Necessity of vaccination
There are a number of important reasons why fruit trees need to be grafted. This:
- Splitting and breaking of branches. Over time, as well as under negative weather conditions, plants become weaker and require additional care to maintain good condition and, accordingly, productivity. Grafting is the salvation of a damaged pear and its rejuvenation.
- Growing new varieties of pears - more resistant and less whimsical. The grafting material can also improve the taste of the fruit.
- Saving space in the garden by planting other crops on the pear tree. Through grafting, gardeners are switching to a more modern method of planting young trees.
Tree grafting is considered a serious procedure comparable to surgery.
To quince
Quince is the most common rootstock for pears. This option is successful for several reasons: it allows you to reduce the height of the tree, saving space in the garden, speed up the fruiting process and at the same time improve the taste of the fruit. Due to the short stature of the rootstock, harvesting from such a tree, as well as caring for it, will require less effort from the gardener. The only drawback is low frost resistance.
In regions with harsh and long winters, plants may freeze or fail to yield, so grafting pears on quince trees there is not advisable.
When to vaccinate
Spring is considered a suitable time for vaccination activities. With the onset of stable warmth and snow melting, experts note a high degree of survival of the new crop. The operation must be completed before the sap flows, otherwise the plant may suffer greatly. Pear budding in summer is carried out most often in July and less often in August, the survival rate is slightly lower than in the spring season, but also quite good - from 75%. The main condition is to cover the scion area from the active rays of the sun.
How to plant a pear tree in the summer with a closed root system
In autumn and winter, the procedure is carried out as a last resort. During this period, the tree is at rest, all processes in it are slowed down, and nutrition flows only to the root, not reaching the crown. Therefore, another culture is unlikely to take root. In addition, there is a serious risk for plants to freeze and die.
m
Dates
The scion should lag behind the rootstock in development. If this condition is met, the operations are successful. In winter, vaccinations are carried out indoors; in other seasons, the timing is correlated with weather conditions, sap flow, and method.
in spring
Wait until moderately warm weather sets in.
Vaccinations are given if the temperature is about 15°C during the day and does not drop below 0°C at night. Cuttings take root well during the period of active sap flow; its onset is determined by external signs:
- the buds begin to swell;
- the bark acquires a warm, slightly pinkish tint and lags behind well.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
Advice! Use a sharp blade to make a small cut in the bark of the trunk, and use the tip of the knife to unscrew the edge. It lags behind easily, which means it’s time to vaccinate the pear.
In the spring, it is precisely by the second sign that gardeners determine the vaccination period. It is not tied to a specific date because it depends on the weather.
| Moscow region | Northwestern regions | Ural | Siberia | Southern regions |
| second half of April | last ten days of April | from the last days of April to May 15 | from the last days of April to May 15 | from late February to March |
In summer
Not all vaccinations given in the spring take root. In this case, the pears are re-grafted during the summer sap flow. The period suitable for the operation is determined by the cortex. In July and August, young, healthy pear shoots are taken, they are cut off on the day of the operation, this is a plus for summer vaccinations.
There are also disadvantages:
- heat;
- bright sun.
In order for the cutting to take root, the gardener has to protect the operation site from sunlight.
| Moscow region | Northwestern regions | Ural | Siberia | Southern regions |
| last ten days of July, from August 1 to August 10 | July 25-31, August 1-10 | August 1-10 | August 1-10 | August |
in autumn
You need to know weather statistics for several years. It can be used to determine when frost may begin. Finish vaccinations one month before their due date. Errors in calculations affect the results. Cuttings that do not have time to take root die from the first frosts.
| Moscow region | Northwestern regions | Ural | Siberia | Southern regions |
| September 1-20 | September 15-30 | September 20-30 | September 20-30 | from September 20 to October 30 |
in winter
Seedlings are grafted for spring planting. They are preparing for surgery in the fall. The rootstock and scion are prepared. This method is not suitable for everyone. To store grafted plants, you need to have a room suitable for temperature and air humidity.
Suitable rootstocks for pears
Propagation of pears by cuttings - at home in summer
The ideal option is to graft the pear onto other varieties of this tree - semi-wild, but also growing favorably in the present climate. The other plants listed below are possible as rootstocks, but the success rate of such grafting will be low.
For plum and cherry plum
Cherry plum is better grafted onto pear. The material is prepared after the end of frost. A small tree grows, which is in good health and quickly begins to bear fruit.
Pear can be grafted all year round, but winter is considered the most inappropriate time.
On black rowan
The rootstock is used to improve the quality of pear fruits and in the presence of a situation where the tree grows on not very suitable - wetland. The finished tree will have a comfortable, small crown. Subsequently, tying up the shoot will be required.
In Irgu
Grafting a pear with shadberry, chokeberry or quince material can only produce low-growing trees. Over time, the size of the young plant will become different from the rootstock and it will be necessary to build a frame for the plants.
To the apple tree
You will get an unusual tree if you combine a pear with an apple tree. It will be possible to observe both apples and pear fruits on it. Many gardeners succeed in such vaccination, but there is a risk of a negative result. The procedure is performed according to 2 schemes: copulation or through a T-shaped cut.
On the hawthorn
Thanks to the use of hawthorn, the pear becomes less whimsical and becomes resistant to drought. The plant begins to bear fruit early; they are large in size and rich in taste. The finished plant will have thorns.
For cotoneaster
Cotoneaster allows you to obtain a frost-resistant pear with a tart taste of fruit, capable of growing on different soils. Cotoneaster seedlings easily adapt to the climate.
Go wild
When combining wildflower and pear plants, there is a good chance of getting a frost-resistant, easy-to-care crop that also has a large and strong root. However, the pears will be small in size. A common method is grafting by cuttings.
Necessary equipment
Grafting a plant onto another tree is not a difficult task. Even a beginner can handle it if he chooses the right tools and materials. In addition to the scion and rootstock, you will need the following things:
- A piercing knife is used for bud grafting. A copulating knife is suitable for grafting cuttings. Instead, you can use a garden knife, which will save money;
- A pruner is a necessary tool; it allows you to cut cuttings to the required length, as well as cut off a grafted shoot. It can be replaced by ordinary garden shears or a saw;
- Electrical tape, bast wool or plastic film are materials with which you can tie the graft to the tree;
- Labels to indicate the variety if different varieties of pear are used on one tree;
- Garden varnish for healing cuts.
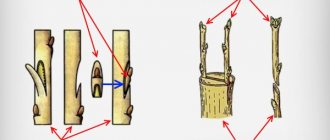
Grafting methods
There are several simple step-by-step schemes by which you can graft a pear. However, each individual case has its own method. Thus, modern copulation is better suited for working with a young tree that has not yet strong branches. In the spring, gardeners graft the pear plant onto the bark. Beginners should give preference to a simple method - using a peephole.
Spring grafting of pear bark
To plant a pear whose area size does not match the size of the plant being grafted, the following method is used:
- Waiting for the weather to warm up outside. In this case, you need to be in time before the sap flows near the tree.
- Separate the bark from the pear trunk so that a small pocket of about 5 cm is obtained.
- A prepared cutting is inserted inside. The scion should have a sharp edge.
- The work is secured with tape. You can additionally wrap the top with film, which will protect against negative external influences.
The tree can be grafted into a split or side cut, bark, or through cuttings
Additionally! In the summer, grafting is carried out only after sap flow has completed, in order to cause less harm to the tree and make it easier to separate the bark.
Into the cleft
It happens like this:
- The trunk part of the pear is cut down: a stump approximately 20 cm high should remain.
- The cut is split in the center - depth 5 cm.
- For convenience, a wedge is inserted. 1-2 cuttings with oblique cuts 3-4 cm in length are placed on opposite edges.
- The wedge is immediately removed. The grafting area is lubricated with garden pitch.
- A fastening bandage is made.
Side cut
Lateral grafting consists of the following steps:
- A section of the tree at a height of 10 cm from the ground is cleared of branches and wiped with a cloth.
- Using a knife, a cut is made in the form of a “T” symbol and 3 cm long.
- The shield of the grafted plant is cut off with a special budding tool. The cut parameters must match perfectly.
- The cortex of the T-shaped incision is carefully opened and the new bud is placed into it.
- The area is pressed with your hand and tied with tape. The kidney should remain on the surface, the shield should be under the bandage.
Butt budding is similar to the described method, but instead of a T-cut in the rootstock, a shallow lateral cut is made.
Attention! Experts recommend doing budding on the northern part of the tree.
Cuttings
Another well-known, but rather rare method is ablation. It is suitable only for young plantings and includes the following steps:
- Preparing the scion and rootstock sites: cleaning their top layer.
- The cuttings are connected in the required areas.
- A tight bandage is applied to the area of their contact, which will need to be removed after several months.
Required tools and materials
A gardener has several knives in his arsenal. One ordinary garden one. They use it when cuttings are prepared. Using a budding knife, a high-quality eye graft is made. To push back the bark, it has a special protrusion, and the blade is concave-convex with a sharp end.
It is convenient to graft with cuttings using a copulating knife with a straight, sharp blade. Oblique cuts are smooth and of the required length. You need quality tools with a carbon steel blade.
Branches of large diameter are sawed off with a garden saw with a blade of at least 35 cm. The graft is tied with electrical tape, plastic film, or special tape that decomposes over time. The cuts are covered:
- varom;
- paint;
- mullein mixed with clay in a 1:1 ratio.
Cuttings purchased from a nursery are labeled with the pear variety.
Rules and recommendations for the pear grafting procedure
Based on the described vaccination procedures, some general conclusions can be drawn:
- Preparation of buds or cuttings is carried out in advance: the branches you like are selected and cut. In the warm autumn or at the end of winter and the beginning of the spring season, it is possible to collect high-quality material for vaccinations.
- If you have the opportunity to choose a rootstock, you should graft the pear onto a pear of a different variety, since other plants are less likely to take root.
- Spring and summer pear grafting is done; at other times of the year it is better to refrain from such stressful activities.
- The procedure is performed carefully, exactly according to the instructions.
- A special knife is used for the operation. Under no circumstances should tools such as an axe, drill, awl, etc. be used.
Stages of grafting into cleft
Is it possible to graft a pear onto a pear - choosing a rootstock
The best way is to graft a pear onto a pear. The following varieties can be selected as rootstocks:
- Wild forest pear - it is more resistant to frost and drought. Seedlings are grown with picking. In general, the compatibility of wild varieties with cultivated ones is normal.
- The Ussuri pear is the most winter-hardy, but it cannot grow at all on alkaline soils. Drought resistance is normal, but lower than that of wild forest pear. It is used as a rootstock in the regions of the Urals and Siberia (not used in the middle zone).
- Seedlings of cultivated varieties are used much less frequently, although their use is also acceptable. For example, in the middle zone you can use the Tonkovetka variety.
Also, quince and some other trees and shrubs can be used as a rootstock - they all have their advantages and disadvantages, and are described in a separate article.
Vaccination in different regions
Experts allocate different time frames for carrying out the procedure in Russia, depending on the place of residence. So, in the south, the favorable period begins in February-March, in the middle part and in the North-West of the country - from mid-spring, in the Urals, in Siberia - from the end of April to the 2nd half of May.
Northern regions
A special vaccination schedule must be followed in the northern regions. Buds form here in June; in August their possible number can reach 10–15. Due to the harsher climate, it is not worth waiting until all the eyes of the pear are ripe. Another specific feature of growing fruit trees is the constant movement of juices. Therefore, for example, in the Urals they begin to graft pear trees at the end of April, the deadline is the 3rd quarter of August.
Important! When choosing the timing of vaccination, not only the time of year is taken into account, but also the specific region in which the crop is grown.
For lemon
Is it possible to graft a pear onto a lemon? For novice gardeners, this question may cause confusion. I.V. Michurin once practiced this option, but he failed to achieve high results. The main problem is the poor compatibility of stone fruit and pome crops. And even in garden conditions, this hybrid would not have been able to survive, since lemon is too heat-loving and demanding of conditions.
Newbie mistakes
When performing the procedure, it will be useful for novice summer residents to know what to avoid:
- Stretching out the event time. If the cut is made for a long time, it may dry out and oxidize during the process.
- Using poor putty (var).
- The bandage is not applied tightly enough. Untimely weakening of the clamps during the development of the graft begins to compress the bark.
- Incorrect position of the grafted plant.
- Removing branches from the rootstock, which can become a possible cause of death of the graft.
- Poor quality, unsharpened instruments.
Clonal rootstocks of the PG series
Breeder R.D. Isaev was involved in the development of dwarf clonal rootstocks for pears. They are numbered and are mainly used in nurseries. Each of them has its own characteristics:
- PG-2 – the roots are well branched, so the trees do not require frequent watering, soil fertility does not matter, garter is not needed, good early fruiting and productivity of grafted plants;
- PG-16-17 - good winter hardiness and disease resistance are added to the above advantages;
- PG-12 - has all the advantages of previous rootstocks, branches well.
Grafting onto these rootstocks works well, and the trees live a long time.
Caring for a pear after grafting
In the first time after the procedure, it is very important to carefully monitor the condition of the pear. After about a couple of weeks, the tree needs to be inspected. So, provided that the kidney has not dried out and has a pleasant greenish color, we can conclude that the procedure was successful. Usually in November the binding made is removed, however, if it is placed carefully and does not squeeze the plant, then it can be left until the onset of spring.
Regrafting is an effective method of plant propagation
In the spring, before the buds swell, the grafted plant should be cut 1 cm above the grafting site. The cut is coated with a special coating. During the spring and summer months, it is necessary to systematically water, loosen the soil near the pear trunk, and remove weeds. The tree is transplanted to a separate area after a year from the date of operation.
Attention! It is proper care of the plant after grafting that ensures the active growth of fresh, tasty fruits.
Before the grafting procedure itself, you need to carefully study the materials and ask gardeners about all the nuances of how to graft a pear. Knowledge and practical skills guarantee 90% of the success of the event.
Selection, preparation and storage of cuttings for grafting
To graft trees correctly, you need to prepare the necessary material in advance. You can purchase a suitable scion from a specialized nursery or from more experienced gardeners. Success depends half on the quality of the cuttings.
A cutting is an annual shoot that is separated from the tree. When choosing, we are guided by the following principles:
- For cuttings, use the tops of branches or side shoots. They should grow this season.
- The bark on a suitable material should be intensely colored, smooth, glossy, even.
- The cutting point on the shoot should be limited by the bud ring.
The selected cuttings are cut off immediately before the bud ring. You can leave part of the young shoot (with two buds) on the tree.
To carry out grafting in the spring, cuttings are harvested after the autumn leaves have fallen. For the middle zone, the optimal period is October. Experts recommend taking shoots that are located on the south side.
Branches 30-40 cm long with a diameter of 0.5-0.7 cm are suitable for cuttings. In this case, the wood should be green and moist.
From such a shoot, the central section is cut off so that at least 3-5 leaf buds are preserved on it. Each cut is covered with garden varnish.
It is convenient to connect all prepared cuttings in bunches with different varieties. Then, for the winter, they are buried in a trench about 25 cm deep. They are installed vertically or horizontally. Sprinkle straw and soil on top. Additionally, cover with burlap so that air can flow freely to the cuttings.
It is convenient to connect all prepared cuttings in bunches with different varieties
In winter, it is constantly monitored to ensure that a thick layer of snow is maintained above the trench.
You can also store cuttings in small quantities in the refrigerator. The material is placed in plastic bags, pre-wrapped with a damp cloth.
As a storage option, use boxes with wet sawdust. They can be installed on glazed balconies or loggias. It is important that the approximate storage temperature is in the range of 0-+4 °C.
In the spring (several days before grafting), the cuttings are sorted out, leaving only strong and healthy specimens. The day before the event, all sections are renewed and placed in a solution of a growth stimulator.
In the southern regions, cuttings can be harvested in early spring, before the movement of sap in the plants begins.
The rootstock should also be prepared in advance. The site of future vaccination is carefully inspected. The tree must be strong and healthy, without visible damage or disease. The ideal rootstock is considered to be seedlings aged from 1 to 3 years. If you plan to graft skeletal branches, then you can use plants under 10 years of age as a rootstock.
Another point is that the dimensions of the rootstock must correspond to the dimensions of the scion. If grafting is done into a cleft, the tree must be larger than the cutting. There are also methods when the scion and rootstock must perfectly match in diameter.
Recommendations
It is recommended to vaccinate in early spring before sap flow begins. This procedure gives almost 100% results. To determine the optimal timing, monitor the temperature outside. After nighttime fluctuations become insignificant, vaccination is performed.
It is recommended to vaccinate in early spring before sap flow begins.
But sometimes vaccination is necessary at other times. To achieve a positive result, you should follow the advice of experienced gardeners, and also know the solution for the most difficult situations.
Winter pear grafting: myth or reality
Experienced gardeners call winter grafting not a myth, but a reality. The result is a strong varietal plant. Vaccination in winter can be carried out from December to March.
In such a situation, the improved copulation method is used. The use of other options is also possible, with the exception of bark grafting.
The following is used as a scion:
- wild roots;
- frost-hardened cuttings;
- annual plants dug up in the fall.
The grafting is done indoors, when the scion and rootstock are still dormant. The grafted seedling is stored until spring in a cellar with low temperatures. The main advantage of the winter procedure is the high probability of a positive result.
What is a columnar pear grafted on?
Columnar pears are compact dwarf plants whose height does not exceed 2 m. The uniqueness of this species is that the fruits are formed along the main trunk. Outwardly, such plants resemble a column with no side shoots.
The ideal option as a rootstock for a columnar pear is quince or serviceberry. Good results can be achieved by grafting a low plant onto a wild plant. In the latter case, strong plants with good immunity, a long fruiting period and high yields will grow.
Good results can be achieved by grafting a low plant onto wild
To prevent the columnar pear from losing its characteristics, formative pruning is constantly carried out.
The disadvantage of using game as a scion compared to quince is that fruiting will occur much later. For example, a pear grafted onto a quince bears fruit 2-3 years after planting, and a wild one - 5-6 years.
Is it possible to graft a dwarf pear onto a tall one?
Dwarf pears are special hybrids that are grafted onto low-growing rootstocks. It is thanks to this that they acquire the properties of short stature and compactness.
Grafting a dwarf pear onto a tall bush is possible in compliance with all the rules, but there is simply no reason to carry out the procedure. The properties of the hybrid will degenerate.
Vaccination in different regions
In the southern regions of the country, vaccination is much easier than in the temperate zone. But most of the country is located in the risky farming zone.
In the middle and northern parts of the country, gardeners often encounter various natural disasters. Therefore, in such areas, strong winter-hardy plants are used for rootstock, which can more easily withstand weather surprises.
It is advisable to use game, quince, and hawthorn as a rootstock. Here it is important to provide for situations of different growth rates. For this reason, various fortifications are pre-prepared.
How to regraft a columnar pear
Dwarf pears are grown by seeds or by grafting cuttings onto quince, game, or game. They can be propagated by seedlings, cuttings, and seeds. But the most effective option is re-vaccination.
Re-vaccination is carried out in a new place in the spring (late April - early May). The procedure is performed in the morning or evening. The rules are the same as for conventional grafting of fruit trees.
The step by step guide is as follows:
- In the fall, cuttings 70-80 cm long are harvested.
- On the selected rootstock, all fruit-bearing branches are trimmed to a length of 40 cm.
- The grafting is performed using one of the following methods: into a split, behind the bark, or into a side cut.
- The joining area is treated with garden varnish and wrapped with tape.
If the grafting is carried out correctly, the cutting will take root in 3-4 weeks.
At what height is it correct to plant?
Any vaccination is performed in accordance with the recommendations of each method.
Any vaccination is performed in accordance with the recommendations of each method.
To determine the height, do the following:
- The soil is raked away from the rootstock trunk so that the root collar appears.
- The branches are carefully cut from the soil to a length of 10 cm.
- The cleaned part of the barrel is wiped with a rag.
- An incision is made on the root collar for grafting.
This way you can do any option.
Is it possible to graft a pear in the fall?
If we consider pear grafting from the biological side, then it can be performed at any time of the year, since life processes in trees do not stop with the onset of cold weather.
In the southern regions, due to the climate, vaccination is carried out even in winter.
In autumn, vaccination should be done as early as possible so that the scion takes root before the onset of frost.
Benefits of autumn pear grafting
There are not too many advantages to autumn vaccination. At this time, the processes of sap flow and vital activity slow down. This condition has a positive effect on the rootstock. The plant will withstand any injury to the bark and wood faster and easier.
There are not too many advantages to autumn vaccination
The following strengths should also be noted:
- a large amount of grafting material, since it is in the fall that shoots are pruned;
- people already have more time to work in the garden;
- Since fresh material from the current season will be used for grafting, there is no need to save the cuttings until spring.
Grafting is an important procedure in gardening. Thanks to this technique, it will be possible to develop new varieties, rejuvenate any old trees, improve the quality of the harvest, and also heal wounds. Grafting is not very difficult, so if you follow all the instructions and rules, this is a real task for novice amateur gardeners.
Have you grafted a pear tree onto another tree? How was this done and what was the result? Share your experience in the comments.