How much copper sulfate is in a tablespoon, teaspoon, glass, matchbox (grams)
Copper sulfate is widely used in agriculture.
It is used to protect against fungal diseases, and also as a top dressing to compensate for copper deficiency in plants. It is recommended to use vitriol in accordance with dosages. They are indicated in the instructions for use on the packaging and in the literature concerning the preparation of solutions for spraying plants. The quantity is indicated everywhere in grams, but at the dacha it is not always possible to use scales to measure accurately. Putting it by eye is not good. It is very important to maintain proportions here. Signs of approximate weight come to the rescue: of a particular fertilizer is contained in a tablespoon, teaspoon, matchbox, glass (in grams) . We are interested in copper sulfate . Let's see.
Copper sulfate contains:
- In a matchbox: 22-25 g.,
- In a glass: 220-250 g.,
- Per tablespoon: 16 g.
- Per teaspoon: 5 g.
We decided to weigh ourselves to check how accurate this data is.
How many grams of magnesium sulfate are in a teaspoon. how much fertilizer is in a teaspoon...?
| substance | tea spoon | tablespoon | Matchbox | glass 200ml |
| ammonium nitrate | 4 | 17 | 17 | 170 |
| dolomite flour | 8 | 25 | 34 | 340 |
| ash | 2 | 8 | 10 | 100 |
| fluff lime (slaked lime) | 3 | 9 | 12 | 120 |
| lime flour | 8 | 22 | 30 | |
| potassium salt | 5 | 17 | 22 | 220 |
| potassium magnesium (potassium sulfate + manganese) | 5 | 16 | 20 | 200 |
| calcium nitrate | 5 | 15 | 20 | 200 |
| copper sulfate | 5 | 16 | 22 | 220 |
| iron sulfate | 5 | 16 | 22 | 200 |
| urea (carbamide) | 3 | 10 | 13 | 130 |
| sodium nitrate | 6 | 18 | 24 | 240 |
| nitroamophoska | 5 | 14 | 18 | 180 |
| nitrophoska | 5 | 15 | 20 | 200 |
| colloidal sulfur | — | — | 13 | 130 |
| soda ash | — | — | 12 | 130 |
| potassium sulfate (potassium sulfate) | 6 | 20 | 26 | 260 |
| ammonium sulfate | 5 | 12 | 16 | 160 |
| double granulated superphosphate | 5 | 15 | 20 | 200 |
| simple granulated superphosphate | 5 | 17 | 22 | 220 |
| superphosphate powder | 6 | 18 | 24 | 240 |
| phosphorus flour | 9 | 26 | 35 | 350 |
| potassium chloride | 5 | 14 | 18 | 180 |
how much does fertilizer weigh in a 10 liter bucket?
How to calculate the amount of active substance and fertilizer.
Sometimes plant care recommendations indicate the weight of the active substance rather than the fertilizer itself. For example, it is recommended to add 6 grams of nitrogen per square meter. Note, not urea, not ammonium nitrate, but nitrogen.
In such cases, the following formula is applicable. The required amount of active substance (in our example it is 6 g of nitrogen) must be multiplied by 100 and divided by the percentage of nitrogen in the fertilizer. Let's take ammonium nitrate as an example. The percentage of nitrogen in it is 34%. Let's do the calculation:
600g: 34 = 17.65, well, that’s about 18 grams. This means that in order for the earth to receive 6 g of nitrogen per 1 square meter, we need to take 18 grams of ammonium nitrate, and this can easily fit into a salt spoon (table above).
Let’s calculate as an example: per 3 square meters you need to add 8 grams of phosphorus. We have double superphosphate, the percentage of active phosphorus in it is 40%. We count:
800g: 40% = 20g. 20 grams of double superphosphate is a matchbox (table above).
Our experiment
We found that 1 teaspoon contains 7 g of copper sulfate:
In 1 tablespoon - 25 grams of copper sulfate:
In 1 matchbox - 23 grams of copper sulfate:
It is worth noting that the data may differ from time to time. The weight greatly depends on the volume of the spoon or glass; fertilizers are taken with or without a slide. So the data we obtained is very different from the generally accepted data. Let's compare:
- In a matchbox: 22-25 g (we have 23 g),
- In a glass: 220-250 g (not measured, but it is believed that 1 faceted glass holds 10 matchboxes),
- In a tablespoon: 16 g (we have 25 g),
- In a teaspoon: 5 g (we have 7 g).
Important: Our experiments on measuring fertilizers such as urea, superphosphate, copper sulfate, ammonium nitrate showed one very important thing: a matchbox is the most accurate unit of measurement. In all cases, it was precisely the weight of fertilizers in a matchbox, given in reference books and obtained by us in experiments, COICH! Therefore, it is advisable to measure the amount of fertilizer using a matchbox.
How many grams of agricola are in a teaspoon? How many grams are in a teaspoon (table)
Good afternoon, today we will tell you how many grams are in a teaspoon. Using kitchen charts makes it easier to measure ingredients to prepare a recipe. Especially if you don’t have scales, measuring spoons and measuring cups on hand. But in every kitchen there is a teaspoon. You can get used to such measuring utensils. And in the future it will even be very convenient and quick to measure in spoons. If you have never done this before, we recommend you try it. Very comfortably!
Attention! Using a teaspoon as a unit of measurement, do not forget that different products with the same volume have different weights.
How many grams in a teaspoon
| 6 | |
| Sawdust horse manure (litter) | 5 |
| Horse dung | 8 |
| Cow dung fresh | 9 |
| Slurry | 12 |
| Dry sawdust | 8 |
| Humus | 8 |
| Bird droppings | 5 |
| garden soil | 12 |
| Dry peat | 5 |
| Tea spoon | In grams (with a slide) | In grams (without slide) |
| gelatin | 5 years | 3 years |
| starch | 10 g. | 7 years |
| flour | 10 g. | 5 years |
| Sahara | 7 years | 5 years |
| salt | 10 g. | 7 years |
| soda | 12 | 8 years |
| dry yeast | 4 years | 3 years |
| milk powder | 12 | 7 years |
| citric acid | 7 years | 5 years |
| baking powder | 5 years | 3 years |
| protein | 8 years | 5 years |
| powdered sugar | 10 g. | 7 years |
| instant coffee | 2.5 g. | 2 years |
| cocoa powder | 5 years | 3 years |
| ground red pepper | — | 1.79 g. |
| ground black pepper | — | 2.33 g. |
| allspice ground | 2.4 g. | |
| ground cinnamon | 8 years | 5 years |
| egg powder | 6 years | 4 years |
| semolina | 7 years | 4 years |
| buckwheat | 8 years | 5 years |
| millet | 8 years | 5 years |
| oatmeal | 6 years | 4 years |
| pearl barley | 8 years | 5 years |
| barley groats | 7 years | 4 years |
| corn grits | 7 years | 4 years |
| rice | 8 years | 5 years |
| poppy | 5 years | 3 years |
| dry grass | 3 years | 2 years |
How many grams of copper sulfate are in a spoon (teaspoon, tablespoon)?
Copper sulfate is actively used in agriculture as a fungicide and fertilizer, so many gardeners will be interested to know how it can be quickly measured without scales using ordinary spoons. In this article we will learn in more detail how many grams of copper sulfate are in a teaspoon and a tablespoon, and how it can be weighed without scales in grams.
Note: a tablespoon and a teaspoon contain the same amount of copper and iron sulfate (you can easily measure iron sulfate using the indicated values).
How much Humate is in a tablespoon?
It’s easy to figure out that 100 ml of this mixture is equivalent to a tablespoon
, in which the fertilizer is located.
humate
in this form is extremely convenient to use.
Interesting materials:
How to disable file caching in Windows 10? How to disable the Windows key while gaming? How to disable the Windows button on a gaming keyboard? How to disable the Recycle Bin in Windows 7? How to disable the Windows 7 Startup Update setting? How to disable Norton Internet Security on Windows 10? How to disable Windows update at startup? How to disable sandboxing in Windows 10? How to disable tiles in Windows 10 start? How to disable file deletion confirmation in Windows 7?
How to measure copper sulfate without scales in grams?
To disinfect and fertilize different types of plants in the garden or vegetable garden, different amounts of copper sulfate may be required, so below are ready-made calculations of how much it will be in spoons (for ease of calculations, we will use the mass of sulfate in a tablespoon of 15 grams):
- 300 g of copper sulfate = 20 tablespoons.
- 100 g of copper sulfate = 6 tablespoons + 2 teaspoons.
- 90 g of copper sulfate = 6 tablespoons of copper sulfate.
- 80 g of copper sulfate = 5 tablespoons + 1 teaspoon.
- 70 g of copper sulfate = 4 tablespoons + 2 teaspoons.
- 60 g of copper sulfate = 4 tablespoons of copper sulfate.
- 50 g of copper sulfate = 3 tablespoons + 1 teaspoon.
- 40 g of copper sulfate = 2 tablespoons + 2 teaspoons.
- 30 g of copper sulfate = 2 tablespoons of copper sulfate.
- 25 g of copper sulfate = 1 tablespoon + 2 teaspoons = 5 teaspoons.
- 20 g of copper sulfate = 4 teaspoons of copper sulfate.
- 10 g of copper sulfate = 2 teaspoons.
- 9 grams of copper sulfate = approximately 2 teaspoons.0
- 6 grams of copper sulfate = 1 teaspoon + pinch.
- 4 grams of copper sulfate = 1 teaspoon - a pinch.
- 2 grams of copper sulfate = approximately half a teaspoon.
- 0.9 – 1 gram of copper sulfate = a fifth of a teaspoon = on the tip of a knife.
We also recommend a review of how to weigh other types of fertilizers using spoons: how many grams of fertilizer are in a spoon.
In conclusion to the article, we can conclude that the ability to measure copper sulfate and other types of fertilizer using ordinary spoons will significantly save your time if you do not have accurate scales at hand. We leave our advice and reviews on how to measure copper sulfate with a tablespoon or a teaspoon (or other methods) if you don’t have scales in the comments to this article and share it on social networks if it was useful to you.
Hi all! I am Inna, the author of articles on this blog. An enterprising housewife with more than 4 years of experience in a cleaning company. I will be happy to answer all questions on the topic of articles in the comments! Always ready to share my useful tips!
How to prepare a solution of copper sulfate?
The most common solution in use is a one percent solution; to prepare it, take 100 grams of powder per ten liters of water.
The dry mixture is poured into a container and diluted with a small amount of warm water, 3-4 cups or 500 ml. The water temperature for better dissolution is approximately 45-50 degrees Celsius.
Dissolve slowly and let this mixture sit for 20-30 minutes. Heat the remaining water (9.5 liters) until hot, but not boiling, and mix with the prepared solution in a bucket. It is impossible to heat the solution during the preparation process, using any heating devices!
If you need a 2% solution, then take 2 times more vitriol for the same amount of water, that is, 200 grams per 10 liters of water. For a 3% solution - 300 grams, for 5% - 500 grams per bucket or 10 liters of water.
How many grams of lime are in a matchbox. How much does it weigh in grams?
If you need to apply fertilizer, but there are no scales at hand, then a tablespoon and a teaspoon, a matchbox, a glass and, of course, a bucket can help you out.
A 10 liter bucket includes:
• fresh horse manure – 8 kg;
• the same on a sawdust bed – 5 kg;
• fresh cow manure – 9 kg;
• dry lowland peat – 5 kg;
In a faceted glass with a capacity of 200 cubic meters. cm includes:
• ammonium sulfate – 180 g;
In a matchbox with a capacity of 20 cubic meters. see includes:
• superphosphate powder – 24 g;
• granulated superphosphate – 22 g;
How much slaked lime is in a tablespoon? How many grams of fertilizer are in a tablespoon or table of measures
Gardeners who use mineral fertilizers to fertilize their plantings have countless bags, bags and packets of multi-colored powders and granules in their garden shed. But what people in the country usually don’t have are scales to dispense precise doses of fertilizers in grams.
No questions! Gardening is simple, they publish a table of measures, from which you can always find out how many grams of fertilizer are in a glass, a tablespoon, a regular bucket or a matchbox.
Reference table “Fertilizer weight measures”
| Fertilizer name | grams in tablespoon | Gram in a matchbox | Gram in a glass 200 ml. | grams in teaspoon |
| Ammonium nitrate | 17 | 17 | 170 | 4 |
| Dolomite flour | 25 | 34 | 340 | 8 |
| Ash | 8 | 10 | 100 | 2 |
| Limestone flour | 22 | 30 | 300 | 8 |
| Slaked lime | 9 | 12 | 120 | 3 |
| Calcium nitrate | 15 | 20 | 200 | 5 |
| Urea | 10 | 13 | 130 | 3 |
| Sodium nitrate | 18 | 24 | 240 | 6 |
| Potassium sulfate | 20 | 26 | 260 | 6 |
| Ammonium sulfate | 12 | 16 | 160 | 5 |
| Double superphosphate in granules | 15 | 200 | 200 | 5 |
| Superphosphate granules | 15 | 22 | 220 | 5 |
| Superphosphate powder | 18 | 24 | 240 | 6 |
| Phosphorite flour | 26 | 35 | 350 | 9 |
| Potassium chloride | 14 | 18 | 180 | 5 |
| Nitroammofoska | 14 | 18 | 180 | 5 |
| Nitrophoska | 15 | 20 | 200 | 5 |
| Potassium magnesium sulfate | 16 | 20 | 200 | 5 |
| Potassium sulfate | 20 | 26 | 260 | 6 |
Entries 1 to 19 of 19 entries
Reference table “Weight of fertilizers and soils in a 10-liter bucket”
| Name | Weight, kg |
| Ready compost | 10 |
| Humus | 8 |
| Ash | 5 |
| Dry peat | 5 |
| Horse manure on a bed of sawdust | 5 |
| Fresh horse manure | 8 |
| Sod land | 12 |
| 12-13 | |
| Slaked lime | 6-7 |
| Fresh cow dung | 9 |
| Slurry | 12 |
| Dry sawdust | 8-10 |
| Bird droppings | 5 |
Entries 1 to 13 of 13 entries
We wish you success and good harvests!
Use of copper sulfate
This fungicide is used in the garden, as well as at home, to protect plants from a number of diseases:
- Alternaria
- ascochyta blight
- moniliosis
- scab
- grape mildew
- spotting
- white spot (septoria)
- downy mildew
- rust
- late blight, etc.
In addition, when spraying against diseases, copper sulfate is a simultaneous foliar feeding. Copper deficiency usually occurs in plants growing on acidic sandy and peaty soils.
Other uses of copper sulfate:
- as an antiseptic against mold and rot on wooden structures
- for soil disinfection
If this fungicide was actively used in the spring-summer period, then it is better not to use it before winter so as not to oversaturate the soil with copper ions.
Consumption rates
As a rule, a 1% solution is used with a consumption rate of about 10 liters per 100 m2. To prepare the working fluid, dissolve 100 g of copper sulfate in 10 liters of water or 10 g per 1 liter of water.
General rules for diluting copper sulfate:
- Apple, pear, quince: for scab, phyllosticosis and other spots, moniliosis, drying out 100 g of the drug per 10 liters of water, first spraying in early spring before buds open, at a consumption of 2-5 liters per tree. Can be repeated 2 weeks before harvesting apples and pears.
- Apricot, peach, plum, sweet cherry, sour cherry: against clasterosporosis, coccomycosis and other spots, moniliosis, leaf curl, dilute 50-75 g per 10 liters of water, first spraying in early spring before buds open, at a consumption of 2-3 liters per tree .
- Gooseberries, currants: for anthracnose, septoria and other spots, dilute 50-75 g per 10 liters of water, first spraying in early spring before buds open, with a consumption of 1.5 liters for an average-sized bush.
- Spraying potato tubers against late blight before planting: 2 g of the drug per 10 liters of water. It is more convenient to put the planting material in a vegetable net and dip it in the prepared solution.
- Indoor flowers - watering against a complex of diseases - dilute a teaspoon (without a slide) in 2 liters of water to get a sky-blue solution, water at the root or spray on the leaves.
For spots on vegetables, for example with ascochyta blight on cucumbers, plants can be sprayed with a 0.5% solution of copper sulfate and urea: 5 g of vitriol and 10 g of urea per 10 liters of water, repeat twice at weekly intervals.
To disinfect open ground soil and greenhouses from diseases a week before planting seedlings or sowing seeds, water the soil with a 3% solution of copper sulfate (30 grams per liter of water). Such treatment will also protect potatoes from late blight.
To treat the root system before planting, dilute 100 g of the drug in 10 liters of water, soak the root system (bulbs or tubers) for 3 minutes. Then remove from the solution and rinse thoroughly in running water. Bulbs or fleshy tuberous roots, then air dry before planting.
How to dilute copper sulfate
Dilute the required volume of powder, for example, 100 g of copper sulfate, in a small amount of water (500-700 ml), poured into a plastic bucket and heated to a temperature of 40-50 degrees (dissolution is better), add water while stirring to increase the volume of the working solution up to 10 l. Do not use metal utensils! Before pouring the prepared solution into the sprayer, strain through a filter, for example, through nylon tights.
Treatment of tomatoes with copper sulfate against late blight
Tomatoes are plants sensitive to errors in treatment with copper-containing preparations. In order not to burn the leaves, but to defeat late blight, a very weak concentration is enough, only 0.2% solution. Prepare a copper-soap emulsion: grate 200 g of laundry soap and dilute it in a small amount of hot water; separately in a glass jar, dilute 20 g of copper sulfate, use a wooden stick to stir, pour the fungicide into the soap solution in a thin stream, stirring constantly and bring the solution to 10 liters of water.
You need to spray the tomatoes with this solution over the leaves, the scheme is as follows:
- spray the seedlings for the first time, a week after planting in a greenhouse or open ground
- further, depending on the weather, if the summer is dry and there is little rain, then do not spray until the August cold snap, make do with preventive treatments with phytosporin, if the summer is damp and cool, treat every 10-12 days.
Spray in calm weather, trying to wet the back of the leaves.
When can you eat fruits and vegetables after spraying with copper sulfate?
Most vegetables can be eaten 14-15 days after spraying, with the exception of:
- melons (cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkins, watermelons, melons) - they can be sprayed 5 days before harvesting
- tomatoes can be sprayed against late blight and other diseases 7-8 days before harvesting tomatoes
Important: rinse all fruits thoroughly with running water several times - copper is not absorbed by the plant and does not penetrate into the fruit, it remains on top of the fruit shell and is dangerous only if the fruits have a soft skin, such as peaches, or the fruits are cracked.
Fruits and berries that cannot be washed well before eating - raspberries, strawberries, apricots, peaches, grapes, some varieties of currants (with soft berries) - can be sprayed with copper preparations at least 1.5 months before the harvest ripens: one treatment before flowering, and the second by ovary.
Copper sulfate for root rot, blackleg, fusarium
To save cucumbers, zucchini or pumpkins from root rot (symptoms: wilting of bushes in hot weather, yellowing of leaves, dying off of ovaries, stopping the growth of greens), you can prepare the following solution: 1 teaspoon of copper sulfate, 1 teaspoon of zinc sulfate, 1 tbsp. . a spoonful of simple superphosphate per 10 liters of water. Water the cucumber bushes with a freshly prepared solution at the rate of 5 liters of liquid per 1 square meter. m of land.
Watering against blackleg and fusarium of vegetables and flowers: dilute 5 g of the drug per 10 liters of water.
How to treat wooden structures with copper sulfate
Copper sulfate is an excellent antiseptic; it can be used to treat any wooden structures in a summer cottage - the walls of greenhouses and hotbeds, walls and structures of cellars, sheds, gazebos, wooden flooring, fences. It is better to apply the solution by spraying, on small surfaces with a brush or sponge (work with gloves). Let dry and repeat the treatment two more times. The coating must be renewed after 3-4 months.
In some cases, for longer protection time, you can add clay to the solution to create a creamy mass; use it to coat the supporting posts of a fence, the porch of a country house, or support beams in greenhouses.
You need to know that deeply ingrained mold cannot be removed or destroyed with copper sulfate; it is better not to use such material, since the boards lose their strength, and mold from them can spread to neighboring ones; in such cases, it is worth using preservative, non-washable antiseptics.
Copper sulfate as fertilizer
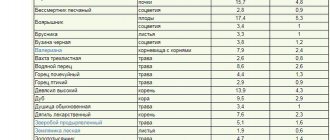
Copper sulfate is applied only on soils poor in this element, for example, chernozems contain copper in sufficient quantities, a little less, but not fundamentally, in sod-podzolic and gray forest soils, but peat-bog and in some places sandy and sandy loam soils contain little copper, therefore Once every 5-6 years, in early spring or autumn, you can add copper sulfate: consumption 1 g per 1 sq.m.
For foliar feeding of vegetative plants with signs of copper deficiency (manifested primarily on young leaves), the dosage is 1-2 g of copper sulfate per 10 liters of water.