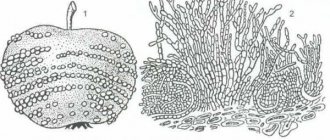
Tomatoes are among the most popular agricultural crops. Almost every summer cottage has beds with this plant.
Dear readers! For you, we have created communities on social networks in which useful articles and interesting ideas are published several times a day! Subscribe and receive useful content in a convenient format!
Tomatoes are susceptible to many diseases: fungal, viral, bacterial, caused by insect pests, etc. In this article we will talk about blossom end rot. You will learn what this disease is, why it occurs and how to treat it.
What is blossom end rot of tomatoes?
Blossom rot on tomatoes
Blossom blossom of tomatoes is a non-infectious disease. Most often it occurs due to calcium deficiency in the plant. This element is part of the salts that are needed to form tomato pulp. If there are not enough of them, then tissue necrosis begins in the fetus and the apex turns black.
REFERENCE. The apex is the part of the tomato that is farthest from the stem.
Causes
There are many reasons for the appearance of gray-brown spots and rotting of fruits. This may include factors such as susceptibility to infections. Poor care, environment, local climate and much more. Most gardeners think that blackening of tomatoes occurs only when tomatoes are infected with late blight, but this is far from the case. First, do a visual analysis of the bush and the tomatoes themselves. For example, if the flesh is hard inside but lacks juice, this is blossom end rot.
Rot on tomatoes indicates their defeat
Also, in addition to infectious diseases: blossom end rot, late blight and fusarium, which will be described below, the cause of rotting can be:
- lack of moisture, while tomatoes absorb vapors from the air and a chemical reaction occurs in the fruits, causing them to turn black;
- lack of magnesium and boron in the soil.
Because rot spreads instantly. Every time you water or do other care, inspect the bushes so that at the first sign you can begin to fight the disease.
Why does disease develop in tomatoes?
There are many reasons for calcium deficiency. The most important of them is the insufficient amount of this microelement in the soil. Among others, the following can be noted:
- Moisture deficiency in the soil. Because of this, calcium is simply not absorbed by the roots of the plant.
- Excess moisture in the soil. When water stagnates in the soil, as well as the proximity of groundwater, calcium is washed out of the soil. Accordingly, the plant has nowhere to get the required amount of this microelement.
- Chemical composition of the soil . If the soil is too saline or acidic, it will not have enough calcium.
- Root injuries. Tomatoes take nutrients from the soil using the root system. If it is damaged, the plant will not be able to receive microelements and will begin to hurt. Including apical rot.
- Stress. Tomatoes are a crop that does not like sudden changes in growing conditions. Watering with cold water, a sharp change in temperature - all this negatively affects tomatoes and leads to calcium deficiency. For example, when watering with cold water, the roots cannot absorb nutrients for some time.
The cause of blossom end rot on tomatoes
The main causes of rot on the tops of fruits are:
- lack of moisture,
- calcium deficiency.
With intense fruit filling, calcium is involved in the construction of cells that allow the fruit to increase in size. In this case, the root system absorbs calcium and first carries it through the vessels of the stem to the apical part, that is, to the growth point to continue upward development of the stem. Then into the leaf apparatus, calcium is also needed by the leaves. And only lastly does calcium enter the fruit.
During intensive filling, fruits require an increased amount of calcium, and receive it last, according to the residual principle. And when there is little calcium, the cells do not have time to line up, and in the area of the flower scar where the flower has fallen off, the first manifestation of the disease begins.
Why is this happening? There are several reasons.
- Incorrect or irregular watering. Calcium, along with water, is distributed throughout the plant. In hot weather, strong evaporation occurs from the leaves and stems. And if at this time the plant lacks moisture, and cannot replenish it by absorption from the soil, then it begins to pull it out of the fruit, trying to survive during the dry period. This often happens when the dacha is far away and it is not possible to water the plants regularly.
- Calcium is not absorbed by the roots because, on the contrary, there is excess moisture in the soil. This happens when watering is frequent, and the plants are also mulched with a thick layer of grass, which prevents the evaporation of excess moisture. The soil becomes acidic and interferes with the absorption of calcium.
- Calcium – potassium imbalance. Calcium is an antagonist of potassium. With frequent fertilizing with ash, which is a phosphorus-potassium fertilizer, excess potassium interferes with the absorption of calcium. And, conversely, excess calcium with frequent feeding with calcium nitrate does not allow potassium to be absorbed, then the fruits will not fill well. Therefore, the golden mean is important.
Signs of infection
Initial stage of the disease
The most important symptom of the disease is the appearance of a yellow-brown spot on the top of the tomato. In this case, signs of blossom end rot begin to appear on fairly developed fruits. During the ripening process, the spot becomes dark brown and seems to be pressed into the inside of the tomato.
Blossom rot is not the result of infection or pest action, but the affected area is often the site where fungus soon begins to develop.
Another symptom of the disease is rotting of the fruit pulp without external changes. In this case, it is impossible to detect the disease before harvesting.
REFERENCE. A tomato affected by blossom end rot turns red earlier than others. But usually on one bush almost all the fruits suffer from blossom end rot.
Can spraying baking soda help stop blossom end rot?
If you are a supporter of organic farming, at the initial stage of damage to tomato plants by blossom end rot in a greenhouse, it makes sense to protect the plants from possible infections with a baking soda spray. Baking soda spray on tomatoes does not actually kill the fungi, but the sodium bicarbonate changes the pH balance of the foliage so the fungal spores cannot germinate. Therefore, in the initial stages of infections, baking soda is used as a preventative fungicide, but it does not spray well and does not adhere well to foliage. Adding horticultural oil or dish soap to the solution will give the spray some stickiness.
Prepare a solution with which you think you protect tomatoes from diseases, add a heaped tablespoon of baking soda, a teaspoon of vegetable oil and a small amount of fairy to a bucket of water and spray the tomato plants with this solution the day before harvesting, let the spray dry in within one to four hours. Avoid spraying plants in direct sunlight or at temperatures above 26°C, otherwise you risk burning the foliage. Spray early in the morning or evening when it is cool. In outdoor areas, reapply baking soda sprays after heavy rain.
Baking soda can accumulate in the soil, robbing it of magnesium and calcium, leaving plants unable to absorb iron. This can cause the leaves to turn yellow or the growth of your tomatoes to slow down. Try not to use baking soda sprays more than once every 14 days.
You can read more about the uselessness of using soda in the garden here >>>
Treatment of blossom end rot in tomatoes and is it possible to save the plants?
Blossom rot does not affect the entire plant, so if detected in a timely manner, the bush can be saved.
Firstly , you need to pick off the affected fruits. Under no circumstances leave them to rot in the garden beds. Sick tomatoes should be disposed of outside the garden.
Secondly , the plant needs to be fed with fertilizer with a high calcium content (for example, calcium nitrate or potassium chloride). Saturation with this microelement will stop the development of the disease.
Thirdly , cultivate the soil. Loosen it if it gets crusty. Water if it is completely dry.
Affected fruits must be destroyed
What medications to treat for the disease
Chemicals are the most effective remedy for blossom end rot. The fact is that they already contain the required dose of calcium.
IMPORTANT! Before feeding tomatoes, they must be watered abundantly. This way, minerals will be better absorbed by plants.
Among the most effective drugs:
- Calcium nitrate. Spraying with a solution (10 g per 10 liters of water).
- Calcium chloride. Spraying with a solution (30 g per 10 liters of water).
- "Brexil Sa." Treatment of leaves and stems with a solution (10 g per 10 l of water).
- "Nutrivant PLUS" and "Fertivant" . Spraying with a solution of 2 drugs (30 g per 10 liters of water).
Nutrivant PLUS
Treatment with these agents should be carried out every 1.5 - 2 weeks after detection of the disease. If new fruits do not show signs of blossom end rot, then spraying can be stopped.
Treatment with folk remedies
If you prefer traditional methods, then, first of all, you need to pay attention to wood ash, soda, chalk and oak bark . Fertilizers based on these products are rich in calcium. Fertilizers are applied in liquid form and mainly by foliar application (spraying). Only the chalk “chatter” is applied at the root.
- Ash based fertilizer. 1 glass is sifted and mixed with 1 glass of boiling water. The concentrate is infused for a day, after which it is diluted with 9 liters of water.
- Chalk "chatterbox". Watering with a solution (100 g per 10 liters of water) under the root.
- Oak bark is ground into crumbs. A teaspoon of the product is poured into 1 liter of water and boiled for 10 minutes. Then the concentrate is diluted with 9 liters of water.
- Soda solution. 2 teaspoons are diluted in 10 liters of water.
Treatment with solutions should be carried out once a week. The entire bush is processed. And fruits, and leaves, and stems. Particular attention should be paid directly to tomatoes. If symptoms of blossom end rot no longer appear, treatment should be stopped.
IMPORTANT! There is no need to process tomatoes after the signs of the disease disappear. An excess of any microelements is also harmful to plants.
How to fight in open ground
The same preparations are used for open ground and greenhouses.
Fitosporin
Fungicide created on the basis of the bacterial strain Bacillus subtilus 26D. For tomatoes they produce a special product “Fitosporin-M TOMATO”. The complex of phytobacteria is called upon to help in the treatment of a whole range of tomato diseases. Enriching the product with microelements helps to locally influence the problem.
- for spraying, prepare a solution of 10 g per 20 liters of water;
- for watering at the root: 20 g per 6 liters of water. 0.5 liters are poured under each plant;
- for soaking seeds before sowing 1.5 g per 100 g of water.
Brexil ca
Brexil is a chelate complex containing the microelement calcium in a form accessible for absorption by the plant. The drug is recommended for prevention and treatment.
- non-toxic;
- has a high degree of digestibility by the leaf plate;
- contains glycosides to enhance the penetration of minerals into plant cells;
- It can be applied both with watering and with foliar feeding.
Nutrivant plus tomato
The drug is effectively used as a top dressing. However, the manufacturer provides the formula 6N-18P2O5-37K2O+2MgO+0.02B+0.08Fe+0.04Mn+0.02Zn+0.005Cu+0.005Mo+Fertivant. It follows from this that the drug will not retain calcium and cannot improve the situation with tomato blossom end rot.
Rescuer 3 in 1 ampoules
The drug contains:
- insecticide-acaricide;
- fungicide;
- growth regulator
However, the manufacturer conceals information about the active substance. At the same time, he prescribes all the tomato diseases known to him. The information is not presented correctly and you should refrain from using it.
Megafol
The drug is made in Italy. Contains amino acids, nitrogen and soluble form of potassium. Recommended for use in the garden and greenhouse immediately after planting tomatoes, and then every 10-15 days. The solution is prepared from 0.2 liters of water per bucket as a top dressing. It is unlikely to help as a remedy for axing.
HOM or copper oxychloride
Copper-containing preparations work great as fungicides, but unfortunately they are powerless if calcium is not absorbed.
Bordeaux mixture
An excellent remedy for late blight, but it does not help against blossom end rot.
Mulching and pinching
Step-sonning is a mandatory operation. Stepchildren take nutrients and water from the plant. Mulching somewhat delays the evaporation of moisture, but cannot replace watering.
How to deal with rot on tomatoes in a greenhouse?
Methods of combating blossom end rot on tomatoes growing in a greenhouse are also aimed at eliminating calcium deficiency in the soil and creating favorable conditions for plants.
Small differences are due to the fact that tomatoes in a greenhouse are less susceptible to atmospheric influences.
Firstly , watering is carried out only by hand. Therefore, it is important to establish a regime of watering and subsequent loosening of the soil.
Secondly , it is necessary to regularly ventilate the greenhouse to ensure a flow of fresh air.
Otherwise, you can use the same means as in the fight against blossom end rot on open ground tomatoes.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of pathology
Blossom blossom can completely destroy a tomato crop.
Previously, it was believed that the appearance of pathological lesions was associated with a fungal infection. Late blight provoked infection with a disease that destroyed almost the entire crop of vegetables from the nightshade family.
Today, the main reason for the appearance of lesions on bushes has been identified - calcium deficiency in the tops of tomato fruits.
That is, the fruits of the vegetable crop do not receive a sufficient amount of calcium salts, which are an important material for the normal formation of the skin and pulp of the fruit. Lesions first appear on the tip, that is, on the most distant part of the tomato from the branch, since against the general background of deficiency, this part of the tomato is most susceptible to calcium starvation.
Lack of calcium, and therefore the factors that provoke the development of blossom end rot on tomatoes, arise for several reasons:
- insufficient amount of moisture for the plant (the microelement simply cannot be constantly absorbed by the bush from the soil);
- increased acidity or salt content in the soil (in low-lying areas this occurs due to stagnation of moisture, the close location of groundwater and poor drainage lead to impoverishment of the site and a lack of an important microelement in the soil);
- damage to the roots of the plant (during agrotechnical treatment of plantings, in particular loosening the soil, the root system of tomatoes can be damaged, this leads to the fact that beneficial substances from the soil and the necessary moisture cannot be absorbed in the required mode to meet all the needs of the cultivated plantings);
- stress for the crop (these include sudden changes in weather conditions, drafts, watering with too cold water in hot summer weather, and others).
Farmers who grow unusual tomato varieties in greenhouses, such as those with an oblong shape or those with huge fruits, note a frequent problem with disease. The fact is that non-standard shapes and sizes also lead to starvation of the plant, taking too many nutrients from the soil.
Are there resistant varieties?
One of the most effective methods of resisting blossom end rot is the selection of disease-resistant varieties.
Early-ripening and large-fruited varieties and hybrids of tomatoes are most susceptible to the disease. For example, “Azhur”, “Sprint Timer” and “Alabai”. During development, tomatoes of these varieties very quickly consume too much energy. Therefore, if they are not carefully looked after and fertilized, they may get sick.
The varieties and hybrids least susceptible to blossom end rot are “Bolshevik”, “Belyi Naliv”, “Pandarose”, “Volgogradsky”, “Lunny”, “Benito”, “Astrakhansky”, “Raisa”, etc. Most of these tomatoes are unpretentious in care and can withstand climatic changes and irregular watering regimes.
Variety White filling
Tips and tricks
To avoid problems with the appearance of blossom end rot, follow these recommendations:
- choose varieties that are resistant to disease;
- disinfect seeds for 30 minutes before sowing in a 3% solution of potassium permanganate;
- prepare the soil by adding slaked lime to reduce acidity;
- add a glass of ash to each hole;
- Water in a timely manner, preferably in the evening;
- mulch the ground using hay, straw, and pine needles.
Disease prevention
It is much more effective to prevent the occurrence of a disease than to fight it. Prevention of blossom end rot is carried out throughout the summer season. It is very important to take into account the climatic characteristics of the region, as well as the fertility and chemical composition of the soil.
In addition, it is very important to properly care for tomatoes: water and feed them on time, rooting, treating with insecticides and fungicides, loosening the soil, etc.
The fact is that crown rot is not the result of an infection or fungus. In most cases, the disease is associated with improper care of plants and soil.
That's why:
- Carry out regular loosening on heavy soils and with high groundwater levels.
- Do not allow the soil under the tomatoes to dry out.
- On heavy soils, carry out liming in the fall after the end of the dacha season.
- Mulch tomato bushes.
- Fertilize the soil on the site in spring and autumn.
- Keep an eye on your tomatoes and conduct regular inspections for diseases and pests.
Tomato varieties resistant to blossom end rot
Experts say that there are no varieties of tomatoes for growing in greenhouse conditions with 100% resistance to blossom end rot.
However, there are many tomatoes that are highly immune to blossom end rot:
- Alpatyeva 905a;
- Astrakhan;
- Volgogradsky 4/95;
- Leah;
- Lunar;
- Rychansky;
- Benito f1;
- Bolshevik f1;
- Grand Canyon;
- Embellishment f1.
Blossom rot, like most other tomato diseases, is easier to prevent than to fight it later.
Therefore, it is important to carry out preventive measures for the treatment and care of these plants at all stages of their development.
Recently searched:
How to prepare seeds so that tomatoes do not get sick?
Treating seeds in potassium permanganate
Proper preparation of seeds will prevent disease even for those varieties that are more prone to blossom end rot than others.
In order to prevent disease, tomato seeds must be pickled in a solution of potassium permanganate or iron sulfate before planting.
- Etching with potassium permanganate. A 3% solution is prepared. The seeds are soaked in it for 30-40 minutes. Then the planting material is washed in warm water and dried.
- Pickling with iron sulfate. A solution is prepared (1 g of vitriol per 1 liter of water). The seeds are soaked in it for 24 hours. After this, the planting material is also washed and dried.
IMPORTANT! If your soil is too low in calcium or you severely damage the plant's roots, seed dressing still won't help.
How to protect tomatoes from blossom end rot disease
It is well known that plants with strong immunity are practically not affected by diseases and do not suffer from pest attacks.
Photo of growing tomatoes in a greenhouse
To strengthen tomato seedlings and adult plants, they should be protected in the following ways:
- To make seed material more resistant to diseases, it is soaked in special preparations that stimulate their growth before planting in a permanent place;
- After this, it is recommended to place the seeds in a weak solution of potassium permanganate for 30 minutes;
- Also, seed material can be kept for 24 hours in liquid succinic acid or 1% zinc solution. Succinic acid is diluted in the following proportion: 17 mg of the drug is diluted in a liter of water
; - To strengthen tomato bushes, it is recommended to apply a solution of lime nitrate “per leaf”. To prepare this fertilizer, you need to dilute 8-10 g of the drug in a bucket of water. It is necessary to carry out foliar feeding with lime nitrate no more than once every 3-4 days;
- When the fruits begin to actively ripen, it is recommended to treat the tomato foliage with calcium chloride. Such a solution should be prepared as follows: no more than 4 g of the drug is diluted in a bucket of water. This type of leaf feeding is carried out once every 3-4 days;
- You can also feed tomatoes with calcium in another way - feed the plants “sheet by leaf” with milk of lime. This substance is diluted in an amount of 1 g in a bucket of water. Foliar feeding of tomatoes with lime milk should be carried out no more than 2 times every 7 days;
- Tomatoes in a greenhouse can be fed with universal fertilizers for nightshade plants. But you must strictly follow the dosage of the drug according to the instructions on the package. The most effective way to improve plant immunity is to use a solution of the following drugs: a combination of “Nutrivana PLUS” and “Fertivant”. You can prepare it like this: dissolve about 60 g of drugs in 20 liters of water.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Where does blossom end rot come from?
Blossom rot is a disease that is associated with calcium deficiency. Without this element, the plant cannot fully form the fruit, on which tissue begins to die. The tomato begins to turn black.
How to feed tomatoes so they don't get sick?
First of all, fertilizers containing calcium. Foliar feeding, that is, spraying, is much more effective.
Does the soil need to be tilled?
Tomatoes get calcium from the soil, so it also needs to be processed. On acidic soils, liming is carried out in the fall. This is necessary to reduce the acidity of the soil. Liming can also be carried out in the spring, but the effect will be slightly lower.
Only the very tip of the tomato turned black. What to do with him?
Pluck from the branch and throw outside the garden or summer cottage. There is no need to eat a diseased tomato, even if you cut off the infected part. Eating contaminated tomatoes can cause gastrointestinal upset and several days of fever.
The tomatoes on the tomato bush are turning black. What to do with the plant itself?
Treat using the methods described. If treatment does not help, then the infected bush should be pulled out and burned outside the summer cottage.
Treatment of tomatoes with calcium nitrate against blossom end rot
The main reason for the development of blossom end rot is a lack of calcium. This problem can be solved using calcium nitrate. Also, the disease progresses with a lack of phosphorus and manganese, then it makes sense to apply a special complex fertilizer for tomatoes. Watering with calcium nitrate solution also helps in the early stages and for the prevention of blossom end rot.
Calcium nitrate, calcium nitrate, calcium nitrate is an inorganic salt of nitric acid. This fertilizer contains little nitrogen, about 15.5%. But there is calcium - it reduces the risk of fruit blossom end rot.
Calcium nitrate granules easily dissolve in water; the solution must be watered at the roots of the plants (treating the leaves is pointless): 4 tbsp. (60 ml) for half a bucket of water (3.5 l). Calcium nitrate for blossom end rot of tomatoes is effective only while the plant is in the flowering stage; when the fruits reach a size of 2 cm, this method of adding calcium will no longer help. Calcium nitrate alkalizes the soil, so such fertilizers are used only on acidic and neutral soils in spring and summer. Some fertilizers made specifically for tomatoes and vegetables already contain calcium nitrate. Always read product labels and instructions.
Terms and rules for processing tomato beds
Both chemicals and folk remedies are used immediately after identifying symptoms of blossom end rot. The duration of treatment is determined by the degree of neglect of the disease. But with regular spraying, the condition of the affected tomatoes returns to normal in a short time.
In greenhouses and greenhouses
To effectively combat blossom end rot in closed beds, it is necessary to eliminate calcium deficiency in the soil and normalize the conditions for growing tomatoes.
Caring for both greenhouse tomatoes and those growing in an open area is almost the same. There are only minor nuances that allow you to cope with rot when growing in a greenhouse:
- Tomatoes should only be watered by hand. It is necessary to create a watering schedule. Moistened greenhouse soil needs to be loosened.
- It is necessary to regularly ventilate the greenhouse and let fresh, dry air inside.
But in general, the fight against greenhouse blossom end rot is carried out using the same means and methods as those that appear on tomatoes in open ground. Plants are treated with a solution of calcium chloride or limestone nitrate every 3 days. The frequency of treatment with fungicides and mineral fertilizers is indicated in the instructions on the package.
In the open ground
If the disease has just begun to develop and the first symptoms have appeared, then the rot can be stopped by observing the norm of watering during the dry summer months. For tomatoes, the optimal moisture level is such that the soil does not dry out deeper than 3 cm.
To ensure that ground moisture evaporates more slowly, tomato beds are covered with mulch - sawdust, straw.
If the cause of blossom end rot is drying out of the soil, then these measures are sufficient to normalize the condition of the plants.
If calcium deficiency in tomatoes is caused by a disturbed mineral composition of the soil, then fertilizing will have to be used to combat fruit rotting. Moreover, it is necessary to act in two stages:
- Urgently eliminate calcium deficiency by applying mineral fertilizers. This will save this year's harvest.
- In the fall, apply fertilizer under digging to prevent the appearance of blossom end rot in the next growing season.