Many gardeners are concerned about the question of how to increase the yield of cucumbers in greenhouses and open ground, what methods and methods exist for this.
You need to start with the selection of varieties. It is best to opt for productive varieties, bred specifically for certain regions and time-tested. You can, of course, for experimental purposes try to grow varieties of cucumbers that are exotic for your latitude, but in this case you won’t have to count on a rich harvest.
CARBON DIOXIDE FEEDING
The problem of a lack of this substance often arises in greenhouses or greenhouses, where plants actively use it during the day. It is enough to spread pieces of dry ice around the greenhouse or light a gas burner - this will supply the air with an additional dose of carbon dioxide. An alternative is to install a container with mullein.
Control of stepchildren and ovary
In order for the plant not to waste extra energy and nutrition, all efforts should be directed in the right direction. To do this, carefully examine young plants for stepsons and abundant ovary. Many people believe that the first ovary should be completely removed from the plant, thus stimulating further abundant growth. But most people only agree on thinning the ovaries. To do this, you need to carefully examine the plant and leave only one ovary in one axil. Do not spare the first cucumbers, as overloading the plant at the initial stage can affect the overall yield.
HELP IN POLLINATION
If there are few insects, then to increase the number of ovaries, the need for artificial pollination inevitably arises. To carry out this procedure, carefully insert a brush or cotton swab into the male flower and, after collecting pollen, move it to the female flower. Another way is to attract natural pollinators. To do this, spray the cucumbers with sugar syrup by dissolving a spoonful of sugar in 1 liter of water. Or give preference to self-pollinating or parthenocarpic cucumber varieties.
Formation of lashes
The purpose of formation is to stimulate the formation of new shoots, since it is on them that female flowers are formed that produce ovaries. The main lash is pinched after the 5th leaf, and the rest - after the 3rd leaf. It is necessary to monitor the number of shoots - if there are too many of them, the plant will not be able to nourish all the ovaries. Moreover, the bush will weaken, and this in turn will lead to the risk of contracting diseases.
Cucumber hybrids and some varieties do not require pinching of the main vine, because most of the flowers produced on them are female.
CORRECT WATERING
When cultivating cucumbers, watering is of great importance. It must be done daily or every other day, and the water must be warm - not lower than the air temperature. The most favorable time for watering is early morning or evening after sunset. When the air temperature drops, cloudy days and rain occur, soil moisture increases, so watering should be temporarily stopped. And during periods of long heat, on the contrary, sprinkling is used - the plants are watered from a watering can, while reducing the amount of water by 2-3 times.
What to do to increase the yield of cucumbers: effective methods
Carrying out artificial pollination
Experienced gardeners and gardeners, in order to increase the yield of all fertile crops, strive to attract a large number of insects to their garden plot, which usually pollinate plants. For these purposes, enterprising owners try to plant a large number of aromatic herbs, honey plants, and spicy crops near vegetable and garden crops.
If self-pollinating varieties of cucumbers are planted, it’s simple here. But other plants need pollination through the artificial transfer of pollen from the male peduncle to the female.
If cucumber is grown in greenhouse conditions, the recommendations include daily ventilation of enclosed areas so that bees can penetrate to flowering plants. If the climatic conditions are cloudy, the summer is too rich in rain, and there are very few insects, the plants must be pollinated artificially.
For these purposes, a convenient cosmetic brush is used, with the help of which movements are carefully performed first in the male inflorescences, after which they are carried out with a brush in the female peduncles.
Feeding
To get a lot of good harvest, the plant was high-yielding, there are certain requirements for a fertile substrate. The soil must be well drained, cultivated, fertile and structured.
Also, the soil should be rich in vitamins and minerals. It should be saturated with organic microelements, which enter the soil along with vermicompost, bird droppings, garden compost, peat, and wood ash. And also the soil must contain minerals supplied along with mineral fertilizers.
An important role is played by the introduction of additional elements of fertilizing, by watering or applying fertilizers in dry form (it is applied under the root system or by irrigating the foliage).
Such fertilizing is important throughout the growing season; the first fertilization procedure is carried out at the time when the first pair of true leaves appears on the plants, the last one when fruiting ends.
Some of the most common types of fertilizers are:
- Chicken droppings;
- Mullein;
- Wood ash;
- Humus or compost;
- Fermented infusion of herbal plants;
- Milk;
- Yeast;o
- Mineral fertilizers.
You can use not only waste from chickens; droppings from pigeons, turkeys, and ducks are also suitable. This type of feeding is one of the most valuable; it contains almost all the necessary elements - macro and microelements and minerals.
To carry out feeding you need:
- Take a small container.
- Sprinkle litter.
- Pour warm water on top.
- Stir well.
- Close with a tight lid.
Wait for three days. The consumption of this type of fertilizer is one liter per bush of fertile plant. Add under each bush after each heavy watering and thoroughly loosening the soil.
Such a solution should not be allowed to come into contact with the foliage of the cucumber crop.
In the same way, you can breed waste from other domestic animals:
- sheep;
- horses;
- cows;
- pigs.
Only the composition is diluted a little differently, two liters of the concentrated composition are diluted in ten liters of water, after which each individual garden crop is added.
Wood ash is used in its pure form; you can sprinkle a small layer of pre-sifted ash under a separate bush of plants. Or you can dilute 100 grams of wood ash in ten liters of liquid and water the plants.
Place a packet of fresh yeast in a bucket of water. They must ferment for a day. After that, the bushes are carefully added, preventing careless contact with the foliage of the plantings.
You can also dilute fresh milk with water in half, add plants every two weeks, thanks to this you can activate their growth and development. Mineral types of fertilizers have the same properties:
- nitroammophoska;
- potassium sulfate;
- superphosphate.
Use humus or rotted compost. Such products are used to mulch the soil around the cucumber plant.
Thanks to the organic layer, the evaporation of valuable moisture from the deep layers and root system of the plant is prevented, and when it begins to gradually decompose, the plants receive valuable nutritional elements. You can fertilize with the help of ordinary weeds, which are likely to be found in every area.
To do this, the weeds must be cut into small pieces using pruners or a sharp knife, poured into a container, and filled with water. Let the composition ferment for seven to eight days under the rays of the sun. After which the composition can be used for the irrigation procedure. Water no more than once a week.
Also, do not forget that everything in the greenhouse should be well prepared before sowing the seeds. If you choose the right soil and also feed the cucumbers correctly, you will significantly increase the yield.
Strengthening the root system
The better developed the root system of cucumbers, the greater the chances of getting a good harvest. You can help the plant form additional adventitious roots by pressing the stem to the ground and sprinkling it with moist soil.
This technique must be used if you find that the root system is diseased (for example, affected by rot) - this can be seen in sunny weather, when the upper parts of the plants begin to clearly “wither”. Then you can remove half of the ovaries, lower the whip to the ground, and sprinkle its lower part well with fertile, moist soil.
Proper watering of cucumbers
To increase the yield of cucumbers in open ground, as well as indoors, it is necessary to set the correct temperature. To grow a good greenhouse and crops, you should follow the correct watering procedure.
Growing and properly watering cucumbers requires maintaining the correct soil moisture - it should be moderately moist, but not waterlogged; stagnation and dampness are unacceptable. If the soil is excessively waterlogged, this is fraught with the development of fungal infections and seed rotting. It is recommended to carry out the watering procedure only with warm water, its temperature should be at least 20 C. Watering is carried out only in the early morning or in the evening, after sunset. When watering, you need to make sure that the water does not fall on the bush, but under the root.
Growing cucumbers in open ground to increase yield
When growing cucumbers in open ground, be sure to carry out pinching. This will increase the bush's yield. For a good result, you must adhere to one of two main stepson schemes:
The first is to remove all unnecessary branches and leave one main branch, which will produce the harvest. This method is relevant if the owner sows cucumbers very densely and the stems are located in a vertical position along the trellis. With this scheme, the garden bed will have a neat and well-groomed appearance, and harvesting will become simple, because all the fruits are in plain sight.
Stepsonning in the second way is not the complete removal of stepsons, but only up to the 4th or 6th leaf. This ensures the formation of a lush and fertile cucumber bush. Here the main task is to pinch the top in a timely manner: this stimulates the development of lateral shoots, on which female flowers often grow. Before planting cucumbers, it is important to know that male pollinating flowers are formed on the main branch, and female ones on the neighboring ones. When planting a bush, it is necessary to provide good conditions for the development of lateral canes, but do not forget to remove the stepsons. Many lateral shoots prevent the ripening of a rich harvest.
Mulching
Mulch protects cucumbers from sudden temperature changes, which are especially harmful to this crop. Soil covered with mulch retains moisture longer and depletes more slowly. And weeds do not grow under it, which means it does not require weeding.
Pinching
In order to increase the number of female flowers on plants, and hence fruiting, cucumbers need to be pinched periodically. In addition, this procedure, along with proper watering, helps get rid of bitterness in the fruits. Pinching cucumbers in a greenhouse and open ground has its own characteristics.
TIMELY FRUITS HARVEST
The plant needs to be helped by ridding it of ripened fruits and giving the opportunity for the formation of new ovaries. It is recommended to pick fresh cucumbers every day - this will help increase the yield significantly. Timely harvesting will help preserve the freshness of cucumbers. If you neglect this, you can allow them to overgrow, and then they will turn yellow and become unfit for consumption.
Method number 4: pinching the lashes of cucumbers
Some gardeners believe that there is no great need for pinching cucumbers. However, if plant growth is not controlled, male flowers will predominate on the bushes. And for the formation of the harvest, female ones are also needed.
To increase cucumber yield:
- All lateral lashes growing below the fourth true leaf are removed;
- Side shoots from the axils of 5–6 leaves are pinched to 20 cm;
- Scourges at the level of 30, 40, 50 cm, etc. tied to a trellis;
- The top of the bush is cropped at a height of 1.5–1.6 m.
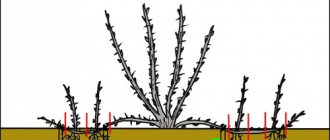
| Note. On average, each shoot retains 3–4 ovaries and the same number of leaves. |
Photo by G. Kuzmitskaya: 3–4 cucumber ovaries are preserved on each shoot.
Feeding cucumbers in open ground
Cucumbers in open ground need to be fed less often than in a greenhouse, but in general the feeding technique is similar: in the first period of the growing season, fertilizing with nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers is recommended, and from the moment of bud formation, flowering and ovary formation, potassium fertilizing with the addition of boron, iodine and manganese .
Organic fertilizers, mullein and bird droppings, contain all the necessary micro- and macroelements, and are also considered environmentally friendly. Therefore, it is recommended to feed cucumbers with mullein (half a liter of mullein per 10 liters of water), or with an infusion of bird droppings (infuse 1 liter of droppings in 15 liters of water for 3 days). The consumption of the working solution is 1-1.5 liters for each cucumber plant.
It is also recommended to fertilize with an infusion of wood ash, with the addition of boric acid and iodine.
Ash contains a large amount of potassium in a form that is easily accessible to plants, so the amount of working solution should not exceed 0.5-1 liters per plant. Root feeding with ash should be done, trying not to wet the leaves. The frequency of feeding is 10-15 days.
Feeding with ash solution on the leaves, foliar, is carried out only for open ground cucumbers. During the flowering and fruiting period, it is recommended to perform three foliar feedings, generously wetting the cucumber leaves. When feeding with ash, it should be remembered that nitrogen fertilizers should be excluded during this period.
To attract insects, you can add sugar to the ash solution at the rate of 50 grams per bucket. You can also add several crystals of potassium permanganate to the ash solution to prevent fungal diseases.
To strengthen cucumber ovaries, you can use a superphosphate solution (30-40 grams per bucket of water). Leaves are generously irrigated with the working solution early in the morning or in the evening.
Technique 2. Remove side shoots from cucumbers
This method will give results when it comes to late-ripening varieties of cucumbers. After July 15th, you need to carry out pinching, which involves removing side shoots and ovaries from the leaf axils. For early and late ripening, it is necessary to carry out such activities before the middle of the season. At the end of July, you need to leave 2 strong stepsons on the bush, which will replace the main stems that bear fruit.
Pinching helps the plant expend energy on the formation of ovaries. In the future, you will be able to collect several kilograms more greens than before. If cucumbers bear little fruit or there are no ovaries at all, this is most likely due to a large number of side shoots. To prevent this phenomenon, it is important to pay attention to stepsoning. Stepchildren that have reached a length of 4-6 cm must be removed so as not to harm the stem and flowers. The procedure can be carried out using scissors or manually. Pull back the leaf and then begin trimming the side shoot that is hiding behind it.
Pinching is most useful for cucumbers grown in greenhouse conditions. Such plants often lack light, and this procedure can improve lighting.
Sorry, there are no surveys available at this time.
Feeding cucumbers in greenhouses and greenhouses
Greenhouse and greenhouse cucumbers need nutritional fertilizing with fertilizers more often than their “free” counterparts. The reason is simple: nutrients from rainwater do not enter the greenhouse, bird droppings remain on the roof of the greenhouse, and the closed space does not contribute to the pollination of flowers.
The amount and concentration of fertilizers for cucumbers in a greenhouse must be optimal - greenhouse plants do not forgive overdoses. Many summer gardeners do not use mineral fertilizers when growing greenhouse cucumbers, being content with natural substances: mullein, bird droppings, herbal infusions, yeast, milk and kefir.
The first feeding of cucumbers is carried out 10-15 days after planting the seedlings with a solution of slurry or bird droppings. The slurry is diluted 5-6 times, and bird droppings - 10-15 times with water. Add 200 g of wood ash to 10 liters of solution. If there are no organic fertilizers, feed with mineral fertilizers per 10 liters of water: ammonium nitrate - 10-15 grams, superphosphate - 20-30 grams, potassium chloride - 15-20 grams.
In subsequent feedings, the doses of fertilizers are increased by 1.5–2 times. After each feeding, water the plants with clean water to wash away fertilizers from the leaves, which can cause burns.
In addition to mineral fertilizers, microelements are added to the liquid fertilizer - 0.5 grams of boric acid and 0.3 grams of manganese sulfate per 10 liters of water.
After fertilizing, after drying, the soil is loosened to ensure good gas exchange. To ensure that fertilizers are better and more evenly distributed in the soil when fertilizing, water the soil before fertilizing.
The roots of cucumbers become exposed as the plants grow, so they must be covered with fresh, moist soil. Adding moist soil promotes the formation of additional roots and improves root nutrition.
Technique 3. We tie up the vines of cucumbers.
To harvest twice as many cucumbers and at the same time provide them with protection from pests, you need to tie up the vines. If the plant has not reached 30 cm in length, this is not necessary, otherwise you may damage the stems.
Older and taller bushes can be placed on a trellis, arches or mesh. Tying can be done in two ways: horizontal and vertical. The first one is suitable for a whole bed, the second one is suitable for individual plants, so difficulties may arise with it.
If you tie up the cucumbers, you will be able to protect them from mechanical damage and fungal diseases, the spores of which are in the soil and from there they move to planting.
How to feed cucumbers if the leaves have become pale or yellowed
Pale leaves on cucumber plants indicate a lack of nitrogen. In this case, foliar feeding of cucumbers with carbamide (urea) will help. The solution is prepared at the rate of 50 grams of urea (matchbox) per 10 liters of water. After dissolving the urea granules, abundant irrigation of the leaves is carried out.
If the foliage has just begun to lighten, you can add a little mullein to the irrigation water. In this case, you need to water at the root.
White cucumber leaves tell us about a lack of potassium. The lack of potassium in the soil will be compensated by root feeding with potassium sulfate, at the rate of 15 grams of fertilizer per 1 m2 of bed.
If the leaves of the cucumbers have turned yellow, it is necessary to take urgent measures to feed the plants with complex fertilizers, but only if the yellowing of the leaves is not a symptom of a disease - fusarium or downy mildew. If damage to fungal diseases is excluded, then feed the cucumbers with a solution of carbamide (urea) at the rate of 20-25 grams per 10 liters of water; you can add a little iodine (15-20 drops) and a few crystals of potassium permanganate to the solution.
Some summer residents practice feeding cucumbers with ammonia, spraying a solution of 5 ml of ammonia per 10 liters of water. I can’t vouch for the effectiveness of feeding ammonia; I didn’t have the opportunity to test it.
Nettle infusion helps save cucumbers from yellowing leaves. Take a third of a bucket of chopped nettles and add hot water, steep the nettles until the liquid begins to ferment, and then strain through cheesecloth or a colander. Consumption of nettle infusion is 1 liter per bucket of water. The diluted infusion should be watered 1 liter per plant.
Irrigating cucumber plants with a baking soda solution helps protect the plants from yellowing leaves and powdery mildew. The solution is prepared at the rate of 1 tbsp. spoon of baking soda per 10 liters of water.
Dates and method of planting
Cucumbers are grown both by seeds and seedlings. Seeds are planted germinated or dry (if the ground is not warmed up). The holes are spilled with warm water, several seeds are placed in each. Dry soil is poured in a small layer on top. No more watering needed! Next, the bed is covered with polyethylene until the emerging shoots become stronger.
Sprouting of young plants
If necessary, seedlings can be thinned out by pinching. As they grow, the cucumber lashes are carefully laid out on the ground without turning them over. Growing cucumbers on a trellis or net is considered no less convenient. Depending on preferences, it can be 0.5-1 m high. Plant lashes are either thrown over a support or tied to it with twine. This method has many advantages: space is saved, the vines are ventilated, they have enough light, the vegetables are clean, and it is convenient to care for the bush.
To facilitate the harvesting process, make a trellis
When the soil temperature reaches 17-18°C, the pre-watered seedlings can be planted. It is grown in advance (about a month in advance). The seeds are soaked and heated in a damp cloth. They will germinate in a week. Seedlings are taken from the greenhouse along with a lump of earth, and from the pot in the same way, so that the thin roots are not damaged. The holes are spilled with hot (not boiling water!) water. The planted sprouts are mulched to retain moisture. Mulch also inhibits the growth of weeds.
Feeding cucumbers with yeast
To keep cucumbers plump, many summer gardeners feed the plants with yeast fertilizers. Yeast dressing for cucumbers is prepared from live yeast at the rate of 10-15 grams of baker's yeast per 10 liters of water. The water should be warm. For every 10 liters you need to add 30-40 grams of sugar and leave in a warm place for three days.
The mash is used immediately before fertilizing, mixing a liter of mash into a bucket of warm water. The consumption rate of yeast fertilizer is up to 1 liter for each cucumber bush.
In the absence of live yeast, you can take dry yeast at the rate of 1 tbsp. spoon on a bucket of water.
Fertilizing cucumbers with yeast is carried out only during fruiting, in warm weather, after watering the cucumber bed with warm water. The frequency of feeding cucumbers with yeast is 2-3 times during the growing season.
How to get a big harvest of cucumbers: mulching
To improve the yield of cucumbers, it is recommended to mulch the soil. Not every vegetable grower knows how to properly mulch an area, so you should familiarize yourself with the features of this process in advance.
Many people are interested in when is the best time to mulch the soil. This should be done a few days after transplanting the seedlings into the garden.
To mulch fertilized soil, you can use special films or any non-woven materials. You should avoid using fresh grass, as slugs can breed in it, causing the bushes to rot.
See also
How to properly plant cucumbers in a greenhouse step by stepRead
Some argue that the best material for mulch is perforated film. When using this material, seedlings are planted in small slots. In summer, perforated film must be used very carefully, as it heats up quickly.
The easiest way to mulch and speed up the ripening of cucumbers is to use plastic film. In this case, it is enough to simply cover the planted bushes with film and make several slits in it. It is recommended to periodically remove the film and weed the area, since polyethylene will improve not only the growth of cucumbers, but also weeds.
Feeding cucumbers with infusion of rye bread
Feeding cucumbers with an infusion of black bread is similar to fertilizing with yeast and helps to avoid the appearance of yellow leaves. To do this, a stale loaf of rye bread is soaked in a bucket of warm water in the evening, and in the morning the bread is kneaded, mixed, filtered and 20-30 drops of iodine are added to the infusion immediately before spraying so that the iodine does not evaporate.
The infusion is diluted in water at the rate of a liter of bread infusion per bucket of water and watered, spending up to 2 liters for each cucumber bush.
You may also find the following materials useful:
- Tomato seedlings have stretched out - what to do?
- How to grow good potatoes
- Growing tomatoes: how and when to do it right
- How to properly form tomato bushes to increase yield
- Unusual ways to plant potatoes or how to grow potatoes in a barrel
What determines the yield of cucumbers?
The amount of harvest directly depends on:
- varieties of cucumbers;
- soil;
- the presence of special trellises;
- plant care.
There is also a factor that gardeners cannot influence - seasonal weather fluctuations.
Secrets to increasing the yield of cucumbers
- In order for the ground to warm up faster in the spring, it should be covered with black material.
- A small greenhouse or a tunnel made of arcs can protect cucumbers from the cold.
- If there is not enough space on the site to grow a crop, it can be planted in barrels. For such planting, varieties that have strong climbing are used.
- Growing cucumbers on trellises will make it easier to care for and harvest vegetables, and also save space in the garden.
- Watering is best done early in the morning. By evening the earth overheats and cold water can damage plant roots.
- The largest harvest can be obtained at the beginning and end of summer. Because cucumbers only need 12 hours of daylight to grow well.
- It is important to hill up cucumbers so that the plants can develop additional roots, as well as create protection for the stem from fungus.
- To increase the formation of female flowers, reduce watering before flowering. The bush activates the growth of flowers to avoid death.
- Experienced gardeners advise removing the very first ovaries. At the time of their formation, the plant has a weak root system, so after the procedure it will direct its forces to strengthen the bush
Growing cucumbers is not an easy task. But with the right approach to agricultural technology, you can grow cucumbers in a greenhouse, greenhouse, open ground, and even on a balcony or window in a house. To increase the number of fruits, you should pay attention to productive hybrids and know when the plant needs to be watered and fed. Then the cucumber bushes will delight you with a rich and tasty harvest.
If you haven’t mulched, be sure to hill up the cucumbers
Hilling protects plants from the wind and helps retain moisture in the soil longer
This procedure increases the plants' resistance to strong winds, promotes good root formation, and also helps retain moisture in the soil (while preventing the cucumbers from getting wet).
Hilling up cucumbers is necessary when they already have 3-4 true leaves. This is done the second time after 10-15 days.
But it should be understood that simply adding soil to the stem of a plant can lead to poor water flow to the roots. To solve this problem, cucumbers can be planted in 2 rows. Then you can water them in the intervals between the rows.
Secret 2: When growing seedlings, constantly increase the volume of the pot
All pumpkin plants do not develop well in a small volume of soil. The roots of cucumbers should not intertwine into a ball. If this happens, then in the future it will affect the growth, and most importantly, the yield of your cucumbers. Over the course of a month of seedling growth in a cramped pot, the roots intertwine and age. That is, you will plant a plant with a non-functional root system in the ground. It takes about a month for such seedlings to adapt, which means the harvest will shift significantly.
Cucumbers love a large pot volume
There is no point in trying to grow adult cucumber seedlings in a glass, or even in a liter volume. You will get a pampered plant on a thin stem with consumptive leaves. The longer the shoots of cucumber seedlings, the more weakened the plant you have grown. Therefore, once a week, transplant the cucumbers into a larger pot if the planting dates are delayed. But it’s best to follow advice 1 and not sow cucumbers too early.
Of course, don’t forget about feeding cucumber seedlings! Once every 10–14 days, feed cucumber seedlings with liquid seedling fertilizer according to the instructions. If you bought a universal fertilizer, the concentration for seedlings should be 10 times lower, otherwise the fertilizer may burn the roots. Cucumbers prefer organo-mineral or organic fertilizers - for example, a weak solution of mullein infusion.
In what soil is it better to plant cucumbers, read here >>>
Preparing the soil for planting
This crop loves light and is sensitive to soil fertility. Therefore, try to place the beds from north to south, the optimal height for them is 25 centimeters.
Be sure to apply organic fertilizer immediately before planting. Folk remedies are also suitable for this.
Usually ordinary cow manure is used: it is applied in a rotted state in a ratio of 4-6 kilograms per 1 square meter of land. If you don’t have manure, use chicken manure diluted with water in a ratio of 20:1 or any other mineral fertilizer.
Start arranging future beds and planting seed between mid-May and the end of June. At this time, the plants have the greatest chance of sprouting safely and producing high-quality cucumbers.