Home / Pests and diseases
Back
Published: 06/10/2019
0
2/5 — (2 votes)
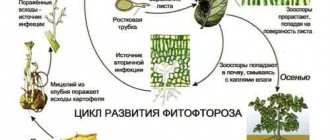
The correct name for this disease is cladosporiosis, but almost no one uses this term in everyday life. Agree, the popular name “brown spot” is much easier to pronounce. The causative agents of this disease that is destructive to tomatoes are conidia.
These microorganisms are a type of fungus, but they are fundamentally different from it. Conidia, unlike simple fungal spores, grow directly on the mycelium and are almost weightless. They are easily carried around the site even by a light breeze. This is why the infection spreads so quickly from diseased tomato bushes to healthy ones.
Brown spot rarely occurs on tomatoes grown in greenhouses with an artificial microclimate. In ordinary greenhouses and garden beds, the fungus often affects tomatoes.
Conidia of brown olive spot spread to tomatoes by air, through working equipment, watering, and with the help of insects and birds.
Conidia are extremely tenacious. They easily survive frosty winters and long droughts.
But it is not the causative agent of the fungus, but the fungus itself that affects tomatoes. He loves high ambient humidity and high temperatures. Here are the reasons why brown spots form on tomato leaves.
- 1 Manifestation of the disease and its consequences
- 2 Treatment methods
- 3 Disease prevention
- 4 Tomato varieties resistant to brown spot
Description and signs of tomato cladosporiosis
Tomato cladosporiosis, or brown olive spot, is a disease caused by the pathogen Cladosporium fulvum cooke. The disease develops from the bottom of tomato bushes upward, interferes with photosynthesis processes and leads to leaf wilting. If left untreated, it can cause a loss of about 30% of the crop.
Brown spot on tomatoes can be recognized by its characteristic symptoms. At the beginning of the development of the disease, light olive marks appear on the front surface of the leaves, arranged in a chaotic manner. Over time, they grow and form wide brown spots. A silvery coating appears on the underside of the leaves. In order to notice signs of the disease in time, it is necessary to inspect tomato bushes closer to the surface of the ground on a weekly basis.
Cladosporiosis, if left untreated, can destroy tomatoes in just a month.
Why does it occur on tomatoes?
The appearance of the disease is provoked by changing weather conditions. When the air humidity rises to 90% and the temperature reaches 25°C, the first outbreaks of the disease are possible. This can happen in April or in mid-summer.
Spores begin to awaken under favorable external conditions, and until then, without much loss, they overwinter in the soil, on plant debris, on greenhouse structures, on consumables (twine, pegs) and gardeners’ working tools.
The disease moves from the ground to the lower parts of the plants, then moves higher. If most of the leaves of a tomato bush are colonized by Cladosporium fulvum conidia, the entire bush will die.
In some especially favorable years for the pathogen, cladosporiosis penetrates the petioles, peduncles, stalks, and fruits of tomatoes. In this case, the tomatoes turn brown, shrivel and fall off. The death of the entire plant occurs very quickly.
Reasons for appearance
Most often, cladosporiosis spreads to tomatoes from contaminated soil. Fungal spores can remain viable in soil and plant debris for up to ten months, even in conditions of drought or severe frost.
In some cases, cladosporiosis is transferred from plant to plant along with wind and dust, and the disease is also spread by pests. The fungus begins to be active in warm weather with high humidity.
Attention! From the moment of infection with cladosporiosis until the appearance of the first symptoms, it usually takes about two weeks.
What kind of disease is this
Alternaria blight is caused by a group of fungi that affect many crops - fruit trees, berry bushes, legumes, cereals, sunflowers.
Each type of pathogen specializes in one or a few plants, without attacking others.
The fungus that causes disease in tomatoes parasitizes all members of the Solanaceae family, for example, eggplants and potatoes.
This disease is also called macrosporiosis, dry spot or Alternaria spot.
Development conditions
Brown spotting on tomato seedlings develops gradually. The first symptoms of the fungus appear during the flowering period of the bushes at an air temperature of about 22-25 ° C. The risk of the disease especially increases at a humidity level of more than 80%, so most often the disease affects tomatoes in a greenhouse.
At first, barely noticeable yellow spots appear on the leaves and shoots of the tomatoes, but the bushes themselves look healthy. During flowering, it is recommended to frequently inspect the lower surfaces of the plates of the plant and, if there is a whitish coating, remove the affected parts.
As the disease develops, the tomato leaves turn brown and the growth of the bushes slows down. If left untreated, cladosporiosis affects all shoots and fruits, the plates and ovaries begin to fall off en masse. The development of the disease is additionally provoked by lack of ventilation in the greenhouse or thickening of plantings in open ground.
Main symptoms of the disease
The first signs of brown spotting are the appearance of small spots of yellow, brown or brown color.
. Along the edges of the spots, a border of purple, violet or black-brown color is clearly visible. These spots are also clearly visible on the reverse side of the leaf blades. If the humidity of the air and soil is increased, then a coating of fungal spores appears on the spots.
Gradually the color of the spots becomes lighter, but their dark border remains. The tissue in the center of the spots gradually becomes thinner, and thin foliage develops holes in this place.
Photo of brown spot on leaves
On a note!
When plants are massively affected by cladosporiosis, the foliage begins to dry out and fall off ahead of schedule. In many crops (in particular, garden strawberries), up to 100% of the foliage can be affected by brown spot.
From the foliage, the disease gradually spreads to the remaining parts of the plant - petioles, shoots, fruits. Cladosporiosis contributes to a sharp decrease in yield.
Pests in the garden!
How to deal with cutworm (cabbage, potato, garden) How to get rid of wireworms How to deal with mole crickets
The fruits do not grow, begin to deform, their color changes to brown, crack and begin to crumble. New flowers and fruits do not form, and those that have already appeared dry out and fall off.
How to deal with brown spot (cladosporiosis) on tomatoes
There are several ways to combat brown spot on tomatoes. For prevention or for mild symptoms, folk and biological remedies are used. In case of severe damage to the bushes, systemic chemicals are used.
Chemical preparations for tomato cladosporiosis
Chemical agents bring the fastest and most pronounced effect against cladosporiosis of tomato bushes. There are several of the most reliable drugs:
- Acrobat MC. A reliable fungicide gets rid of cladosporiosis, prevents its return and protects tomatoes for two weeks. To prepare the solution, you need to dilute 20 g of the drug in 4 liters of water and spray it in dry weather without strong wind.
Spraying of tomatoes with Acrobat is carried out no later than a month before harvesting the fruits. - Quadris. The fungicidal agent helps with cladosporiosis, late blight and powdery mildew of tomatoes. The drug is used like this: stir 6 ml in a bucket of water and spray the plantings. For greenhouse tomatoes, the dosage is increased to 10 ml per 10 liters of liquid.
Tomatoes are sprayed with Quadris every two weeks. - Abiga Peak. The fungicidal drug is intended for the treatment of Alternaria blight, cladosporiosis and other fungal diseases of tomatoes. To spray the bushes, you need to stir 50 g of the substance in a bucket of water. Treatments are carried out at intervals of 10-14 days.
When using Abiga Peak, the fungicide consumption should be about 5 liters per 100 m2
Great care must be taken when working with chemicals. It is necessary to use gloves, goggles and a respirator when spraying to avoid getting drugs into the eyes and mucous membranes.
Advice! In the absence of symptoms of the disease, treatments begin when weather conditions are favorable for the development of the fungus.
Treatment of tomato cladosporiosis with biological preparations
Tomato cladosporiosis can be treated not only with chemical, but also with biological means. They show a good effect, but act much softer:
- Fitosporin. To prepare a biological product, you must first dilute 100 g of the product in 200 ml of water, and then mix the resulting stock solution with 10 liters of liquid. Tomatoes are processed once every two weeks, with special attention paid to spraying the lower leaves from the inside.
In rainy weather, it is recommended to carry out treatment once a week. - Gamair. It is necessary to dilute 2-10 tablets in a bucket of water and spray the tomatoes at the moment the buds open. Treatments are repeated every two weeks.
Gamair for tomatoes is especially beneficial in rainy, cold summers - Alirin-B. To prepare the solution, you need to stir 2-10 tablets first in 300 ml of water, and then add to a volume of 10 liters. The shelf life of the drug is no more than a day, so spraying is carried out immediately.
The drug Alirin-B can be combined with Gamair to enhance the effect
Biological agents are allowed to be used, including during the fruiting period of tomatoes. They do not cause any harm to ripening tomatoes.
Advice! For better adhesion of biological preparations to tomato leaves, laundry soap can be added to the finished compositions.
Folk remedies for tomato cladosporiosis
Treatment of cladosporiosis of tomato seedlings with folk remedies is carried out when the symptoms are mild. In this case, home remedies help stop the development of the fungus and prevent its reappearance:
- Garlic infusion. To prepare the product, you need to grind the seasoning head, add 1 liter of water and add 5 ml of iodine. All components are mixed thoroughly, topped up to 10 liters, and then the bushes are sprayed on the leaves.
Garlic infusion additionally helps protect tomatoes from pests - Milk solution. To treat cladosporiosis of tomato seedlings, it is necessary to mix milk and clean water in equal proportions, and then add 20 drops of iodine and add a bucket of liquid to the components. The drug is also used to treat bushes leaf by leaf.
A milk solution with iodine strengthens the immunity of tomatoes and promotes abundant fruiting - Chlorine solution. You need to dilute one tablet of the chemical in 10 liters of water, and then add 40 drops of iodine. The product is used for watering tomatoes in cool, cloudy weather.
You can water tomato bushes with chlorine solution only on pre-moistened soil.
It is necessary to use folk remedies for treating tomatoes against brown spot from the beginning of the growing season until its end. Homemade solutions can strengthen the bushes’ immunity and help avoid most fungal diseases.
Agricultural technology
Not only folk and chemical remedies help cure tomatoes from cladosporiosis, but also proper agricultural technology. When growing a crop you must:
- control soil moisture and prevent it from becoming waterlogged;
- regularly loosen the beds with tomatoes to a shallow depth;
- Feed tomato bushes with mineral fertilizers at least three times a season;
- Thin out plantings as necessary, preventing them from thickening.
When growing tomatoes, you need to inspect the lower part of the bushes weekly. All damaged leaves are urgently removed, and if fungus is suspected, emergency spraying with fungicidal preparations is carried out.
Ways to fight
If you don’t take precautions, not a single bush is immune from cladosporiosis, so if you notice the first signs of the disease, you need to urgently begin to solve the problem. Treatment must be approached systematically, carefully studying the means and following the instructions in order to get a positive result.
At an early stage of infection, it will be necessary to suppress sporulation so that the fungus cannot spread further
It is important to create unfavorable conditions in which the source of the disease cannot survive. Blocking fungal activity may vary depending on the method of control
There are a number of drugs on the market that can help you get rid of cladosporiasis. We present to your attention a description of effective control methods.
Agrotechnical
This option is only suitable for prevention, and during treatment this method will be more of an auxiliary factor
It is important to carry out seasonal cleaning and disinfection throughout the entire area and in the greenhouse. As mentioned above, the fungus can remain for a long time on tools and in the soil, so treatment is required
If you have a greenhouse, you will need strong, hot potassium permanganate, which is used to wash absolutely all components of the structure.
The greenhouse must be ventilated regularly if the temperature outside is very high. Tomatoes do not need heat; often the windows are always open at night. Watering should be according to a structured schedule so as not to exceed the standard air humidity. Make sure that the bushes are kept at a distance from each other - this will avoid crowding, which leads to the development of cladosporiosis.
Experts recommend mulching the area with dry hay and watering at the roots. If you are planting seedlings for the first time, you must follow the recommendations of agricultural technicians - pruning tomatoes, removing lower foliage, pinching to limit the growth of indeterminates
Experienced gardeners know how important it is to carry out all these manipulations; this is the only way to encounter plant diseases much less often and save the harvest
Chemical
To combat such a serious infection, it is important to choose effective means, namely fungicides that can attack and destroy the fungus. There are many drugs on the market, but it is important to know which of them can lead to a positive result in the shortest possible time
Fitosporin is in great demand; it is important to follow the instructions and use it correctly. The main ingredient in the composition is copper, it is also contained in such a preparation as “Oxychom”
In addition, they use Bordeaux mixture, the drugs “Bravo”, “Ridomil”, “Profit Gold”. Such chemistry is used to destroy the disease and the source of the problem, but it is important to observe safety measures and processing times.
The product “Ordan”, which contains copper oxychloride and cymoxanil, is in great demand. This means can be used for prevention and also to fight infection. These are poisonous compounds that accumulate on the bushes and can remain on the fruits for some time. This method should be resorted to only when the infection has acquired an aggressive form, and no other methods help.
Biological
If the infection is not yet so active and the damage has not spread to the fruits, you can pay attention to biological fungicides. Such drugs are not too dangerous; they include Fitosporin-M, Trichodermin, Alirin and other drugs
Folk
This is perhaps the most health-friendly treatment option. For prevention, plants should be sprayed with a mixture of water and whey solution in a ratio of 10:1. Household disinfectant solutions can prevent the disease. If you see white spots on the foliage, treat the bush with a solution of 15 drops of iodine and 5 liters of water, add half a liter of milk so that the liquid sticks to the plant
It is important to feed the bushes with calcium chloride
When you have dealt with the disease, you will need to carry out soil treatment, that is, mulching after watering. If the damage was widespread, spill a solution of biological substances.
Features of treatment in a greenhouse
The methods of combating cladosporiosis of tomatoes in greenhouses are quite standard. But in the process of treating fungus, it is worth considering some nuances. If characteristic symptoms of brown spot appear on the bushes, you must:
- Depending on the degree of damage, trim or completely remove affected plants from the beds.
- Spray the soil on which the tomatoes grew with a disinfectant - a fungicide or a solution of potassium permanganate.
- Spray neighboring bushes with biological or chemical preparations to prevent or eliminate the first symptoms.
It is recommended to treat all greenhouse surfaces with antiseptic disinfectants. After treatment and preventive measures, through ventilation is arranged in the greenhouse to reduce the humidity level.
Advice! With the onset of autumn, it is recommended to treat the greenhouse with sulfur bombs; they will get rid of the causative agents of cladosporiosis remaining in the soil.
Prevention of tomato cladosporiosis in a greenhouse
There are many ways to treat tomatoes against cladosporiosis in a greenhouse, but the main focus should be on prevention. The causative agent of brown spot feels best at a humidity of about 80% and in a temperature range of 20-30 ° C. To prevent the development of the disease, you need:
- regularly improve the soil composition with compost and rotted manure;
- water tomatoes only as needed when the soil dries out;
- do not plant the crop in the same place where other nightshades previously grew;
- annually update the top layer of soil in the greenhouse;
- promptly remove plant debris from the beds;
- Every spring and autumn, disinfect the frame surfaces, walls and ceiling of the greenhouse with antiseptic solutions.
Even before planting, it is recommended to soak tomato seeds in fungicidal agents. This helps strengthen the crop’s immunity and increases its resistance to brown spot.
Tomatoes resistant to cladosporiosis
Brown leaf spot of tomatoes occurs less frequently on varieties with high immunity to fungal diseases. Among the most popular varieties are:
- Delicacy. Determinate mid-season tomato for open ground grows up to 50 cm in height. It produces round, juicy fruits with good taste, weighing up to 100 g; tomatoes are suitable for salads and canning.
The Delicatessen tomato is drought-resistant and not susceptible to cladosporiosis and other fungi - Pink Paradise. Hybrid high-yielding tomato grows up to 2 m, recommended for cultivation in greenhouse conditions. It bears fruit 74 days after germination and produces up to 4 kg of tomatoes per 1 m2.
Tomato Pink Paradise requires tying to a support - Vezha. The indeterminate variety bears fruits up to 120 g in weight, suitable for growing in low greenhouses. The first tomatoes ripen in mid-July.
Tomato Vezha produces up to 16 kg of fruit per 1 m2 in greenhouse conditions
Hybrid varieties with good immunity are less likely to suffer from brown spot and other fungi in unfavorable conditions. But they still need to be grown in compliance with the rules of agricultural technology, since the bushes do not have absolute resistance to disease.