Plum is one of the most popular fruit trees , known to summer residents in almost all regions of Russia.
This stone fruit has a huge variety of varieties and is the leader among all fruit trees in terms of the number of species. Yellow, red, blue, large or smaller plum, it pleases with its rich harvests, attracting more and more people who want to plant such a tree on their plot.
There are effective ways to propagate plum trees yourself and grow an excellent harvest on this tree. Plum is very susceptible to propagation: it takes root easily, produces shoots, and has fairly high adaptive properties.
Let's consider artificial (grafting, cuttings) and natural (root shoots, seeds) methods of plum propagation.
Propagation by green cuttings
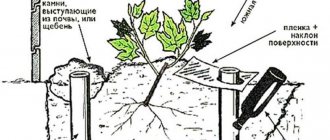
This method of propagating plums is the most common for dark varieties .
The soil for planting the green cuttings is prepared in advance - a mixture of peat and sand will create an optimal microclimate; before direct planting, good soil moisture and fertilizer are necessary (for example, superphosphate - 1 tsp per 10 liters of water).
On the mother tree, shoots are selected that will be cut - hard and acquiring a varietal reddish tint.
The shoots are cut with a sharp blade, each is divided into several cuttings 25-30 cm long, each of which should have two or three leaves. After pruning, the cuttings are placed in water with growth stimulants for 12-16 hours.
After the preparatory work, the cuttings are planted in the ground approximately 3 cm deep (without covering the bottom leaf), the distance between plantings is 7x7 cm.
Experienced gardeners recommend creating a good microclimate for the planted cuttings - carefully moisten the soil several times a day, cover the planting with film , making sure that the temperature under it does not rise above 30˚C.
After 15-20 days, the film can be removed, during which time the first roots should appear and the plants will need ventilation and oxygen.
The shoots are cut with a sharp blade, placed in water with growth stimulants, and planted in the ground about 3 cm deep.
The choice of time for propagation by cuttings determines the success of the result. Cuttings are cut in mid-summer , preferably early in the morning or evening; during the germination process, it is important for them to avoid excessive heat and cold, which is why a greenhouse film is installed.
For the winter, it is recommended to sprinkle the established cuttings with peat or fallen leaves to avoid frostbite of the young roots.
How to root green cuttings correctly:
Optimal timing
Green cuttings should be pruned at the time of greatest activity, in the stage of intensive growth and vegetation, which begins in June.
Favorable days
Russian yellow gooseberry - advantages and disadvantages
Harvesting cuttings is carried out from the beginning of June to mid-July in areas with moderate climatic conditions. A visual sign to begin the procedure is the appearance of redness at the base of young growing shoots.
Note! It is preferable to prune early in the morning before the heat sets in or on a cloudy day to maximize moisture retention in the cuttings.
How to propagate by root shoots?
A universal method is to propagate plums from root shoots , which are recommended to be removed, as they take away the fruit-bearing forces of the mother tree.
A small young shoot (up to 50 cm in height) from this shoot can become planting material. The shoot should grow at a distance of approximately 1 m from the main tree, be well developed, and not affected by insects.
When choosing, a developed root system is important, which will allow the shoot to easily take root in a new place.
The shoot is carefully separated from the main roots of the mother plum , and the place where the root is cut is sprinkled with ash. The separated shoot is placed in well-moistened soil, in a shady place, where it will adapt to new conditions - independent growth.
The shoot is separated from the main roots of the mother plum, placed in well-moistened soil, and the top is pinched off.
Its top is pinched . As a rule, after a month fresh leaves will appear on it - this means that the rooting process was successful.
Plum is an unpretentious plant that can reproduce by root shoots and adapt independently, which only confirms this. However, a young seedling needs good care and timely fertilization.
A month after transplanting the plum shoot, the first feeding is required - saltpeter, azofoska, nettle infusion or cow manure, which are diluted in water . Feeding can be done every two weeks to ensure the plant gets stronger.
Breeding Features
All breeding methods are effective in accordance with the type of fruit crop and the region of cultivation.
Depending on the type of plum
If you have a mother tree of suitable age and size with a well-formed root system, propagation by cuttings will be successful. If the tree does not meet the standards, it is better to give preference to the root shoot method or layering.
Depending on the region
Before starting the process, you should find out how the plum tree propagates depending on the region. Suitable climate for rooting summer cuttings in temperate zones.
Grow plum from seeds? Maybe!
Plum propagation by seeds is also often used by gardeners. In this case, the preservation of varietal properties is unlikely; special observations of seedlings, control and selection of the best are required; only then will a varietal plum be obtained.
More often, this method of propagation is used to obtain a rootstock. You may be interested in our publications:
- How to grow plums from seeds at home?
- How to prune a plum tree?
- When and how to properly pick plums from a tree?
To plant seeds, you need to prepare planting material. Famous breeder V.N. Shalamov writes that the fruit from which the seeds are taken must be completely ripe ; after removal, it is left until it lies down, only then the seeds are taken out of it.
They are freed from pulp, washed and dried under natural conditions, avoiding sunlight. The dried seeds are transferred to a plastic bag, closed and stored at room temperature until autumn or spring planting.
The fruit from which the seeds are taken must be completely ripe; after removal, it is left until it lies down, only then the seeds are removed from it
The process of seed ripening for plums of different varieties takes up to 180 days . During this period, many breeders suggest mixing selected plum pits with wet sand and storing them in a refrigerator or a special box dug into the ground and protected from water, insects and rodents.
After such storage, many seeds hatch, which means the planting results will be more successful.
Planting of prepared seeds occurs in spring or autumn , in well-prepared and fertilized soil (V.N. Shalamov recommends fertilizing 1 sq. m of planting bed with a mixture of humus (4-6 kg), superphosphate (70 g), potassium salt (30 g) , ammonium nitrate (30 g) and lime (50-90 g).
Planting should be done before the onset of frost or after the soil dries out after snow cover.
The seeds are placed in the ground to a depth of 2-3 cm, root down or in the place where the root should appear, the distance between the seeds is 30x10 cm. The seeds are covered with fertile soil.
During the entire growth period, the soil must be freed from weeds, moistened and loosened, and pest damage must be carefully avoided. After 1-2 years, selected seedlings can be transplanted to a permanent place .
The criteria for viability and future yield are how the seedling has grown during one season. The better the growth, the higher the winter hardiness and viability.
Further care
Care consists of maintaining heat and water balance in the greenhouse:
- watering and spraying 2-3 times a day;
- daily ventilation to avoid condensation;
- one-time fertilizing with mineral fertilizers;
- protection against diseases (pathogenic fungi and bacteria can develop in a waterlogged environment).
With the onset of autumn cold, the polyethylene is removed, and the plantings are insulated with a mulch layer (peat, dry leaves) and covered with geotextiles. The seedlings are planted in a permanent place next spring.
Reference. Depending on the variety, with proper care, cutting roots appear in 15-30 days.
Grafting as a way to preserve a varietal species
This method is the most successful for preserving the varietal qualities of plums. Rootstock, i.e. The base on which the graft is made is usually grown from a seed, or less often from root shoots.
Excess leaves and branches are removed from the water supply in advance , and it is watered abundantly to activate sap flow. The age of the rootstock should not exceed one year; it is desirable that its mother tree be a winter-hardy plum.
The scion can be a bud or a cutting; each has its own grafting methods.
Excess leaves and branches are removed from the plant in advance, it is watered abundantly, the scion can be a bud or a cutting
Grafting with a bud is called budding . Using a special budding knife, a bud is cut from a varietal tree - a strip of bark about 3 cm and about 0.5 cm thick with a highly developed bud. An incision is made in the rootstock at a level of approximately 4 cm from the soil, into which, by carefully bending back the bark, a shield with a bud is inserted.
Budding can also be done in another way, when the scion is cut out with a wedge with a spike up to 15 cm above the bud, which is inserted under the prepared tongue on the rootstock. In this case, it is recommended to graft two buds on one rootstock at once - at a distance of approximately 4 cm and 11 cm from the soil, in order to increase the success of grafting.
The budding site is carefully tied with polyethylene, leaving only the bud open. The bandage is removed 3 weeks after vaccination.
Grafting with cuttings takes longer to prepare . Cuttings are prepared in advance and stored during the autumn-winter season and grafted in two ways: into a split or behind the bark.
Splitting assumes that the rootstock and scion are approximately the same thickness, but this is not a necessary condition. The rootstock is cut off horizontally and a vertical split with a depth of no more than 3 cm is made in the center (if the rootstock is a stump left over from an old plum tree, then the depth does not exceed 7 cm).
The cutting should be cut so that 4-5 eyes remain above the intended alignment. The lower part of the cutting is cut off with a wedge in the same way as the rootstock (no more than 3 cm for a young rootstock). When touching, the scion and rootstock should press tightly against each other.
You should not touch the cuttings and rootstock with your hands, this can infect the grafting site and the future tree will not take root.
Grafting behind the bark is carried out only with active sap flow, then the bark easily moves away from the rootstock. It is carefully cut, if it is intended to graft several cuttings at the same time, then in several places.
The cuttings are cut obliquely and connected to the rootstock. The connection should be tight, it is desirable that the wood layers come together.
After connecting the cuttings to the rootstock, the grafting site is tightly bandaged with polyethylene, electrical tape or a special elastic tape. The remaining open areas are thickly covered with garden pitch.
Until the first leaves, it is advisable to protect the graft from moisture and excess solar heat - the grafting site is shaded and covered with a transparent bag.
Grafting behind the bark is carried out only with active sap flow, then the bark easily moves away from the rootstock
Rooting cuttings
Propagation of plums by air and ground layering, unlike cuttings, does not require constant “intervention” in the rooting process, which means it is ideal for those summer residents who come to their plot only from time to time.
Air layering
To achieve a good result, it is necessary to begin rooting the cuttings on time. The best time is spring, a week before the plum blossoms. During this period, intensive movement of sap occurs, and you can easily separate the bark from the shoots without damaging the wood.
To form air layering you will need:
You should not despair if you do not have the opportunity to purchase sphagnum moss - you can replace it with coconut fiber or a substrate consisting of coarse river sand and turf soil with the addition of perlite.
- For rooting, choose healthy, well-developed shoots from last year. You can give preference to two-year and even three-year-old branches, but in this case there is a risk that the power of the root system formed over the summer will not be enough to fully root and nourish the new seedling.
- At the base of the shoot, make two parallel cuts, at a distance of 10-15 mm from each other, and carefully remove the layer of bark between them, being careful not to damage the wood.
- To increase the area of root formation, 2-3 more vertical furrows are cut above the annular cut, and to prevent “healing of the tree”, thin chips or matches are placed under the incisions.
- The sections are treated with a root formation stimulator and wrapped in a layer of moist sphagnum.
- A layer of plastic film is placed around the moss, which is carefully fixed with electrical tape, above and below the incision site. So roots form much more intensively in complete darkness; it is better to give preference to black, opaque films.
- During the summer you will only need to water the moss occasionally to keep it moist. This can be done with a medical syringe, injecting water through punctures in the film.
- A month before the onset of frost, the shoot is separated from the mother plant and planted in a growing area. To prevent the seedling from freezing, it is carefully insulated.
Ground layering
Plums formed by a bush or having low-lying branches are suitable for rooting in this way.
To form ground branches you will need:
- sharp knife;
- root formation stimulator;
- hairpin or thick wire;
- substrate made of river sand and peat.
The work order consists of the following steps:
- On a selected branch of last year's growth, make several shallow cuts in the bark and insert matches or wood chips under it.
- Treat the incision sites with a root formation stimulator.
- In the place of future rooting, select soil and replace it with loose substrate.
- Bend the shoot to the ground, place it in a groove 4-5 cm deep, and press it to the ground with a wire or pin.
- The top of the branch, 10-20 cm long, should be above the soil surface. If it spreads along the ground, then it is raised and fixed with a peg and rope.
- The rooting area is watered. To prevent the soil from drying out in this place, it is covered with a film or thoroughly mulched.
- Separation of the seedling from the mother plant is carried out in the fall 30-40 days before the onset of frost or in early spring.
What is plum growth and the reasons for its appearance
Shoots are shoots that form in the root zone of a tree; in crops with a superficial root system, shoots may appear far from the main trunk. In most cases, from correctly and timely transplanted shoots, full-fledged, fruit-bearing trees grow; in some cases, grafting is necessary to obtain a harvest. The growth of shoots from the root may be associated with the method of cultivation (more shoots are formed in self-rooted trees, grafted plums often grow without shoots), but there are other reasons for the appearance of shoots.
In a tree planted high or when watering with a stream, the roots are exposed, resulting in damage to the trunk. The offspring will grow continuously; the situation can be corrected by sprinkling the roots with a good layer of soil.
Trimming a significant portion of branches
When a tree has undergone critical pruning, the balance of development is disrupted due to improper distribution of nutrition. The root does not receive enough substances from the photosynthesis of the crown; the tree tries to compensate for the losses by growing new shoots.
Mechanical damage to the trunk and root
Carefully monitor the health of the tree, treat wounds with garden varnish, and replace digging the soil with loosening. Remove foreign objects from branches, such as a tag, knotted rope, or tight graft wrap. As the stems grow, the element will gradually cut into the bark, disrupt the sap flow process, and the root will produce new shoots to obtain normal nutrition.
Incompatibility of rootstock and scion
If the scion and rootstock are incompatible, the appearance of root shoots is inevitable due to metabolic disorders. The problem can be recognized by thickening of the bark at the grafting site, yellowing of the leaves on the branch, and sometimes on the tree. In addition to the appearance of abundant growth, immunity to frost and productivity will significantly decrease; if the stems growing from the root are not removed, the tree will die. The incompatible rootstock must be removed and the cut area treated with slaked lime.
Overgrowth forms when there is a lack of moisture during dry periods, and also if reliable protection has not been organized before wintering. The second reason is relevant for both young and adult trees. When a significant part of the branches and roots freezes, the plum tries to recover due to the growth. The mother tree gradually dries out, it is better to cut it down and use the shoots for propagation.
The intensity of fruiting and the quality of the fruit depend on proper care in the spring. Basic procedures on site...