carried out in the morning or evening. A hose or drip irrigation system is used.
Care
Timely implementation of agrotechnical techniques will increase the marketable yield of the Nayada variety. Compliance with watering standards will allow the tubers to gain maximum weight. Potatoes are moistened in the morning or evening. The procedure begins with the appearance of sprouts with a height of 5 cm. The amount of water per bush is from 4 liters.
The dry period requires increased moistening of potato plantings. Water consumption increases to 6 liters. on the bush. The earth is saturated with moisture to a depth of 50 cm.
The budding period takes a lot of nutrients from the plant. Potatoes of the Naiad variety are watered once a week during the flowering stage. The amount of water per bush reaches 15 liters. A convenient way to water is to direct hoses or a drip system into the furrows.
Loosening
The first time the procedure is performed after a seven-day period. Soil aeration improves. Seed germination on loose, light soils accelerates. During subsequent stages of loosening, proceed with caution. Young tops or tubers will respond negatively to damage.
For large sowing areas, it is advisable to use a walk-behind tractor or cultivator. Mechanical attachments will improve soil characteristics and remove weeds.
Mulching
The characteristics of the Naiad variety on heavy or loamy soils are improved by mulch. The organic shelter enriches light sandy soils with nutrients. For mulching potatoes use:
- mown grass or straw;
- humus;
- peat;
- sawdust;
- rotted leaves.
Characteristics of the stages of soil preparation before mulching:
- Weed the area thoroughly;
- the soil is loosened to a depth of 5 cm and moistened;
- apply fertilizers;
- After a few days, cover with mulch.
Hilling
The procedure stimulates the growth of underground shoots, which increases the yield characteristics of the Naiad variety. The first hilling is carried out at the emergence stage. Young plants receive protection from return frosts. The growth of bush stems is stimulated.
The second time the procedure is carried out at the stage of laying buds. Young tubers form on the stolons. Hilling will saturate the soil with oxygen. A correctly carried out process will increase the yield of Naiad potatoes.
During flowering, potato bushes are not disturbed. The next hilling begins after the tops have grown. The total number of treatments reaches 4-5 times per growing season.
Characteristics of the hilling technology of the Nayada variety:
- carry out the procedure after rain or in cloudy weather;
- combine hilling with weeding of potatoes;
- the day before, fertilize with a fertilizer solution;
- use a sharp, convenient tool for work.
How to harvest and store crops
Harvesting is carried out after yellowing and lodging of the tops in the fall on a dry sunny day. You need to dig up the bushes with a shovel and pull the tops. The resulting tubers are dried, checked for quality and sent for storage. Root crops should be of medium size without damage or signs of disease.
Tubers suitable for storage are transferred to the basement or cellar. The room should have the following:
These conditions must be observed to preserve the harvest. Exposing the tubers to sunlight can cause them to sprout. Moisture can cause crop rot.
Important! The keeping quality of the variety is 93%. The shelf life of potatoes can be increased by treating them with copper sulfate before storing them.
Harvesting and storage
One root system produces up to 10 tubers by the end of the growing season. According to the yield characteristics, the Nayada variety brings 190-360 centners per hectare.
Harvesting begins after the foliage has dried in sunny weather. The dug up tubers are dried and sorted by quality. Potatoes of medium and large size without symptoms of disease are sent for storage. The storage period is increased by treating the crop with copper sulfate.
The high characteristics of the Nayada potato variety cover the existing shortcomings. Proper care minimizes crop losses.
Favorite among gardeners and summer residents from all over the world - Naiad potatoes: description of the variety, reviews
The Russian variety Nayada is loved by farmers from different regions of the country, and by summer residents from Belarus, Ukraine, and Moldova. These potatoes are well adapted to weather changes and bear fruit well in any climate, from cool to southern.
| Ripening time | Starch content, % | Weight of tubers, gr. | Number of tubers in a bush | Productivity, c/ha | Keeping quality, % | Peel color | Flesh color | Country of selection |
| Mid-season | 12,4–16,4 | 72-126 | 6-10 | 193–373 | 93 | Yellow | White | Russia (USSR) |
Description and characteristics of the variety
Naiad potatoes are part of the line of domestic mid-season varieties. The ripening period is 80–85 days (from full germination).
Distinctive features of tubers:
The taste of the variety is excellent: chefs use the tubers for a variety of dishes. Table appointment - VS. Potatoes do not darken or fall apart during heat treatment. The pulp is moderately crumbly. Tubers can be fried, stewed, baked, boiled in their uniforms.
The bushes are medium-sized, with strong shoots. The length of the tops is 50–65 cm. In 1 root system, 6–10 tubers ripen, uniform in shape and size. Large and medium-sized potatoes predominate. Keeping quality - 93%.
Where you can grow potatoes (suitable areas):
The variety tolerates temporary temperature drops well, is cold-resistant and drought-resistant. Productivity does not decrease in hot weather.
Landing
Tubers begin to germinate from the 1st–2nd decade of April (20–25 days before the planned planting). To activate it, farmers recommend spraying the seed material with Bioglobin, Epin, Silk.
Tubers are sprayed with fungicides against fungal pathogens: Acrobat MC, Pennkozeb. You can use 1% Fitosporin or Bordeaux mixture for disinfection. The insecticidal agents Microcin and Tsimbush are used against Colorado potato beetles and mole crickets.
Potatoes are planted in the classic way - in even or double rows. If the area is marshy, farmers advise raising the plantings: planting them in ridges 20–30 cm high. The depth of the holes is 8–12 cm.
Growing and care
Naiad potatoes require standard agricultural practices. Hill up 2-3 times, the surface of the beds is loosened after moisture and rain.
During prolonged drought, bushes are watered at the rate of 4–6 liters per bush. Make sure that water saturates the ground to a depth of 50 cm. When flowering begins, potatoes need moisture: water once every 7–10 days, the water norm is up to 10–15 liters per bush. The time of the procedure is morning or evening. They use a drip system, sprinkling technology, and hoses. Water is directed into the furrows or under the roots.
First fertilize with nitrogen compounds:
At the height of tuber setting, solutions of potassium sulfate and superphosphate are needed.
Diseases and pests, how to fight
Potato Naiad practically does not suffer from viral and bacterial infections. Farmers give the following characteristics of the variety’s resistance:
| Sustainability | Name |
| Weak | Phytophthora green mass |
| Moderate | Scab, late blight of tubers |
| Strong | Cancer, nematode |
With high humidity and against the background of a late blight epidemic in the area, the risk of infection increases. Signs of infection are brownish lesions on the tops and leaf blades. When tubers are damaged, depressed spots appear.
For preventive purposes against late blight, bushes are sprayed with biological agents (Trichodermin, Fitosporin), copper preparations (Kuproksat, Bordeaux mixture), and contact fungicides (Gamair, Alirin). The frequency of processing is from 2 to 8 times. Interval - 7–8 days.
Treatment with Epin, Albit, and Ordan helps against scab. Crop rotation is maintained on the site and weeds are removed. In case of massive damage, the affected bushes are taken out of the field and burned.
Source
General description and characteristics of early, late and mid-late varieties
Early potato varieties are classified according to ripening dates as follows:
Late varieties according to ripening dates are distributed as follows:
When choosing seed material, it is recommended to be guided by how quickly the variety ripens, where it comes from, and in what climatic conditions it will be planted. When considering late potato varieties for planting, read the description of the crop and look at photos of the future harvest so as not to make a mistake in your choice.
Important! Tubers of early ripening varieties and hybrids are rarely subject to fungal infections.
When choosing a variety for planting in the difficult climatic zone of the Moscow region, you should remember about protection from pests and diseases. In this region, it is better to plant early and mid-early potatoes, since late ones may not have time to ripen.
In the southern regions of Russia, late varieties are cultivated, since summer weather lasts there from May to September.
Chemical composition, trace elements and vitamins
The main indicator of the quality and nutritional value of potato tubers is their chemical composition. The amount of water in early potatoes is 78-87%, in mid-ripening potatoes it ranges from 73 to 82%, and in late potatoes – 70-83%. The rest is the proportion of dry matter.
The main component of dry matter is starch, its share in grams:
The amount of sugar, proteins, acids and vitamins is presented in the table:
| Potato varieties by ripening time | Sugar, g | Proteins, g | Acids, g | Vitamin C, mg | Energy value, kcal |
| Early | 0,5-1,3 | 0,7-1,6 | 0,1 | 15-18 | 61 |
| Average | 0,5-0,8 | 0,8-2,6 | 0,1 | 16-20 | 76 |
| Late | 0,5-0,9 | 0,7-2,1 | 0,1 | 12-17 | 80 |
Potato tubers also contain mineral salts - 1%, fiber - 1%, fats - 0.1%, organic acids - 1.6%.
Characteristics of tubers and yield
The most popular early varieties in Russia are Timo, Impala, Zhukovsky early, Kholmogorsky, Gala, Romano. They are distinguished by a short growing season and strong immunity, that is, resistant to diseases. A harvest of 35-60 tons is obtained from each hectare. The tubers are medium-sized, weighing from 80 to 190 g.
Late: Asterix, Saturna, Zarnitsa, Picasso. These potatoes contain a lot of starch, so the tubers boil quickly. The harvest is stored for a long time. The weight of the tubers ranges from 60 to 150 g.
The yield of late potatoes reaches 300 centners per hectare, depending on the variety and climatic conditions. Due to the long growing season, late species are susceptible to late blight and scab.
When choosing planting material for mid-season varieties, it is necessary, first of all, to pay attention to resistance to late blight disease, since the growing season coincides with the timing of its spread. The harvest of mid-season potato varieties is harvested and stored in August.
Region for cultivation and planting dates
For each climatic zone, the types of potatoes suitable for cultivation are zoned. Only if the planting material is correctly selected can you achieve a good harvest and not waste time and energy.
Moscow region
Belongs to the zone of problematic agriculture. Summer here is not always warm and dry. The climate is moderate continental, its main distinguishing features are mild winters and rainy summers with night and day temperature changes. The first frosts may occur in early September. In such conditions, early varieties should be planted. The best for this climate: Impala, Zhukovsky early, Spring, Udacha, Sineglazka.
It is recommended to begin preparing planting material on the 20th of March. Tubers are germinated until sprouts appear at a temperature of +20...+24°C. Then they are placed in a cool place for hardening.
Reference. Folk omens advise watching dandelions: as soon as the first buds appear on these plants, this means that the ground has already warmed up enough for potatoes to be planted in it.
Siberia
The region has a sharply continental climate with spring frosts and a short summer with heavy rains in August. Early and mid-early varieties have been bred for this region : Tuleevsky, Nevsky, Adretta, Impala, Udacha, Lyubava. Tubers in Siberia are planted from mid-May to mid-June.
Siberia is located in three time zones, so there are no average potato planting times for such a vast territory. Local summer residents are guided by the time of the last frost on the ground.
Many people follow folk signs and look at a birch leaf not far from the site. If it has reached the size of a penny, this means that the soil has warmed up to the required temperature and it is time to plant potatoes.
To ensure that the seedlings germinate quickly and receive as much spring sun as possible, in Siberia the seed material is germinated before planting. The harvest is harvested in early September.
It is famous for its short warm period, so early and mid-season potatoes are cultivated here : Udacha, Timo, Riviera, Impala, Gala, Nevsky. Frosts are a common occurrence here even in June.
The best time to plant potato tubers in this region is June 10-12, when the danger of frost has already passed. In the Urals, it is customary to plant potatoes under straw, which, being above the plantings, releases a large amount of nitrogen. In this case, the bushes grow powerful and the tubers grow large.
Central Russia
This region is characterized by a temperate climate and high humidity. It is summer-like warm here from May to October. Varieties developed for these areas:
Potatoes in the middle zone are planted at the end of April - beginning of May in soil heated to 8°C.
For the south of Russia, hot summers and lack of moisture are common. In this region, they manage to harvest early varieties twice a season: Udacha, Impala, Alena, Zhukovsky.
To plant for the winter, late varieties are grown : Temp, Picasso, Nikulinsky. The warm summer period in the south of the country lasts from March to October.
The best early, late and mid-late varieties
To decide on the choice of variety for planting, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the main characteristics of the most popular potatoes.
Naiad
Mid-season, unpretentious, nematode and cancer resistant potatoes.
Moderately susceptible to late blight on tops and resistant to tubers. Moderately resistant to scab virus. Suitable for cultivation in most regions of Russia.
It has large oblong tubers, of which there are 6-10 under the bush. Productivity is 193-370 c/ha.
Growing regions: Northern, Northwestern, Central, Volga-Vyatka, Central Black Earth, Ural, Far Eastern.
Madeira
Mid-early table variety. The tubers are oval, smooth, weighing 106-136 g. The average yield ranges from 202 to 481 c/ha. Resistant to scab, brown spot, potato cancer.
Moderately resistant to late blight. Unpretentious in cultivation. The main feature of the variety is that it requires careful digging of the soil. Madeira potatoes easily absorb nitrogen, so they should be fed less nitrogen fertilizers than other varieties.
This variety has a pink color and thin skin. The tubers are elongated, with a flat, smooth surface, without eyes, weighing 100-150 g. Virgo potatoes are resistant to diseases and pests.
It has a high yield: up to 1 kg of tubers are obtained from one potato bush per season. It is undemanding to soil quality, so it is grown everywhere in Russia.
Gull
Mid-late variety . It is planted in May and harvested in September. The tubers are yellow, oval-shaped, with eyes, weighing from 70 to 125 g. The main advantage is that it is perfectly stored.
The average yield is 240-400 c/ha. Chaika potatoes are suitable for growing in the Volga-Vyatka and North-Western regions. The variety is resistant to potato blight, but suffers from late blight and scab. Seeds should be treated with fungicides before planting.
Atlant
Late variety. Suitable for cultivation in the Central region. The average yield is 164-234 c/ha. The tubers are oval-round, with medium-deep eyes, weighing 90-119 g. The harvest is perfectly stored.
Potatoes are resistant to the pathogen of potato cancer and golden nematode, moderately susceptible to late blight on tops and tubers. Resistant to wrinkles, streaking and leaf curl. Suitable for growing on all types of soil.
Late ripening variety. The tubers are large, weighing from 100 to 250 g, with small eyes. Under one bush, 7-9 tubers of different sizes are usually formed. Potatoes tolerate transportation well and are stored for a long time.
Tempe potatoes are grown in well-irrigated fields as they are drought tolerant. Under favorable conditions, the yield reaches 550 c/ha. The variety is resistant to late blight and cancer, but is susceptible to viral diseases. Treatments against wireworms, nematodes and Colorado potato beetles are required.
Asterix
Elite universal variety with a late ripening period. It has medium-sized, oval-shaped tubers, weighing 80-120 g. From 10 to 12 tubers are formed under each bush.
Resistant to cancer, fomosis, leaf curl, late blight of tops and tubers. It is also not affected by nematodes. But Asterix potatoes are susceptible to virus Y. Therefore, bushes of this variety must be treated with insecticides against aphids and leafhoppers.
Agria
Mid-late potato, recommended for cultivation in the Central and Central Black Earth regions . The tubers are elongated oval, yellow in color, with superficial eyes. Weight – 72-135 g.
The variety is resistant to potato canker and golden nematode, but is susceptible to late blight and common scab. It is moderately affected by leaf curling and is slightly damaged by mosaic.
Krinitsa
Mid-season variety. The average yield is 498 c/ha. It has round yellow tubers. Potatoes Krinitsa (Krynitsa) are resistant to nematodes and moderately resistant to viruses, late blight, and common scab.
Multi-tuberous, therefore, when growing, it requires more sparse planting. Loves mineral feeding. In the second half of the growing season, in case of drought, additional irrigation is needed.
Purple Haze
Mid-season variety with a powerful root system and 10-15 tubers per bush. It has a high yield - 182-309 c/ha. It can be stored for a long time. Resistant to potato blight and leaf roll virus.
Moderately susceptible to late blight, banded and wrinkled mosaic. Susceptible to nematode. Prefers fertile soils; in poor, heavy soil the yield is significantly reduced.
Diseases and parasites
The Nayada variety shows high resistance to cancer pathogens, potato golden nematode. It has moderate susceptibility to late blight on tops and tubers. Naiad potatoes are moderately resistant to common scab and viruses.
Verticillium
The disease is caused by a fungus. Active development occurs after mid-summer in hot weather. The pathogen enters the soil with contaminated manure or compost.
Characteristics of the manifestation of the disease:
- The lower tier of leaves is affected first;
- the leaf blade turns yellow and fades;
- rotten areas form in place of the eyes;
- tuber tissues darken.
Verticillium reduces the yield of the variety by 20-30%. Affected tubers are destroyed. To prevent infection, plantings are treated with Fitosporin.
Late blight
The manifestation of the disease does not depend on the characteristics of the soil, climatic conditions, or temperature. Fungal infection leads to loss of up to 70% of the crop.
Characteristics of disease symptoms of the Nayada variety:
- leaf blades become covered with brown spots;
- a white coating appears on the underside of the leaf;
- gray hardening spots develop on tubers;
- patches of potato pulp die off.
To prevent the disease, the soil and tops are treated with fungicidal agents. Maintain crop rotation on the site.
Potato scoop
Butterflies lay eggs on plant stems. Active development of caterpillars begins at the end of April. Parasites gnaw and eat all parts of the plant. Affected tubers rot.
Characteristics of potato cutworm caterpillars:
- red-brown or light yellow color;
- dark stripe on the back;
- body up to 4.5 cm long;
- pupa yellow-brown;
- lives in shaded, damp areas.
To prevent the proliferation of parasites, regularly loosen the soil and weed out weeds. The bushes are treated with a decoction of wormwood.
Reviews of early, mid-late and late varieties
Experienced gardeners help beginners by leaving reviews and sharing their experience of growing different varieties of potatoes.
Sergey, Tver: “I have been growing the mid-season Nayada potato variety for several years now, after I saw a photo of one farmer’s crop, and then read the description and reviews about it. I’m happy with everything about these potatoes, I especially like the large tubers - the harvest is harvested quickly and without shaking up all the soil around the bush.”
Anna, Pskov : “The soil on my site is depleted, so I planted Madeira - it doesn’t need a lot of nitrogen, and in general it’s an unpretentious variety. I got a good harvest without much effort.”
Irina, Krasnodar : “Last year I planted the late potato variety Atlant, after reading its description and reviews about it and looking at the photo. I was surprised that he wasn’t sick all summer. I planned it for winter storage, it stayed until February. I sorted through it often - there were almost no spoiled tubers.”
Video about the Naiad variety
Unfortunately, there is no video for this variety at the moment. We invite you to watch the video section of our website, where other videos about potatoes and other agricultural crops are posted. We and the entire farming community will be grateful if you send us your video or link about this variety from YouTube or any other video hosting service. If you see this message, it means that we have not yet been able to find a suitable video for this variety.
Similar articles:
Potatoes and all their varieties in detail here → Potato variety “Bryansk New” - description characteristics reviews photo video
Potatoes and all its varieties in detail here → Potato variety "Bonnie" - description characteristics reviews photo video
Potatoes and all their varieties in detail here → Potato variety “Brook” - description characteristics reviews photos video
Potatoes and all their varieties in detail here → Potato variety “Batya” - description characteristics reviews photos video
Potatoes and all their varieties in detail here → Potato variety “Bronnitsky” - description characteristics reviews photos video