Potato cancer is a dangerous fungal disease. It was first discovered at the beginning of the twentieth century on the territory of Austria-Hungary, from where it spread throughout Europe.
Thanks to timely preventive measures and the development of varieties resistant to the pathogen, most farmers have never encountered this disease. But forewarned means forearmed.
From our article you will learn how to quickly respond in case of infection and prevent the spread of fungal spores to neighboring areas.
Description of the disease
Potato cancer, or Synchytrium endobioticum, belongs to the class of chytridiomycetes (Chytridiomycetes), classified as quarantine objects, as a result of which it is better studied than other diseases from this subgroup. The disease is currently being recorded in almost all potato cultivation regions, with the exception of the extreme northern and southern regions.
To date, about 18 pathotypes of the harmful fungus are known, but most of them are not found outside the borders of Central Europe. The most widespread, including in our country, is pathotype I. The fungus produces a thick-walled structure - a sporangium, the diameter of which is 25-75 microns and contains about 200-300 spores.
Synchytrium endobioticum belongs to the category of obligate parasites that can infect a number of plants belonging to the nightshade family. The most favorable conditions for the development of this fungus are high temperatures at +18...+20 °C, as well as a sufficient amount of moisture. Sporangia remain viable for 20-30 years.
Sources of infection
A pathogenic fungus can enter a potato plot in several ways:
- melt water in spring;
- manure from animals fed raw potato fruits;
- through instruments used in the quarantine zone;
- gardener's shoes and clothing;
- the fungus is carried by insects and earthworms;
- diseased potato tubers acting as planting material.
Earthworms are able to live deep in the layers of soil. They act as the main carriers of the fungus. The causative agents of the disease are found at a depth of 50 cm from the surface of the earth. Such cases occur quite often.
The intracellular organism that causes the disease is highly resistant to external conditions. That is why the source of infection can be stored in the ground for 30 years. Dry weather slows down the development of the fungus; some zoospores die as a result of lack of moisture. Due to its viability, the fungus is dangerous and harmful to potatoes.
External signs of damage
As a rule, the main foci of the disease are located in household plots, and the pathogen primarily affects potato tubers and stolons. The lower part of the stems and leaves located on the lower part of potato bushes are affected much less frequently. The root system of the plant is not affected.
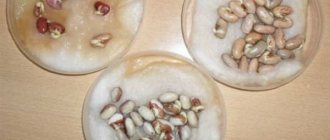
The fungus provokes the appearance of lumpy growths or characteristic tumors with an uneven, wavy surface on potato root crops, which in appearance resemble a sponge or young cauliflower. As a rule, the appearance of growths begins with eyes on tubers. Gradually, the growths increase in size, turn brown, change color to black and destroy.
Throughout the growing season, the disease can spread quite quickly through single-flagellated zoospores. During the summer period, the formation of zoospores can occur repeatedly. In autumn, dormant cysts, covered with a lignified shell, form in root crops. After overwintering in root crops, the cysts germinate under favorable conditions.
In addition to the usual form, leafy, scabby and corrugated forms can form on root vegetables. The scabby form of cancer is characterized by the development of ulcerations and crusts on the surface of root crops. The corrugated form is characterized by the formation of strongly wrinkled root crops.
Prevention of potato diseases
Most potato diseases can significantly reduce the yield. To prevent this, you need to follow certain preventive measures:
- Select potato varieties that are resistant to diseases and pests. It is better to give preference to local varieties that are best adapted to the climatic and soil conditions of a particular region.
- Carry out pre-sowing treatment of tubers with special preparations. They strengthen the planting material and significantly reduce the risk of tubers becoming infected with bacteria and viruses.
- Observe crop rotation - without this condition, tubers can be affected by diseases of other crops, which also pose a danger to potatoes.
Figure 14. Preparations for treating potato tubers before planting
After harvesting, be sure to remove all tops and plant debris. In addition, during the growing process it is necessary to regularly remove weeds, and when the first signs of diseases are detected, preventive spraying should be carried out.
Causes
For plant infection and active germination of the cyst, high soil moisture in the potato field (not lower than 60%) and optimal soil temperatures (+ 18 ... + 23 ° C) are required. The source of infection is infected root crops or cysts in the soil.
Thus, the main causes of potato cancer include the presence of the pathogen in the soil, very narrow crop rotation, cultivation of potato varieties that are not resistant to the disease, the use of seed material of unknown origin, and weather conditions favorable to the disease.
In addition to potatoes, tomatoes and other nightshades are often infected, but unlike potatoes, the infection also affects their root system. The pathogenicity of the disease is very high, regardless of which pathotype has become widespread, and the yield in the affected areas is low. In addition, tubers with cancerous growths are not stored for a long time, which is due to very rapid decay.
Varieties of potato cancer
If you study the photo and description of cancer, you can distinguish several of its classifications depending on the type and location of the lesion:
- neoplasms on a loose structure – the main type;
- the appearance of growths on the leaves that have the shape of a flattened cone;
- the appearance of wrinkled sagging with small depressions inside, a distinctive feature is wavy edges;
- scabby form of the disease, a typical sign is a neoplasm in the form of plaques.
Each type of disease has an identical danger - cessation of growth or death of the plant crop. Moreover, they are all harmless to people or animals. The method of treatment for them is no different.
Fighting methods
Currently, it is possible to effectively fight potato cancer and carry out high-quality treatment only with proper adherence to a set of treatment and preventive measures.
| Methods of prevention and treatment | Technology |
| Quarantine measures | Carrying out control over transported seed and food potatoes, as well as annual inspection of vegetable crops in border areas. |
| Chemical activities | Aimed at eliminating new foci of the disease. Disinfection of soil with a 2-2.5 percent solution of nitrafen (at the rate of 20 liters per sq. m) or 96 percent chloropicrin (at the rate of 150 cubic cm per sq. m). |
| Cultivation of cancer-resistant varieties | Cultivation of varieties “Voke”, “Giant”, “Imandra”, “Temp”, “Frem”, “Chernigovsky-2”, “Mira”, “Pavlinka”, “Zarya”, “Impala”, and “Mira”, which are less susceptible to new pathotypes of cancer. Nemeshaevsky pink”, “Enchantress”, “Victoria”, “Veronica”, “Murmansky”, “Povirovets”, “Chernigovchanka” |
| Agrotechnical measures | Carrying out proper crop rotation using row crops, using organic fertilizers on potato fields, as well as destroying weeds from the nightshade family. |
Vegetable growers who are faced with potato canker damage to their vegetable crops should remember that they absolutely cannot use chemicals on their own to carry out disinfection in their household plots and garden plots. This procedure is carried out exclusively by quarantine and plant protection specialists.
Treatment
The main thing in the fight against fungal spores is to prevent disease. To protect your area from sporangia:
- you need to plant potatoes no more than once every 4 years in the same place;
- other nightshade crops should not be planted nearby;
- it is necessary to destroy all weeds, especially nightshade;
- you cannot purchase planting material from quarantine zones;
- If there are quarantine areas nearby, you need to start growing varieties resistant to potato cancer.
By adhering to such rules, it is possible to ensure that access of a pathogenic fungus to the site will be prevented.
But if suddenly an infection occurs, then it is necessary to fight the disease. The first point will be to notify the plant protection inspectorate in order to create a quarantine zone. Scientists from several countries have created an Agroatlas. It discusses in detail the description of various plants and methods of working with them. A special place is occupied by disease control measures, virus prevention and pest control.
Even if potato cancer does not pose a danger to humans, it is still necessary to remove all contaminated product from cooking. Sick plants, tubers and root systems must be burned or buried in a hole more than 1.2 m deep. In this case, all parts are sprinkled with bleach, filled with kerosene or formaldehyde.
Prevention
2 or 3 years before planting potatoes, it is necessary to cultivate the soil in contaminated areas and during this time it is prohibited to cultivate all agricultural crops. The work is carried out exclusively by specialists, using a 2% Nitrofen solution. In this case, 20 liters of solution are applied per 1 m² of soil.
To disinfect planting material, use a 5% solution of Benomyl or Benleit, as well as a 1% solution of Fundazol. The tubers are soaked for half an hour and planted. Work must be carried out wearing protective rubber gloves, an apron and a mask.
How to deal with the Colorado potato beetle
This is the main potato pest. A massive invasion of these insects can lead to the fact that in a short time, only bare stems will remain of green bushes (Figure 5).
Figure 5. Damage to crops by Colorado potato beetles
After emergence, potatoes need to be treated with drugs against this type of pest.
The better to poison
How to deal with these insects on potatoes? Of course, with the help of special chemicals. Common medications include (Figure 6):
- System chemicals Mospilan, Sonet, Commander, Iskra. They are used three times throughout the entire growing season. But the last treatment should be carried out no later than 3 weeks before harvest.
- Preparations of fungal and bacterial origin Fitoverm, Boverin and Agrovertin quickly destroy young larvae. After one treatment, the drug continues to act, causing the death of insects within a week.
Figure 6. Remedies against the Colorado potato beetle
You cannot use the same drugs for several seasons in a row. Insects gradually become accustomed to certain products, so chemicals need to be alternated.
Remedies for the Colorado potato beetle
Folk remedies also exist. But they are only suitable for small areas, since their use involves significant labor costs. For example, beetles and their larvae can be collected by hand. But since insects easily fly from one bush to another, this procedure will have to be repeated constantly.
Also, to combat insects, spraying with infusions of mint, poplar, basil and black currant leaves is used. The strong smell of the liquid will repel insects. The first treatment is carried out immediately after emergence and subsequently repeated several times per season. Beans or coriander can be planted next to potatoes. The scent of these plants will help reduce the number of pests.
In addition, there is a distracting way to fight. To do this, you need to plant a few tubers before the rest. Large green bushes will attract pests and will be much easier to harvest and destroy.
From the video you will learn a recipe for preparing an environmentally friendly means of combating the Colorado potato beetle.
Symptoms
Light tubercles are visible on infected tubers.
Over time, they acquire a brown color and growths form from them. In appearance, the growths are similar to cauliflower inflorescences. In addition, tubercles appear in the axils of the leaves, on the inflorescences. Please note: cancer does not damage the root part of the bush.
Therefore, recognizing the disease can be very difficult. Only when harvesting does it become clear that the tubers are infected. In hot weather, cancer can be presented in other forms: leaf-shaped, corrugated, scab-shaped:
- Leaf-shaped - growths appear on the peel, taking on the shape of leaves.
- Corrugated - the surface becomes uneven, the skin becomes wrinkled.
- Scabby - small scabs appear on the peel.
Late blight
One of the most dangerous diseases that can cause significant losses. There are known cases when 70% of the crop died from this disease. During the flowering period, white spots appear on the lower leaves. A characteristic whitish coating forms at the border between the affected and healthy tissue. Depressed, hard, dark gray spots appear on the tubers.
To prevent this disease from affecting your plantings, choose only varieties resistant to this disease: Temp, Olev, Planta, Stolovy 19, Sulev, Belorussky 3, Zekura, Udacha, Pamir, Russian Souvenir, Rozara, September. Reject damaged and infected tubers at the stage of selecting seed. Try to choose a place to plant potatoes where there will be no long-term stagnation of moisture after rains or watering. Treat each potato tuber with Maxim fungicide before planting. The following fungicides are suitable for subsequent treatment: Shirlan, Ridomil Gold and Bravo. If the disease has already manifested itself, then treatment with fungicides will not help. Use biological preparations: Agat 25 and Planriz, as well as copper-based products, for example, Ditan M-45.