A complex drug based on calcium salt helps restore metabolism and prevent the development of many pathologies. Affordable and effective, it restores the normal level of one of the main macroelements in the body, relieving a variety of painful symptoms.
Composition and dosage form
Calcium chloride (CaCl2) is formed during the production of baking soda. The substance is used not only in medicine, but also in cooking, cosmetology, and the chemical industry. Without it, it is impossible to produce healthy calcined cottage cheese and hard cheeses.
The pharmaceutical form of calcium chloride is a water-based injection solution. Available in transparent glass ampoules of 5 or 10 ml. The cardboard packaging of the drug contains 10 such ampoules. The concentration of the medicinal compound in 1 ml of solution is 100 mg.
How to replace potassium chloride
In the old days there was no agricultural industry, and our ancestors got out of the situation with the help of organic fertilizers. The chlorine contained in potassium chloride is not tolerated by many plants. Also, excess chlorine greatly acidifies the soil. What contains the most potassium, and what can replace potassium chloride?
Ash
Ash is the number one fertilizer in the garden. The ash contains the maximum concentration of potassium that seedlings need. Ash can be made by burning plants, bark and tree branches.
Note! One kilogram of ash replaces 200-250 g of potassium chloride.
Ash is useful for acidified soils, as it promotes alkalization. Dry matter and ash water are used to feed the soil. Dry ash is simply dropped into the soil, and the solution is watered over the seedlings. Usually they take 200 g of ash per bucket of water, boil it for a while and let it brew for a week. The strained infusion is sprayed onto the plants or watered under the roots.
Ash performs another important function: it fights pests and treats seedlings from diseases.
Banana skin
This folk fertilizer has become widespread among gardeners. Banana skins are collected, dried and ground to a powder. To fertilize a square meter of land you will need a liter jar of dry raw materials. The powder is dropped into the ground.
Potassium sulfate
It is also called potassium sulfate. This fertilizer is completely free of chlorine and is recommended for use on highly acidic and acidic soils. Potassium sulfate protects berry bushes from harsh winters if it is added to the ground before frost. All cruciferous plants love potassium sulfate: radishes, cabbage, reps and others.
The preparation contains a sufficient amount of potassium, which promotes the accumulation of vitamins and sugar in the fruits. This increases the taste characteristics of the fruit. Potassium sulfate is also used in floriculture, since it does not contain chlorine.
How does calcium chloride work?
The product exhibits anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, detoxifying properties, stabilizes the blood formula, helps strengthen vascular walls, and reduces their permeability. Calcium in the drug ensures normal functioning of the muscles and heart, regulates the conduction of nerve impulses, bone tissue synthesis, increases resistance to infections, participates in the absorption of vitamins and minerals, and maintains the necessary balance of electrolytes. Calcium chloride also normalizes the condition of the kidneys, somewhat increases diuresis, relieves and prevents swelling, helps restore the functioning of the adrenal glands, and promotes the release of adrenaline.
After use, about half the dose of the drug binds to blood proteins. Part of it is absorbed by the body. The transformation of calcium chloride occurs in the liver, the excess is excreted in the intestinal contents and urine. The intensity of excretion and absorption of the drug depends on age-related changes, dietary habits, the presence of calcium-containing foods in the diet, and hormonal status.
The benefits of potassium supplements
This microelement ensures the proper development of plants: it accelerates the movement of nutrients in tissues and participates in the formation of the root system. Potassium also has an important effect on the quality of fruits: it improves taste, color and size. Potatoes especially need potassium; without it, they do not acquire a sufficient amount of starchy substances.
Sugar beets also urgently need potassium, since if it is deficient, the root crop cannot accumulate enough sugar. Vegetable and fruit crops accumulate monosaccharides thanks to potassium. At the same time, their taste characteristics improve.
Note! If nitrogen is needed for vegetation, then potassium is needed for the formation of tubers and fruit set.
A sufficient amount of this microelement in the soil strengthens the immune system of seedlings, protects against phytofungi and other lesions. Potassium also develops the resistance of seedlings to unfavorable climatic conditions and drought.
Signs of potassium deficiency in the soil:
- stop in growth and development;
- deformation of leaf shape;
- infection by fungal diseases;
- stunted appearance of seedlings;
- faded and dried leaves;
- blue-green leaf color;
- uneven ripening of fruits.
It is very easy to notice a lack of potassium: old leaves begin to dry out at the edges and turn brown. They quickly wither and fall off.
Indications for use
It is recommended to use a 10% solution of the drug:
- with calcium deficiency caused by malnutrition, systemic diseases, endocrine disorders, intestinal disorders;
- when there is a need for increased doses of calcium: age-related changes, periods of active growth, postpartum complications, general physical exhaustion;
- for bleeding of various origins;
- with nutritional edema;
- for hepatitis;
- with rickets, osteomalacia;
- for tuberculosis;
- for kidney inflammation;
- for allergic reactions;
- in case of intoxication with fluorine, magnesium, oxalic acid preparations.
During childbirth, calcium chloride is necessary to prevent eclampsia and to stimulate contractile activity of the uterus.
Symptoms of calcium deficiency
The lack of calcium chloride in tomatoes primarily affects young shoots.
The growing points gradually die off, and the shoots themselves become thinner, become sluggish and drooping. If the deficiency manifests itself at the stage of formation and ripening of fruits, brown dry spots may be observed on them.
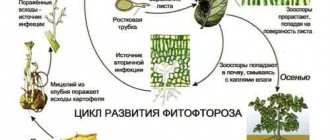
Sometimes the symptoms of calcium deficiency are confused with manifestations of late blight, but in this case, to eliminate the problem, it is enough to feed the bushes. Cone-shaped tomatoes are more susceptible to the disease than others. Top rot quickly spreads to the entire fruit, making it unfit for consumption. Affected tomatoes differ significantly from healthy ones. They are drier and do not produce seeds.
Symptoms of element deficiency are:
- lethargy of leaves and shoot tips;
- frequent branches breaking;
- long fruit ripening;
- lightening and curling of leaves.
When is calcium chloride contraindicated?
The injection drug should not be used in cases of increased blood clotting, thrombosis, vascular atherosclerosis, or in conditions of hypercalcemia. Pregnancy and breastfeeding are also contraindications. An exception may be an individual indication when the benefit to the mother outweighs the risks to the child.
It is necessary to refuse therapy if you have an allergic reaction. Its possible signs: increased swelling, severe skin itching following administration, bronchospasm, suffocation.
How to fertilize
Fertilizing the soil with minerals is carried out during autumn or spring digging. The procedure is repeated every year, as the nutrient reserves of the soil are depleted.
The plant needs feeding
To fertilize tomatoes, add the following to the soil:
- Dolomite flour. It consists of limestone ground into powder and may contain a small amount of impurities: clay and sand. It is also effective for neutralizing acidic soils. Its components are capable of binding radionuclides, which makes it possible to grow an environmentally friendly vegetable. Dolomite flour is added to the soil at the rate of 500-600 g per 1 m²; for highly acidified soils it will require 2 times more.
- Slaked lime is less commonly used for feeding tomatoes, but is no less effective. The difficulty of applying it is that it can burn the roots and trunk of the bush in direct contact with it, so fertilizer is applied only in the fall in an amount of 500 g per m². On loam, the dosage is increased to 800 g.
- Chalk is applied to the soil in ground form. The fertilizer has a high content of calcium carbonate. In spring or autumn, about 300 g per m² is applied.
All these substances do not dissolve in water, and this must be taken into account when digging. The lumps are broken up with a shovel or rake to distribute the fertilizer evenly.
Calcium nitrate
Unlike other mineral fertilizers, calcium nitrate can be used to fertilize tomatoes during any period of their growing season. Calcium nitrate is highly soluble in water and is quickly absorbed by plants.
The calcium variety of nitrate should not be applied to the soil at the same time as phosphorus and sulfur fertilizers: this negatively affects metabolic processes in the plant and reduces the percentage of calcium nitrate consumption. Tillage is carried out for the first time at the stage of growing seedlings. This guarantees:
- normal development;
- increase in yield by 10-15%;
- resistance to temperature changes and drought;
- higher resistance to various viruses and fungi;
- rich taste of tomatoes, as well as good presentation.
For 20 g of calcium nitrate, take 100-120 g of sifted wood ash, 10 g of urea and 10 liters of water. Water the tomato seedlings with this solution at the root, avoiding contact with the stems and leaves: this can cause burns.
Folk remedies
Calcium deficiency can be compensated for using folk remedies.
To do this, 200 g of wood ash is boiled in 3 liters of water with 30 g of crushed eggshells. Boil the mixture for at least an hour over very low heat. There is no need to add boiled liquid.
After cooling, seedlings or adult plants are sprayed. Treatment should be carried out in dry weather, as precipitation will make spraying useless. To make the solution stick better to the leaves, you can add laundry soap to it.
Source of the article: https://fermoved.ru/pomidoryi/kalcij-hloristyj.html
Side effects
When an injection is administered, the following body reactions are likely:
- burning pain along the veins;
- redness of the skin of the face, a feeling of heat in the mouth, face, neck and throughout the body;
- decreased heart rate, arrhythmia;
- pain in the stomach, abdominal cavity;
- nausea, vomiting.
Within 20–30 minutes after the medicine enters the bloodstream, the discomfort weakens and passes. If the injection is administered too quickly, cardiac problems may occur.
Compatibility of potassium with other baits
It is important to know which substances are not recommended for use with - potassium chloride fertilizer is incompatible with lime, dolomite flour, calcium carbonate and chalk. Combines well with ammonium sulfate, manure, diammophos, bird droppings, ammophos. Before direct use, urea, saltpeter, and superphosphate are added to the fertilizer.
When processing plants, you need to remember the rules for working with chemical compounds. We are talking about protective equipment (apron, respirator, goggles and gloves), protection from animals and children, washing the skin with running water in case of contact. The instructions indicate the rules for storage and use. It is important to follow the humidity recommendations, otherwise the fertilizer will become clumpy, making it difficult to apply.
How to use calcium chloride according to instructions
In most cases, calcium chloride injections are prescribed by infusion: through droppers, at a rate of no more than 6 drops per minute. This way the drug causes fewer painful side effects. Jet injection is practiced less frequently. Intravenous injections are given slowly: administering the dose over 3–5 minutes. Subcutaneous and intramuscular injections of the drug are prohibited. The product does not dissolve in soft tissues, forming compactions and foci of necrosis.
The daily dose depends on the age and physical condition of the patients:
- For adults, the drug is administered in a volume of 5–10 ml per day;
- Children are dosed from 0.5 to 4–5 ml.
It is allowed to divide the daily dose into several parts and administer them at equal time intervals. In emergency cases, it is allowed to take calcium solution orally: consume the contents of the ampoules orally:
- for children and adolescents, the maximum dose is about 5 ml of the drug at a concentration of 10%;
- Adults can drink about 10–15 ml of the product per day.
The exact scheme, as well as the duration of the course of therapy, is determined individually.
Application of KCI in the garden
To saturate the soil with potassium, adhere to the following dosages:
- autumn: 100/200 g per square meter;
- spring: 30-45 g per square meter.
Experienced gardeners advise diluting KCI with water and watering the area. 30 g of substance is consumed per bucket. To feed the seedlings more efficiently, the total dosage is divided into three parts and the soil is fertilized three times per season.
Potato
Fertilizing a potato field must be careful, since an excess of chlorine reduces the production of starchy substances in the tubers. If the soil is sandy, it is better to replace KCI with cement dust. Heavy soils take potassium chloride fertilizer well. The potato field is fertilized during autumn plowing: 100 g KCI per m2.
Tomatoes
This crop is also sensitive to chlorine, so it should be used very carefully. The site is fertilized in the fall after clearing the crop. In spring, it is recommended to use potassium sulfate instead of KCI.
cucumbers
Potassium nutrition is necessary for cucumbers to form strong and tasty fruits. However, this crop may perceive potassium chloride negatively. Therefore, first do a test: water several seedlings with diluted agrotuc and observe the reaction. If the crop accepts the fertilizer well, irrigate all the bushes: half a liter jar per seedling.
Potassium fertilizers for cucumbers are applied 5 times per season in open ground and 3 times in greenhouse conditions. Seedlings need to be watered in pre-moistened soil: either after precipitation or after watering the beds.
Carrot
Agrofertilizer is applied when planting carrot seeds in beds. Make a deep groove (up to eight centimeters), lay down the powder and sprinkle with earth. Seeds are planted on top in the usual way. Chlorine has the ability to go deep into the soil, so its effect will not affect the condition of the seeds. The carrots will receive the necessary potassium for their development and will grow large and straight.
Fruit trees
Mature fruit trees tolerate the presence of chlorine in the soil well, so they can be safely fed with potassium chloride. One plant will require 130-150 g of agrofertilizer diluted in water. On fertile soils, less fertilizing is required (100-110 g); on sandy soils, the dosage is increased to 160-180 g.
However, use the drug carefully when fertilizing cherries, sweet cherries and apricots. These trees do not tolerate chlorine well. Pear and apple trees are conditionally tolerant to chlorine preparations. It is advisable to apply KCI after deep watering of trees or after heavy rain.
Note! Gardeners do not recommend feeding potassium chloride to the vineyard, since this plant does not tolerate chloride compounds.
Flower beds
To feed gladioli, add 15 g of agrotuk to a bucket of water - after the fifth leaf is formed. After the peduncle appears, add 20 g per bucket of water.
Peonies are fed during flowering: 10 g of powder is dissolved in a bucket of water.
Note! Chlorine negatively affects plant growth, so application rates cannot be exceeded.
Rose bushes are fed twice during the flowering period. 20 g of powder is dissolved in a bucket of water.
Calcium chloride in cosmetics
The drug solution is popular as part of masks for deep cleansing of facial skin. You can use them at home:
- Apply the contents of the ampoule with a cotton swab to clean skin, repeat the procedure several times after each layer has dried;
- wash your hands with solid, fragrance-free toilet soap and apply foam to your face;
- rub the soap over the skin until characteristic pellets appear under the palms;
- Continue massaging until the entire mass is peeled off the skin.
This “rolling” removes dead particles of the epidermis, dissolves remaining sebum, softens and eliminates various imperfections, and narrows pores. Regular use normalizes sebum secretion and eliminates inflammatory processes. The mask is especially useful for dull, oily and problematic skin.
Potassium chloride
Chlorine is also beneficial for plants, although its content in the soil must be strictly adjusted. Without chlorine, photosynthesis is disrupted, plant leaves quickly dry out and fall off, and suffer from chlorosis.
Potash fertilizers with chlorine can be different:
- potassium chloride;
- potassium chloride electrolyte;
- 40% mixed potassium salt;
- raw potassium salts.
The chlorine content in potassium fertilizers negatively affects many vegetable and berry crops, so I use the fertilizer only for autumn plowing of the site. Recommended soils for autumn plowing: clay, loam. Fertilizing the soil in autumn will not harm the plants, since chlorine will be washed out of the fertile layer during the winter. On sandy soils, potassium chloride is applied in the spring.
Note! Chloride fertilizers are useful for fodder and sugar beets, asparagus and celery.
Potassium chloride (KCI) is a free-flowing white powder or granules. Sometimes the granules are of a different color: this depends on the addition of additional substances to the agrochemical. In the garden it is better to use granular powder; it is absorbed faster by the soil. This powder is especially useful for chlorine-intolerant crops, as it is quickly washed out of the soil.
Experienced gardeners prefer to use granules, as they linger longer in the soil and gradually release beneficial compounds to the plants. If there is no need for emergency fertilizing with KCI, it is better to use a granular form of fertilizer.
Note! Potassium chloride is not suitable for indoor flowers.
KCI in granules has its own characteristics: it is suitable for emergency plant nutrition. The granules instantly dissolve in water and release nutrients to the soil. This agricultural product is more expensive, since an additional granulation technique is used to create it.
Potassium chloride does not combine well with:
- dolomite flour;
- chalk and lime.
Disadvantages of Potassium Chloride:
- contains a lot of chloride compounds;
- It is hygroscopic and inconvenient to store;
- does not combine with lime, chalk and dolomite flour;
- Requires caution when working due to its high toxicity class.
To protect plants from the influence of chlorine, it is recommended to use this agrochemical in the off-season or after heavy rains. In this case, chlorine is quickly washed out of the ground, and potassium remains.
It is necessary to work with KCI in protective clothing, observing safety precautions.
Description and physico-chemical characteristics of potassium chloride
Potassium chloride is a chemical compound in the form of small crystals of white or gray color, odorless, good melting. Another variation of the drug is an odorless red powder with a predominant salty taste. Both are capable of dissolving well in water without precipitation, but are difficult to react with ammonia and hydrochloric acid.
- salt formula – KCl;
- molar mass – 74.55 grams / mol.;
- density at 20 °C – 2.15 g/cm3;
- melting point – 776 °C;
- boiling point – 1407 oC;
- solubility in water at 20 °C – 34 g / 100 ml.
The method of production is neutralization of hydrochloric acid with potassium hydroxide.
When using potassium chloride as a fertilizer for plants, preference is given to granular, coarse- or fine-crystalline packaging of a gray, white or red substance. Coarse-grained pink potassium chloride is used in plant growing.
The impressive particle size will extend its life on the surface or inside the soil: in this form it is less susceptible to dissolution during precipitation. The content of the active ingredient in the supplement varies in the range of 52-99%.
What plants and what soils can be fertilized?
Which plants respond well to fertilizing with potassium chloride? First of all - potatoes, beets, carrots, sunflowers. Corn, tomatoes, cucumbers, and cereals will be welcome. A large amount of this fertilizer can negatively affect the health of beans and berry bushes.
To minimize the effects of chlorine, experts advise adding potassium chloride in the fall. In this case, there will be nothing left of it before the growing season begins. On the contrary, due to the prolonged effect, potassium will remain.
Spring fertilization is carried out on wet lands during heavy rains or after watering. Spring fertilization is practiced only on light soils.
As for soils, potassium chloride will enrich sandy, peat, podzolic and sandy loam soils.
Please note that potassium chloride is not suitable for emergency fertilizing. It is carried out in exceptional cases when the leaves are severely deformed and gray spots appear between the veins. But you should be careful - there is a high probability of overfeeding.
Signs of calcium deficiency
Typical manifestations of calcium deficiency include:
- Changes in shoots and leaves. Yellowing, appearance of light spots. Old leaves grow in size, and with them the area of damage increases. The areas take on a dark green color. As it progresses, the leaves curl and change shape.
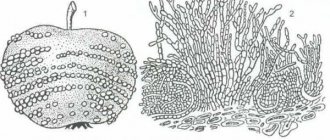
- Damage to tomatoes. Blossom rot breaks out on the fruit. Defects on the tops are colored brownish, and rot appears.
- Growth disorders. The stems do not grow, the fruits become smaller.
- Lightening of the tops of the shoots, while the leaves lighten in parallel.
- The appearance of necrotic foci on the stems, the upper sections of the trunks disappear.
Ode to iodine in the garden
This time I want to write about how medicines sold in pharmacies can be used in the country against diseases and pests.
Our home medicine cabinet always contains such products as iodine, brilliant green, potassium permanganate, aspirin, and hydrogen peroxide. That's what we'll talk about. iodine first
, which I have been using for a long time as a preventive agent on tomatoes, cucumbers, cabbage, raspberries, grapes and eggplants. But I think that the spectrum of its action is much wider, I just don’t know everything about it yet. On tomatoes I use iodine against late blight. Immediately after the emergence of seedlings, I treat them with the following solution: 9 liters of water + 1 liter of whey + 30 drops of iodine + 1 tbsp. l. hydrogen peroxide (to enhance the effect of iodine). Seedlings can be processed every week.
In general, I consider iodine a universal antiseptic. If you combine it with milk, you get an effective remedy against powdery mildew on cucumbers, strawberries, zucchini, and pumpkins. Iodine will play the role of fertilizing on peat and podzolic soils. They are the ones that lack iodine. After wintering, the plants will grow together if they are treated with iodine: it stimulates seed germination well.
I take 20 drops of iodine per 10 liters of water and spray it on tomatoes or cucumbers during the fruiting period. This will hold off late blight for some time if it has already appeared, but there is one small drawback - after treatment with iodine during harvesting, clothes get dirty. It is impossible to remove brown stains, so I advise you to collect processed tomatoes in overalls.
TOOLS FOR HOME AND GARDEN, HANDCRAFTS, ETC. PRICES VERY LOW
I have been using iodine on tomatoes for several years throughout the entire growing season, from seedlings to late fruiting. In addition, iodine promotes abundant flowering, increases resistance to disease, and burns leaves on strawberries due to gray rot. For good formation of a cabbage head, I take 40 drops of iodine per 10 liters of water and pour 1 liter under the root.
Potassium deficiency and excess: manifestations
You can find out about a lack of potassium by characteristic signs that should not be ignored.
- the formed crown suddenly becomes bluish-gray;
- dark brown spots appear on the leaves;
- leaves change their original shape;
- the tops of the plants “rust”;
- the stepsons begin to grow actively;
- the stem remains thin and does not add thickness;
- there is a delay in flowering and budding.
Potassium deficiency occurs in crops planted on depleted soil (peat areas, sandstones, floodplain lands).
Excess potassium manifests itself as follows:
- new leaves are very thin, with signs of chlorosis;
- the tips of the leaves turn gray and dry out;
- internodes are shortened;
- the lower leaves wrinkle;
- the tips of the roots begin to die;
- the growth of green mass stops.
When there is an excess of potassium, plants stop absorbing nitrogen, calcium, zinc, magnesium and other useful microelements.