Vegetable growing » Garlic
0
1568
Article rating
Kira Stoletova
Winter garlic is planted in late autumn. The gardener selects suitable soil, prepares shelter for the crop and selects safe fertilizers. Planting garlic in the Leningrad region and harvesting it will allow you to stock up on a product with a spicy taste for the whole year. The differences between spring and winter garlic lie in the conditions created by the gardener and the time of planting.
Rules for planting garlic
How to choose a day to plant garlic in the Leningrad region
First of all, you need to choose the right day to plant a plant in the fall. It is necessary to calculate before the onset of frost. It is optimal that there are about 50 days before frost.
During these 7 weeks, the garlic will take root in the ground and gain strength. But at the same time he will not release his feathers.
The day of the procedure itself should be fine, but landing in cloudy weather is also allowed. In general, it is ideal to plant garlic in moist soil after rain.
If planting in dry soil, lightly moisten it.
Another important factor is air temperature. Optimally +10+12 degrees. It is impossible to plant in colder conditions - the cloves will not be able to take root.
And if you plant on warm days, the garlic can germinate. In the fall, this is not something that will be beneficial for the vegetable.
Which varieties of winter garlic are suitable for planting in the Leningrad region
For the region under consideration, you can purchase both zoned varieties and varieties of vegetables intended for autumn planting in the Urals and Siberia.
Among specific varieties, it is worth paying attention to Titan, Moskal, Alekseevsky, Lyubasha, Casablanca, Shirokolistny 220, Tonus, Messidor.
From those zoned for the Urals and Siberia in the Leningrad region you can grow Alcor, Spas, Sofievsky, Sibirsky.
IMPORTANT!
Do not buy varieties that were bred for growing in the fall in the Middle Zone and the South. They are not suitable for the Leningrad region.
The best winter varieties
How to plant garlic for the winter
The following varieties are recommended for autumn planting:
- "lyubasha";
- "Ukrainian white";
- "saved";
- “Anniversary Gribovsky”;
- "Anniversary 07";
- "reliable";
- “violet Kharkov”;
- "Messidor".
It should be noted that most gardeners grow the same proven variety every year. Often the owner himself does not even remember its name. It's okay if you don't know the name of your variety. If you are satisfied with the harvest you receive, then grow it without worrying about anything.
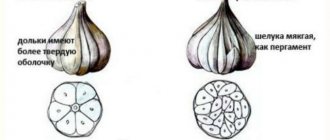
The main thing is not to confuse the varieties of spring and winter garlic. The winter one differs from the summer one in the radial arrangement of the cloves, like tangerine or orange segments, all of them are external and located around the circumference, with the exception of two or three thin segments inside the head. The number, depending on the variety, varies from seven to ten. Spring garlic has significantly more cloves, and they are arranged in several rows.
At what depth to plant garlic?
To prevent the plant from dying in winter, the cloves must be planted at the correct depth.
This is a very important point. In autumn, you should not plant too deep - the bulb will be small. But shallow planting will also cause harm - the cloves will freeze and die.
Therefore, be sure to maintain the depth of planting of garlic. For the Leningrad region it is 10-12 cm.
ON A NOTE.
Approximately the same distance must be maintained between the cloves.
What fertilizers can be used when planting garlic in autumn?
When planting garlic in the fall on poor soils, it is advisable to use fertilizers. The applied fertilizers will nourish the crop, which will allow the garlic cloves to actively grow in the spring.
It is best to use a complex fertilizer made from a mixture of organic matter and minerals. This feeding will completely cover all the nutritional needs of garlic.
The most commonly used organic fertilizers are humus, compost or rotted manure. This will become the basis of the nutritional mixture. By decomposing, organic matter makes the soil fertile.
However, in the fall, garlic primarily needs potassium and phosphorus. They are usually applied in the form of mineral fertilizer. The most commonly used drugs are superphosphate and potassium sulfate. But it is also permissible to use potassium salt and phosphate rock.
Fertilizers are not applied to the planting hole during direct planting, but approximately 20-30 days before the procedure during soil preparation. This is because organic matter takes time to decompose in the soil.
REFERENCE.
The most popular fertilizer is prepared from 50 kg of humus, 200 g of superphosphate and 150 g of potassium sulfate. This amount of fertilizer is enough for 10 square meters of garlic beds.
Useful tips
Planting garlic in the fall before winter.
when to plant garlic in the fall Every gardener has his own tricks and secrets for growing large garlic. Here are some useful tips:
- Regularly update planting material. Every three years, the plantings are rejuvenated by growing one-toothed bulbils from airy bulbs in advance.
- Breaking out the frogs allows you to get larger heads.
- It is advisable to leave several arrows on the bushes in order to determine the period of ripening and harvesting of the heads. The arrows are also useful for collecting air bulbs for landing.
- Observe planting dates, and then carefully care for the crop.
- Try several varieties on your plot, grow new selections. Many new productive varieties of winter garlic have been developed, characterized by frost resistance, large fruit, and resistance to diseases and pest attacks.
- When selecting a variety, take into account the recommendations of breeders and agronomists, your own experience, as well as the climatic conditions of the region.
Not so, it turns out it’s difficult to prepare and plant winter garlic before winter
It is important not to confuse it with spring varieties, carry out all agrotechnical work in a timely manner, and next year an excellent crop harvest will be ensured!
Features of planting garlic in the Leningrad region
Winter in the North-West of Russia is not characterized by stable weather conditions. This fact leaves its mark on the procedure for planting garlic in the Leningrad region.
Firstly, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the timing of planting garlic cloves.
Secondly, the soils in this region are not distinguished by their fertility, so fertilizers must be added to the soil. Here you can immediately mention the mandatory preparation of the bed for future planting of garlic.
Thirdly, it is important to choose the appropriate variety of garlic for the Leningrad region. It is necessary to choose winter varieties that tolerate frost well.
Fourth, maintain crop rotation. If possible, pre-plant green manure to better prepare the soil for planting root crops.
Fifthly, do not forget to pay attention to where exactly you are going to plant garlic. Often in summer cottages in the Leningrad region, groundwater is located too close to the surface.
Therefore, it is very important that the garlic sits at some elevation compared to the rest of the garden, so that the heads do not rot.
TYPES AND DIFFERENCES OF GARLIC
More than 70 cultivated varieties of garlic are known, each of them has its own characteristics, pros and cons, and its own ripening time. Some varieties ripen already in mid-summer, and some only in autumn. Some species require special care, others grow in the harshest conditions.
Below are the most popular types and varieties of vegetables.
| Type of garlic | Garlic variety | Description |
| SPRING GARLIC (planting in spring, less productive) Signs:
| Victorio | 1. High level of productivity. 2. Resistant to pests and fungal diseases. 3. The bulbs are flat-round in shape. 4. The scales are yellow-white. |
| Elenovsky | 1. Productive. 2. It has a white tint on the outside and pinkish on the inside. 3. Resistant to all plant diseases. | |
| Gulliver | 1. Medium late. 2. Good yield. 3. Has a light white color. 4. Not susceptible to pests or any diseases. | |
| Sochinsky 56 | 1. Mid-season. 2. Stable and high-quality harvest. 3. The shape of the head is slightly flat and round. 4. The color of the scales is either white or purple, and the teeth have a pink-violet tint. 5. Resistant to diseases. | |
| Ershovsky | 1. Mid-season. 2. The bulbs are round, slightly flat. 3. No arrows. 4. Excellent productivity. 5. Disease resistant. | |
| WINTER GARLIC (planting in autumn, less productive) Signs:
| Lyubasha | 1. Resistant to frost, aridity, and disease. 2. The bulb is round, slightly flat. 3. The scales are light with veins of purple shades. 4. Has a bright pungent taste. |
| Dobrynya | 1. Productive. 2. Late. 3. The heads are large. 4. Not exposed to diseases. | |
| Sofievsky | 1. Tolerates frost well. 2. The onion is large. 3. Color purple. 4. The taste is spicy. 5. Nematode resistant. | |
| Alcor | 1. High-yielding. 2. The color of the bulb is pinkish, and the cloves themselves are closer to gray. 3. Damaged by yellow dwarfism. | |
| Dubkovsky | 1. High-yielding. 2. The bulb is not large. 3. The taste is spicy. |
Planting schemes step by step
Garlic is planted in autumn either in rows or in a square-cluster method.
Let's consider a step-by-step algorithm for planting garlic on an already prepared plot.
Step 1.
Soak the cloves in a solution of any fungicide for 20-30 minutes.
Step 2.
We make grooves 10-12 cm deep. Leave 20 cm between the grooves. If you plant in separate holes, then the distance between them should be 20 cm.
Step 3.
Lightly moisten the soil at the bottom of the groove (hole).
Step 4.
Place the cloves in the groove in increments of 10-12 cm. Bottom down. Press down lightly.
Step 5.
Cover the garlic with soil.
Step 6.
We water it.
How to properly prepare a garden bed
Having chosen a site for planting garlic cloves, you need to prepare it. In prepared soil, the vegetable grows much better and faster.
The first thing to do is weed the area. Remove all weeds, they will interfere with the development of garlic heads.
Next, dig the ground 20 cm deep. Be sure to loosen the soil so that there are no “rocks”.
Remove all roots and other debris from the area.
Also in the fall, fertilizers, a mixture of organic matter and mineral fertilizers are applied during digging.
After this, after a few weeks you can start planting garlic cloves.
After which you can plant
Crop rotation plays an important role in obtaining a good harvest of spicy vegetables. If you plant garlic cloves in the fall after correct predecessors, you can grow bulbs much larger than when planting after “bad” predecessors.
A bad idea is to plant after root vegetables (beets, onions, garlic, potatoes), herbs and greens, as well as oats and barley.
It is very good to plant the crop after green manure plants. For example, mustard, phacelia or clover.
Acceptable predecessors are representatives of the pumpkin family (cucumbers, zucchini).
The need to apply crop rotation rules is due to the fact that related crops are susceptible to the same diseases and suffer from the same pests.
The second reason is that some crops equally deplete the soil.
Caring for garlic after planting in a given region
Caring for a planted plant in the fall is not too difficult. First, you need to water the garden bed using a watering can. Secondly, mulch with sawdust or dry grass. Thirdly, cover with spruce branches, grass, dry leaves, etc.
This will protect the garlic from freezing in winter.
Instead of mulch, you can use spunbond or any other synthetic covering material. But this does not negate the need to make a full-fledged shelter.
BY THE WAY.
If you have such an opportunity, then throw snow on the garlic bed in winter.
Tips for Growing Garlic
There is a non-standard method of planting winter garlic on growing green manure.
The point of the method is that growing greenery acts as a natural cover for the soil (protects it from frost) and retains snow well in the garden bed. Fast-growing crops are chosen as greens: mustard, peas, oats. Green manure seeds are sown in a garden bed a month before planting garlic, so that by the time of planting a carpet of greenery 20 cm high is formed. In the green field, grooves are cut with a flat cutter, into which the cloves are sown. In the spring, so that the overwintered greenery does not choke out the garlic, it is cut off flush with the soil and left to rot in the rows.
To obtain especially large heads of garlic, select only large cloves for planting. They are planted spaciously, according to a 20 by 50 cm pattern, providing a large area for nutrition. When the garlic shoots out its arrows, the plant is fed with complex mineral fertilizer for onions and garlic or the following composition (per 10 liters of water): 30 g of superphosphate, 15 g of potassium nitrate.
Often in the spring, a gardener observes that young garlic greens turn yellow. There are several reasons for this:
- lack of nitrogen;
- lack of moisture;
- The soil in the garden bed is too dense.
Garlic is provided with watering if the spring is dry and hot. It is imperative to loosen the row spacing to a depth of 3-4 cm. Over the winter, even the loosest soil tends to become compacted. The lack of nitrogen will be solved by feeding winter garlic with urea (30 g per 10 liters of water) or a solution of chicken manure (100 g of product per 1.5 liters of water).
If garlic is grown to produce a large head, the arrows of the plant must be cut off, preventing bulbs from forming. The ripening of aerial bulbs weakens the plant. The arrows are cut off when their tips go down and begin to curl. It is better to cut off the top of the arrow so that the cut tip “looks” down. This trick will prevent rain moisture from getting inside the cut arrow and protect it from rotting.
Winter garlic is often harvested selectively as it is needed for cooking. The final harvesting is carried out when the garlic tops turn yellow. By this time the heads will be covered with husks. The key to long-term storage of winter garlic is its good drying. The vegetable is harvested only in dry weather. The heads are kept for at least 2 weeks in a well-ventilated area at a temperature of +25 degrees. Further storage of garlic should take place at a temperature of +15 +18 degrees and a relative humidity of 50%.
Common mistakes
- Choosing the wrong variety.
Here we can mention both planting a spring variety in the fall and choosing a variety zoned for more southern regions. Still, in the Leningrad region it is necessary to give preference to more resistant varieties of garlic. - Selecting the wrong planting depth.
If you are in doubt at what depth to plant the cloves, simply add 5 cm to the length of the planting material. - The bed is not watered after planting.
For some reason, many summer residents believe that there is no need to water garlic when planting in the fall. Of course, if it rains, then there is no need for excess moisture. But in dry autumn it is necessary to water. - There is no shelter from the cold.
Be sure to cover the bed with grass, leaves and branches. - Choosing the wrong site.
If you have clay soil at your dacha, add sand to it and dig it up. Don't plant cloves below the level of the rest of your garden. - The teeth are too close.
If you want to get large heads of garlic, then plant the cloves further apart from each other. - Applying manure for planting.
Manure (and only rotted manure!) can be applied when preparing the soil, but not for planting garlic.
Danger of diseases
Winter garlic is susceptible to attack by pests and diseases in the same way as the spring variety. For the purpose of prevention, contaminated garlic must not be allowed to enter the planting. To do this, when calibrating, you need to without regret throw away seeds that have traces of pests, rot or mold. If the plant does become infected, you need to fight it.
- Furiosis or bottom rot. It is discovered during the growing season. With it, the bottom softens and the roots die. The garlic is dying.
- Penosporosis. This disease has a second name - powdery downy mildew. This is a fungal disease that affects all parts of the plant. Spreads in high humidity. Slows down plant growth. It is treated with copper-containing preparations and fungicides. Infected heads are not suitable for use.
- Aspergillosis. This is a fungus that appears on garlic as black spores that produce dust when shaken.
- Bacteriosis. Garlic is contaminated by bacteria. During storage, you can see dark stripes running from the bottom and ulcers appearing. Typically, this disease appears when the crop is poorly dried. To prevent disease, it is necessary to observe crop rotation and select only healthy cloves for planting. It is worth treating the garlic in copper sulfate.
- Cervical rot. It appears during storage, although the head becomes infected during the growing season. This occurs from an overdose of nitrogen and excess moisture. Infection occurs during planting from infected seeds. To prevent this from happening, you need to carefully select planting material, disinfect it before planting, and take nitrogen fertilizer only at the beginning of the growing season.
Pests such as root mites, onion flies, and nematodes must be controlled using agrotechnical methods. The use of pesticides is highly undesirable, since both the green leaves and the heads of garlic are edible.
Answers to frequently asked questions
What varieties should be planted in the Leningrad region?
Alekseevsky, Sibirsky, Alcor, Casablanca and many others have proven themselves well.
Is it possible to plant green manure before garlic?
Yes, it is quite. Mustard, clover, phacelia are excellent precursors for vegetables. The tops can be buried in the ground. This will saturate it with organic matter and beneficial nutrients.
When to plant garlic in the Leningrad region?
In general, in Russia, when planting this vegetable, it is recommended to focus on the Feast of the Intercession of the Blessed Virgin Mary. It's October 14th. But in 2022, autumn is relatively warm, so the planting of cloves can be postponed to the 3rd decade of October.
Why mulch the soil after planting cloves?
Mulch retains moisture. This is important so that the cloves take root better.
At what temperature should I plant?
10-12 degrees Celsius are optimal.
Recommendations for cultivation
How to properly plant garlic in the fall for the winter and when is the best time to do it according to the lunar calendar in 2022?
If you plant garlic before winter, it is good to cover the plantings with straw. In the spring, some vegetable growers rake covering material. Especially if the soil is poorly structured. After all, with straw, the roots will not receive enough oxygen. If crop rotation is observed, the soil is systematically enriched, when the humus layer is high, the straw can be left. It will inhibit the growth of weeds and will not harm the germination of the vegetable.
Attention!
The addition of carbamide (urea) will help avoid chlorosis, which develops intensively in April.
When arrows appear, they are not easily cut off by hand. If possible, they are cut off at the base with sharp scissors. Otherwise, a lot of strength and nutrition goes into the arrow itself (not even into the seeds). It is thick and juicy - it needs a lot of moisture and nutrients. Once the culture redirects energy, it will not be possible to reverse the process.
Before planting garlic in winter, you need to calculate the date correctly. When determining the optimal timing, we must not forget about the influence of climate and lunar phases.